Reactivity 3.1.1-3.1.2 Bronsted Lowry Acis
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
proton transfer reaction
reactant loses H+ = loses positive charge
product gains H+ = gains positive charge
Bronsted-Lowry acid-base behaviour
type of reaction between certain species where reactants release H+ and products have a lone pair that can accommodate an additional H+
what does acid and base strength depend on
their equilibria in aqueous solutions
early theories for acid-base behaviour
France Lavoisier 1777:
oxygen is universal acidifying principle “acid = oxygen and nonmetal)
dismissed because of HCl
SWE Arrhenius 1887:
Almost correct, not general enough (only aqueous) = ”substance which dissociates in water to for H+ and anions= acid, substance for OH- and cations=base, the anions and cations can form a salt”
Bronsted Lowry theory
BL Acid= proton donor
BL Base= proton acceptor
H+ said
proton
conjugate acid base pair difference
one proton
conjugate acid-base pair
acids react to form bases and vice versa; the acid-base pairs related to each other in this way are conjugate
H+(aq)
H3O+
condition for a BL acid to behave as proton donor
base present to accept the proton
how to deduce formulas of conjugate acids and bases
add an H for transition to base
add +1 to charge for transition to base
remove an H for transition to acid
add -1 to charge for transition to base
alkalis
soluble bases which dissolve in water to release OH-
amphiprotic species
substances which can activation as both BL acids and bases
must possess a lone pair of e-
possess H that can be released as H+
periodicity “amphoteric”
from left to right, oxides transition from basic metal oxides through amphoteric oxides, which can react with both acids and bases to acidic oxides.
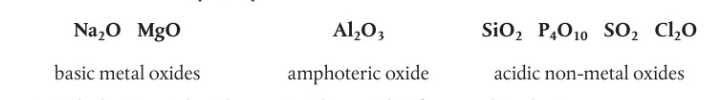
basic metal oxides
react with acids to form a salt and water
amphoteric oxides
react with both acids and bases to form a salt and water
non metal oxides
form weak acids in solution
acid rain
pH of precipitation<5.6, major environmental problem causing negative impact on structural materials, lakes and rivers, and plant life (especially coniferous forests)
nitrogen and sulfur oxides (NOX) and (SOX)
react with moisture in the atmosphere to form weak acids which can then further react to form stronger acids resulting in a complex mix of pollutants in the atmosphere