oxidative decarboxylation
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
what happens when o2 is available during glycolysis
aerobic cellular respiration
stages of aerobic cellular respiration
glycolysis→
oxidative decarboxylation→
Krebs Cycle→
ETC
what does pyruvate turn into during (oxidative decarboxylation) aerobic cellular respiration
Acetyl-CoA
where is pyruvate converted into acetyl-coa
the mitochondrial matrix
what happens to pryuvate in the mitochondrial matrix
it oxidizes, gets decarboxylated, and turns into fragaments
-carboxyl group is removed
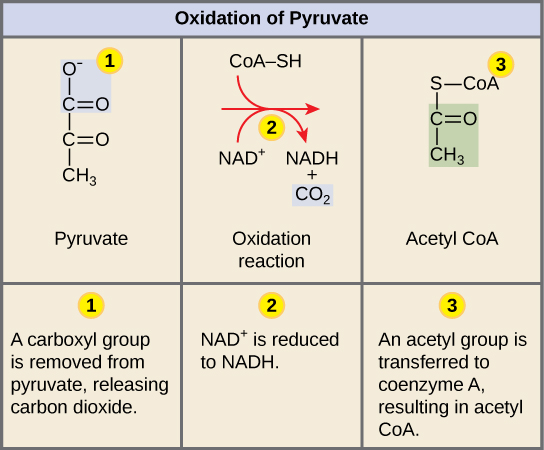
break down of pyruvate getting oxidized by PDH
acetyl group and CO2
what happens to the pyruvate fragments
they combined with co-enzyme A which results in acetyl-CoA
what enzyme is required in oxidative decarboxylation
PDH
pyruvate dehydrogenase
What elements are present in the matrix
pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH)
& Coenzyme A (COA)
how does pyruvate move from the cytoplasm to the intermembrane space
through the pyruvate channel embedded in the outer membrane
-diffusion
how does pyruvate move from the inter membrane space to the matrix
through the H+/pyruvate symporters
where are the H+/pryuvate symporters located
embedded in inner membrane of mitochondria
what direction is H+ and pyruvate moving
both moving into the matrix from inter membrane space
-H+: high to low
-pyruvate: low to high
how is pyruvate moving against the conc. gradient
low to high
why is pyruvate initially in the cytoplasm
because glucose was broken down there during glycolysis
oxidative decarboxylation formula
Pyruvate + Coenzyme A —-PDH—→ Acetyl coenzyme A
why is NAD transforming into NADH in oxidative decarboxylation
NAD⁺ accepts the electrons/hydrogen from the oxidation of pyruvate, which reduces it to NADH.
net production from oxidative decarboxylation (breakdown of 1 glucose)
2 Acetyl CoA,
2 NADH,
2 CO₂
is atp made during oxidative decarboxylation
no, its the only stage where atp is not made
what is acetyl-co a used for
to enter different cycles or generate other compounds
what happens if more atp is needed
-more atp then what is made during glycolysis
it enters Krebs Cycle