DDT - Stroke
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is a stroke
An instantaneous lack of blood in the brain which has resulted in a loss of neurological function. TIA (transient ischaemic attack) is known as a mini-stroke, and is typically a precursor to a stroke
Stroke risk factors
High blood pressure (normal 120/80mmHg), cigarette smoking (15% of all strokes in the UK), atrial fibrillation, diabetes, high cholesterol, carotid stenosis, obesity, Iatrogenic (illness caused by treatments or medical examinations), ethnicity, male risk higher than female
Arteries that bring blood to the brain
2 carotid arteries, vertebral and basilar arteries supply
Effects of stroke on regions of the brain
Anterior cerebral artery
Sensory/ motor control lower body
Mental state impairment
Middle cerebral artery
Upper limbs and face
Broca's Aphasia (LHS)
Posterior Cerebral artery
Visual field
Basilar artery
Locked in syndrome
Cerebellar artery (branched from basilar artery)
Poor co-ordination/ muscle tone
Dysphagia
What is infarction?
Tissue death is caused by a lack of oxygen due to a blockage in the blood supply. The most common area of infarction is the middle cerebral arteries
What is a penumbra and core
Penumbra is the area which could suffer damage from ischaemia BUT it is reversible. The core is damaged areas caused by infarction that cannot be repaired at all. Penumbra is also going to cause apoptosis, rather than core, which will cause necrosis
Inflammatory response to stroke
Neutrophils: Appear in the middle cerebral artery occlusion after a few hours
Lymphocytes: Appear within 24 hours (Makes tissue damage caused by stroke worse)
Microglia: Release pro-inflammatory cytokines
After a while, debris is digested via phagocytosis and beneficial cytokines may be released
Embolism meaning
Something that is able to block blood vessels
Pyknotic meaning
Nucleus shrinkage in necrotic cell
Angiogenesis meaning
Production of new blood vessels
Ways to diagnose strokes
FAST (Face dropped on one side, Arm(s) cannot be raised, Speech is slurred, Time to call 999) MRI, CT which need to be done as soon as possible to understand nature of stroke and deal with it
Treatment methods for strokes
Thrombolysis, thrombectomy, aspirin (stops platelet build up in blood vessels) as well as warfarin (antithrombotic treatment. Prevent the production of vitamin K, vital for thrombosis. Dangerous fo those with clotting factor defects however)
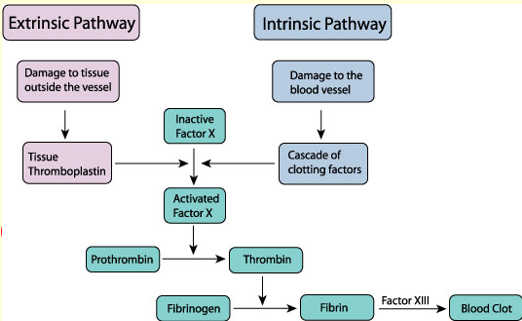
Overview of clotting (both intrinsic and extrinsic)
Window of opportunity for effective thrombolysis
4.5 hours from when the stroke first started
What is mechanical thrombectomy?
A catheter attached to a thin wire is put into the artery at the groin, which then goes to the brain, and is only used for those with severe ischaemic stroke, to remove a blood clot
What is haemorrhagic transformation
Where blood leaks into the brain, from a disrupted blood-brain barrier, which can worsen the effects of a stroke