Geography coasts
1/185
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
186 Terms
What is the definition of the coast
Areas where the land meets the sea
What is the definition of the littoral zone
The wider coastal zone including adjacent land areas and shallow parts of the sea just offshore
Briefly, what are the three things the littoral zone
The land lying between high and low tide levels
The upper beach to the base of the cliffs
The shallow waters adjacent to the coast
Name 5 uses of the coast
Tourism
The navy
Agriculture and farming
Trading point
Electricity and power generation
Aquaculture - food sourcing (eg fishing)
Retail
Animal habitats
Transport (eg ferries)
Leisure
Geology - fossil research
Waste disposal
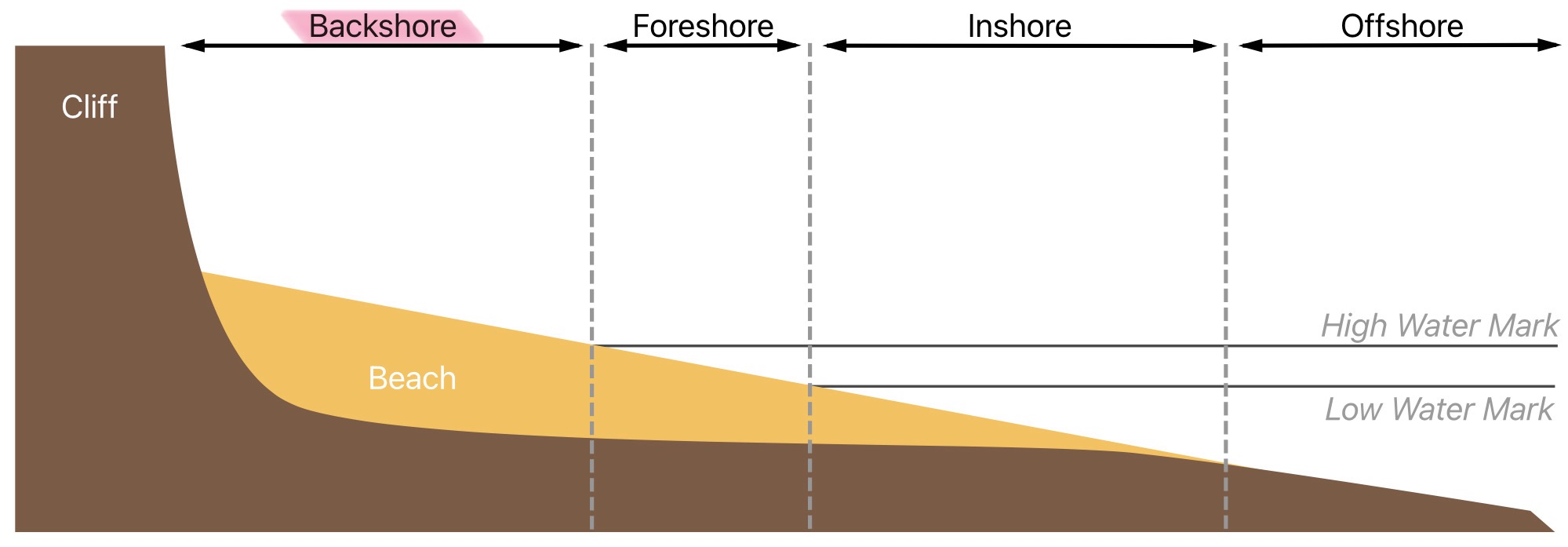
What is the back shore of the littoral zone
The area of the shore lying between the average high-tide mark and the vegetation, affected by waves only during severe storms
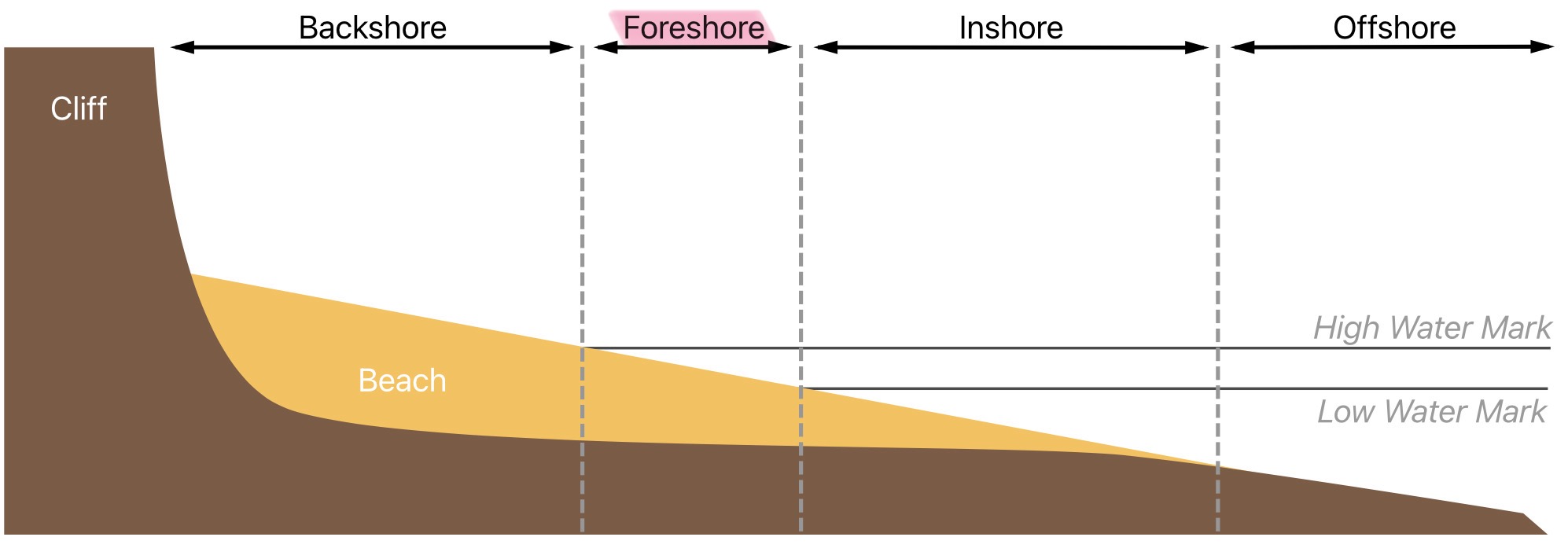
What is the foreshore of the littoral zone
The part of the seashore between the Hugh water mark and the low water mark
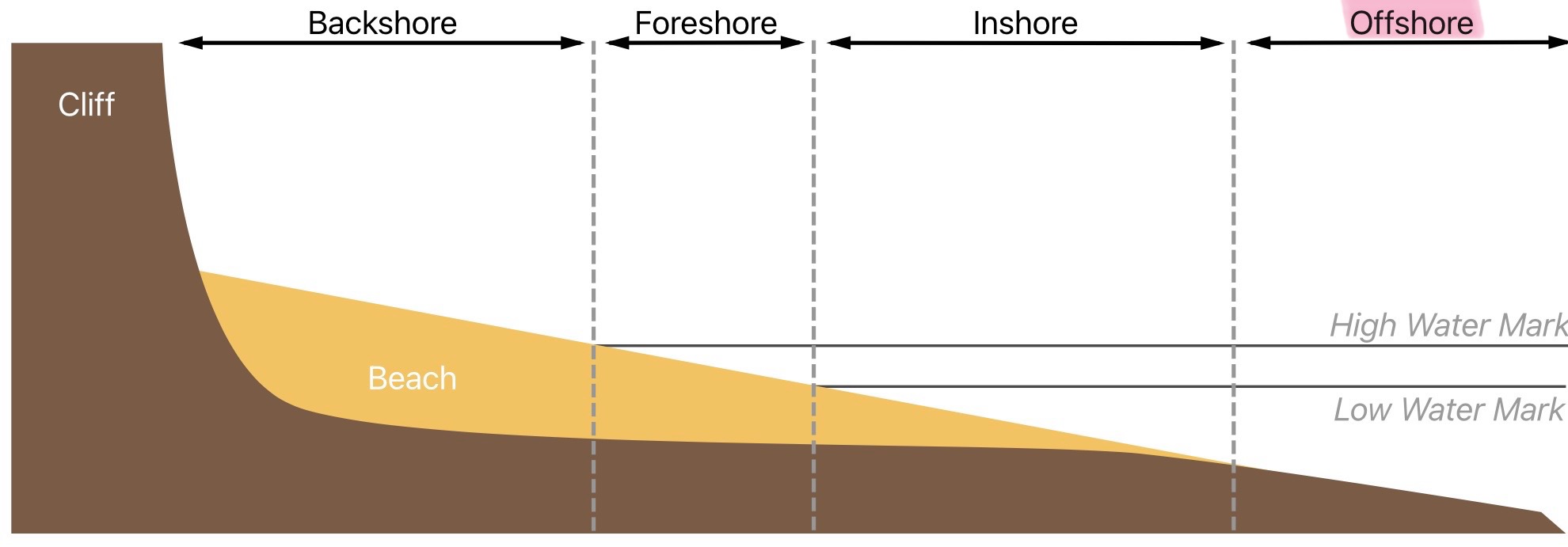
What is the nearshore of the littoral zone
The area between the low water mark and the point where waves cease to have any influence on the land beneath them
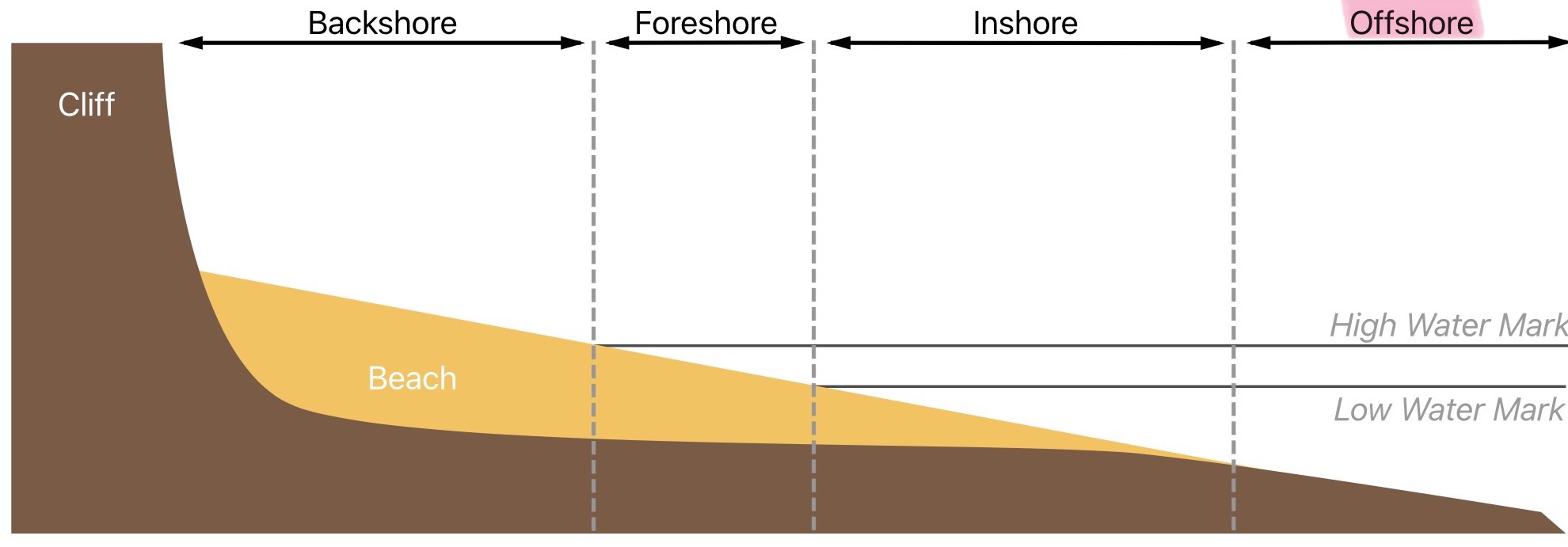
What is the offshore of the littoral zone
The area beyond the point where waves cease to impact upon the sea bed and in which activity is limited to deposition of sediments
Name 4 coastal inputs that affect the coast
Marine
Geology
Atmospheric
People
Explain what is meant by the marine coastal input
Waves (constructive + destructive)
Tides
Currents
Explain what is meant by the geology coastal input
Rock type - igneous / sedimentary / metamorphic
Rock structure
Tectonics
Material from marine deposition, weathering and mass movement
Explain what is meant by the atmospheric coastal input
Climate
Weather
Climate change
Explain what is meant by the people coastal input
Urban planning
Coastal management + defences
Explain one coastal transfer that affects the coast
Long shore drift
What are the two broad coastal outputs
Erosion landforms
Deposition landforms
Name 5 erosional landforms
Cracks
Caves
Arches
Stacks
Stumps
Headlands
Bays
Coves
Wave cut platforms
Blowholes
Name 5 depositional landforms
Beaches
Spits
Tombolos
Sand dunes
Salt marshes
What are the 4 coastal processes that affect the coast
Deposition
Erosion
Weathering
Mass movement
What are the 4 types of erosion
Attrition
Abrasion
Solution
Hydraulic action
Hat are the 3 types of weathering
Chemical
Biological
Mechanical
What does accretion mean
The net accumulation of sediment from deposition leading to the formation of depositional landforms
In dynamic equilibrium of beaches, what is meant by sediment supply
The amount of sand/shingle
In the dynamic equilibrium of beaches, what is meant by wave energy
Whether the waves are constructive or destructive
In the dynamic equilibrium of beaches, what alters the location and shape of the beach
Erosion and deposition
What is meant by dynamic equilibrium in a sediment
Where input and output of sediment are in a constant state of change but remain in balance
Is the coast an open or closed system
What is meant by input in the dynamic equilibrium of beaches
Material or energy entering the coastal system
What are 3 examples of inputs in the dynamic equilibrium of beaches
Tide
Wind
Waves
Human activity
What are stores/sinks in the dynamic equilibrium of beaches
Places where sediment or material is held
What are outputs in the dynamic equilibrium of beaches
Material or energy leaving the coastal system
Name 2 examples of outputs in the dynamic equilibrium of beaches
Sediment transfers
Ocean currents
What is meant by transfers/flows in the dynamic equilibrium of beaches
Processes that move material between inputs, stores and outputs
What is the definition of a landform
A stand alone feature
What is the definition of a landscape
Overall view of an area taking in multiple landforms
What is the definition of concordant geology
A coastline where rock strata or bands of rock run parallel to the coast
What is mean by discordant geology
Rock strata that run perpendicular to the coast, meaning alternating bands of soft and hard rock are exposed at right angles
What is the definition of dynamic equilibrium
A state where a system remains in a constant balance despite constant change
What is the definition of a high energy coast
A coastline with powerful wave action that leads to a net rate of erosion greater than deposition
What is the definition of a low energy coast
A type of coastline where wave action is minimal, typically found in sheltered areas with constructive waves
What is the definition of a ria
A coastal landform created when rising sea levels flood an unglaciated river valley, resulting in a drowned river valley
What is the definition of wave refraction
The bending of waves as they approach an irregular coastline at an angle, causing the wave energy to bocce concentrated on headlands and dissipated in bays
What is the definition of a wave cut platform
A flat, gently sloping rocky surface at the base of a cliff, formed by marine erosion between the high and low tide marks
What is meant by dynamic equilibrium in a sediment cell
Where inputs and outputs of a sediment are in a constant state of change but remain in balance
What are 5 features of a rocky/cliffed coastline
Transition from land to sea is abrupt
At low tide foreshore zone is exposed (wave-cut platform)
Cliffs are vertical
Resistant geology
Could be high or low relief
High energy environment
Are rocky/cliffed coastlines found in high or low energy environments
On a rocky/cliffed coastline, what is landform is likely the foreshore zone
A wave-cut platform
Are sandy coastlines found in high or low energy environments
Name 5 features of sandy coastlines
Transition from land to sea is smoother
Sand dunes are evident
Dune vegetation very important in stabilising coast
Low relief
At high tide beach is inundated
Result from supply of sediment
Low energy environment
Are sandy coastlines found at high or low relief
Where are estuarine coastlines found
Mouths of rivers
Name 5 features of estuarine coastlines
Found at mouths of rivers
Mud flats present, exposed at low tide
Nearer back shore, flats have vegetation present
Gradual transition from land to sea
Low relief
Low energy environment
Are estuarine coastlines found in low or high relief areas
Are estuarine coastlines found at low or energy environments
What is meant by a rocky coastline
Clear distinction between the land and sea
What is meant by coastal plains
Blurred boundary as relief is low and sediment comes from various sources (terrestrial and offshore)
What are the two levels of energy when categorising coasts
High and low
What makes a low energy coastline
Not powerful waves
Sheltered
Rate of erosion is less than rate of deposition
What is meant by a high energy coastline
Powerful waves
Exposed and face large oceans
Rate of erosion is higher than rate of deposition
Name two example locations of low energy coasts
Mediterranean se coasts, east Anglian coast
Name two example locations of high energy coastlines
Atlantic coasts of Norway and Scotland, pacific coasts of Canada and Alaska
Name 3 characteristics of the waves on low energy coastlines
Less powerful (constructive) waves
Short fetches
Calmer conditions
Name 3 characteristics of waves on high energy coastlines
More powerful (destructive) waves Short fetches
Longer fetches
Storm conditions
Name 3 processes that take place on low energy coastlines
Deposition and transport
Longshore drift
Nearshore currents
Name 3 processes that take place on high energy coastlines
Erosion and transport
Mass movement ad weathering
Offshore currents
Name 5 landforms found on low energy coastlines
Beaches
Spits
Salt marshes
Sand dunes
Mudflats
Name 5 landforms found on high energy coastlines
Cliffs
Wave-cut platforms
Arches
Sea caves
Stacks
Who created the classification system used by geographers for coasts
Valentin
What is the direction of the UK’s prevailing wind
South - west
In the UK, where are high energy coastlines found
The west coast of Ireland
The west coast of Scotland
The south west coast of wales and Cornwall
In the UK, where are low energy coastlines found
The east coast of England
The east coast of Ireland
The west coast of northern England
What is the definition of geology
The study of the earth, including the materials that make it up and the process that change it over time
What is the definition of lithology
The study of rocks and their physical properties, such as their composition, texture, structure and hardness/resistance
What is the definition of consolidated sediment
Sediment or rock that has been compacted and cemented over time, forming a solid, coherent mass
What is the definition of unconsolidated sediment
Material ugh as sand, gravel, clay and silt that has not been compacted and cemented to become sedimentary rock
What is the definition of a concord ant coastline
One where beds, layer and rocks are folded into ridges that ru parallel to the coast
What is the definition of morphology
The shape of landscape features, and is influenced by geological structures
What is meant by a discordant coastline
One where geology alternates between strata of hard and soft rock
What is meant by wave refraction
As waves approach the shallower water thy slow down and wave height increases
Waves diverge from the headlands and therefore energy decreases as they enter the bays
Name 3 examples of igneous rock
Granite
Basalt
Dolerite
Name 3 examples of metamorphic rocks
Slate
Schist
Marble
Name 3 examples of sedimentary rock
Sandstone
Limestone
Shale
Name 1 example of unsolidated sediment
Boulder clay
What 2 reasons mean igneous rock erodes very slowly
Igneous rocks are crystalline - the interlocking crystals make for strong, hard erosion resistant rock
Igneous rocks such as granite often have few joints, so there are limited weaknesses that erosion can exploit
What 3 reasons mean metamorphic rock erodes slowly
Crystalline metamorphic rocks are resistant to erosion
Many metamorphic rocks exhibit a feature called foliage on, where crystals are all orientated in one direction which produces weaknesses
Metamorphic rocks are often folded and heavily fractured, which are weaknesses that erosion can exploit
What is meant by clastic
Sedimentary rocks and other sediments composed of pre-existing rock fragments or coasts
What 3 reasons mean sedimentary rocks erode moderate to fast
Most sedimentary rocks are clastic and erode faster than crystalline igneous and sedimentary rocks
The age of sedimentary rocks is important - geologically young rocks tend to be weaker
Rocks with many bedding places and fractures, such as shale, are often most vulnerable to erosion
What 1 reasons means unconsolidated sediment erodes very fast
Material such as sand, gravel, clay and silt that has not been compacted and cemented to become sedimentary is very exposed and unresistant
Wave refraction - when waves approach headlands, what do they do
Converge
Wave refraction - when waves converge towards headlands, do they increase or decrease in height?
Does this mean they have greater or lower erosion? Why
Increase
Greater - wave energy is concentrated
Wave refraction - does more erosion occur at headlands or bays
Wave refraction - when waves approach bays, what do they do
Diverge
Wave refraction - does more deposition occur at headlands or bays
Wave refraction - when waves approach bays does their height increase or decrease?
Does this mean they have greater or lower erosion? Why
Decrease
Lower - wave energy is more spread out
Are rias found on discordant or concordant coastlines
Discordant
What are rias
Long narrow bays
Drowned river valleys
When did rias become drowned
The last ice age
Why did rias become drowned
During the last ice age, there was a rise in sea level
When wave refraction occurs, where is wave energy most concentrated
On both sides of the headland
What is the definition of differential erosion
A geographical process where areas of varying rock resistance erode at different rates, leading to specific landforms
What is the definition of scree
An accumulation of broken rock fragments usually found on the slopes of mountains or at the base of cliffs