quiz 2-microbio lab
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Complex media
Support growth of a wide range of organisms
Selective
Select growth of a specific type of bacteria
Differential Media
Differentiate between bacteria based on different physiological characteristics
What is Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) selective for?
salt-tolerant microorganism
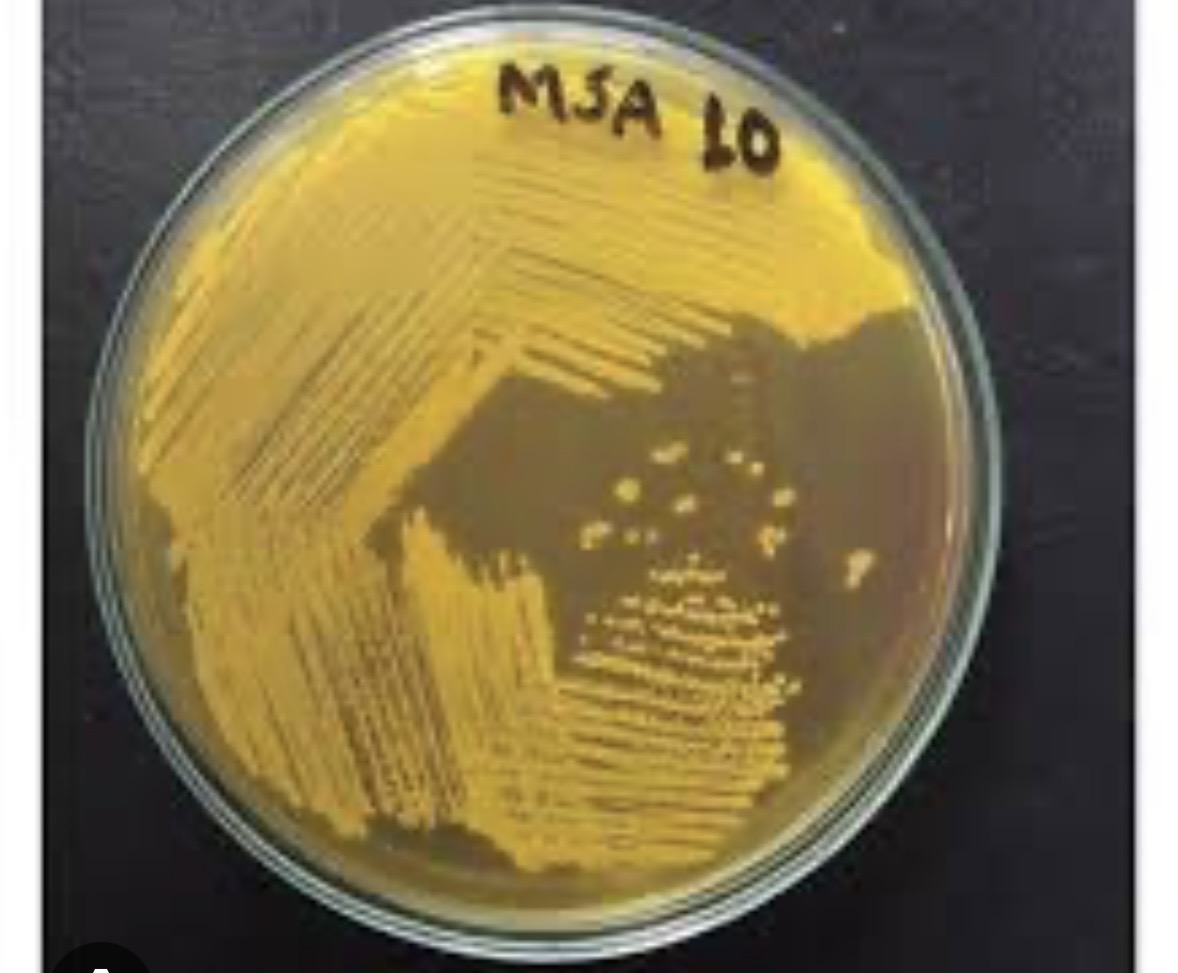
What color is MSA if it can ferment
yellow- mannitol
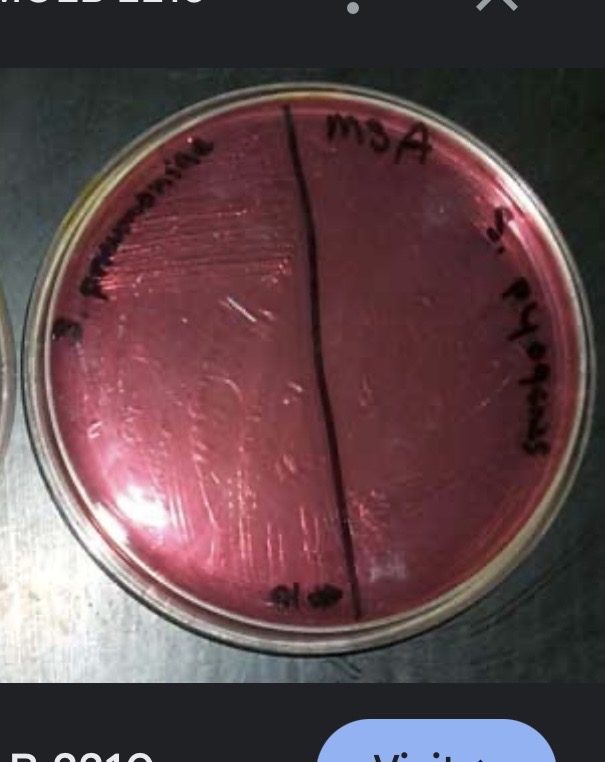
What color if MSA is negative
red/pink
What is MSA differential for and why?
Mannitol fermentation and because it contains the carbohydrate mannitol and the pH indicator phenol red
What is Phenol red added to
pH indicator
What is mannitol added as
carbon source
What is Eosin Methylene Blue(EMB) Agar selective for
gram-neg microorganisms
What do eosin and methylene blue dyes inhibit?
gram-pos
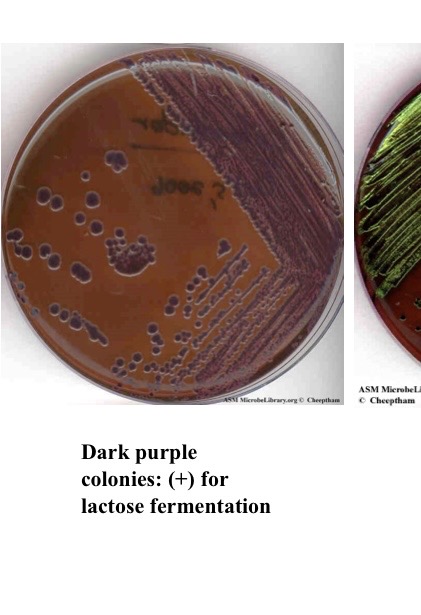
What does purple indict for EMB
pos for lactose fermentation
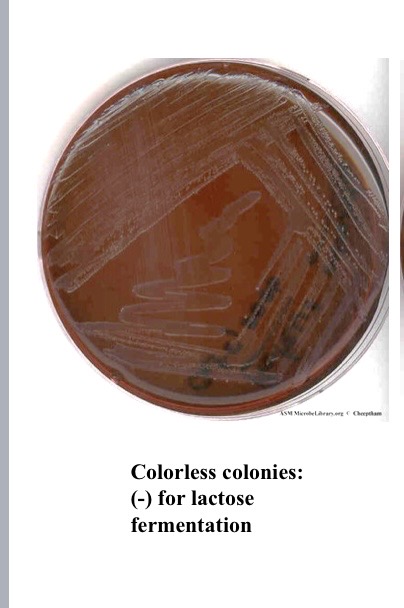
What does colorless indict for EMB
neg for lactose fermentation
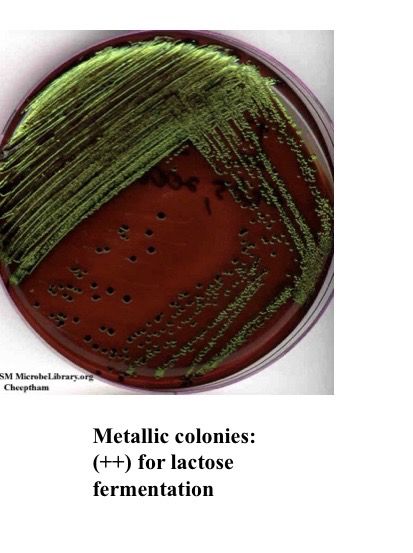
What does metallic indict for EMB
ferments lactose and strong acid production
What is EMB differential for
lactose fermentation
Phenol Red carbohydrate Broth
Test for the fermentation of carbohydrates and gas production
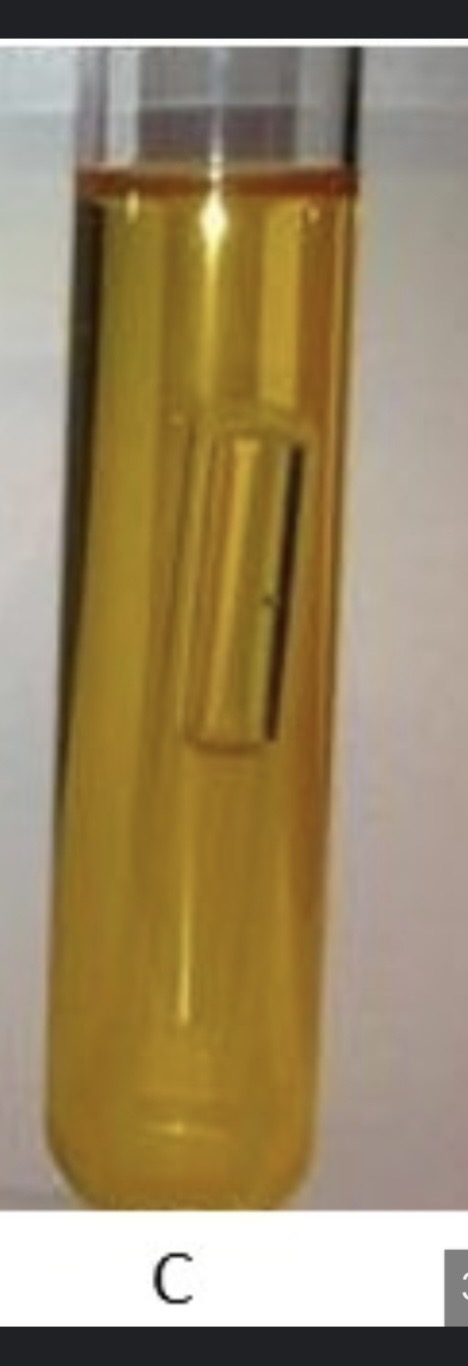

What does it mean if phenol Red is yellow with a positive Durham tube.
pos for fermentation of carbohydrate and gas production
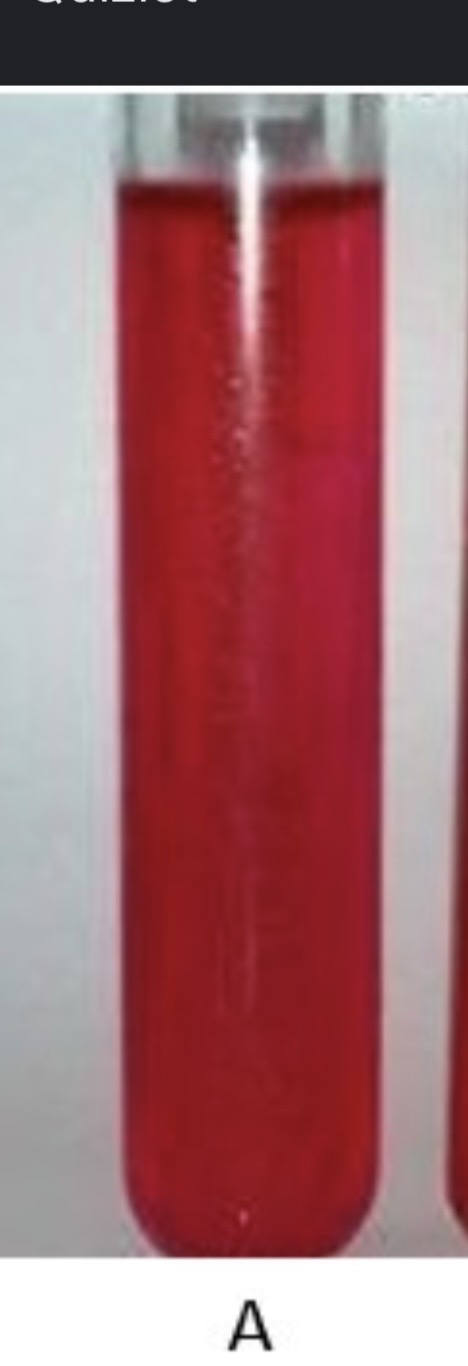

What does it mean if phenol Red is red
neg for fermentation of carbohydrates and gas production
What does the VP(a precursor of 2,3-butanediol) test for
production of acetion
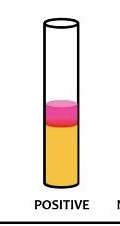
What color is VP if it is pos
Red, after adding Barritt’s reagents
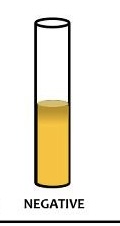
What color is VP if it is neg
No color change/copper color
what does Kligler’s slant test for
Ferment glucose and lactose, and the production of hydrogen sulfide (H2S)

Fully red kligler’s slant
does not ferment lactose and glucose or H2S

Fully yellow
Ferments glucose and lactose and gas but neg for h2s

Yellow slant/black butt
pos for lactose, gas production and H2S

Red slant/black butt
Positive for cysteine desulfurase activity
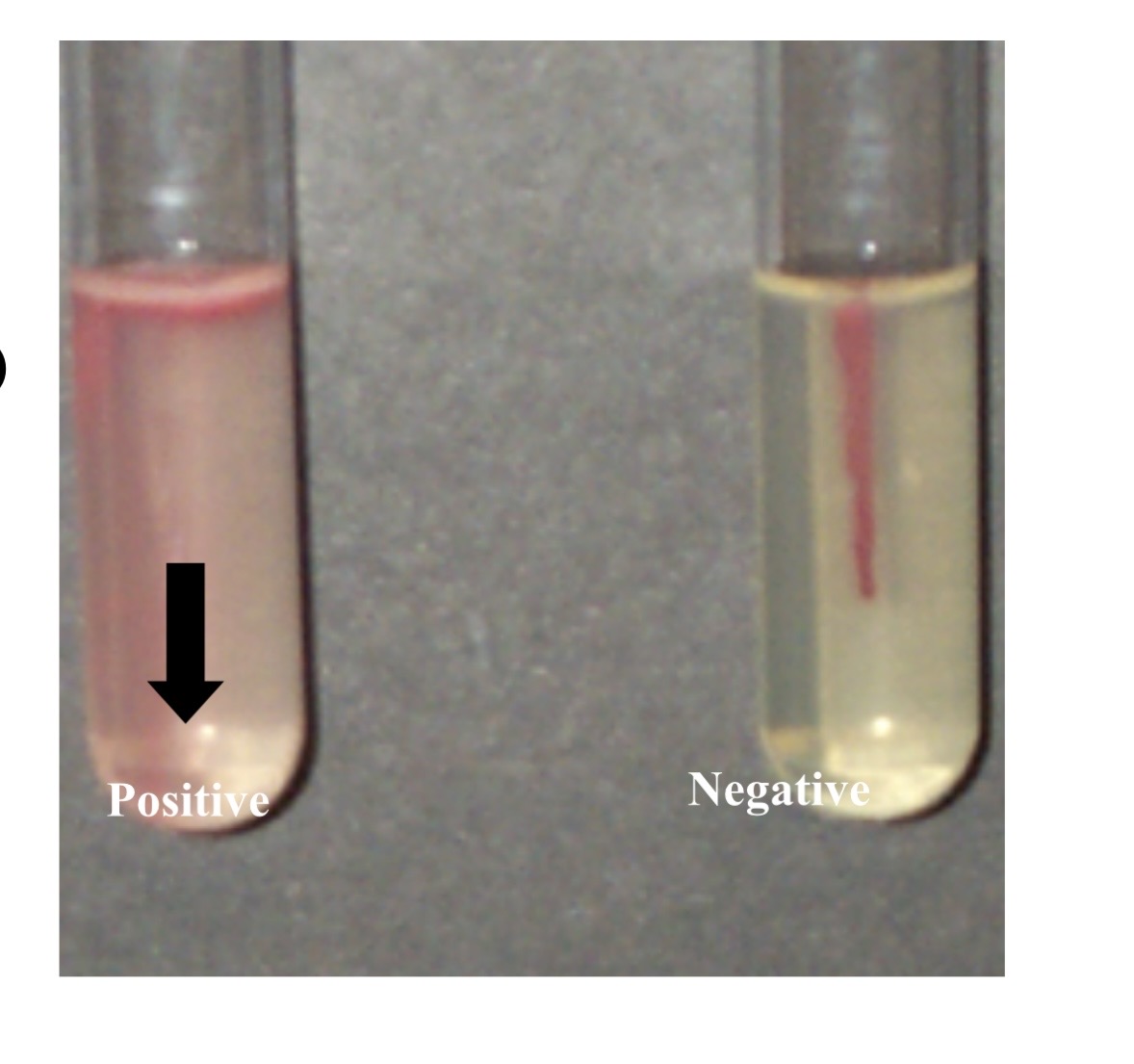
How do you detect Indole production?
Kovac’s reagent
What does the broth in indole contain?
tryptophan
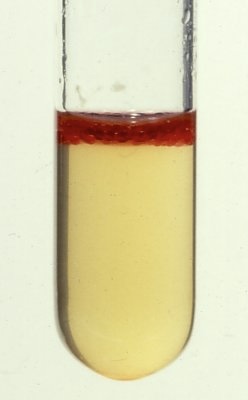
What does it mean if indole is red
pos for enzyme indole

What does it mean if indole is yellowish/clear top
neg for enzyme indole
What does phenylalanine deaminase detect?
presence of enzyme phenylalanine deaminase
what is phenylalanine deaminase detected by
ferric chloride
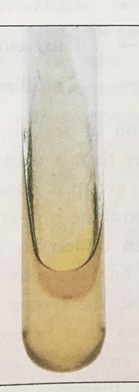
what does it mean if phenylalanine is neg
yellow/clear
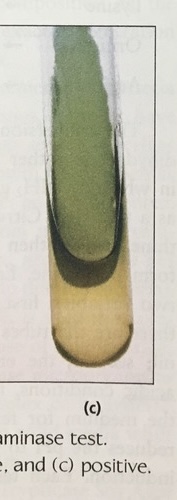
what does it mean if phenylalanine is pos and color
produced the enzyme phenylalanine deaminase and green
Motility test
if motile: move from center
if not motile: stay in center
Antiseptic
Product which destroys or inhibits growth of microorganism in or on living tissue
Ex of antiseptic
Iodine
silver nitrate
triclosan
ethanol
Disinfectant
product which destroys or inhibits growth of microorganisms on inanimate objects
Ex of disinfectant
Cresols(lysol)
bleach
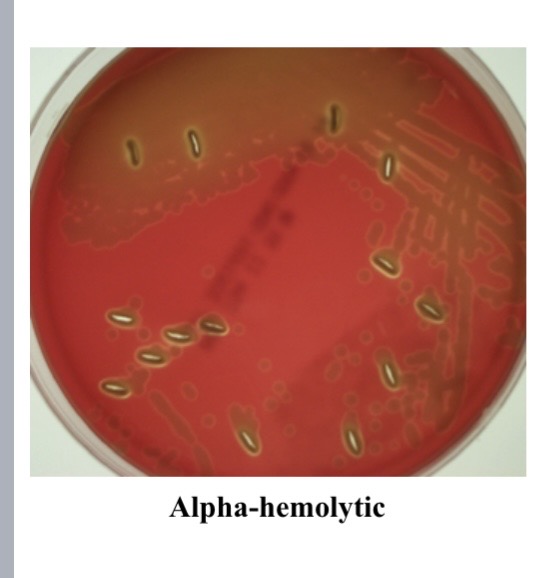
alpha hemolysis
Involves partial hemolysis of blood cells due to damage caused by hydrogen peroxide produced by organism
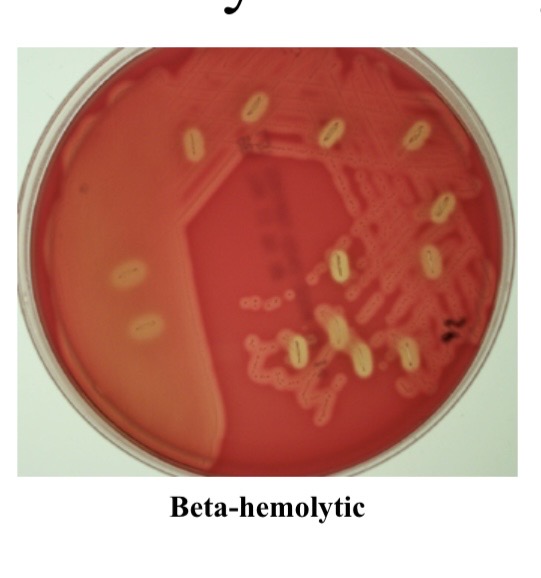
Beta hemolysis
Involves complete hemolysis of blood cells due to the action of cytokines such as streptolysin enzyme
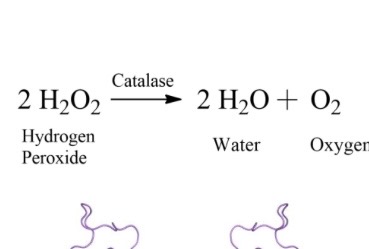
Catalase test
breaks down hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas
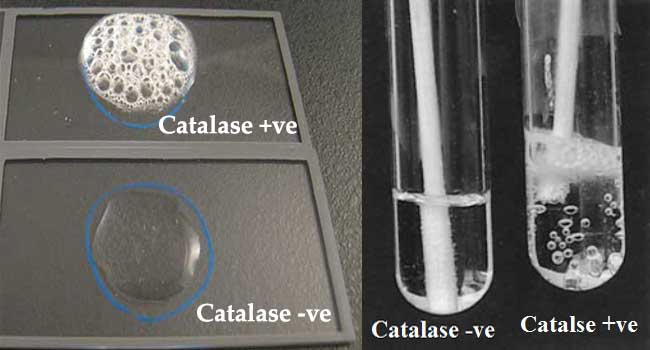
What does it mean if catalase test is pos
Positive of oxygen production (bubbling)
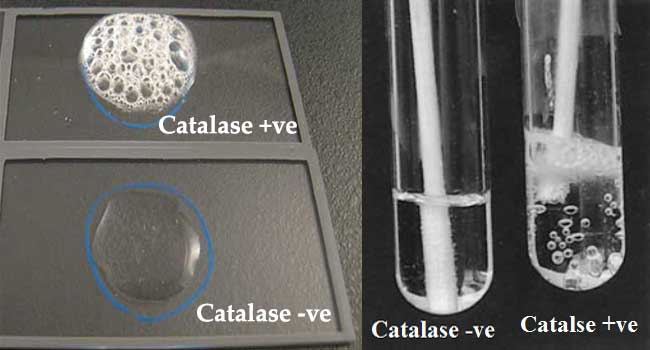
What does it mean if catalase test is neg
it will have no change
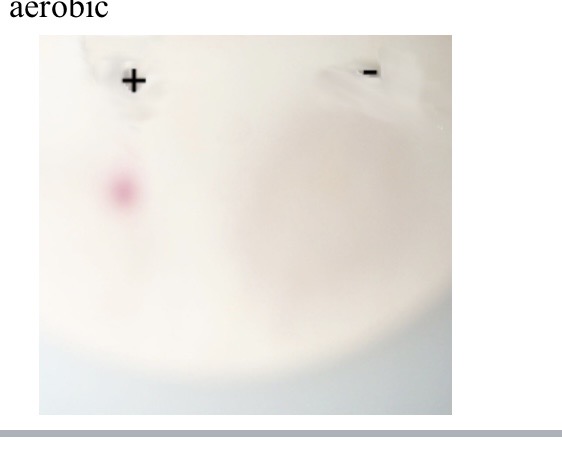
Oxidase test
If enzyme cytochrome oxidase is produced
What does it mean if the oxidase test is positive
pink
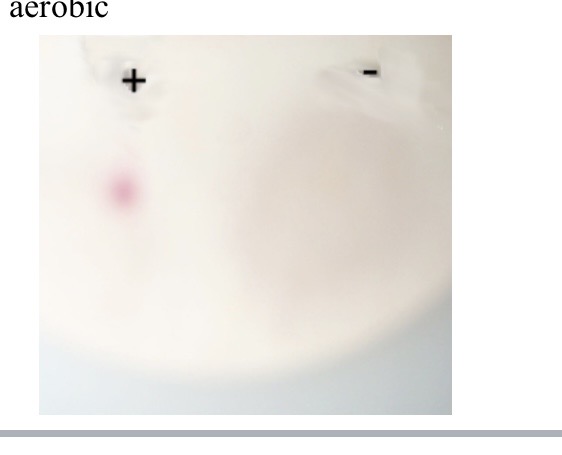
What does it mean if the oxidase test is negative
no color
Minimum bactericidal concentration
Minimum concentration of agent at which the target bacterium is killed rather than inhibited
Simmon’s citrate
test for utilization of citrate as sole carbon source for growth
What is the carbon source for Simmon’s citrate
citrate
pH indicator for Simmon’s citrate
bromothymol blue
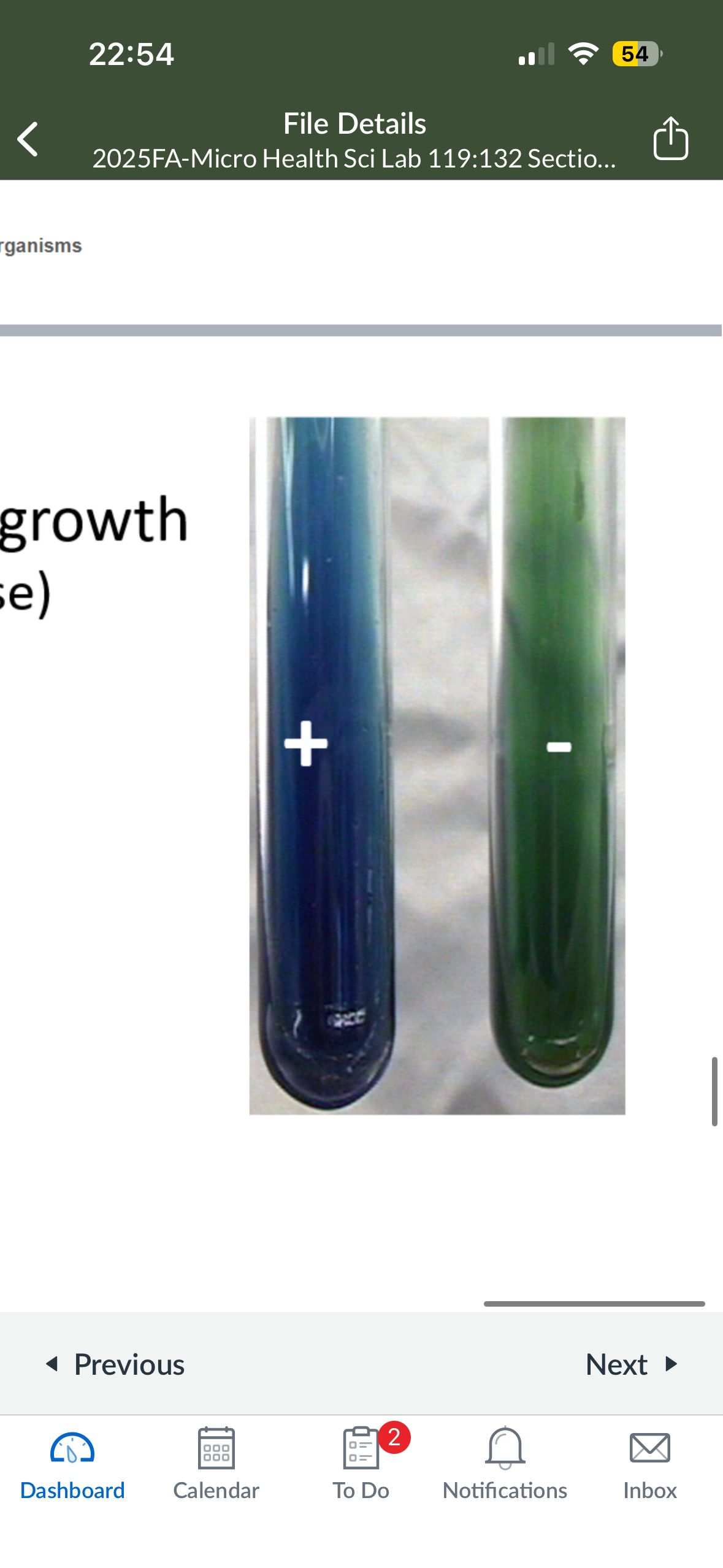

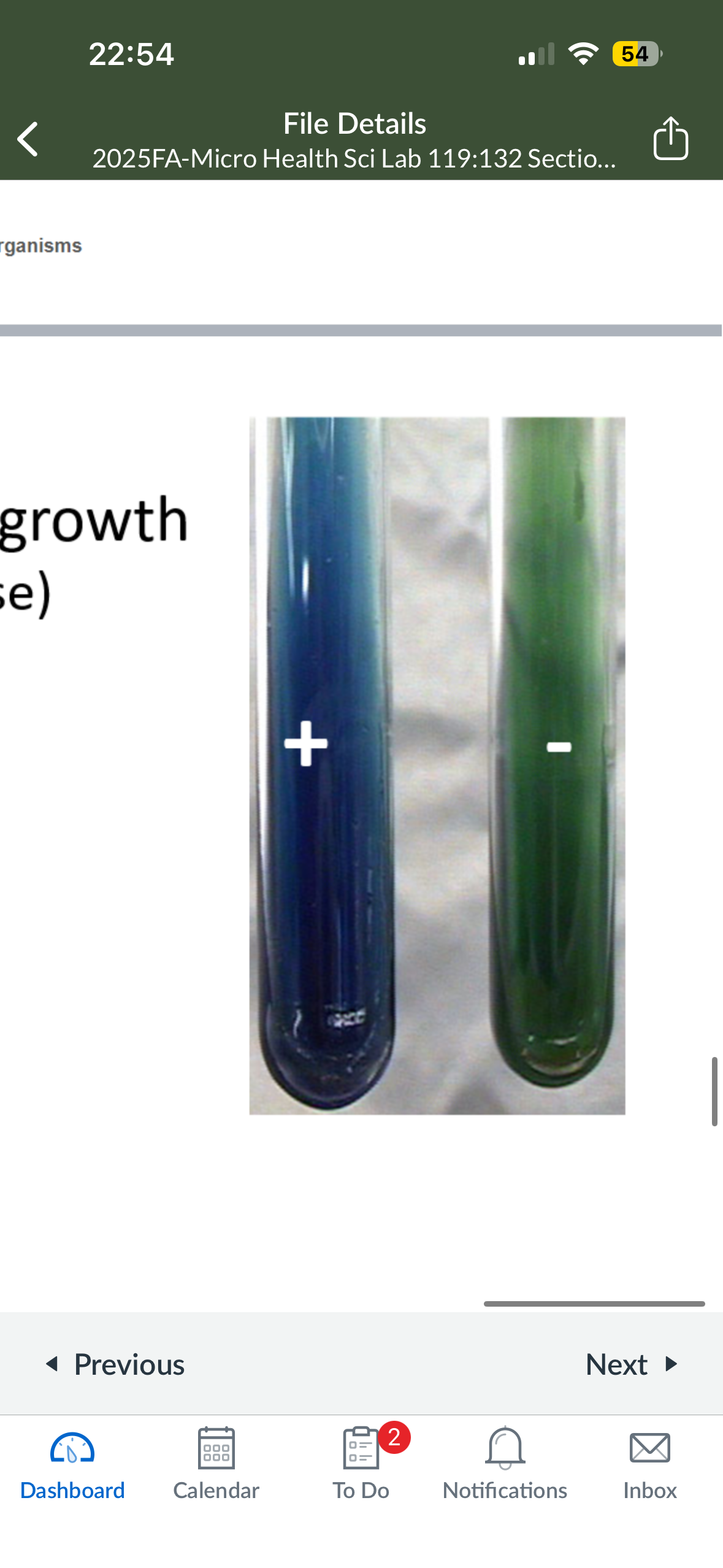
What color does Simmon’s citrate turn into if it is pos
blue
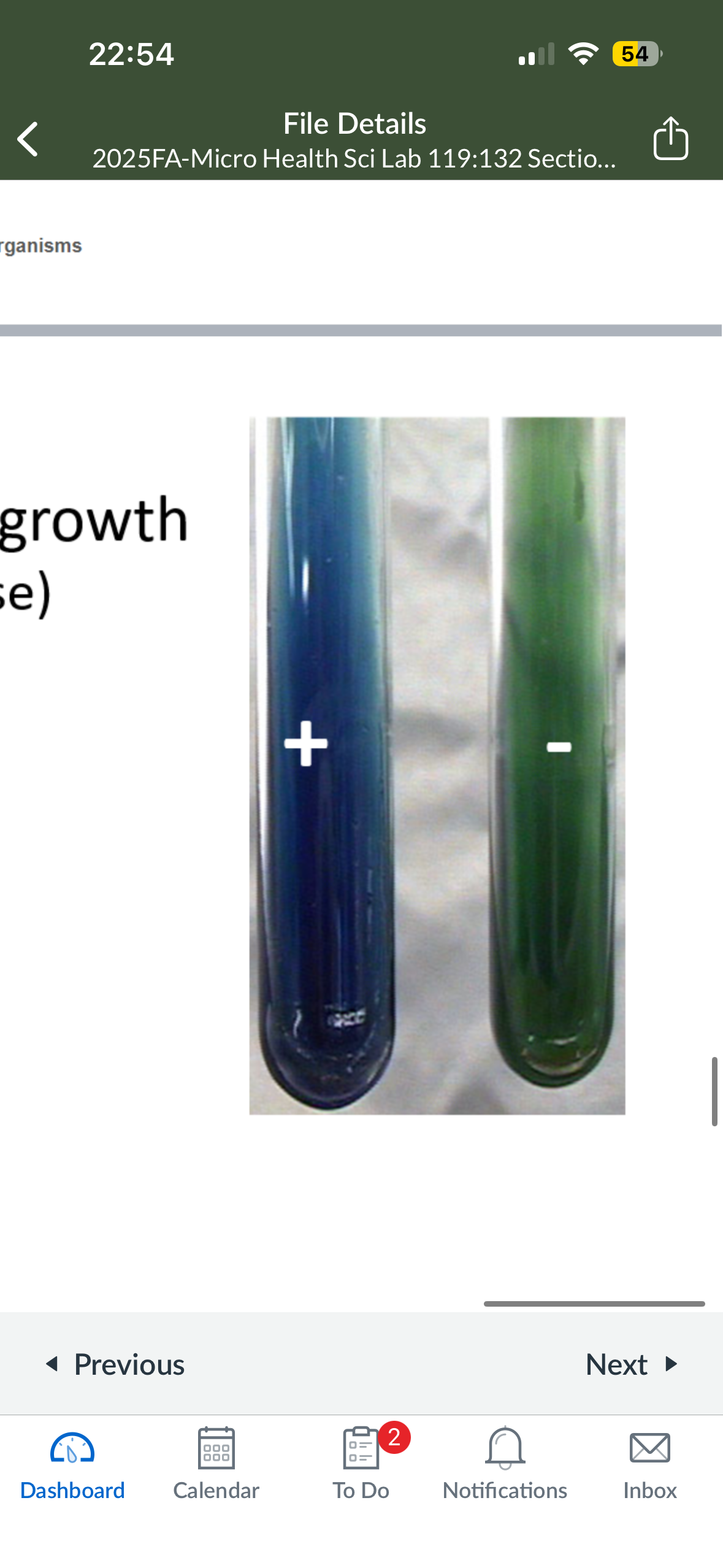

What color does Simmon’s citrate turn into if it is neg
green

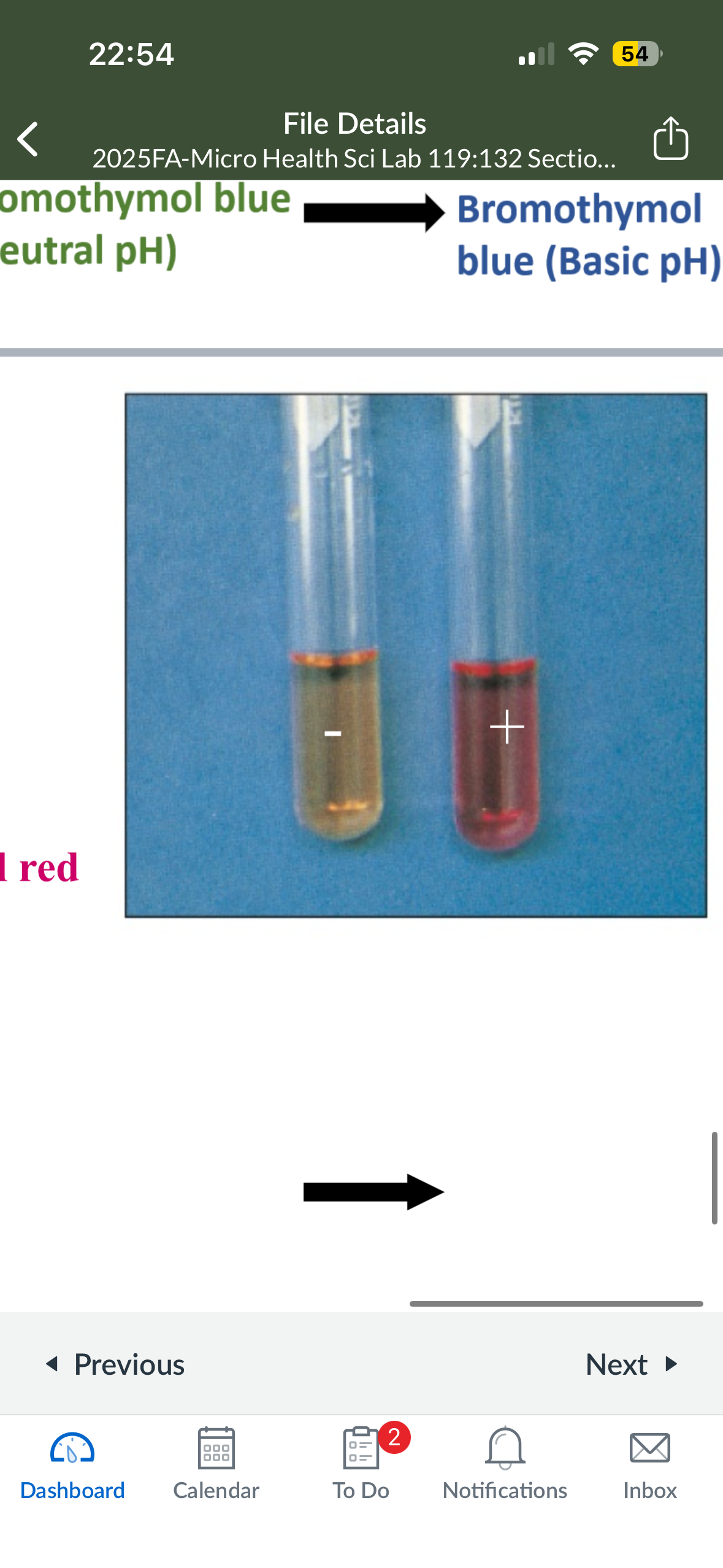
What does Urease test for
production of enzyme urease
What color does Urease turn into if it is neg
yellow
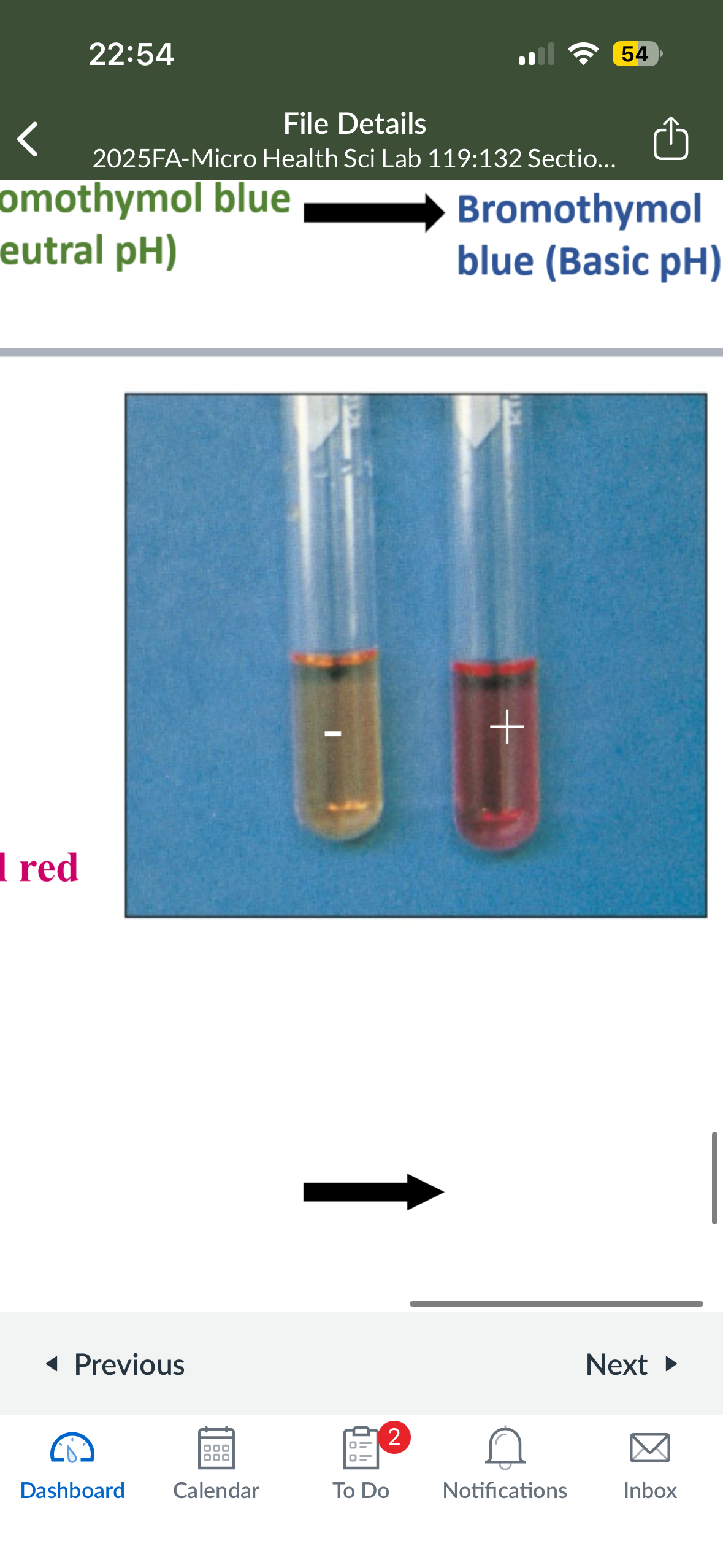
what color does Urease turn into if it is pos
pink
What can UV light do
Used to control microbial growth
Factors that limit usefulness of UV light for decobtamination
cannot penetrate surface
more effective at killing some organisms than other
Strict Aerobe
Needs O2 for cellular respiration
will die without
Facultative Anaerobe
Can use O2 for cellular respiration
If O2 is not present will use alternate electron acceptors
Aerotolerant Anaerobe
does not use O2 for cellular respiration use alternate electron acceptors
O2 is not toxic for them
Strict Anaerobe
Does not use O2 for cellular respiration. Uses alternate electron acceptors
O2 is toxic to them
Oxygen indicator of FTG tubes
Resazurin, red when O2 is present
Reducing agent for FTG
Thioglycolate
Brewer agar plates O2 indicator
Resazurin
Brewer agar plates reducing agent
Thioglycolate
Palladium Catalyst
Making water get released from gasPak
What is the Initial dilution formula?
Initial Dilution =Volume transferred/ total volume
Next dilution formula
Next dilution= Volume transferred/total volume)x previous dilution
What is the stock formula
[stock]= (CFU/Vol.plated)x Dilution factor
Normal flora
Found in specific area of the body due to environmental conditions like pH, O2 availability, moisture,etc.
Blood agar
Enrichment media that is generally used for the cultivation of throat microorganisms
Common throat colonizers releases hemolysins
What is an example of beta hemolysis?
Streptococcus pyogenes, which causes strep throat
What is an example of alpha hemolysis?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the cause of pneumonia. Usually Caused by the Viridans group of streptococcus, which are a normal part of the mouth flora
Non-hemolytic
Sometimes called y-hemolysis, no lysis of red blood cells, andnon-clearing of blood cells around the colony
Examples of non-hemolytic
Enterococcus faecalis is a common inhabitant of the GI tract
Resident flora
Permanently live on and in the human body, forming a symbiotic relationship with the host
Transient flora
Microorganisms that do not permanently colonize the skin because they are found on the surface and can be more easily removed by good hygiene practices.
Kirby-Bauer Antimicrobial Sensitivity Testing
Standardized diffusion procedure that uses Mueller-Hinton agar, a standard mixed medium
Mueller-Hinton Medium
Growth medium to culture bacterial isolates and test their susceptibility to antibiotics.
Chemotherapeutic agents
chemicals that can treat infectious diseases caused by microorganisms
what does Chemotherapeutic interfere with
Microbial metabolism, halting the growth of (bacteriostatic) or killing (bactericidal) the targeted microorganisms
What are the two groups of chemotherapeutic agents
Antibiotics and synthetic drugs
Antibiotics
Made and secreted by other microorganisms, which may be synthesized and modified in a lab
Synthetic drugs
Man-made and synthesized in lab
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
The lowest concentration at which bacterial growth will be inhibited
How is the MIC determined by?
Doing a dilution series of the antibiotics and adding the microorganisms to various drug concentrations
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
Minimum concentration of the agent at which the target bacterium is killed (rather than just inhibited)
How is the MBC determined?
Must perform a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) test.
Take samples from the wells where no growth was observed in the MIC test, and then plate them on an antibiotic-free agar plate.
Enterobacteriaceae
are a group of bacteria that are endogenous to the internal tracts of mammals
What genre does Enterobacteriaceae use?
Salmonella, shigella,enterobacter, Escherichia, Klebsiella and Proteus
UV light
An effective method to kill microorganisms through the production of pyrimidine dimers in DNA that impair DNA replication and gene expression
Are endospores resistant to UV light and other forms of radiation?
yes
What are factors that limit the usefulness of UV light for contamination?
Cannot penetrate surfaces
More effective at killing some organisms than others (ex.Bacterial spores can be resistant)
What do UV light form?
Pyrimidine dimers in the DNA of vegetative cells much faster than it does in endospores, which are resistant structures that offer protections against radiation.
Microaerophilic
Require a limited amount of oxygen
Excess oxygen inhibits oxidative enzymes and results in death
Only grow in environments with limited amounts of oxygen
Fluid Thioglycollate (FTG) tubes
Differentiate organisms based on their oxygen requirements
What is the reducing agent of FTG
Contains sodium thioglycolate, which reduces free oxygen in the medium to water
What is the oxygen indicator of FTG
Resazurin
What color does FTG turn when oxygen is present
pink/red