HAID: Renaissance (All Periods)
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Mannerism
is a term applied to exaggerated styles, striking visual effects characterized by elongated or over muscular figures set in extravagantly contorted panes.
Mannerism
it was a revolt against the fundamental design principles of classicism of clarity, visibility and stability
Florentine Pieta
also known as the Deposition by Michelangelo, likely intended as his own tomb monument, depicting the moment Jesus is taken down from the cross.
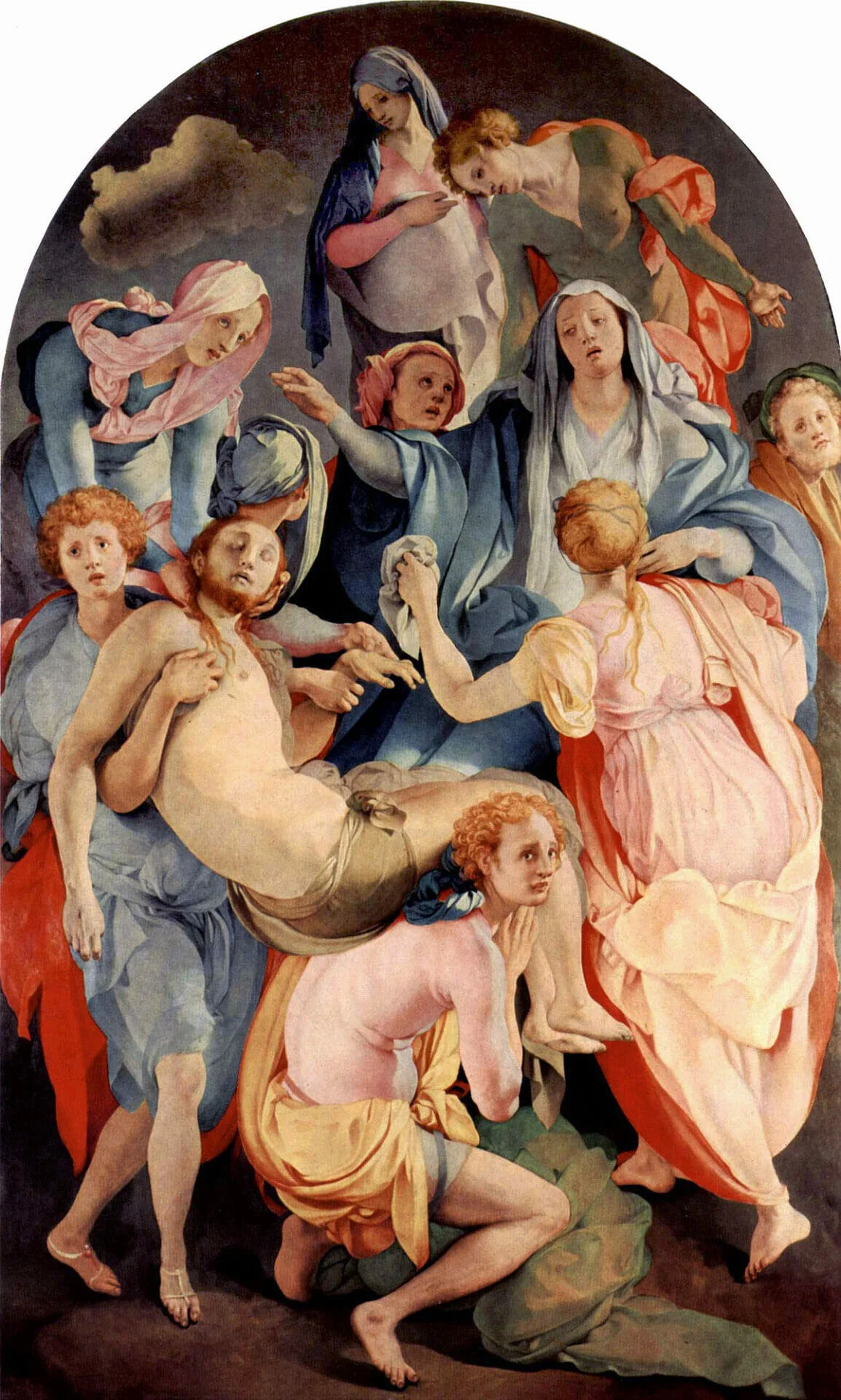
Entobment, Jacopo Pontormo

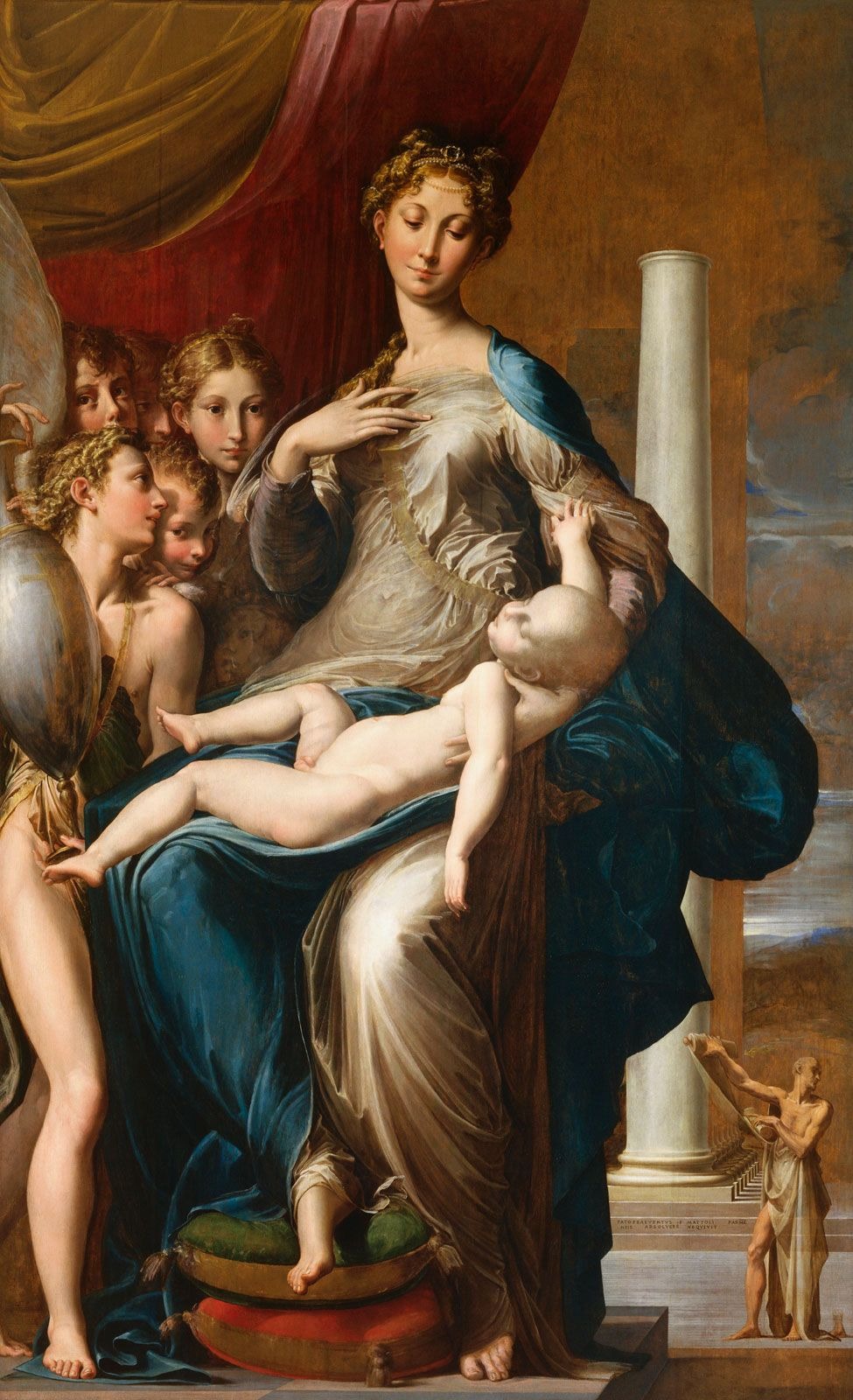
Madonna with the long neck, Parmigianino

Tintoretto
Il Furioso, was called as such for his phenomenal energy in painting and dramatic use of perspectival space and special lighting effects making him a precursor of baroque art
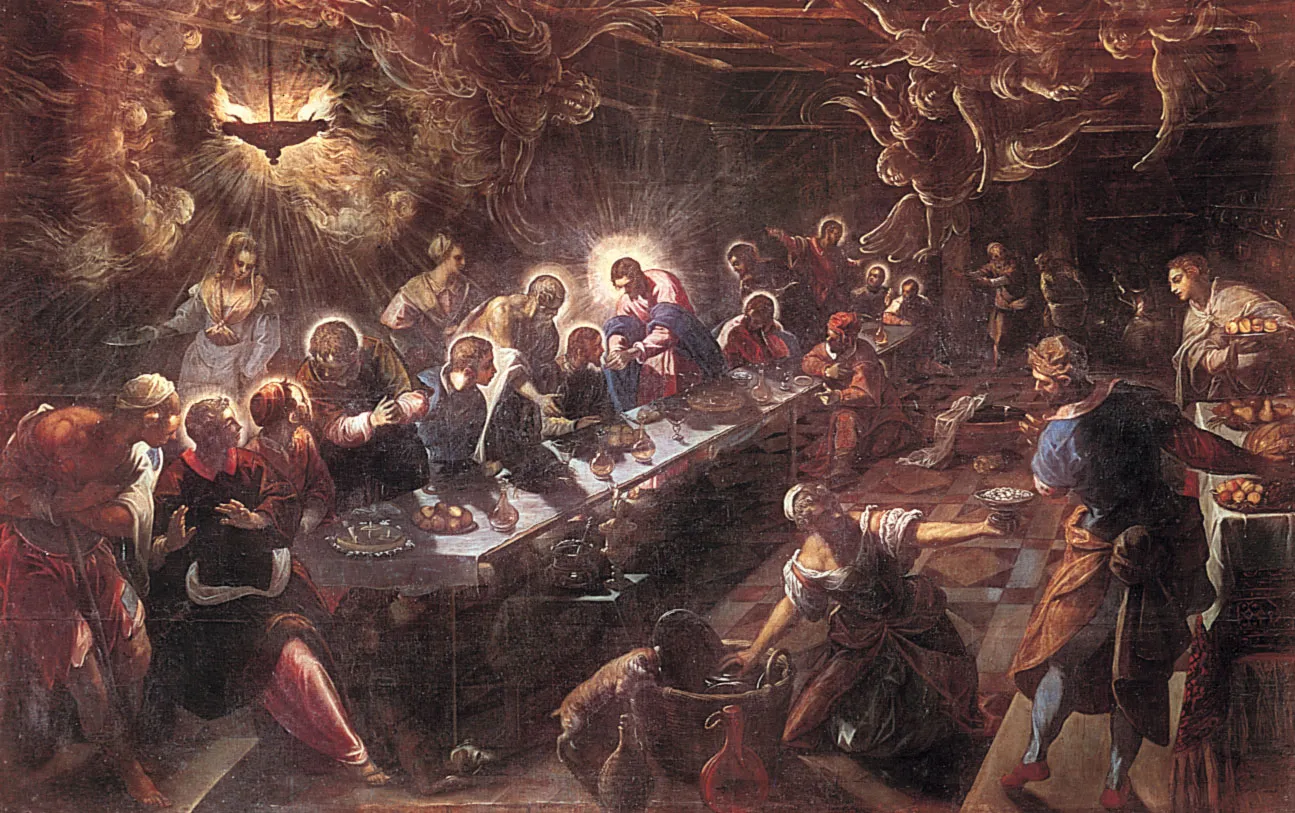
The Last Supper, Tintoretto

Veronese
known as a supreme colorist and for his illusionistic decorations. famous for his paintings of biblical feasts crowded with figures.
Tintoretto, Veronese and Titian
Triumvirate of pre-eminent Venetian painters of the late Renaissance
Baroque
became the official architectural style in France in the 17-18th century with its capital at Versailles
Louis XIV
the sun King of France, known for his absolute monarchy and the expansion of French influence in Europe.
The Royal Academy of France
founded by royal minister Jean-Baptiste Colbert to manipulate imagery for political advantage
religious
during the renaissance period man was freed from the _ restraints of the medieval times
humanism
idealogy that believes that humans purportedly created in the Judeo-Christian God, had been given the ability to some meaningful end
five factors that motivated the renaissance period
The church
Florence
Humanism
The Medici
Church
the greatest patron of the arts
Humanism
gave new subjects to artists in the form of nudes, portraits of actual people and landscapes
Early Renaissance
a style of Italian art and architecture developed during the 15th century characterized by the development of linear pers, chiaroscuro and free use of classical details in buildings
Chiaroscuro
use of light and dark to achieve a heightened illusion of depth
Foreshadowing
a method of rendering a specific object or figure in a picture in depth
Masaccio
first great painter of Italian Renaissance his frescoes were the earliest monuments of Humanism (Holy Trinity)
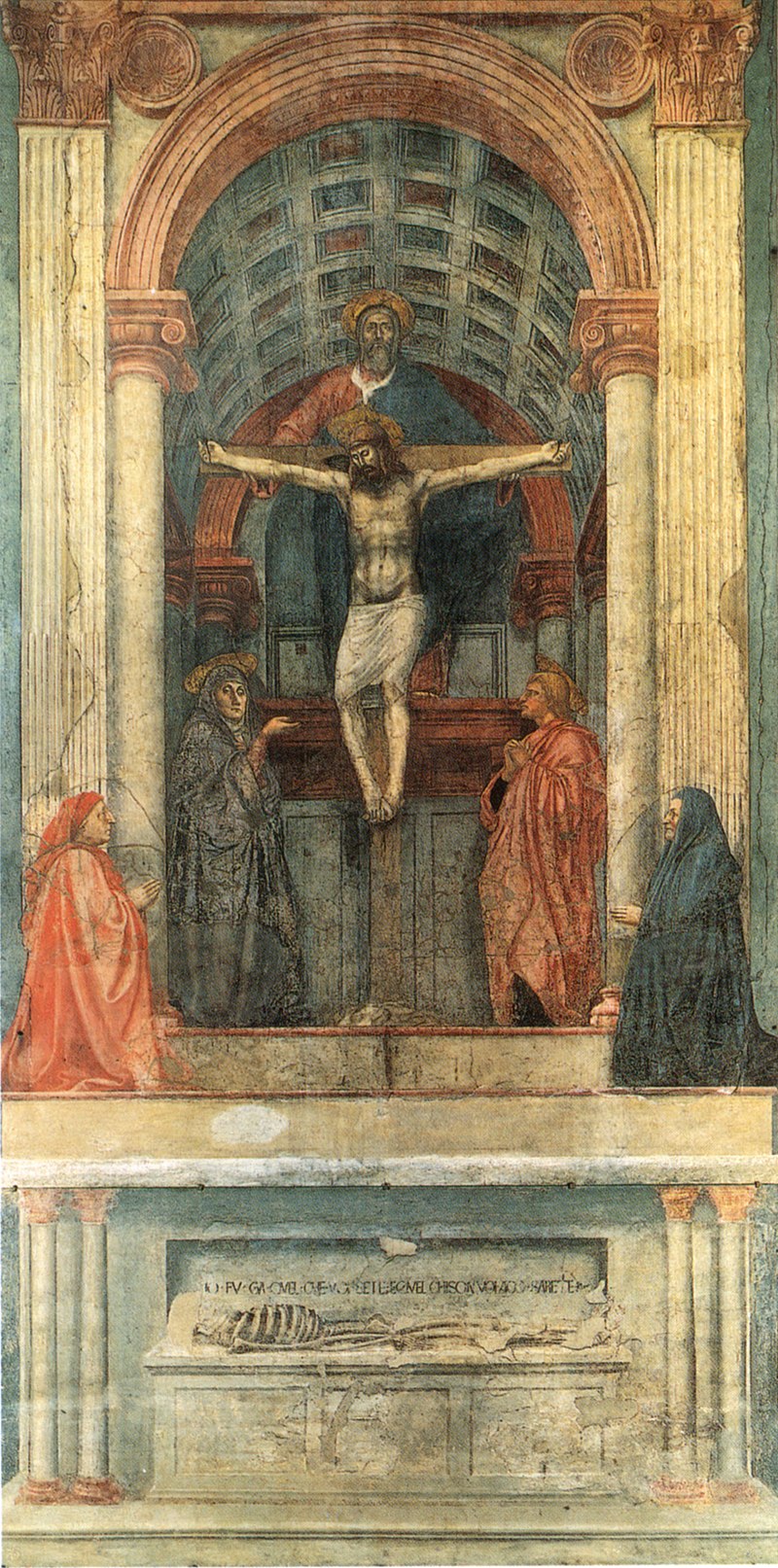
Fra Angelico
a Dominican monk all of his art were religious. Use of luminous, gem-like colors, diffused light slender forms (The Annunciation)

Fra Lippo Lippi
a complete antithesis of Fra Angelico more concerned with physical beauty than the insight or spiritual depth
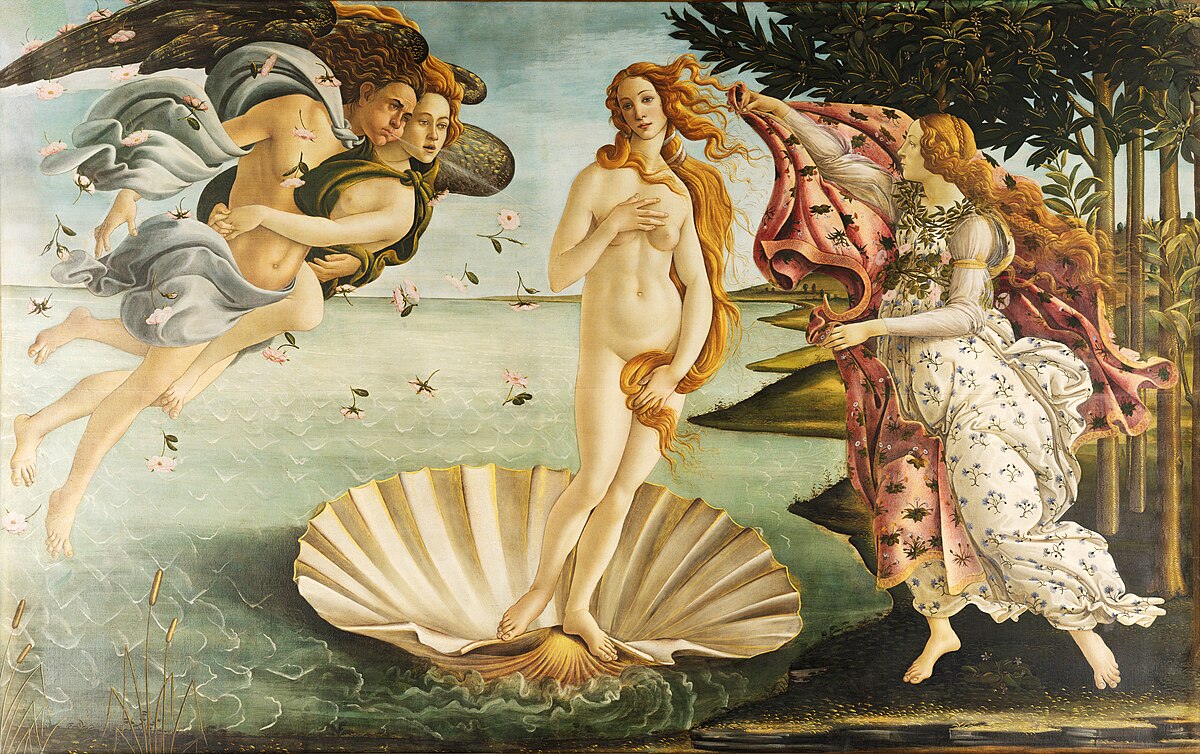
Alessandro Botticelli
interest in Pagan subject matter (Primavera, Birth of Venus)
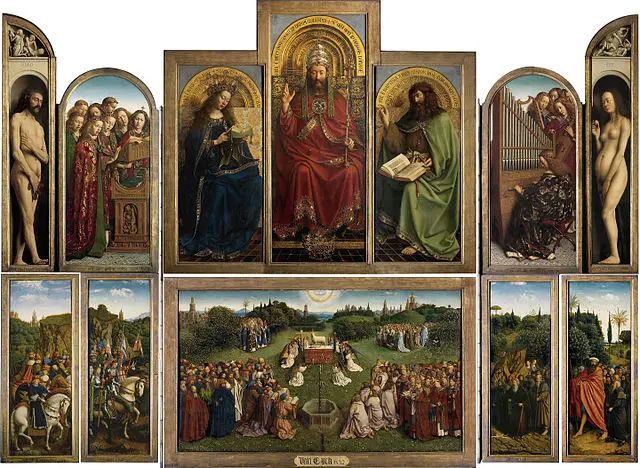
Jan van Eyck
most prominent Flemish painter of Early Renaissance, with his brother Hubert, he perfected the process of painting with oil and varnish. Divided his paintings into panels (triptychs). (Ghent altarpiece)

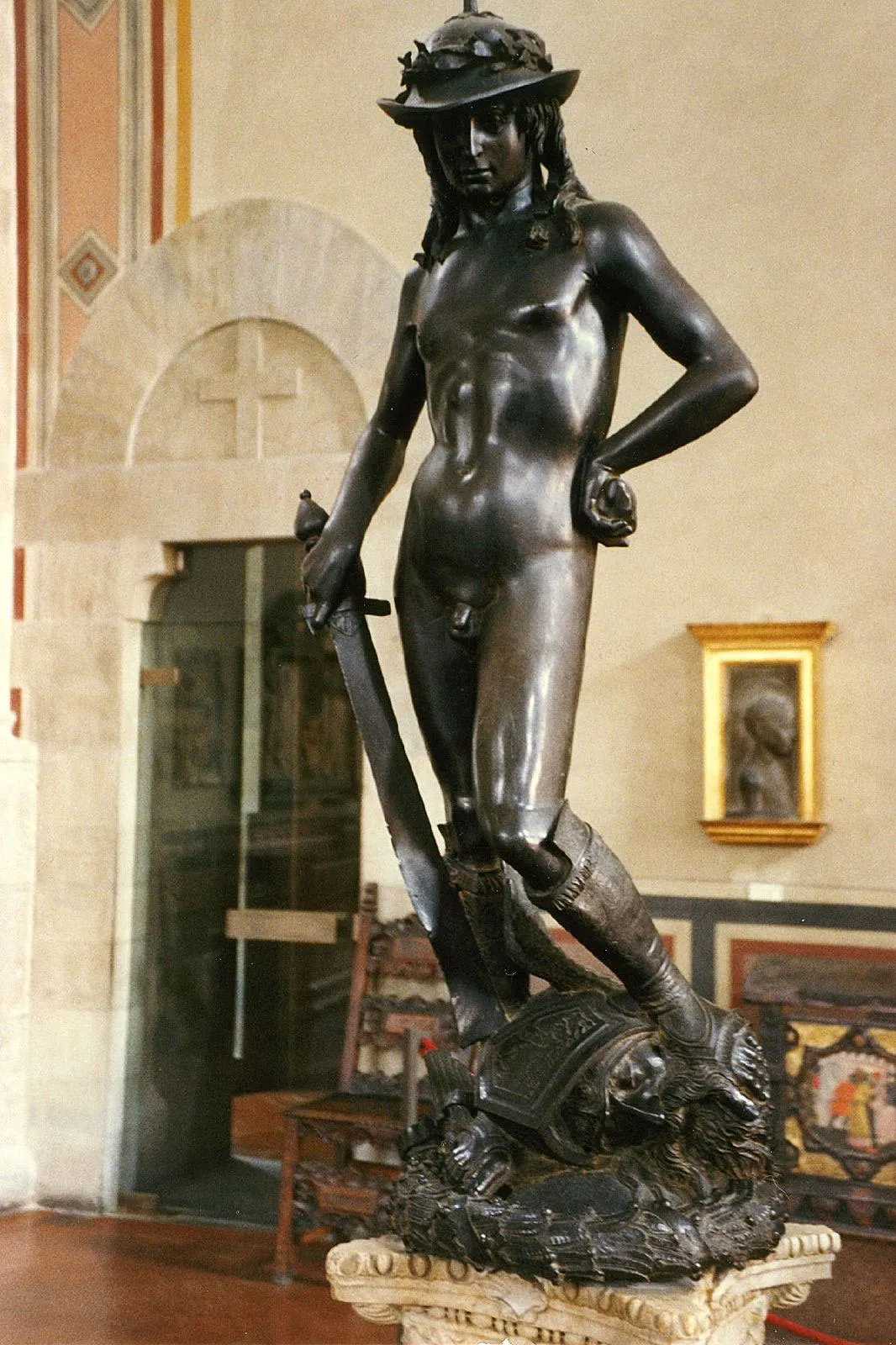
Donatello
sculptor known for sacred theme; was a master of sculpture in both marble and bronze, one of the greatest of all Italian Renaissance artists (David)

Early Renaissance
Period of learning
Designers were intent on the accurate transcription of
Roman elements
Lorenzo Ghiberti
north doors of the Baptistery of San Giovanni, France
Palazzo
is an Italian type of building, are described as palaces or as any urban building built as a grand residence.
Planar classicism
refers to a style that emphasizes flat, two-dimensional surfaces and geometric forms, drawing inspiration from classical architecture, but with a focus on simplicity and clarity rather than elaborate ornamentation.
Early Renaissance Architecture
characterized by emphasis in symmetry, exact mathematical relationships between parts and an overall effect of simplicity and prose.
Characteristics of Italian Renaissance
Ashlar masonry in rusticated finish in horizontal courses
Horizontal cornices and balustrades
Doors and windows finished with molded architrave of the classic type or pediment in triangular or segmental type
Vaulted ceilings without ribs; dome raised om a drum in fresco
Classic orders appear decoratively
Divided three horizontal bands of classic molding under the windows
The Duomo of the Cathedral of Florence
by Filippo Brunelleschi, a distinctive octagonal design of the double-walled dome, resting on a drum and not on the roof itself
Ospedale Degli Innocenti
series of round arches supported by slender columns and framed by pilasters that carried flat horizontal entablure

Palazzo Medici-Ricardi
the building is divided into storeys of decreasing heights by long unbroken bands call string cornices
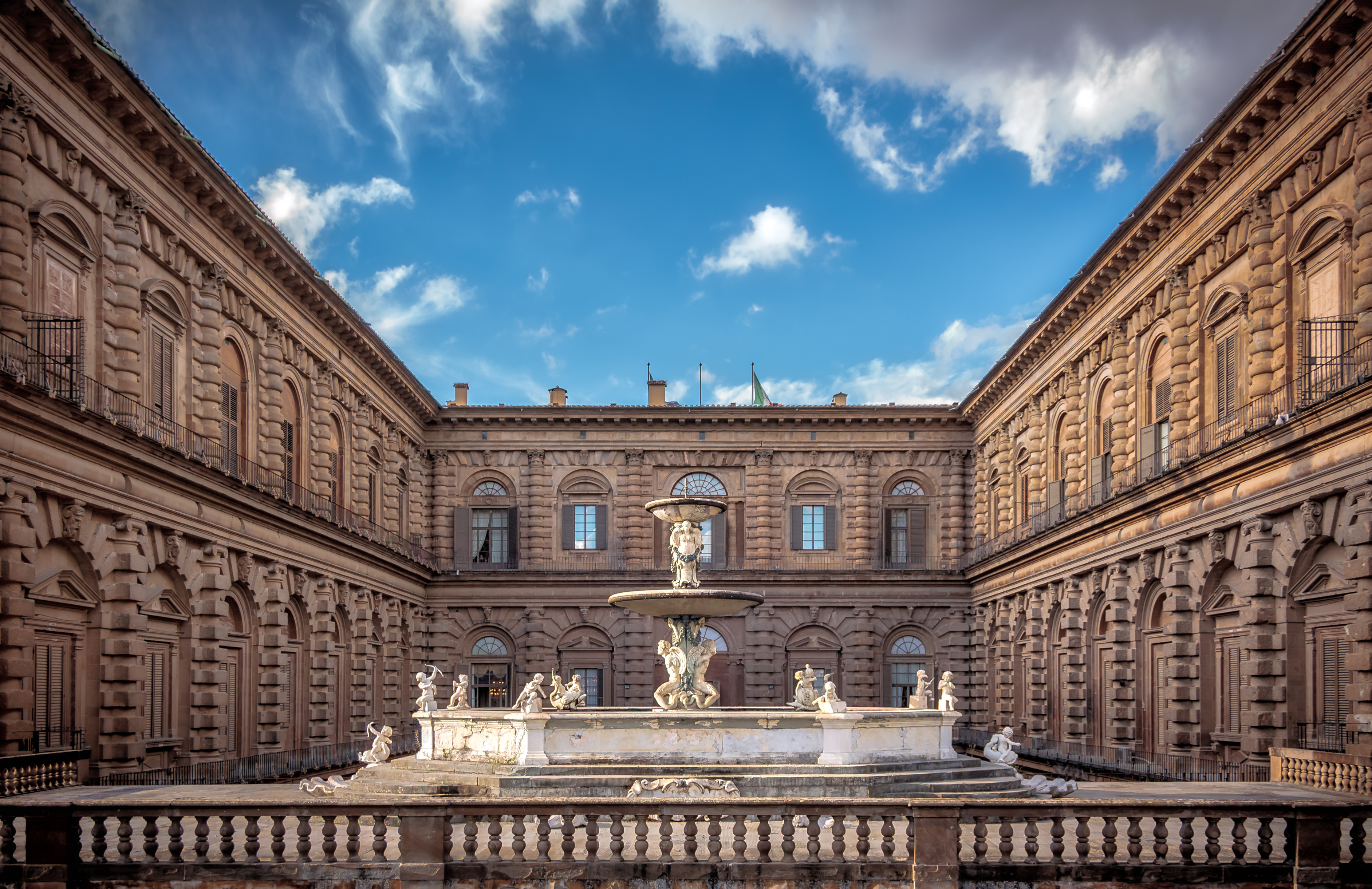
Palazzo Pitti
built by Lucca Pitti it is the largest palace in Italy aside from the Vatican

Palazzo Rucellai
Leon Batista Alberti applied the classical orders of columns to the facade on the three levels
High Renaissance
represented a culmination and convergence of talent
The Big 3 of High Renaissance
Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, Raphael
Sfumato
a modeling technique which consisted of blurring sharp outline with subtle, tonal gradations, imparting a mysterious enigmatic quality, hinting at the subjects spiritual dimension
Leonardo da Vinci
best known artist, attempted to unite science with art
Michelangelo Buonarotti
trained in Florence and is best known as a painter and sculptor. Created a style which laid the foundation for Baroque-Mannerism
The Last Judgement by Michelangelo
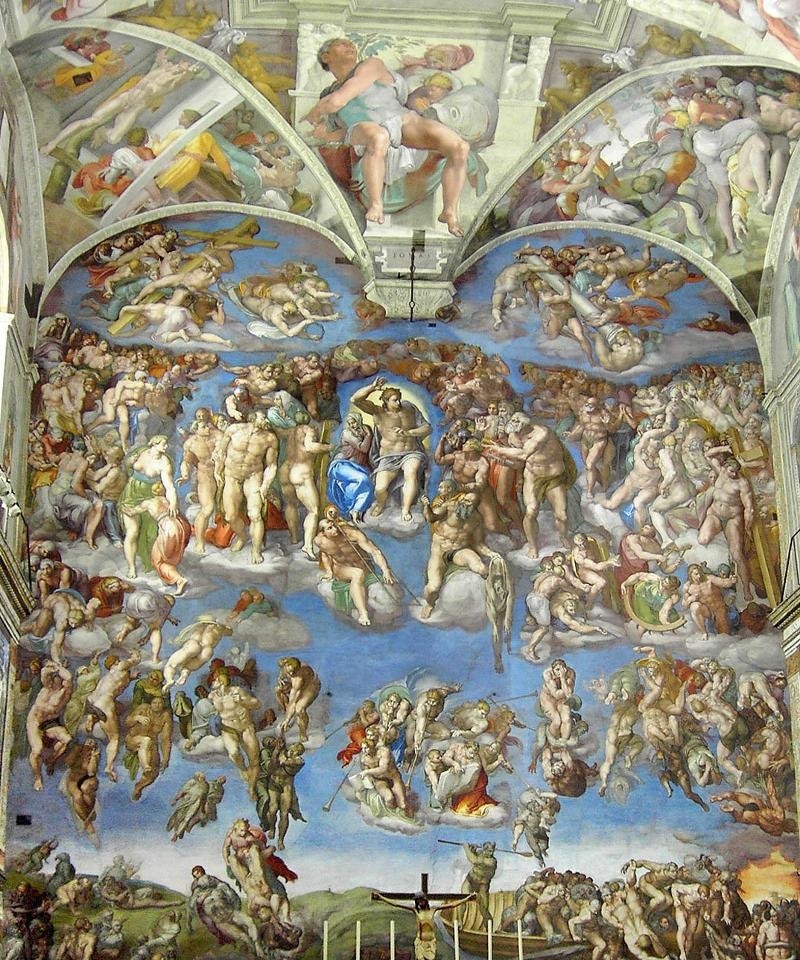

The Creation of Adam
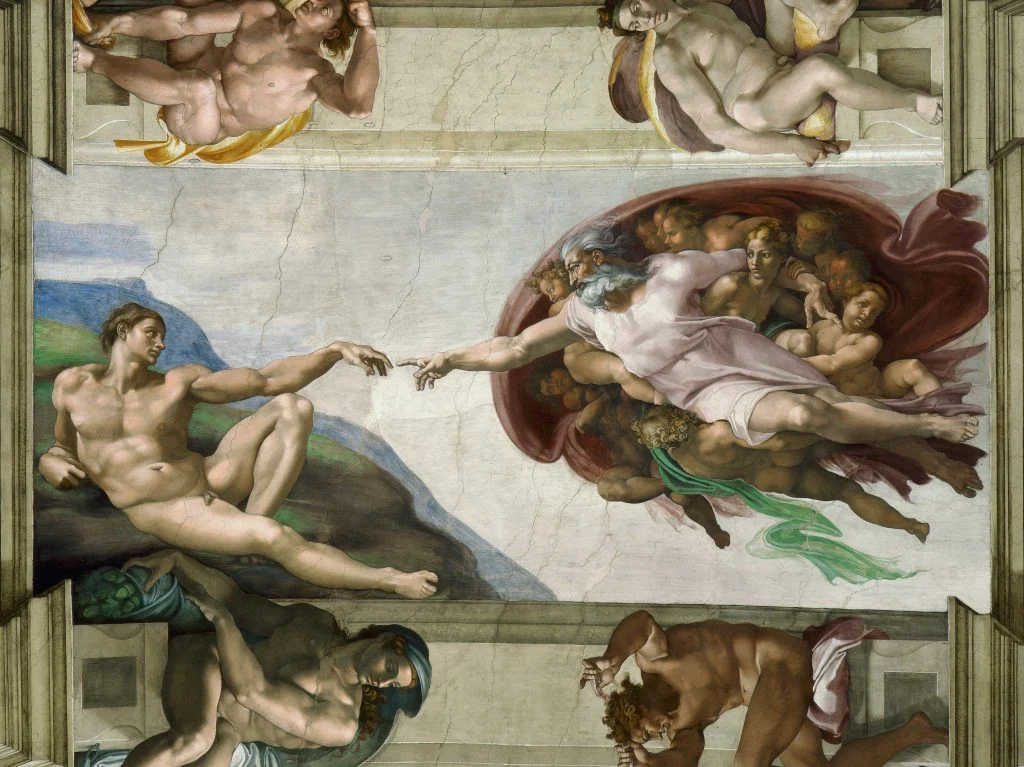

Raphael
Rafaello Sanzo. Trained in Umbria but studied in Florence. Painted gentle calm women in a courteous manner

Giorgone
most famous of the Venetian renaissance painters (Sleeping Venus)

Titian
the leader of the 16th century Venetian school of Italian Renaissance (Assumption of the Virgin)

Albrecht Durer
known as Leonardo of the North, produced more than a thousand woodcuts and engravings
Pieter Bruegel the Elder
greatest flemish painter of the 16th century known for his peasant scenes
Genre painting
refers to a style that depicts scenes from everyday life, featuring ordinary people engaged in various activities, whether at work or leisure
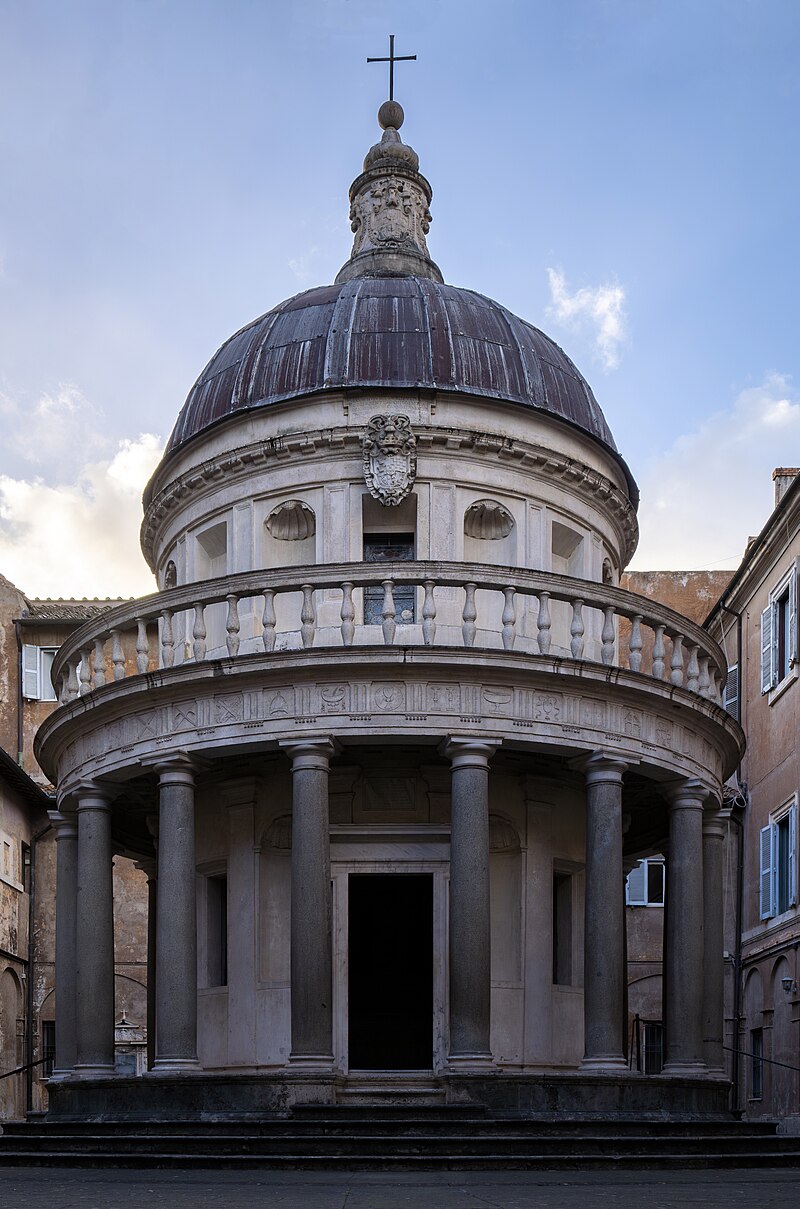
Tempietto by Donato Bramante
small circular chapel erected in the courtyard of San Pietro in Montorio in Rome on the supposed site of the martyrdom of St. Peter

Capitoline Hill
by Michelangelo; composed of the palace of the senate, the conservatory and the Capitoline Museum where the statue of Marcus Aurelius stood
Characteristics of High Renaissance Architecture
impressive staircase in front of the high rusticated base
stringcourse separating the base from the first story
tall pilasters with Corinthian capitals
Alternating arched and triangular pediments over windows
ornamental cartouches over doorways and statuary
circle was a dominant motif
Rustication
type of decorative masonry achieved by cutting back the edges of stones to a plane surface while leaving the central portion of the face either rough or projecting markedly
Renaissance in France
Gothic and Renaissance
Renaissance details were grafted into gothic features
Classical horizontality in French manner and gothic verticality
High mansard roof with dormer windows and lofty chimney
Combination of classic and medieval moldings were used
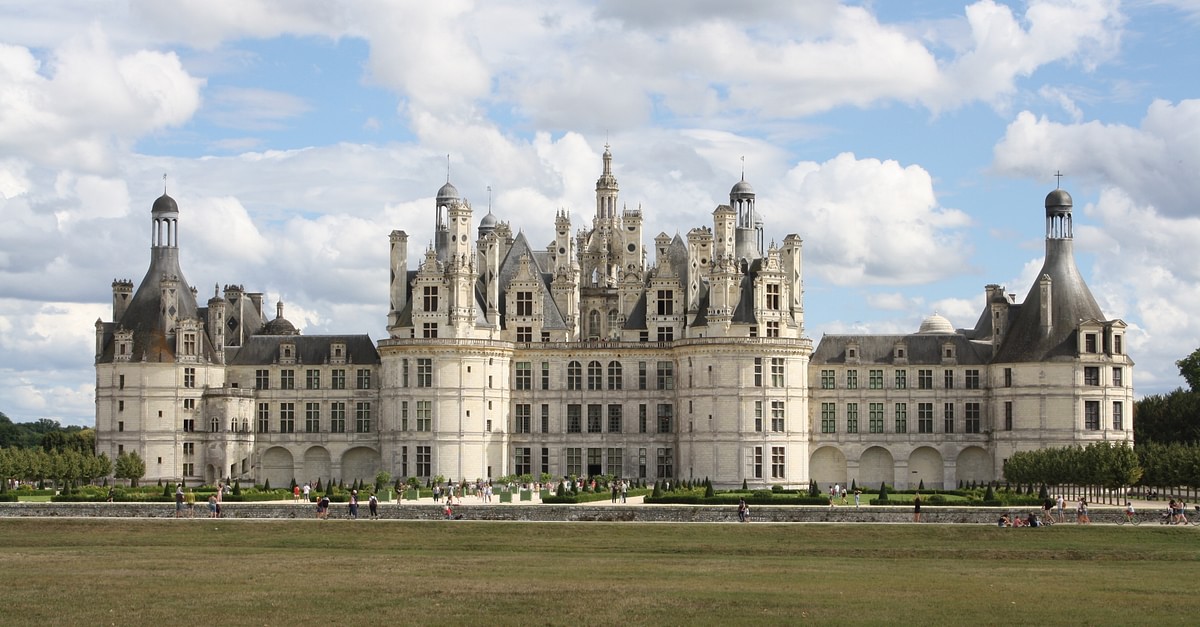
Chateau de Chambord
known for its horseshoe shapes and entrance staircase

Palais de Fontainbleau
the favorite residence of Francis I, is is the largest palace of the 16th Century
Elizabethan Period
the term given to Early Renaissance architecture in England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I.
transitional style between Gothic and Renaissance in England mainly country houses characterized by large mullioned windows and strapwork ornamentation
Hardwick Hall
the numerous and large mullioned windows are typically English renaissance while the loggia is Italian
Loggia
(from the Italian word for ‘lodge’) is an outdoor corridor or gallery with a fully covered roof and an outer wall that is open to the elements. Traditionally, they either ran along the facade of a building or could exist as a stand-alone feature. The open outer side of the loggia is usually supported by several columns or decorative arches.
Baroque
saw architecture, painting, sculpture and the minor arts being used in harmony to produce the unified whole
Rococo
Rock-like forms, fantastic scrolls, and crimped shells
Nicolas Foquet
Minister of France and organized a system for developing the royal court at Vaux-le-Vicomte, showcasing the Baroque style and influencing future palace designs.
Reformation
dealt a decisive blow to the authority of the Roman Catholic Church (particularly corruption and indulgences)
Counter-reformation
a response to reformation inside the Church to eliminate internal corruption
Council of Trent
a consequence of Counter-reformation denounced Lutheranism and reaffirmed Catholic doctrine
Palladian Architecture
was logical, staid and serene
Proto-Baroque Architecture
was vivid, virile and intense
Baroque Architecture
was dramatic, rich, grand and alive
Rococo Architecture
was a profusion and confusion of detail, presenting a lavish display of decoration
Carlo Maderna
Lengthened nave to form Latin cross and built the gigantic facade
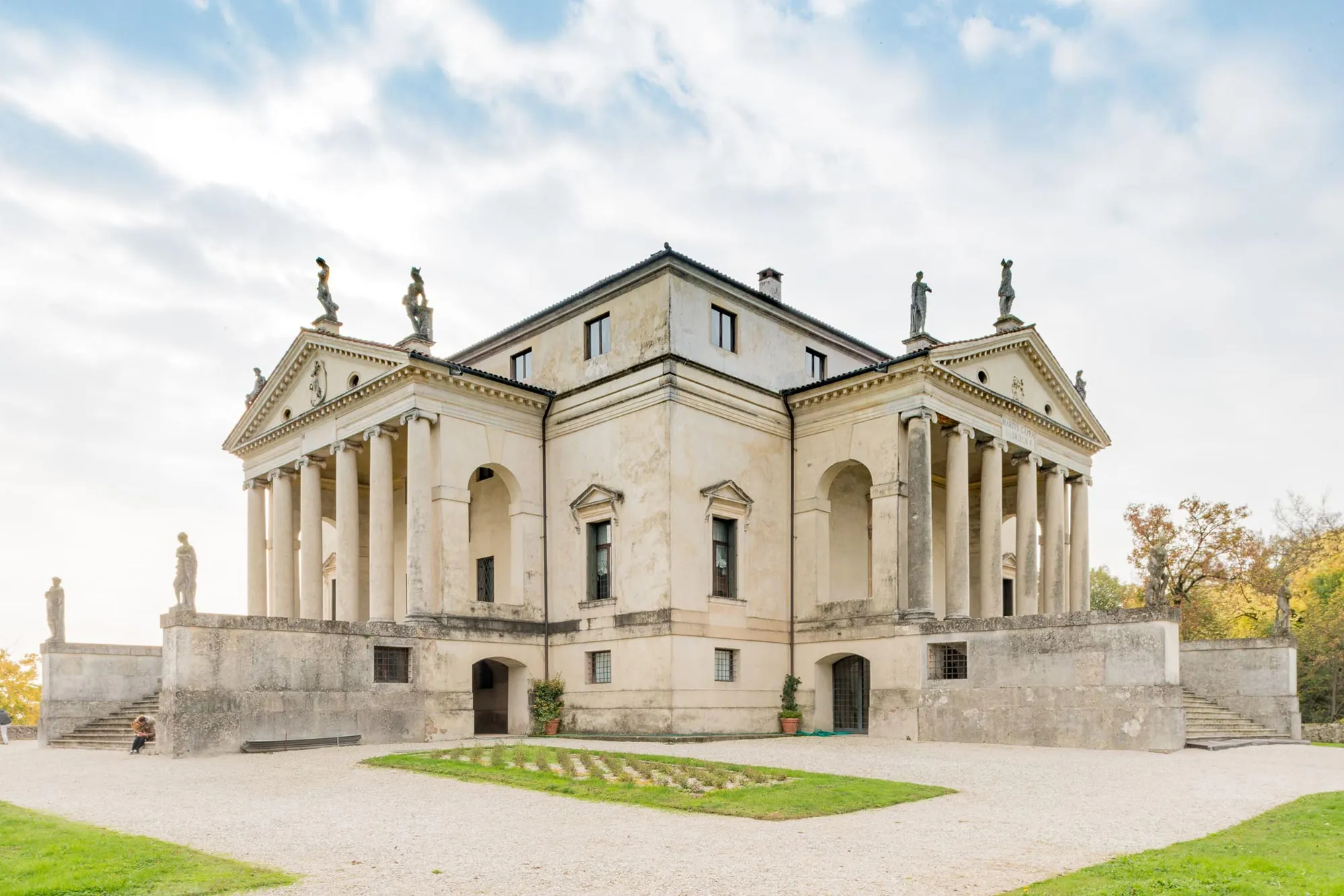
Villa Capra, Andrea Palladio
characterized by the exaggeration of classic features in a square building with pillared portico on each face leading to a central circular hall with dome

Barroco
Portuguese term for imperfect pearl
movement
Baroque is characterized by asymmetrical compositions, powerful effects of _ and strong lighting in a combination of dramatic interpretations of the object matter
France
the largest nation in Europe- strongest and wealthiest during the Baroque period
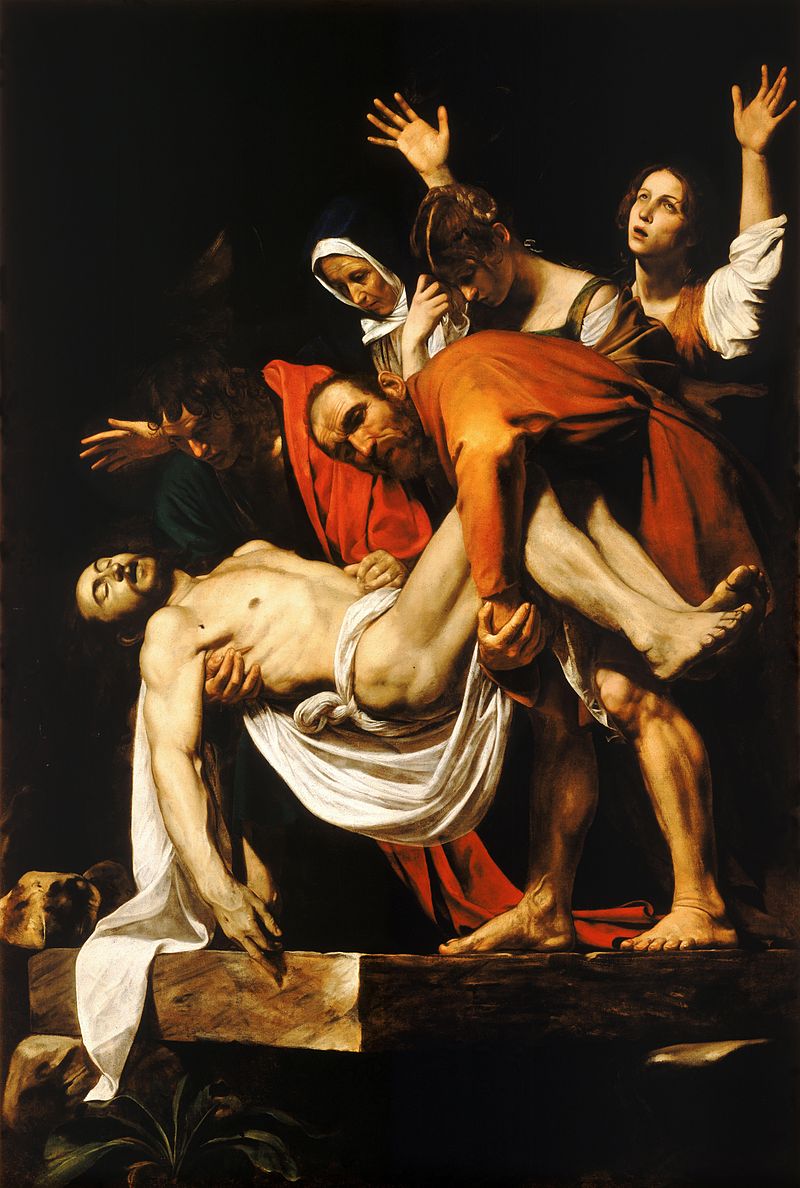
Michelangelo Caravaggio
dramatic, realistic and chiaroscuro technique. chose ordinary people as the figures in his religious works.
tenebrism
use sharply constrasting light and dakr
The Entombment of Chist, Caravaggio

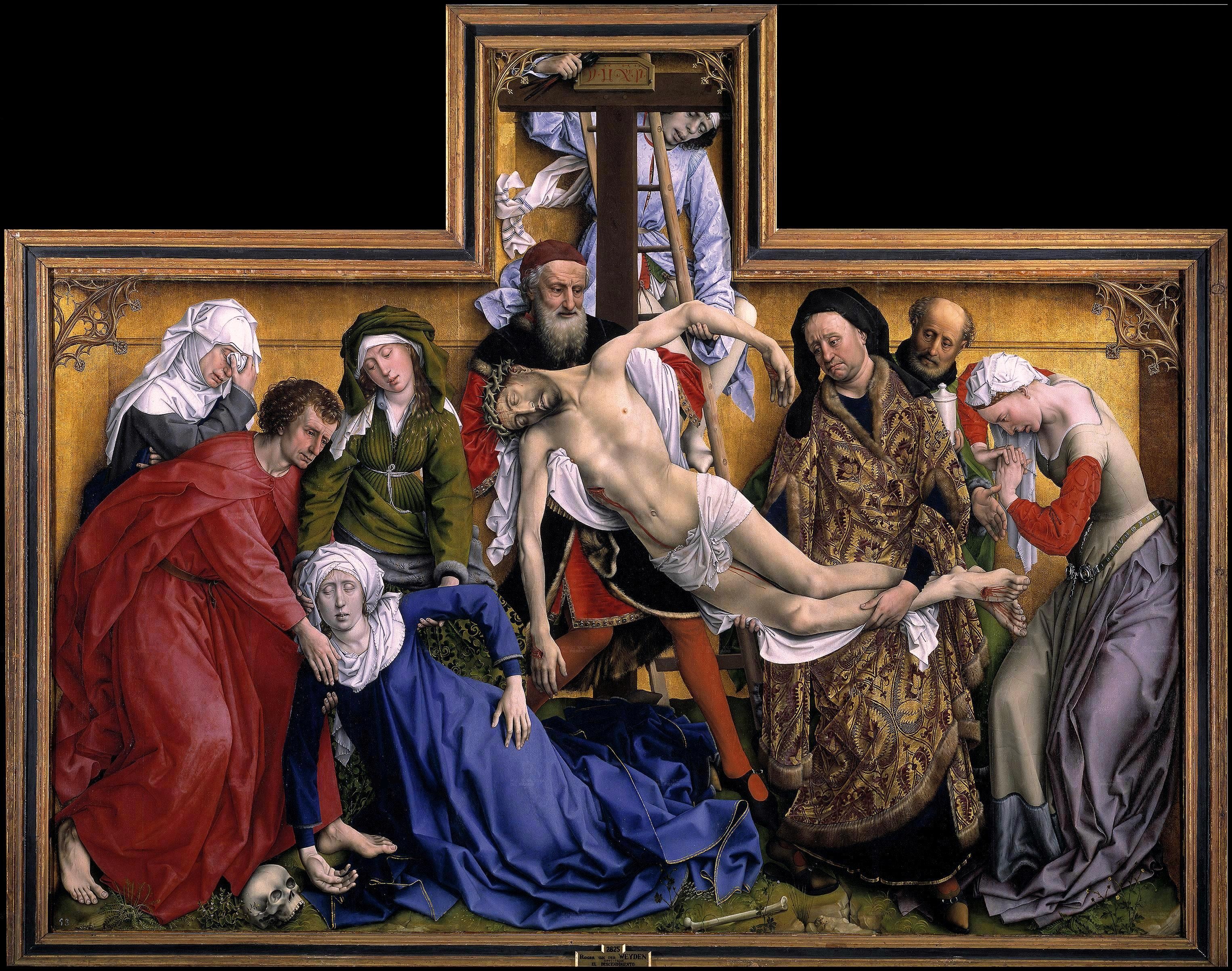
Peter Paul Rubens
greatest Flemish painter of the Baroque, he assimilated Italian ideas with Flemish tradition, most prolific painter and produced about 2,000 paintings
The Descent from the Cross, Peter Paul Rubens
Anthony Van Dyck
aristocratic portraiture that featured with exquisite technique, details of silken fabrics, fine laces and trimmings
Rembrandt Van Rijn
greatest contribution was the development if an artificial technique of handling light and shadow. Graded transitions from light to dark with shadows in warm colors
Jan Vermeer
little Dutch master next to Rembrandt; subject focuses on women at some household chores
Ultramarine blue and Lead-tin Yellow
Vermeer is well known for his use of these colors
Gianlorenzo Bernini
influenced by Michelangelo and by the intensity in animation of Mannerist art.
Baroque Architecture
Preference to curves, double curves and diagonal lines
Pediments in scrolled forms
Flying figures in dangerous looking position
Unity- figures and forms are solidified into masses and cant be separated
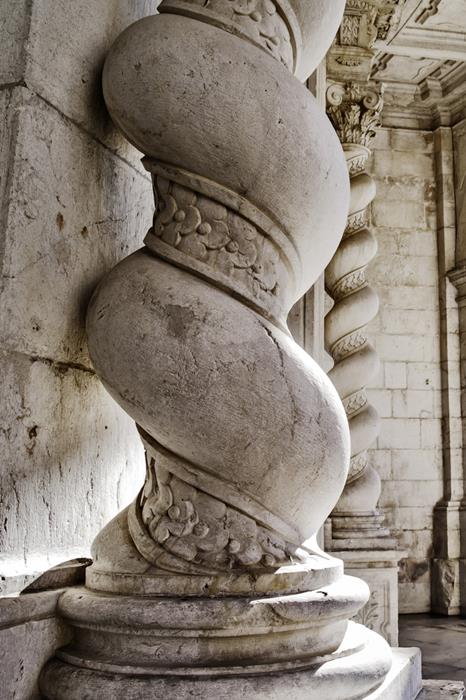
Solomonic columns
columns with twisted shaft

St. Peter’s Basilica
exterior is composed of Corinthian pilasters carried around the entire building giving unity to the entire design
Michelangelo broke the canons of classical proportion by raising the dome over the square room much above its correct
continous whole
in Baroque Architecture surface is treated as a _
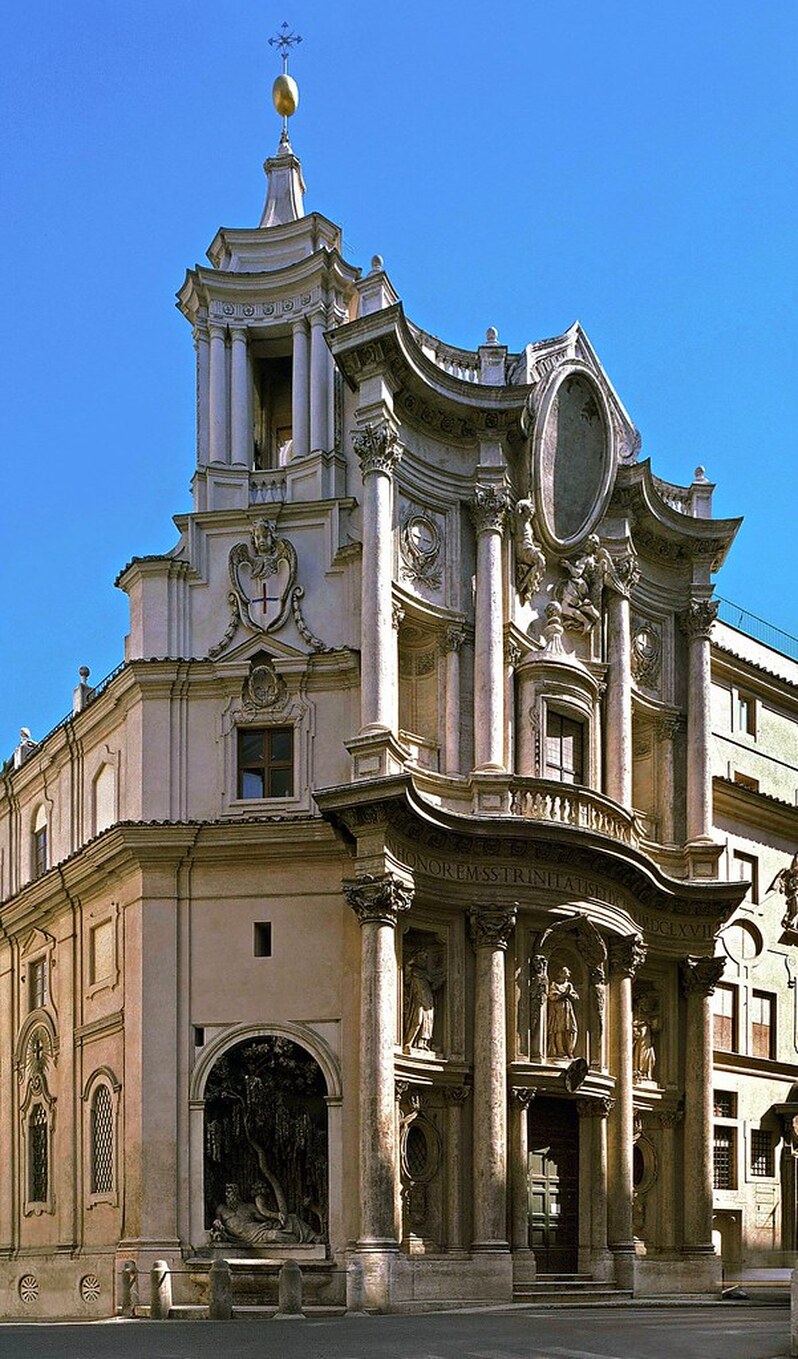
San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane
by Francisco Borromini established his reputation for daring architectural innovations. Featured an alternation of concave and convex elements in the facade and a drum that supported an oval dome.

St. Maria della Salute
284
St. Peter's Square in Vatican City features a colonnade with _ Doric columns arranged in four rows, designed by Gian Lorenzo Bernini to symbolize the church's embrace of the faithful.
Piazza
a public square or marketplace, especially in an Italian town.
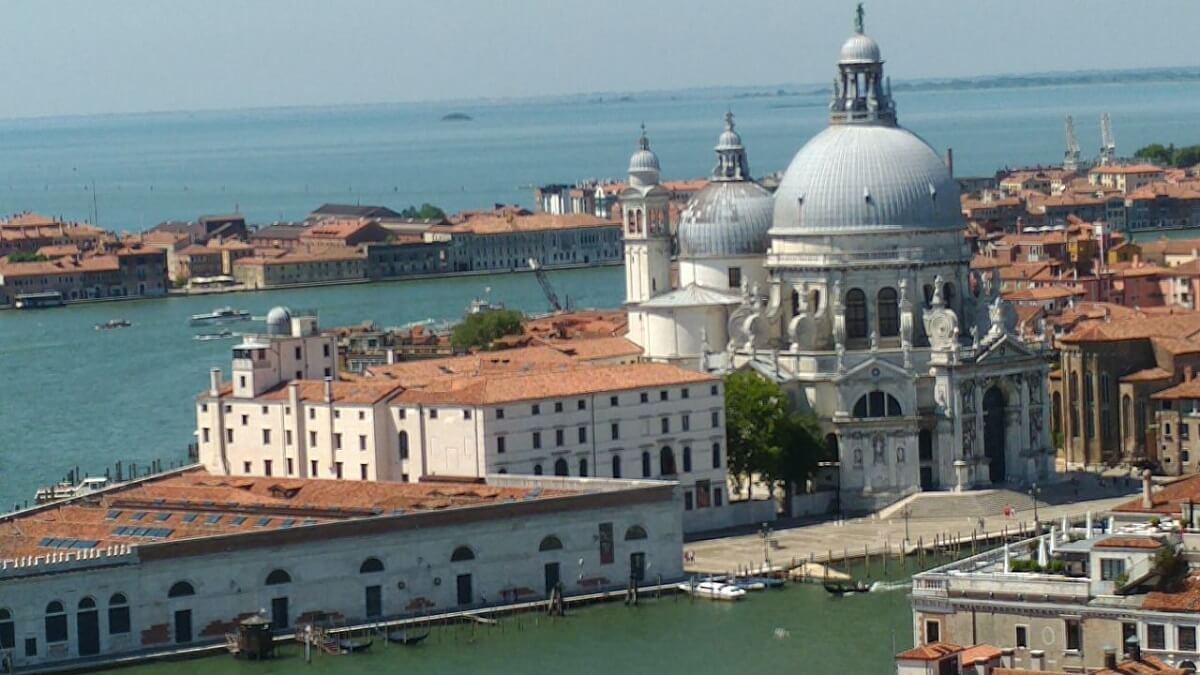
St. Marie della Salute
Roman Catholic church with a vast octagonal building with two domes and a pair of bell towers at the back; one of the largest churches in Venice & features

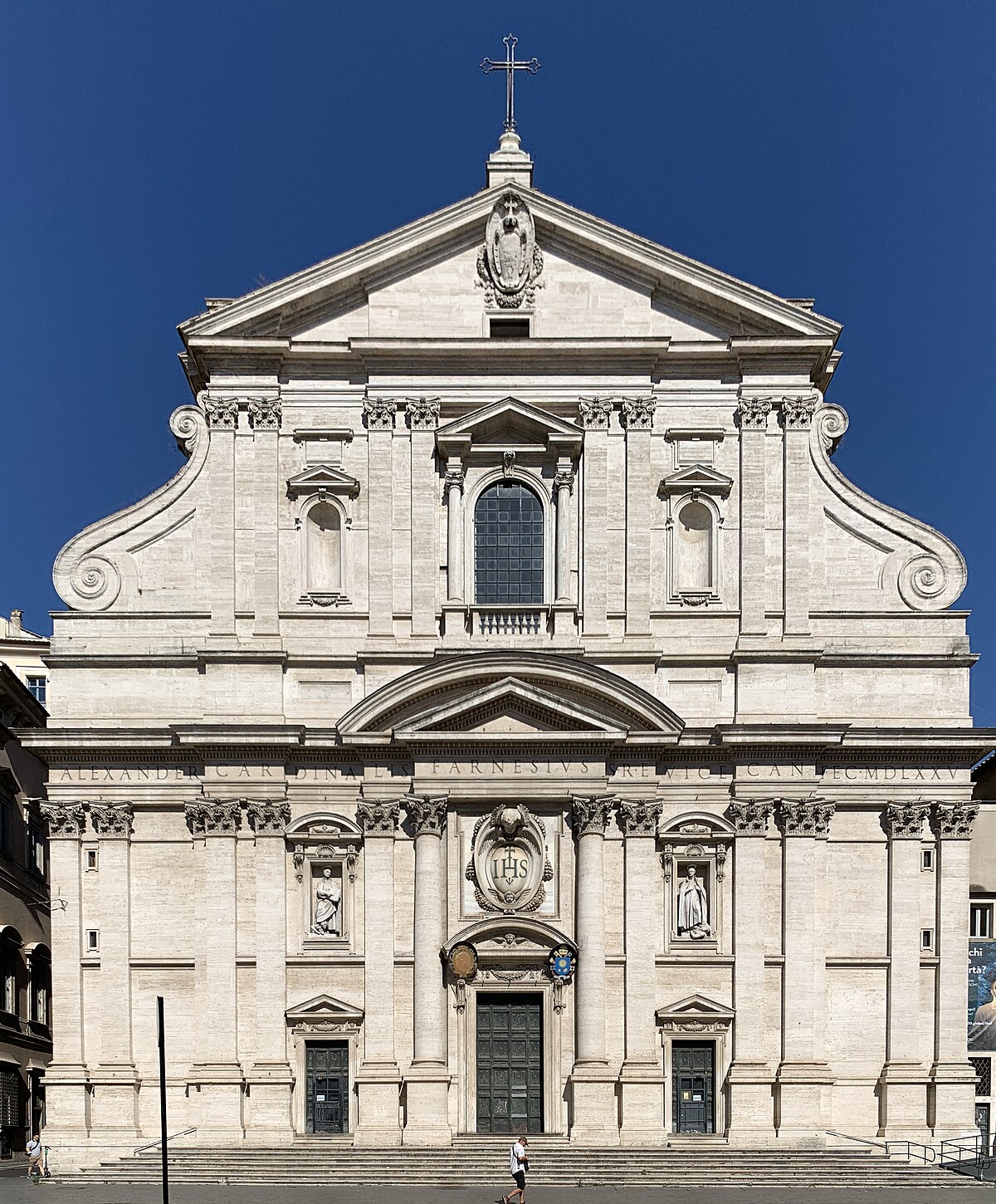
Church of iI Gesu
by Giacomo Vignola, the mother church of the Society of Jesus (Jesuits Order), first truly Baroque facade

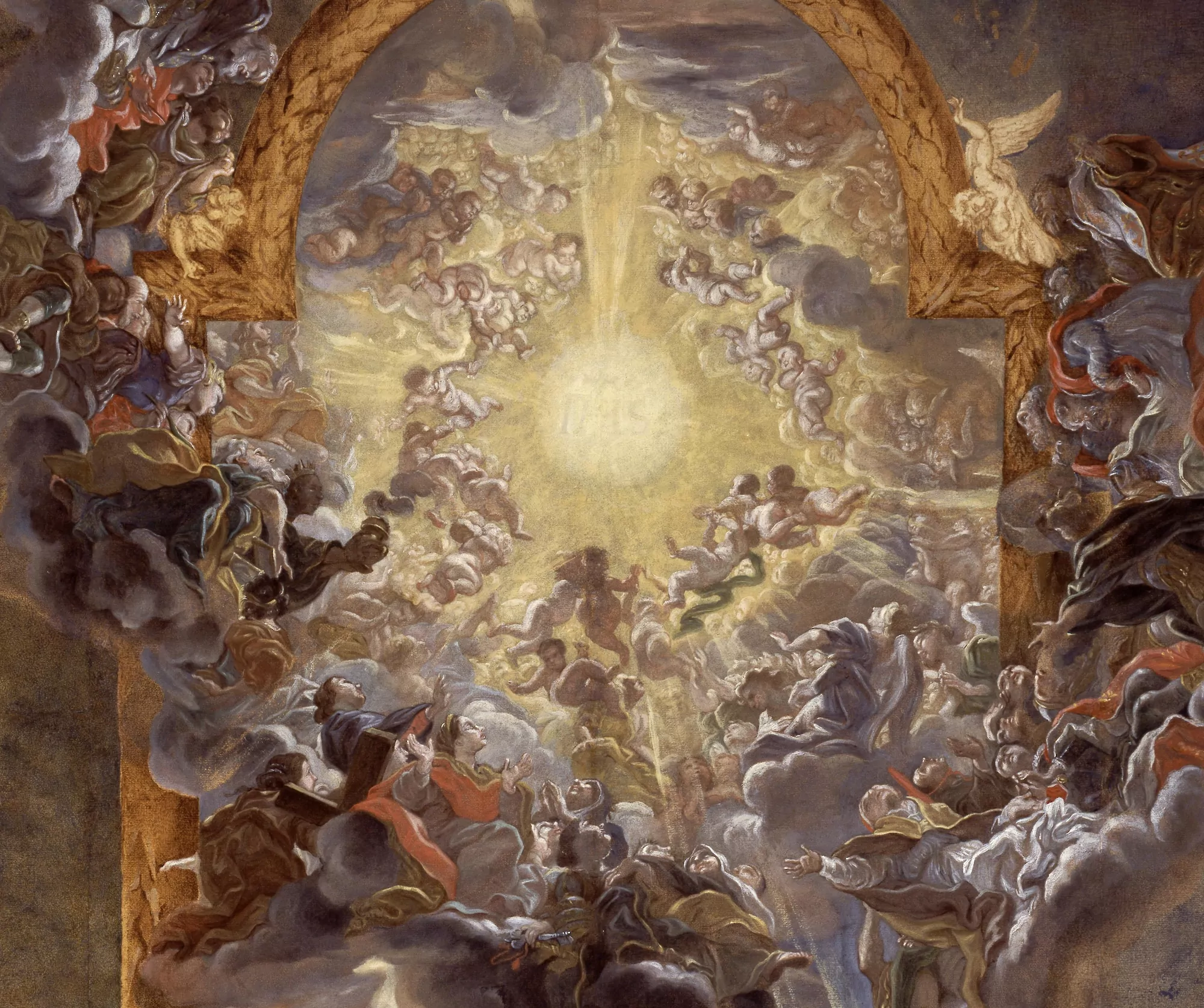
Giovanni Batista Gauli
artist who did the ceiling al fresco of Church of iI Gesu

Palace of Versailles
started by Le Vau continued by Le Brun, Jules Mansart gardens by Andre de Notre
357
Galerie des Glaces at the Palace of Versailles is a grand Baroque gallery famous for its _ mirrors, 17 windows, and ornately painted ceiling, designed to showcase the power and opulence of the French monarchy.
Galerie des Glaces
The Hall of Mirrors