1.08. Telescopes and magnifiers
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Magnification formula
Magnification = new image size / old actual image size
Angular magnification Definition
The relationship between the angular size of the actual object relative to the optical axis AND the angular size of the image relative to the optical axis
Hand magnifier
Positive spherical lens
Distance between object and lens is set by observer
It is usually set to the focal length of the lens which forms a virtual image of the object (virtual - viewed by the eye)
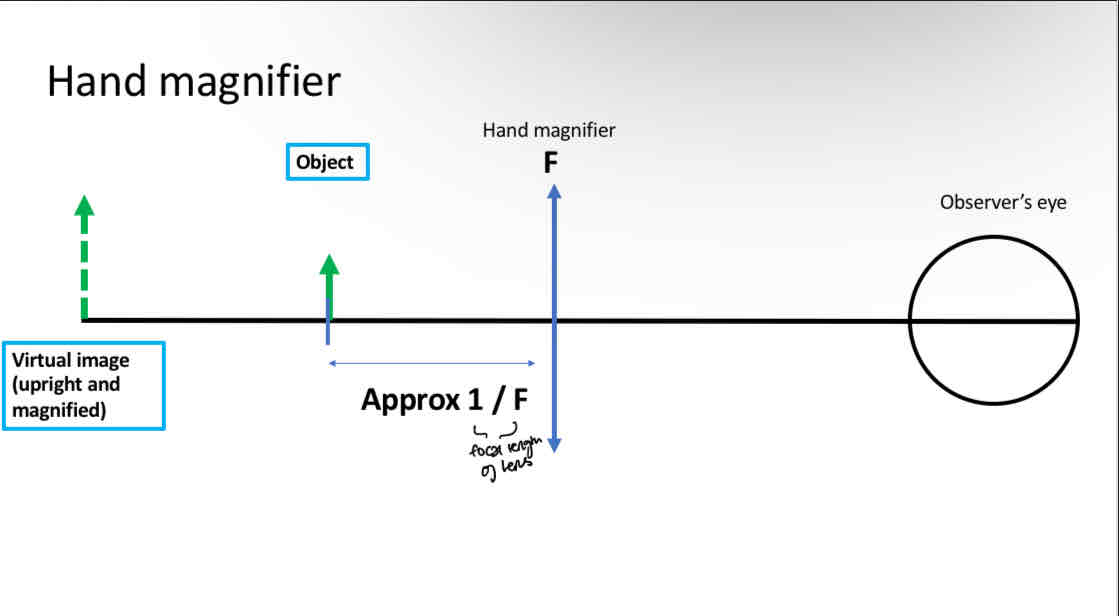
How to calculate magnification of hand magnifier
Equivalent power of magnifier / 4
How to calculate equivalent power of 2 lenses separated by a distance
Fe = F1 + F2 - (d x F1 x F2)
Fe = equivalent power
F1 = power of magnifier lens
F2 = accommodation exerted by patient (or the powerr of the reading addition worn by patient)
d = distance between magnifier and eye (metres)
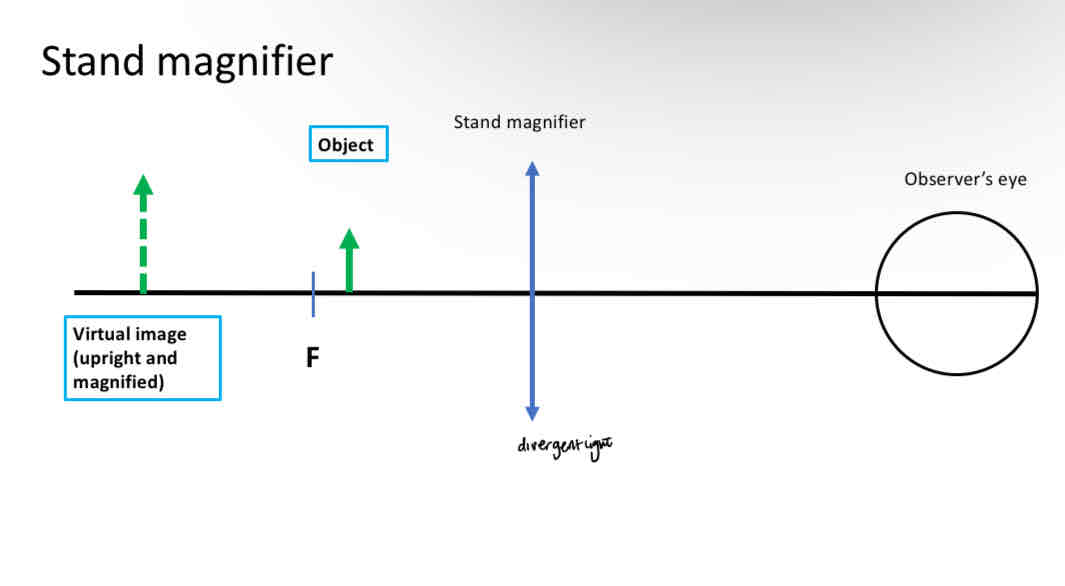
Stand magnifier
Positive spherical lens
Distance between object and lens is set by the frame of the stand magnifier (kept at constant distance from a near task)
Usually shorter than the focal length of the lens
Forms a virtual image of the object
Telescopes
Constist of:
Objective lens or mirror
Eyepeice
What is a telescope with 2 lenses
Refracting telescope
What is a telescope with a mirror and a lens
Reflecting telescope
What are the 2 types of refracting telescope
Astronomical and galilean
Astronomical telescope
Objective - positive lens
Eyepeice - positive lens
Creates an inverted image
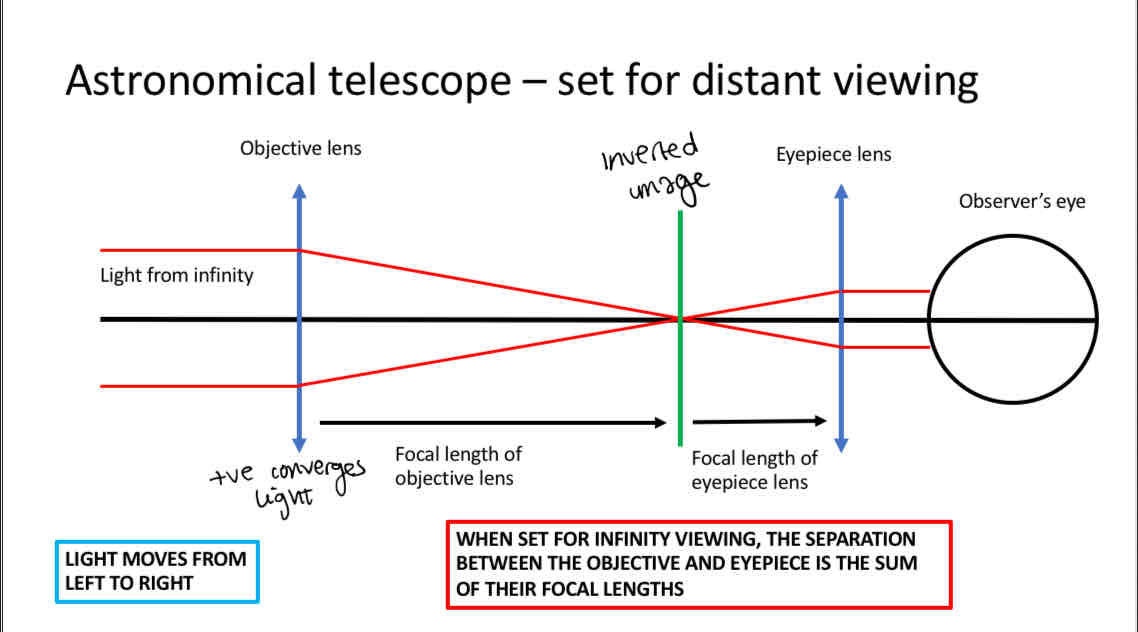
How does an astronimcal telescope create a magnified image
When the focal length of the eyepeice is shorter than the focal length of the objective
Shorter focal length. = higher power so we want this as the eyepeice to get a magnified image
So the doptric power of the eyepeice is greater than objective
How to calculate total length of telescope
Add focal lengths
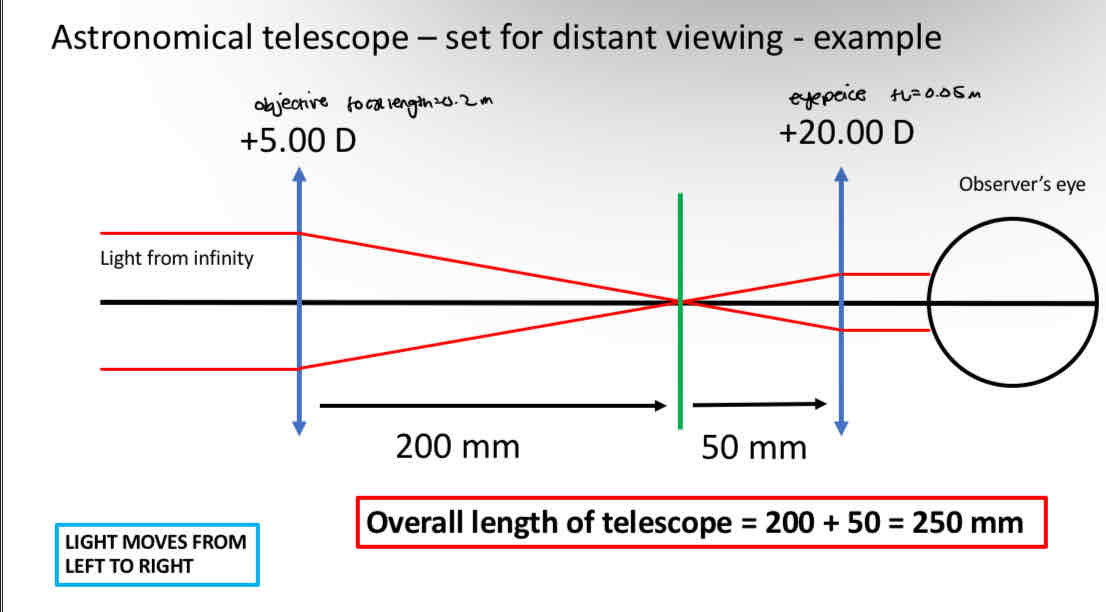
How to calculate magnification for an astronomical telescope

Prisms in astronomical telescopes
Prisms re-invert the image to put it thhe correct way up
Porro prism assembly
Roof prism assembly
Porro prisms
Arranged as a pair to invert the image
Found in binoculars and slit lamps
Ingoing and outgoing rays are not co axial
Invert and translate the image in terms of their beam path to adjust system to match your pd
What dos it mean when Ingoing and outgoing rays are not co axial
Image goes through prism and comes out at a slightly different place
Roof prisms
Found in compact binoculars and many low vision aids
Ingoing and outgoing rays are co axial
Enables the objective and eyepeice lenses to alse be co axial
What does it mean when Ingoing and outgoing rays are co axial
Point straight at eachother
the beam exits along the same line it entered
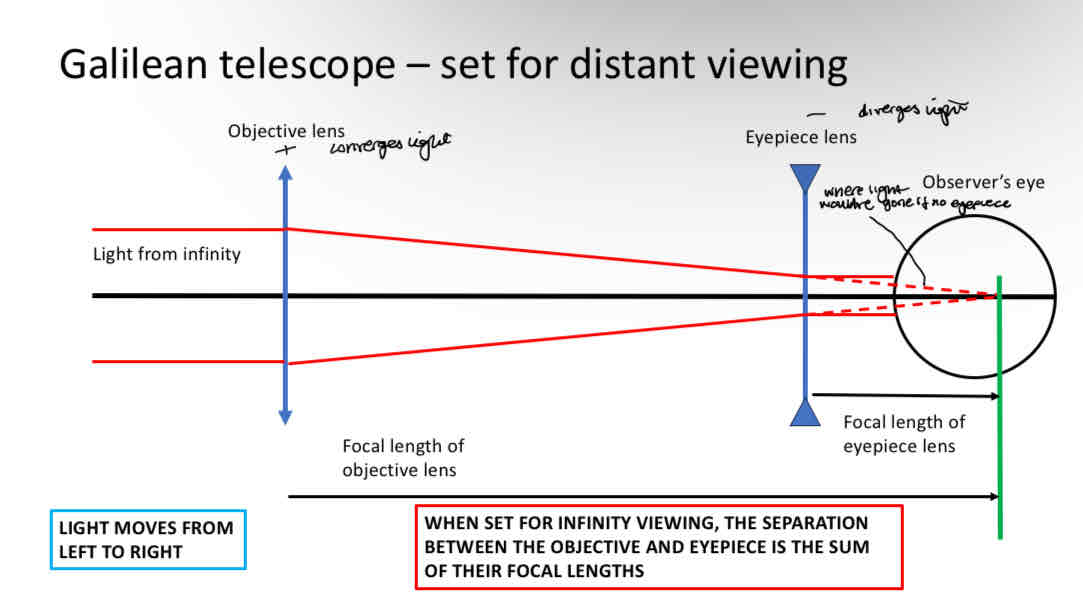
Galilean telescope
Objective - positive lens
Eyepeice - negative lens
Creates an upright image - no prisms needed
Creates a larger (magnified) image if the focal length of the eyepiece is shorter than the focal length of the objective
Eyepeice has more dioptres
Reflecting telescope
Objective - curved mirror
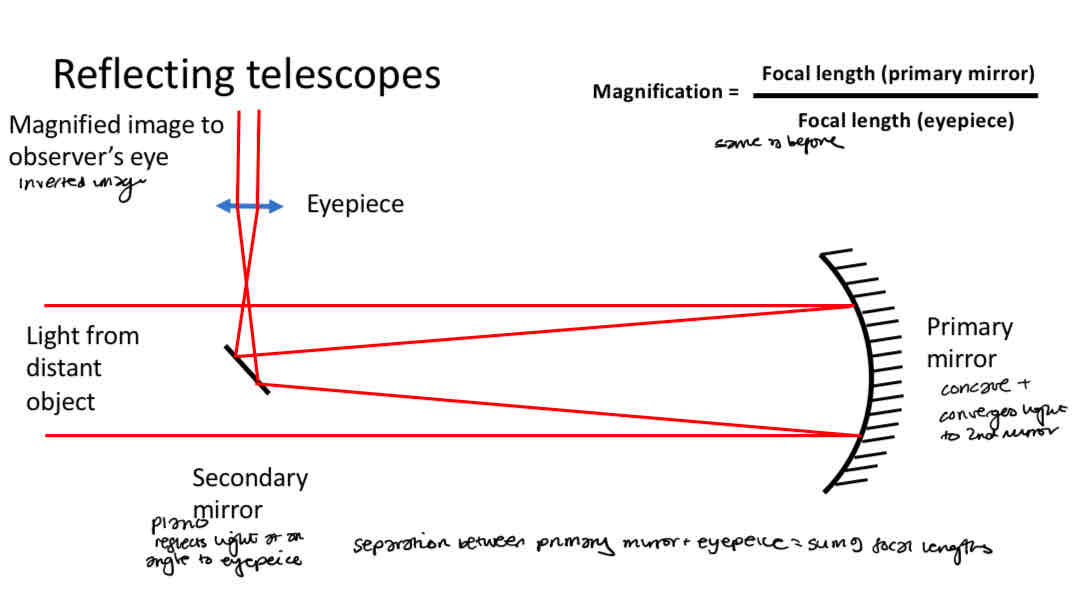
Why do reflecting telescopes have curved mirrors
Curved mirrors dont suffer with chromatic aberration (when a lens makes colors separate, causing blurry edges or color outlines in an image)
Refelcting telescopes - aspects of performance
