Understanding Osteoporosis and Bone Health
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Osteoporosis
Skeletal disorder with compromised bone strength.
Bone Mineral Density
Measurement of bone strength and health.
Peak Bone Mass
Maximum bone density achieved in life.
Involutional Osteoporosis Type I
Aging-related osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
Involutional Osteoporosis Type II
Affects individuals over age 70, both genders.
Secondary Osteoporosis
Bone loss due to medical conditions or medications.
Pre-osteoporosis
Condition affecting 44 million Americans, 68% female.
Osteopenia
Lower than normal bone density, risk for osteoporosis.
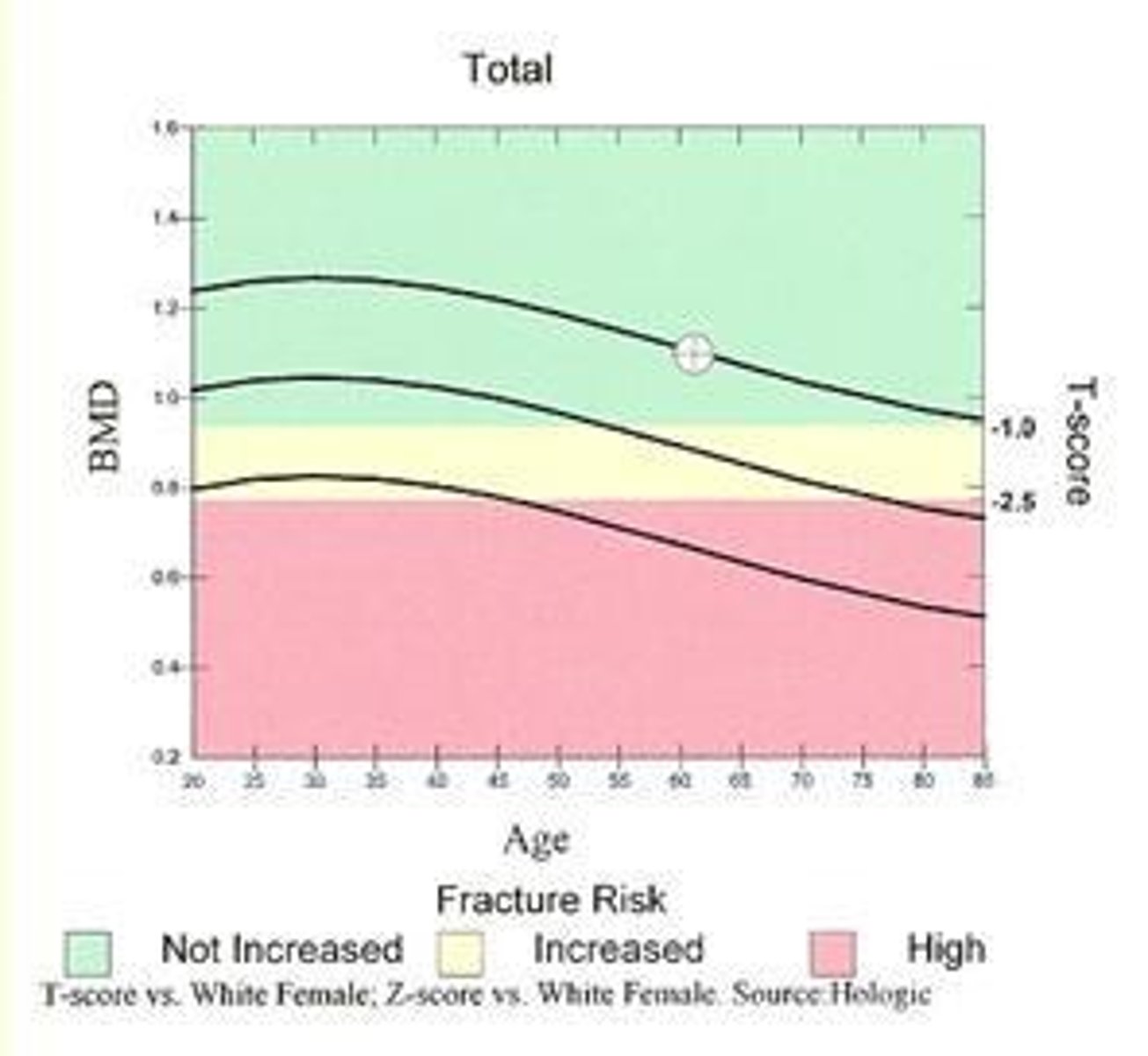
Fracture Risk
Likelihood of breaking a bone due to osteoporosis.
DXA Scan
Gold standard for measuring bone density.
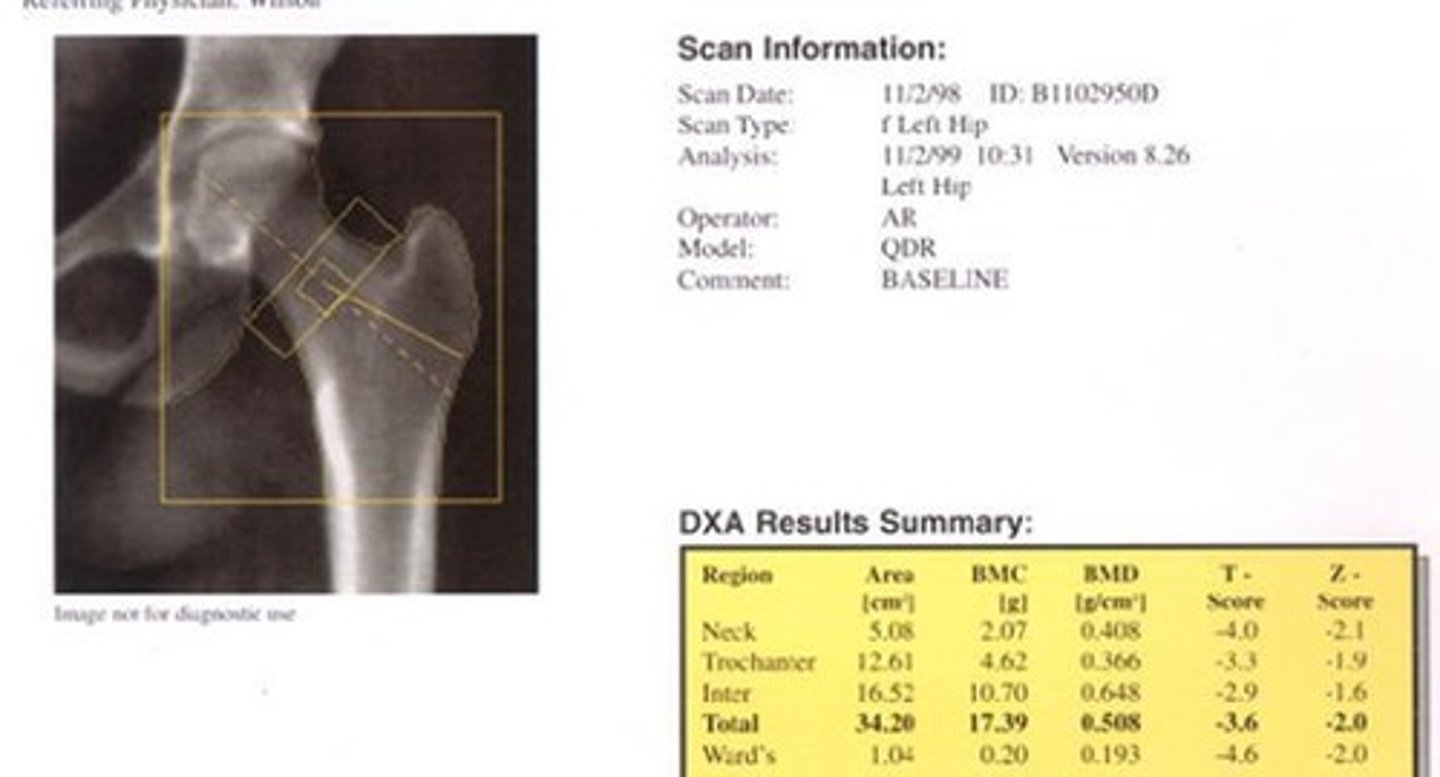
T-score
Comparison of bone density to young adult women.
Z-score
Comparison of bone density to age-matched peers.
Bone Markers
Indicators of bone turnover in the body.
BMD Testing Recommendations
Testing advised for women over 65 and younger at risk.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
Includes low bone mass, female gender, and age.
Calcium Intake
Recommended 1200-1500 mg for bone health.
Vitamin D Intake
Recommended 400-800 IU for calcium absorption.
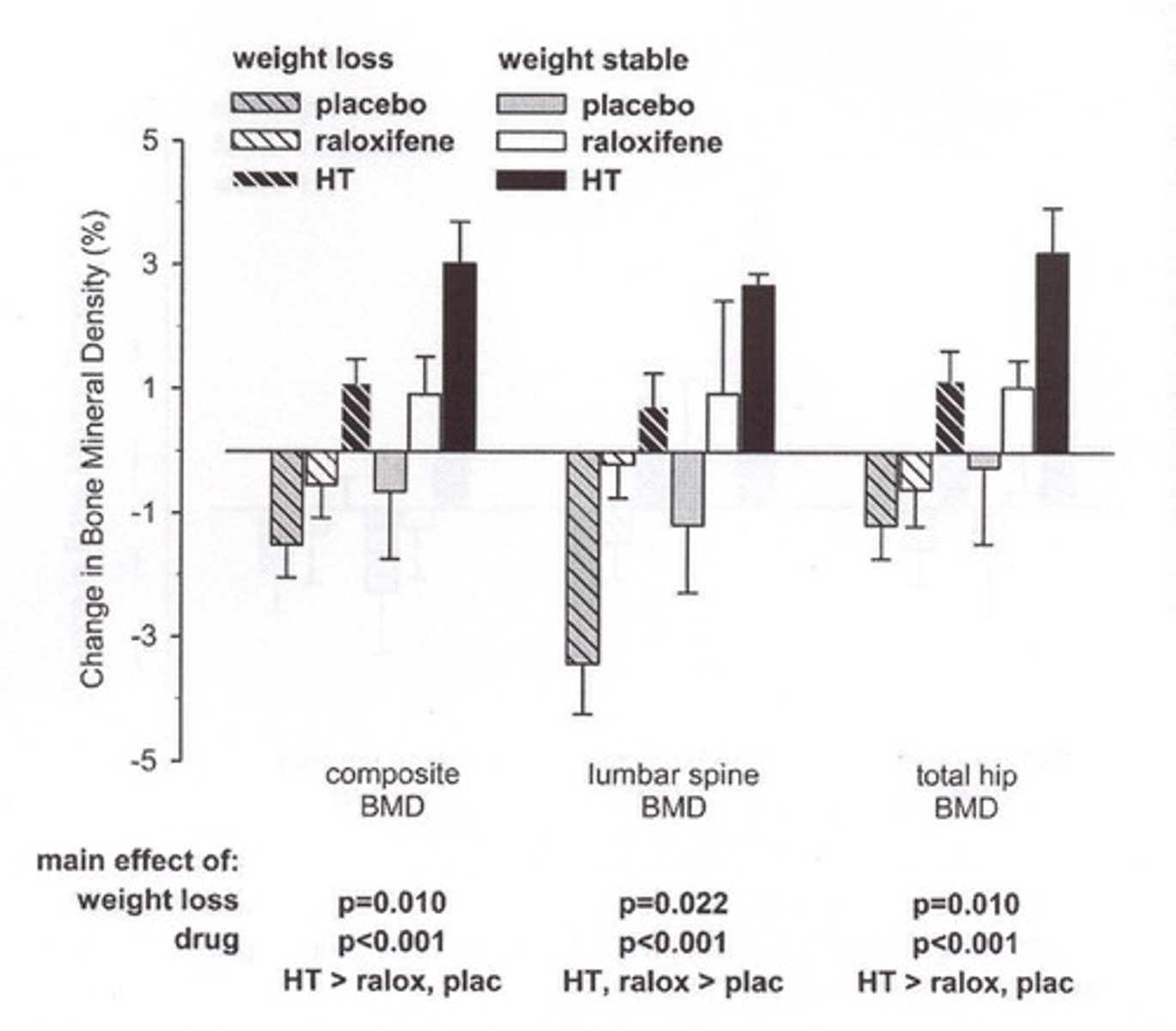
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators
Medications like Raloxifene for osteoporosis treatment.
Bisphosphonates
Anti-resorptive agents for osteoporosis management.
Calcitonin
Nasal medication for osteoporosis treatment.
PTH (Teriparatide)
Hormonal treatment for severe osteoporosis.
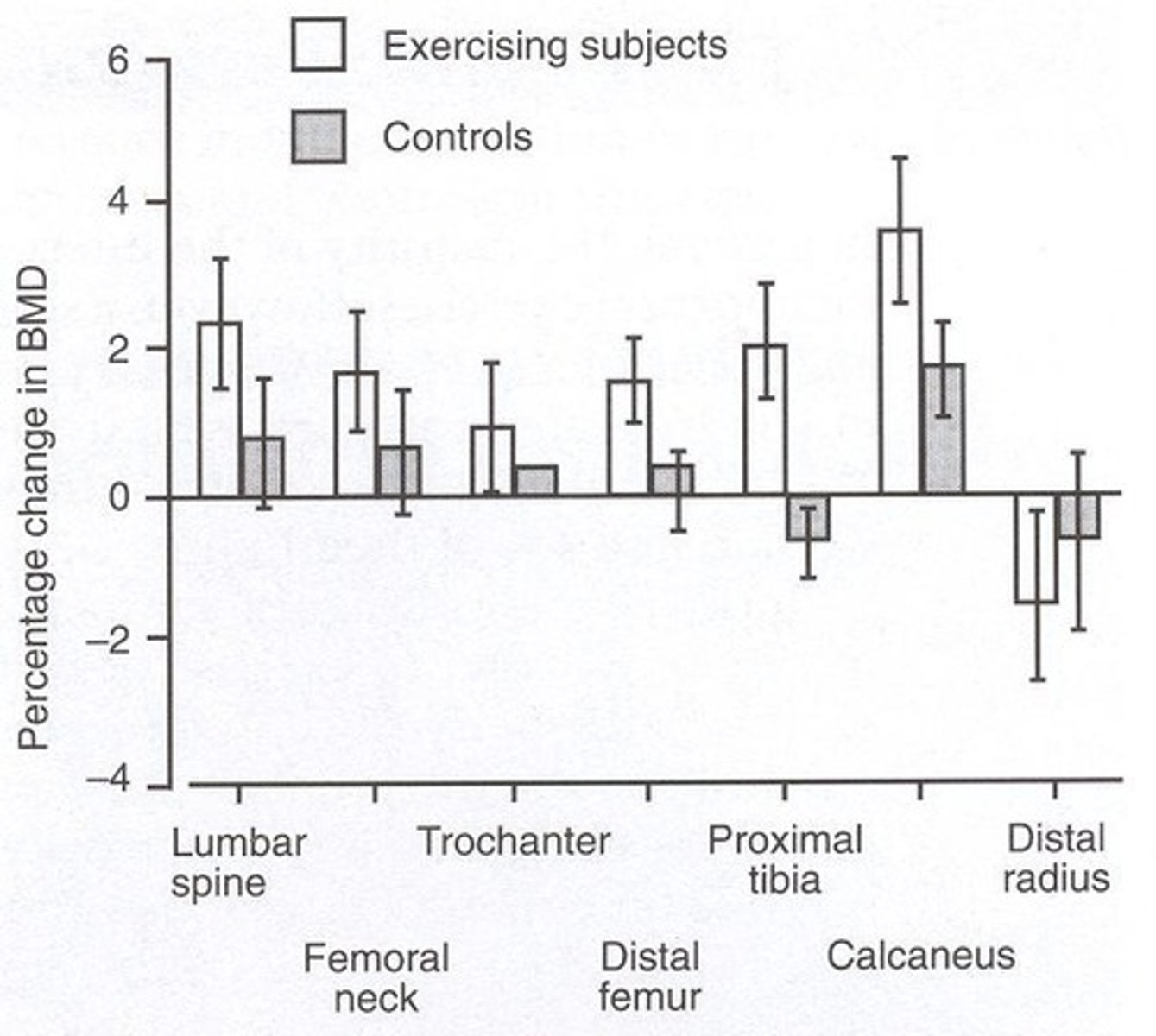
Weight Bearing Exercise
Physical activity that strengthens bones.
Bone Health Strategies
Deposit in bone bank early, minimize withdrawals later.
Spinal Osteoporosis Symptoms
Includes back pain, loss of height, spinal deformity.
Hip Fracture Statistics
50% unable to walk unassisted post-fracture.
Fracture Locations
Common sites include hip, wrist, and vertebrae.
Impact of Osteoporosis
Annual cost of $18 billion due to fractures.
Nutrition for Bone Health
Calcium, Vitamin D, protein, and calories are essential.
Environmental Hazards
Risk factors include poor lighting and slippery surfaces.
Cognitive Impairment
Affects fall risk and fracture likelihood.
Height Loss
Indicator of spinal osteoporosis.
Acute Back Pain
Common symptom of spinal osteoporosis.
Fracture History
Prior fractures increase risk for future fractures.
Smoking
Known risk factor for decreased bone density.
Family History
Genetic predisposition increases osteoporosis risk.
Amenorrhea
Absence of menstruation linked to bone loss.
Anorexia Nervosa
Eating disorder contributing to low bone mass.
Hormonal Changes
Impact bone density, especially during menopause.
Physical Activity
Essential for maintaining bone density and strength.
Age and Bone Loss
Increased risk of osteoporosis with advancing age.
Chronic Conditions
Certain diseases can lead to secondary osteoporosis.
Fracture with a Fall
Indicates increased fracture risk in older adults.
Bone Remodeling
Process of bone formation and resorption.
Angiogenesis
Formation of new blood vessels, important for bone health.
Critical Years for Bone Health
Years around peak height velocity are crucial.
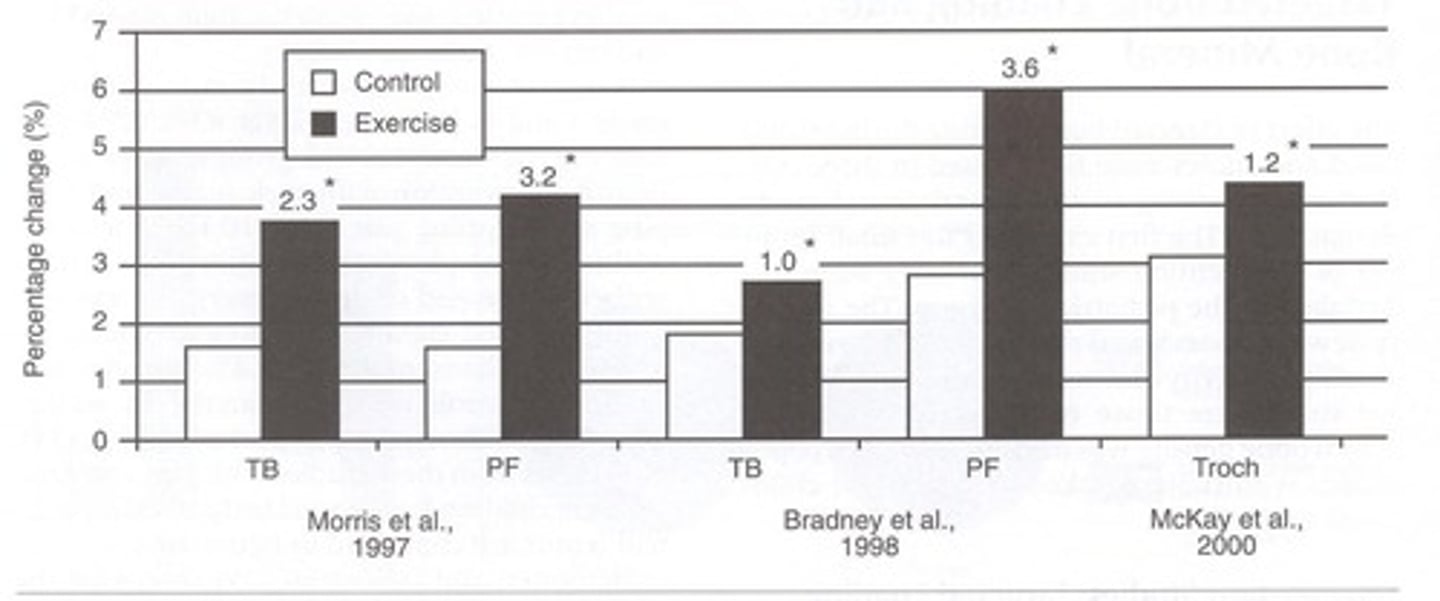
High-Impact Exercise
Effective in increasing bone density in premenopausal women.