Adrenergic and Cholinergic for Final Exam
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
Sympathetic Autonomic Nervous System
-functions involved in "fight" reactions (fear, anger, etc)
-accelerator
Parasympathetic Autonomic Nervous System
-stimulates more tranquil functions ("rest-and-digest")
-brake
Cholinergic agonists
Drugs bind to cholinergic receptors & stimulate parasympathetic system
Cholinergic antagonists
Drugs bind to cholinergic receptors and exhibit no activity
Adrenergic agonists
-Drugs bind to adrenergic receptors and stimulate sympathetic system.
-Sympathetic activation are mediated by the release of norepinephrine (NE) from postganglionic nerves
-NE and E act on adrenergic receptors
-drugs that mimic the effects of NE or E and are called sympathomimetics
Adrenergic antagonists
Drugs bind to adrenergic receptors and exhibit no activity
Adrenergic Drugs
Very broad spectrum of activities, treating many disease states from hypertension, hypotension, heart failure, arrhythmias, asthma, nasal congestion, glaucoma
Steps in Chemical Neurotransmission
Step 1. Neurotransmitter Biosynthesis
Step 2. Neurotransmitter storage
Step 3. Neurotransmitter release into synaptic cleft
Step 4. Interaction with neurotransmitter receptors
Step 5. Termination of neurotransmitter action (uptake, metabolism
a1 receptors
Vascular and skeletal muscle blood vessels (vasoconstriction, increase blood pressure)
a2 receptors
Presynaptic nerve endings, regulate the release of NE
B1 receptor
Heart (increase heart rate)
B2 receptors
Smooth muscles of lungs (bronchodilation)
B3 receptors
Adipose tissues (lipolysis)
Indirect Sympathomimetics
-MOA: Increase the release of catecholamines from sympathetic nerve terminals
-CNS effects primarily due to release of dopamine: Increased alertness and ability to concentrate (ADHD), Depression of appetite (obesity), Prevention and reversal of fatigue (narcolepsy), Euphoria (abuse and addiction)
Mixed Action Sympathomimetics
-Act as releasing agents AND direct receptor agonists (weak)
-Ephedrine: natural herbal product, mild CNS stimulant
-Pseudoephedrine: nasal decongestion
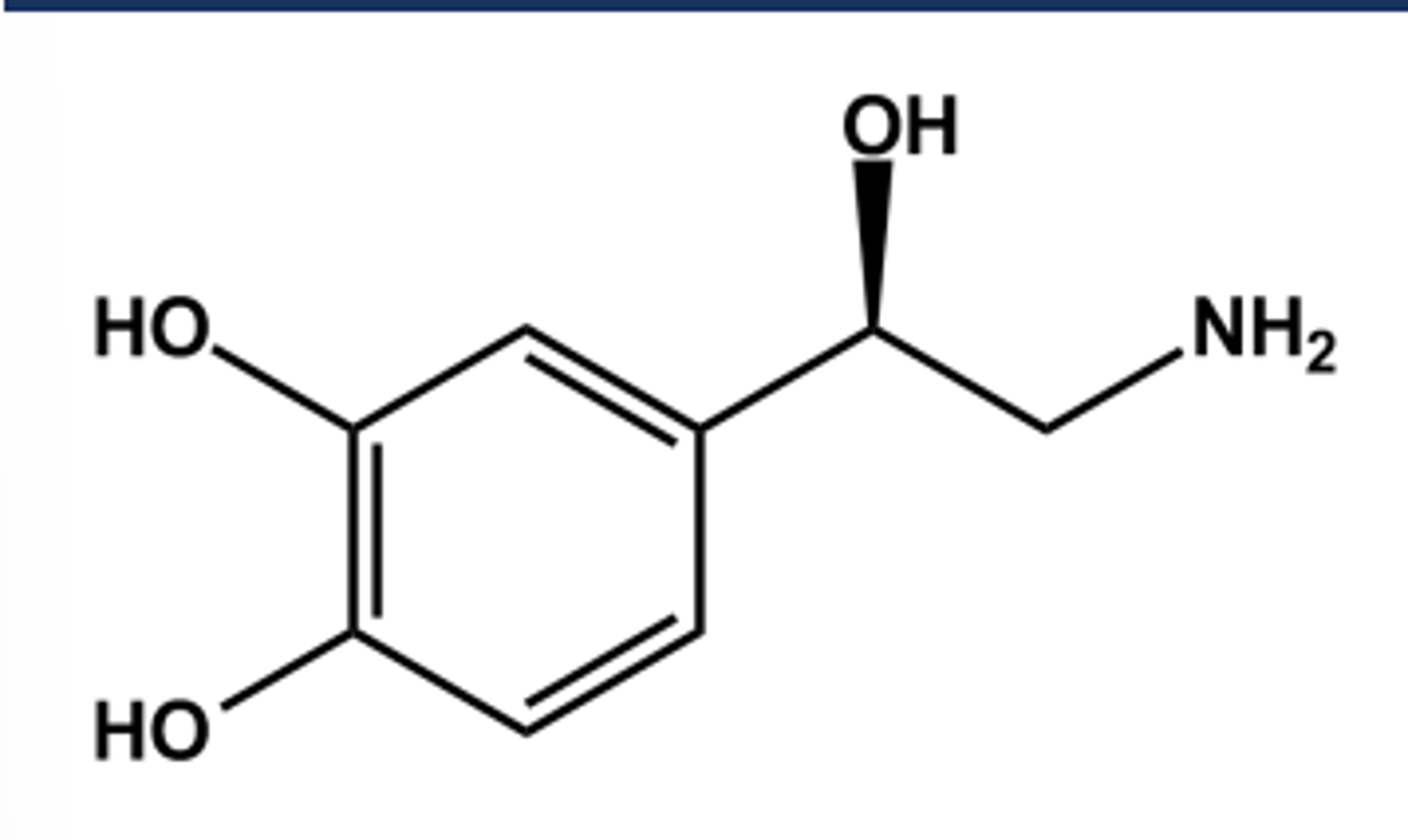
Non-selective Norepinephrine (Levophed)
-LogP = -0.24; pKa = 8.6
- Catechol moiety is easily metabolized by COMT(hence the name!)
- Side chain-OH on a chiral atom.
- S-isomer is inactive
-Potent vasoconstrictor
- Agonist at a1 , a2 and β1 receptors
- Little or no affinity for β2 receptors
Non-Selective Epinephrine (EpiPen)
-LogP = 0.3; pKa = 8.6
-Catechol is still easily oxidized to adrenochrome
- Agonist at a1 , a2 , β1 and β2 receptors
- More potent than NE at all receptors
-No Oral use
-Use: Anaphylaxis
TO GAIN STABILITY IN PHENETHYLAMINE DRUGS
-Modify the catechol to avoid COMT
- Modify atoms around the amine to reduce actions of MAO
Modification of B-hydroxyl
• R isomer is more active than S
• No OH--- high log P, CNS access
Modify Substituents on Ring
• Catechol ---is a COMT substrate
• 3-OH favors alpha
• 4-OH favors beta
• No OH--- high logP, CNS access
Substitute on N
• Alkyl group> 3--- favors beta over alpha
• Alkyl group> 3--- no indirect activity
• Bigger groups--- selectivity towards B2
Substitute at a-position
• Alkyl group--- increases indirect activity
• Alkyl group--- resist metabolism by MAO
• Alkyl group--- high log P, CNS access
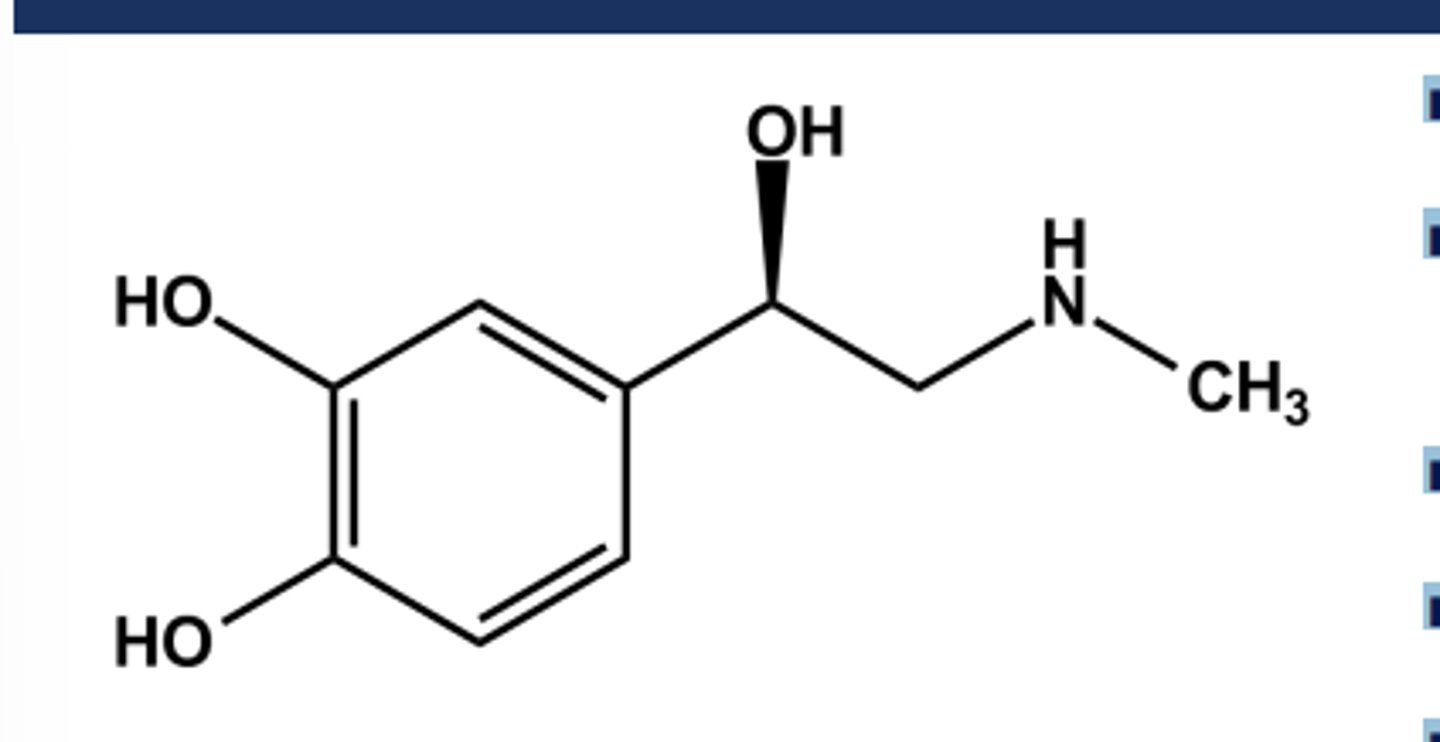
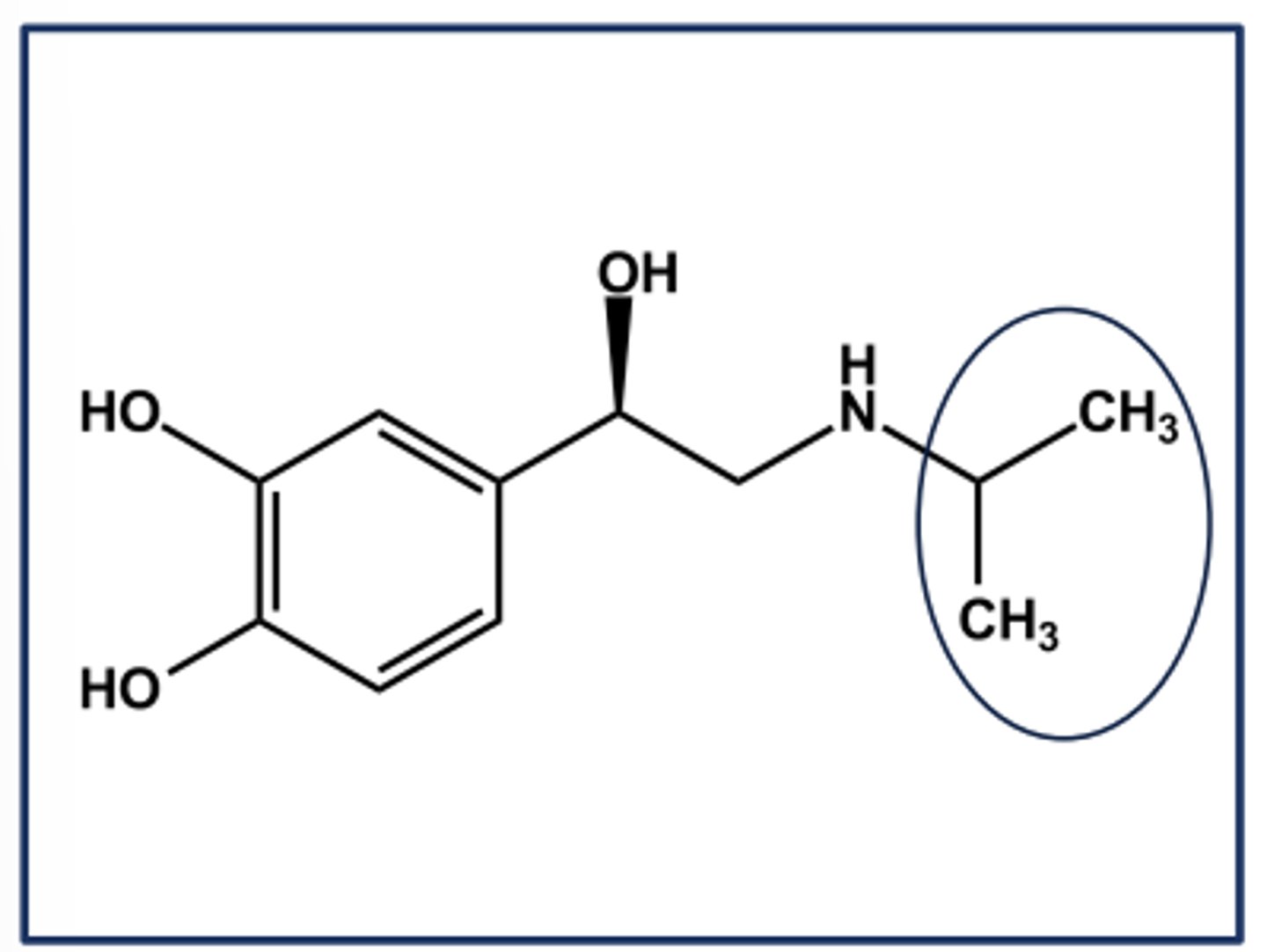
ISOPROTERENOL (ISUPREL®) EXAMPLE OF ΒETA SELECTIVITY
- N-isopropyl norepinephrine
- Gaining β-selectivity over B-selectivity
- Nonselective β-agonist activity
➢ Equal affinity at B1 and B2 receptors
➢ No affinity at either a receptor
- Larger N-alkyl groups continue the trend towards B2 selectivity
-Poor profile due to instability, but very potent
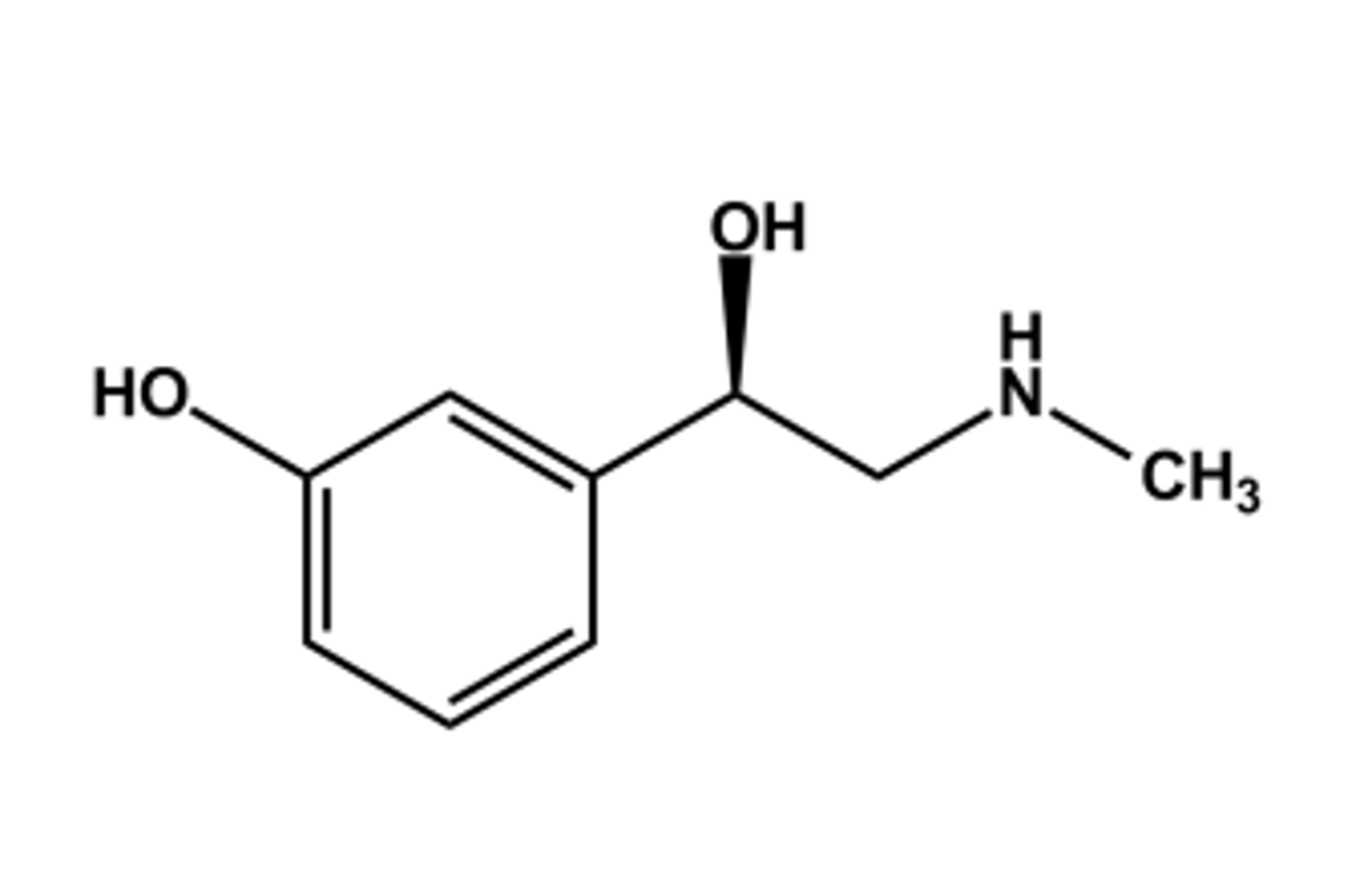
PHENYLEPHRINE HCL
- LogP = 0.9; pKa = 8.9
- α1 -selective agonist, as expected from SAR
- High first-pass effect due to MAO
- T1/2 about 2 hours
- Effects: vasoconstrictor
- Use: decongestant
-Constituent of many combination products
DEXTROAMPHETAMINE SULFATE (DEXEDRINE®)
- LogP = 1.8; pKa = 9.9
- Classic indirect adrenergic agonist
- Better CNS penetration, and catecholamine release (incl. Dopamine)
- Methyl group gives increased resistance to MAO, increased duration, allowed oral activity
- Biotransformed by CYP2D6 (p-hydroxylation)
- Use: ADHD, narcolepsy
- C-II, due to abuse potential
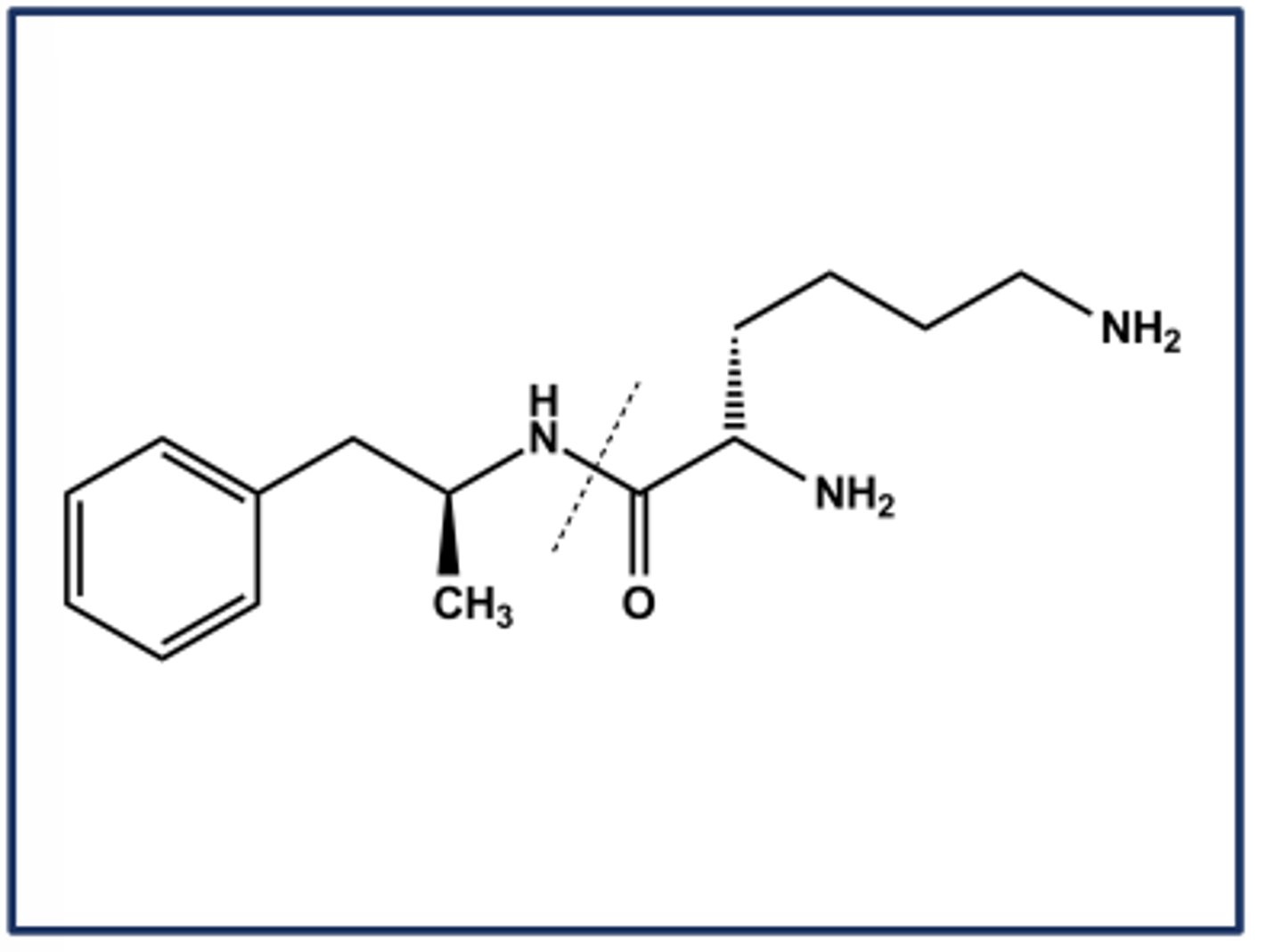
LISDEXAMFETAMINE (VYVANSE®)
- Lysine prodrug of amphetamine
- Activated by amidases in the GI tract
- When injected intravenously the prodrug is still very slowly converted to amphetamine
- Use: ADHD
- C-II
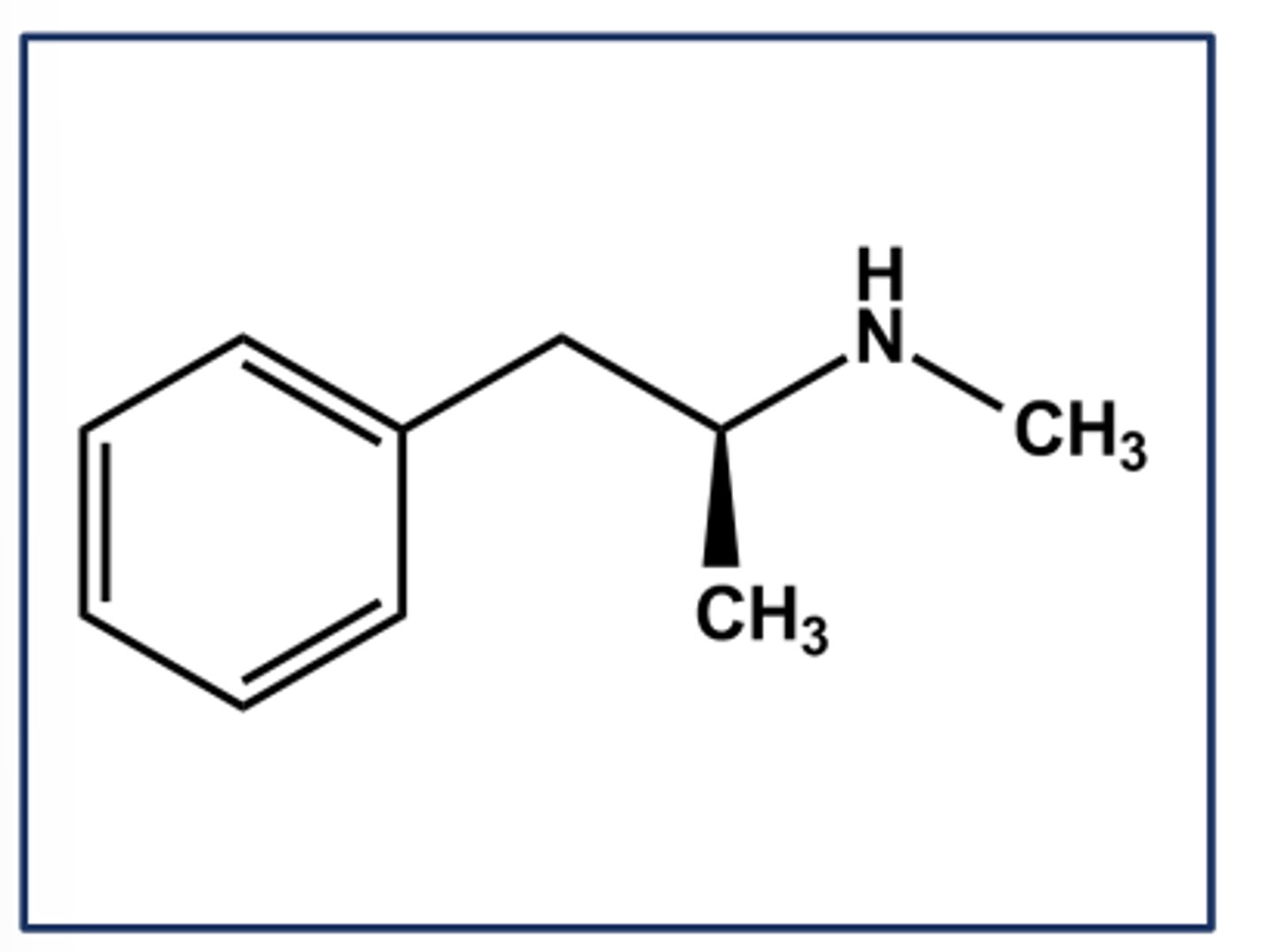
METHAMPHETAMINE HCL (DESOXYN®)
- LogP = 2.2; pKa = 10
- Purely indirect adrenergic agonist (leads to catecholamine release)
- Use: ADHD, obesity
- Can be synthesized easily from pseudoephedrine or ephedrine
- C-II
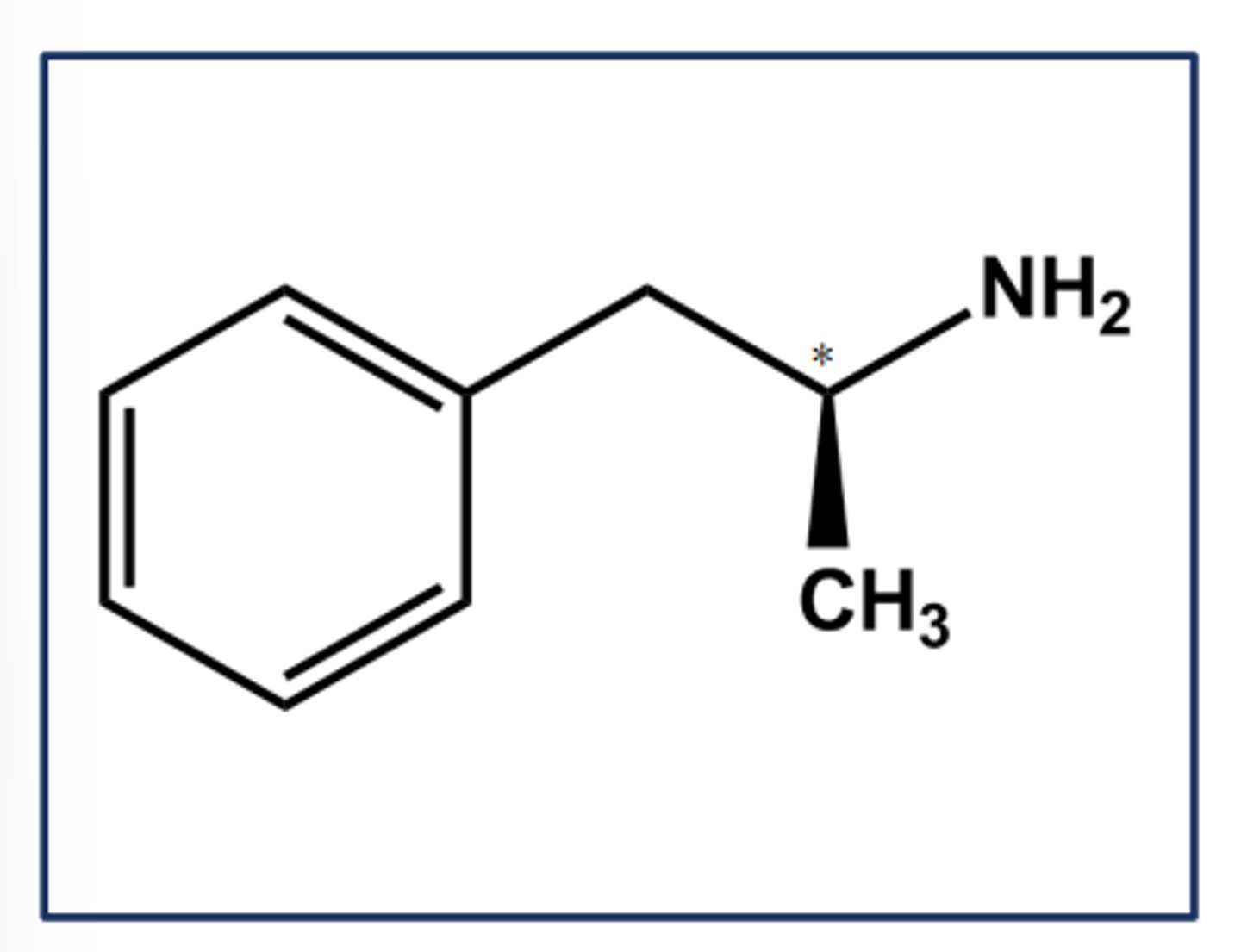
PHENTERMINE HCL (ADIPEX-P)
- LogP = 1.9; pKa = 9.8
- Weak CNS stimulant effects
- Has expected indirect agonist effects
- Not a MAO substrate; 70% excreted unchanged after oral dose; T1/2 4 hours
- Not a COMT substrate (no catechol)
- Use: short-term management of exogenous obesity
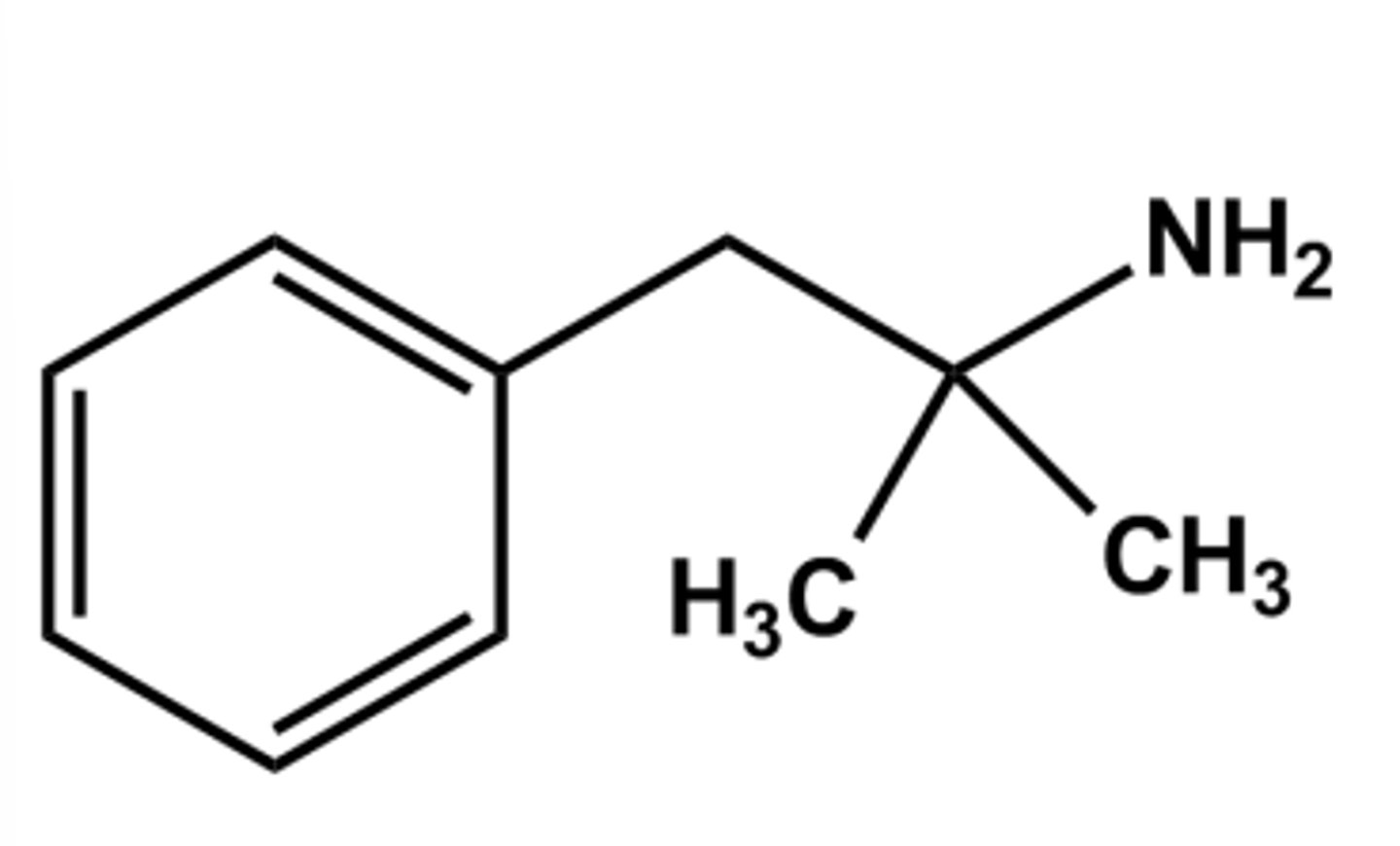
ISOPROTERENOL HAS ONLY ΒETA-AGONIST AND NO ΑLPHAAGONIST ACTIVITY DUE TO...
The N-isopropyl group
THE CONVERSION BELOW WILL...
eliminates COMT biotransformation
increases β2 -selectivity
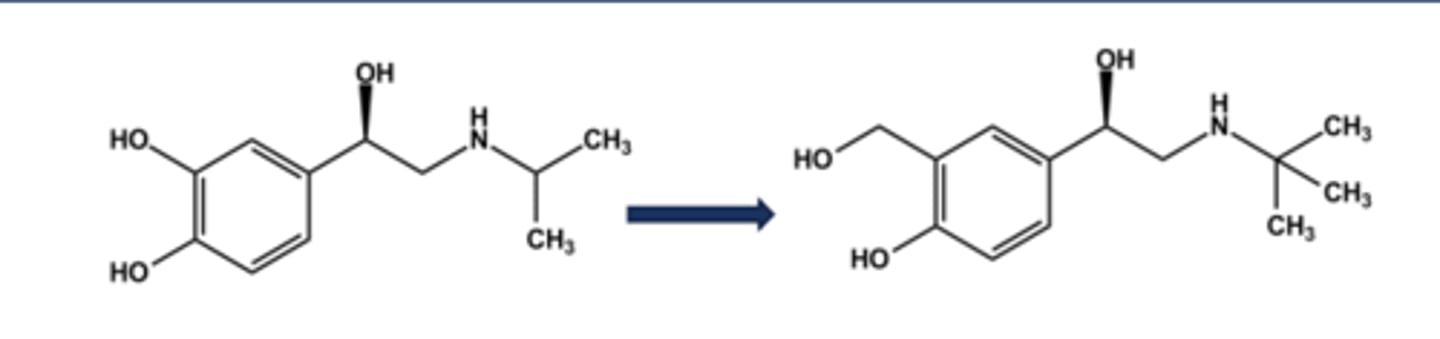
ALBUTEROL (VENTOLIN®, PROVENTIL®, PROAIR®)
- LogP = 1.0; pKa = 10
- Close analog of isoproterenol
- No Catechol, No COMT action, greater stability
- Confers 50x β2 -selectivity
- Although marketed as racemate, activity is only in R-(-)-isomer
- Use: short term relief of bronchoconstriction (rescue inhaler)
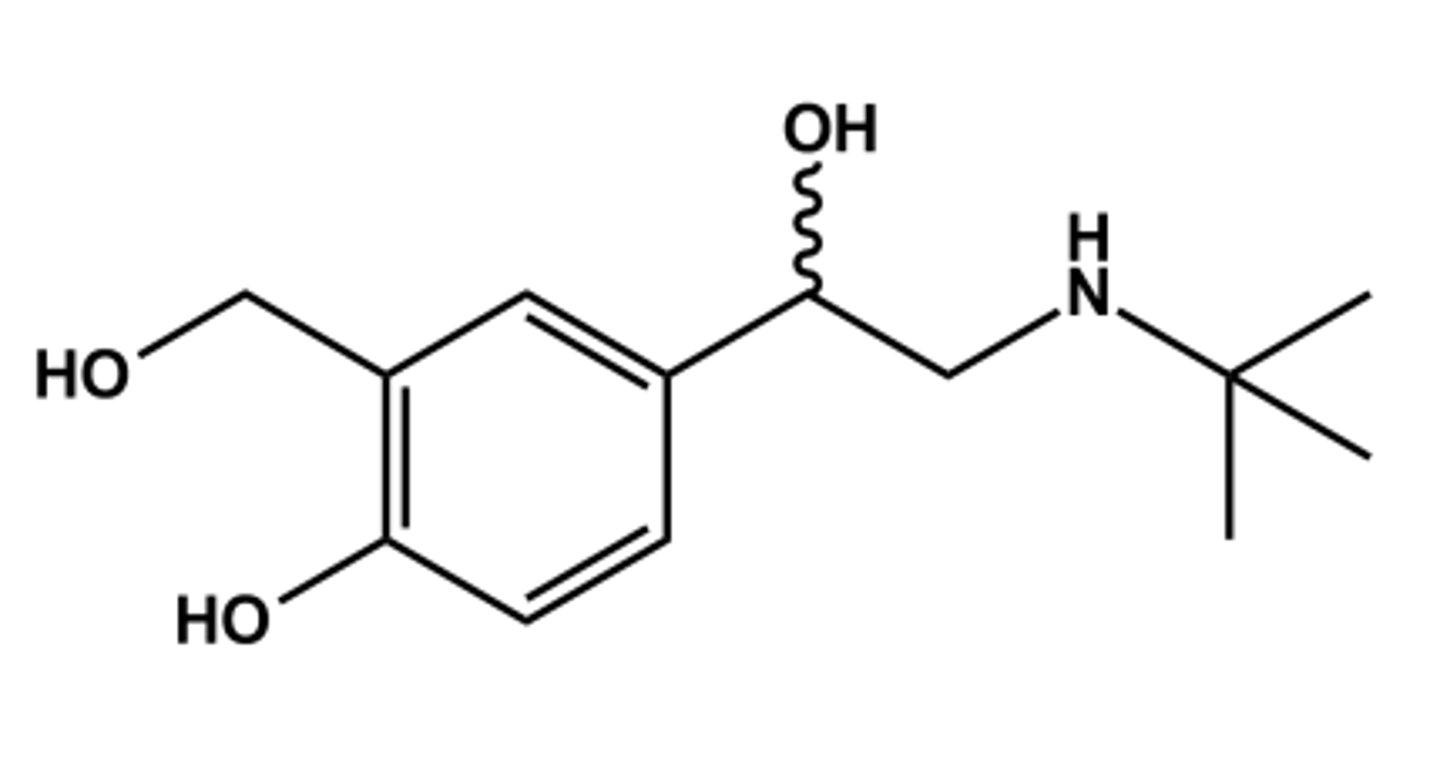
LEVALBUTEROL (XOPENEX®)
- LogP = 1.0; pKa = 10
- R-(-)-isomer has all activity; (Sisomer inactive)
- Animal studies showed S-isomer increases airway sensitivity, but is not true in humans;
- Rationale supporting use of R-(-)- isomer did not hold up, thus not cost-effective vs. albuterol
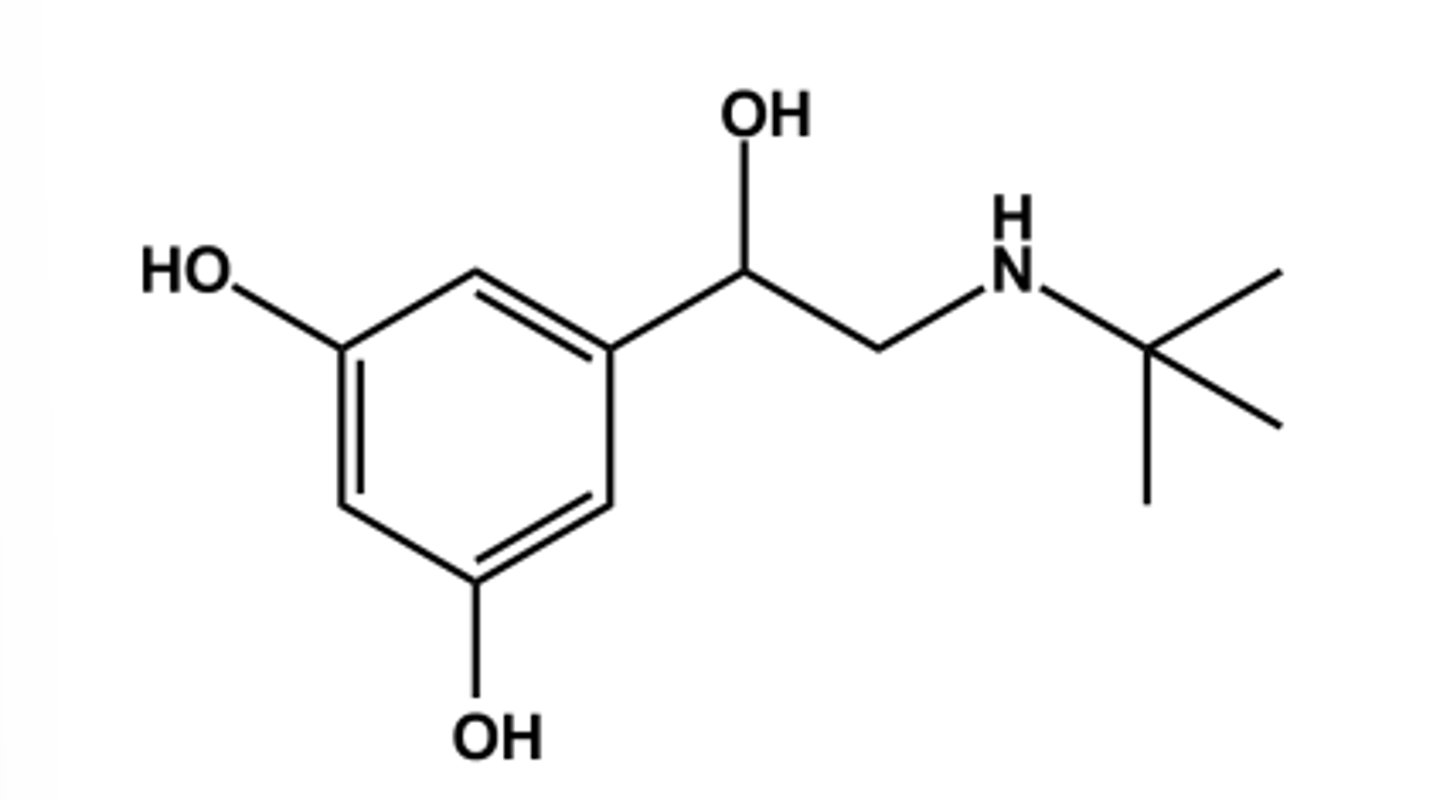
TERBUTALINE (BRICANYL®)
- LogP = 1.2; pKa = 10.1
- Replacing catechol with resorcinol nucleus as another strategy to avoid COMT vulnerability and air instability
- Confers 20x β2 -selectivity
- Use: short term relief of bronchoconstriction via direct inhalation
THIS MOLECULE'S LONG DURATION IS DUE TO...
large lipophilic group on the nitrogen atom
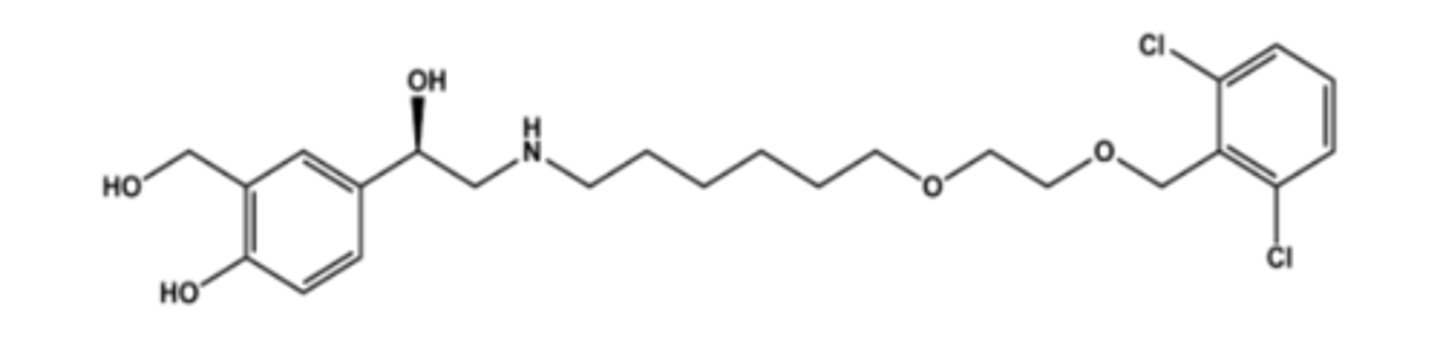
SALMETEROL (SERAVENT®)
-LABA (long acting β2 agonist)
- LogP = 4.2; pKa = 10
- It is substituted albuterol, so β2 -selective
- Takes advantage of lipophilic auxiliary site on β2 receptor (so-called exo-site)
- Diffuses into lipid bilayers and slowly redistributes, providing long duration
-Expect that only one isomer (R-OH isomer) is active; S-isomer likely inactive
- Use: asthma (not acute), COPD
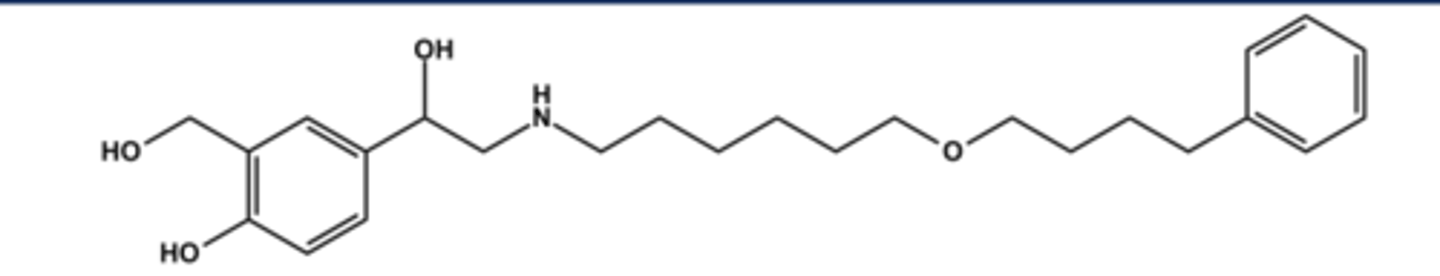
VILANTEROL (IN BREO® & ANORO®)
- LABA (long acting β2 agonist)
- LogP = 4.3+; pKa = 9.4
- Comparable to salmeterol in structure and profile
- Long duration of action, ca. 11 hours
- Not marketed alone but in combination with either an antimuscarinic (as Anoro®) or an antiinflammatory steroid (as Breo®)
- Use: asthma (not acute), COPD
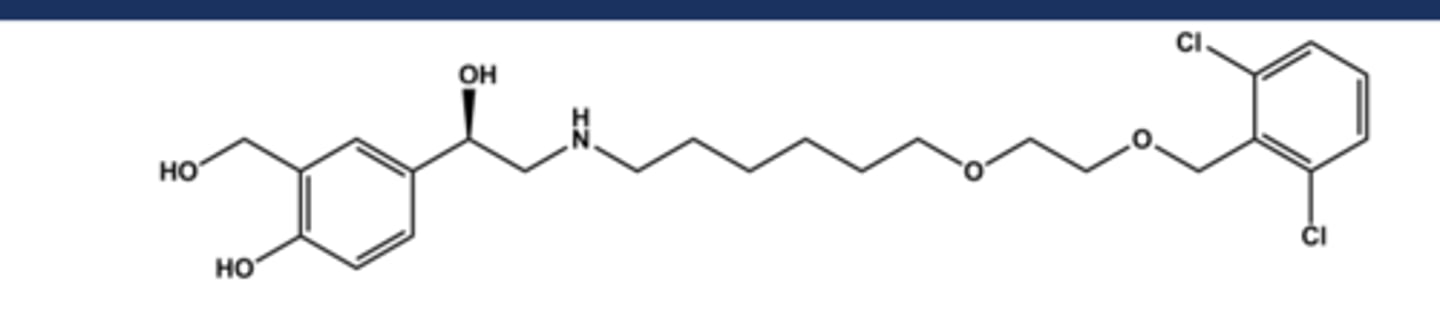
FORMOTEROL (FORADIL®)
- LABA (long-Acting Beta-2 agonist)
- LogP = 2.2; pKa = 9.2
- Two chiral centers; drug is a mix of R,R- and S,S-isomers but R,R has 1000x activity of S,S
- R,R-isomer has been marketed (Arformoterol), but no significant therapeutic benefit justifies the cost for most patients
- Use: asthma (not acute), COPD
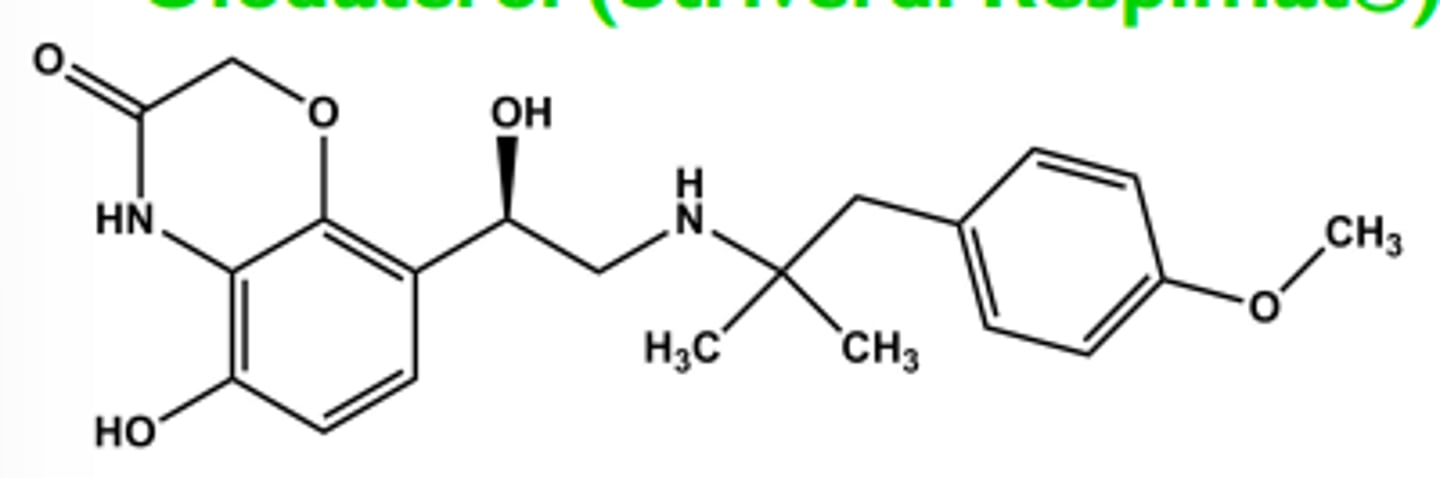
Olodaterol (Striverdi Respimat®)
- Ultra-LABA
- LogP = 3.0; pKa = 9.1 T1/2 ca. 45 hrs; once/day dosing
-One chiral center R-isomer has all activity
- Use once daily for COPD
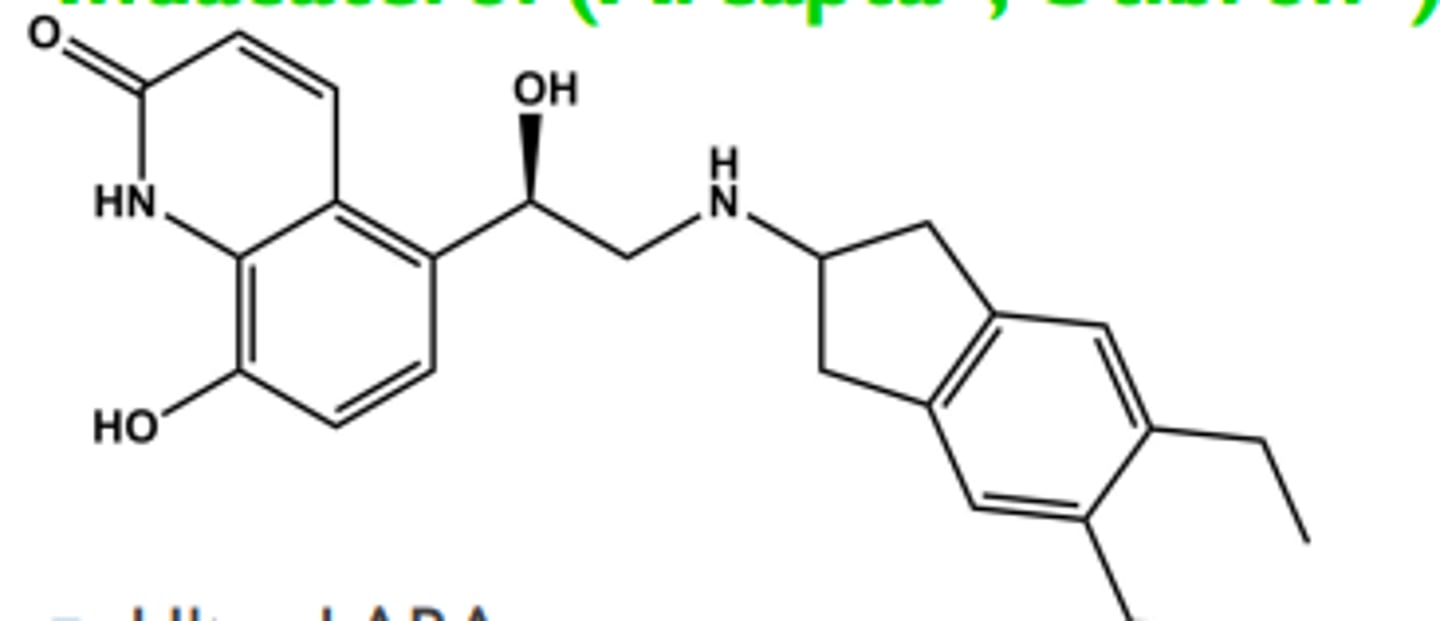
Indacaterol (Arcapta® , Utibron®)
-Ultra-LABA
-LogP = 3.9; pKa = 6.7
- T1/2 ca. 40 hrs; once/day dosing
- One chiral center R-isomer has all activity
- Used once daily for COPD
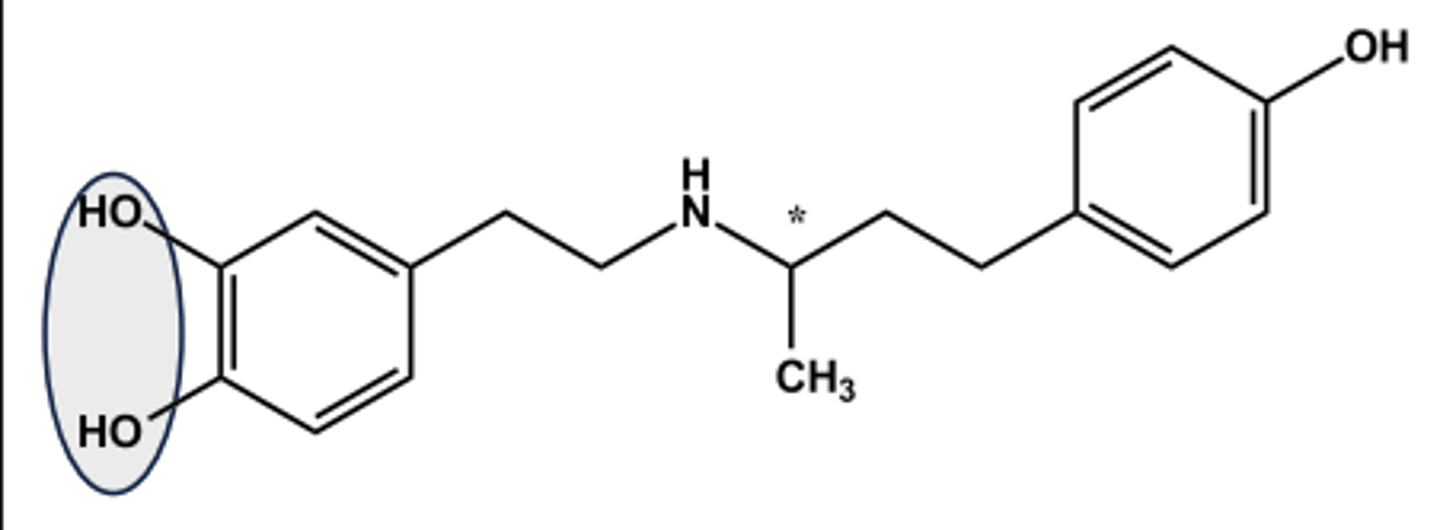
BETA-1 SELECTIVE AGONIST: DOBUTAMINE (DOBUTREX®)
- LogP = 3.5; pKa = 9.5
- Administered as racemate
- (+)-isomer has 10x β1 -agonist activity
- (-)-isomer is potent α1 -agonist; (+)- isomer is potent α1 -antagonist and antagonizes the (-)-isomer
- Net effect in vivo is nearly pure β1 - agonist effect
- Use: cardiac stimulant T1/2= 2 min (why?)
Effects of B-adrenergic Receptor Antagonists
-CV system: Given chronically they decrease blood pressure in hypertensive patients, Mechanisms include blockade of cardiac B1 -receptors, suppression of renin release and CNS effects, Often do not decrease blood pressure in normotensive individuals
-Respiratory system: Blockade of B2 -adrenergic receptors may increase airway resistance, Patients with asthma are particularly sensitive to this
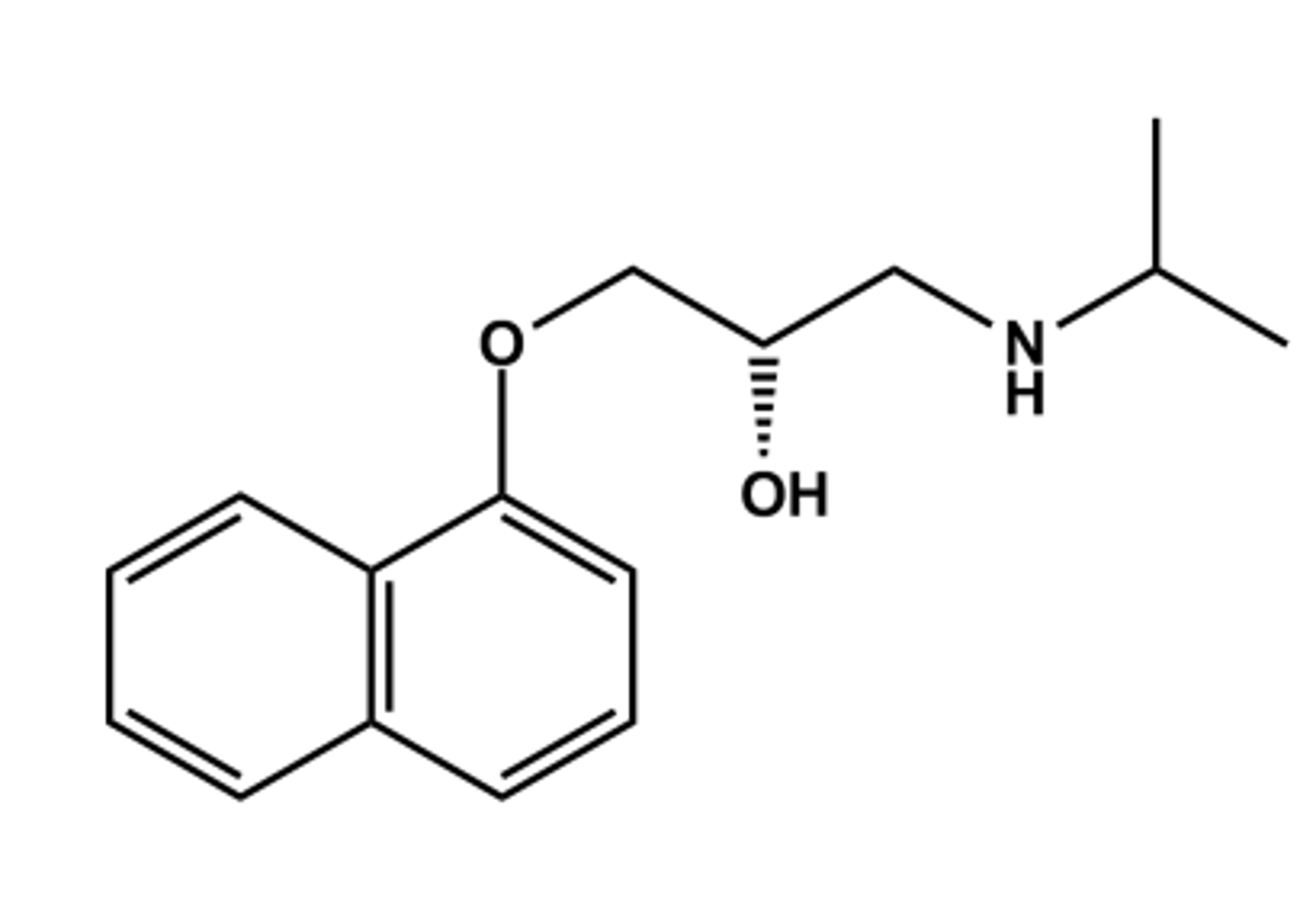
PROPRANOLOL (INDERAL®)
- Prototype nonselective β-antagonist
- LogP = 3.3; pKa = 9.5; T1/2 ca. 4 hr
- High lipophilicity brings facile CNS access; manifests as nightmares
- Liver biotransformation via CYP1A2 (Ndealkylation) and CYP2D6 (aromatic OH)
- Exhibits high first pass effect (ca. 70%)
- Only the S-isomer is active (same configuration as side chain-OH of isoproterenol)
Prototype or benchmark for all β blockers
Propranolol
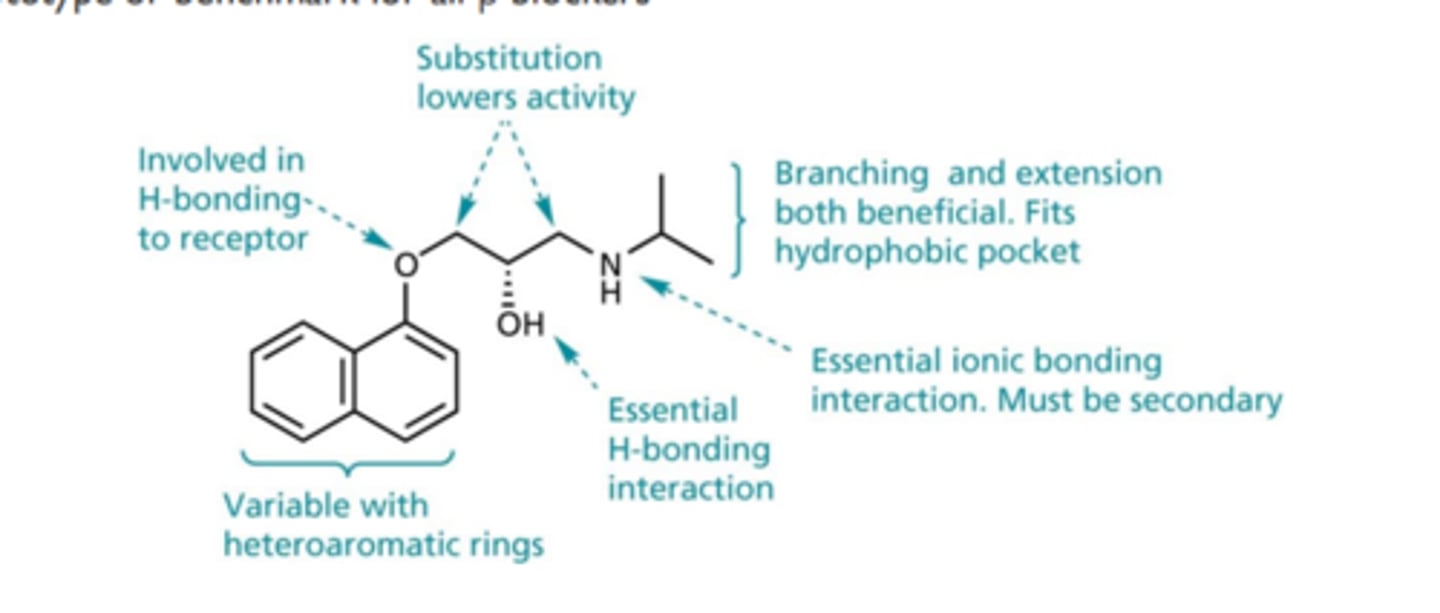
NADOLOL (CORGARD®)
- LogP = 1.0; pKa = 9.7; T1/2 ca. 22 hr
- Developed to overcome short duration and rapid metabolism problem of propranolol
- Less susceptible to CYP450; mostly excreted unchanged, cleared by the kidneys
- Still nonselective at β-receptors
TIMOLOL (TIMOPTIC®)
LogP = 2.3; pKa = 9.2; T1/2 ca. 3 hr
In ophthalmic form (Timoptic®)
Metabolized in liver by CYP2D6 and others
PINDOLOL (VISKEN®)
LogP = 1.4; pKa = 8.8; T1/2 ca. 4 hr
Weak local anesthetic activity
Mixed metabolic profile (2/3 by CYP450 and 1/3 unchanged)
METOPROLOL (LOPRESSOR®)
LogP = 2.2; pKa = 9.7; T1/2 ca. 4 hr
Prototype β1 -selective antagonist
Note "tail" in 4 position. This confers β1 selectivity in general
Metabolized in liver by CYP2D6 and minor by CYP3A4
Serves as prototype for all other β1 - selective antagonists
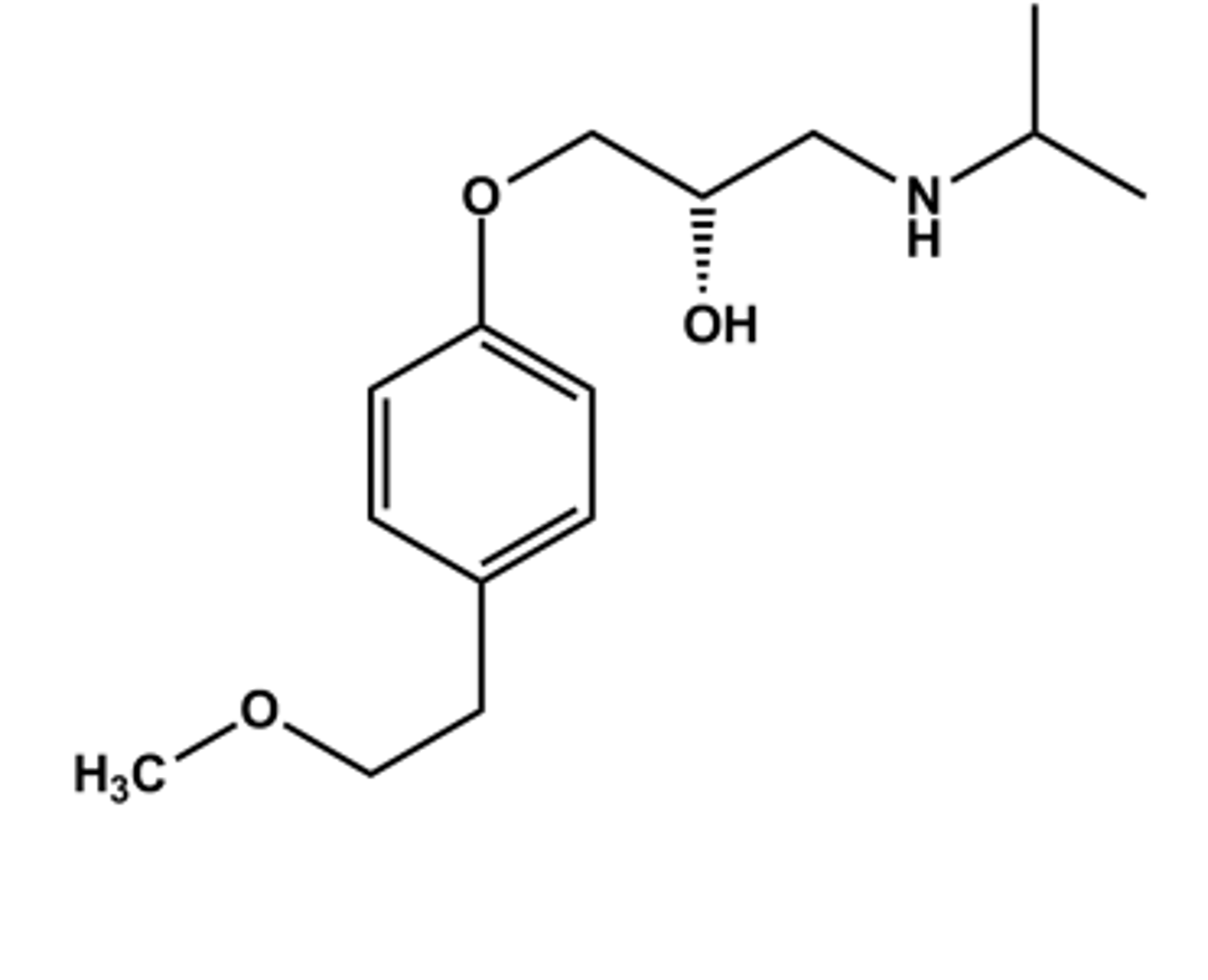
ESMOLOL HCL (BREVIBLOC®)
LogP = 1.8; pKa = 9.5; T1/2 ca. 7 min
Selective β1 -antagonist
Metabolized by esterases following iv administration
Use: rapid & immediate control of arrythmias (supraventricular tachycardias) in surgery
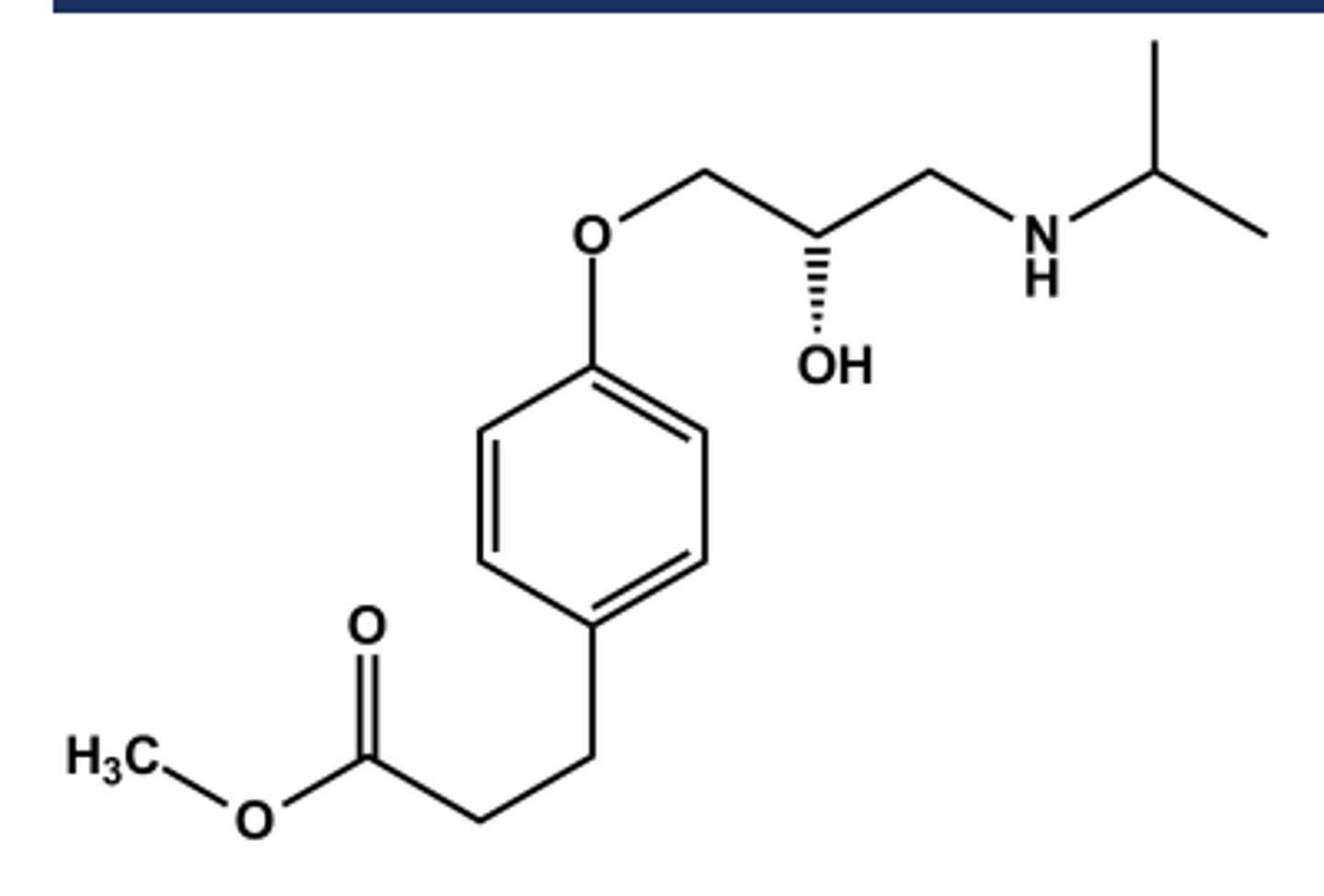
BISOPROLOL (ZEBETA®)
LogP = 1.9; pKa = 9.5; T1/2 ca. 10 hr
Selective β1 -antagonist
Mixed metabolic profile; ca. 50% excreted unchanged, 50% by liver
Marketed as most balanced pharmacokinetic profile
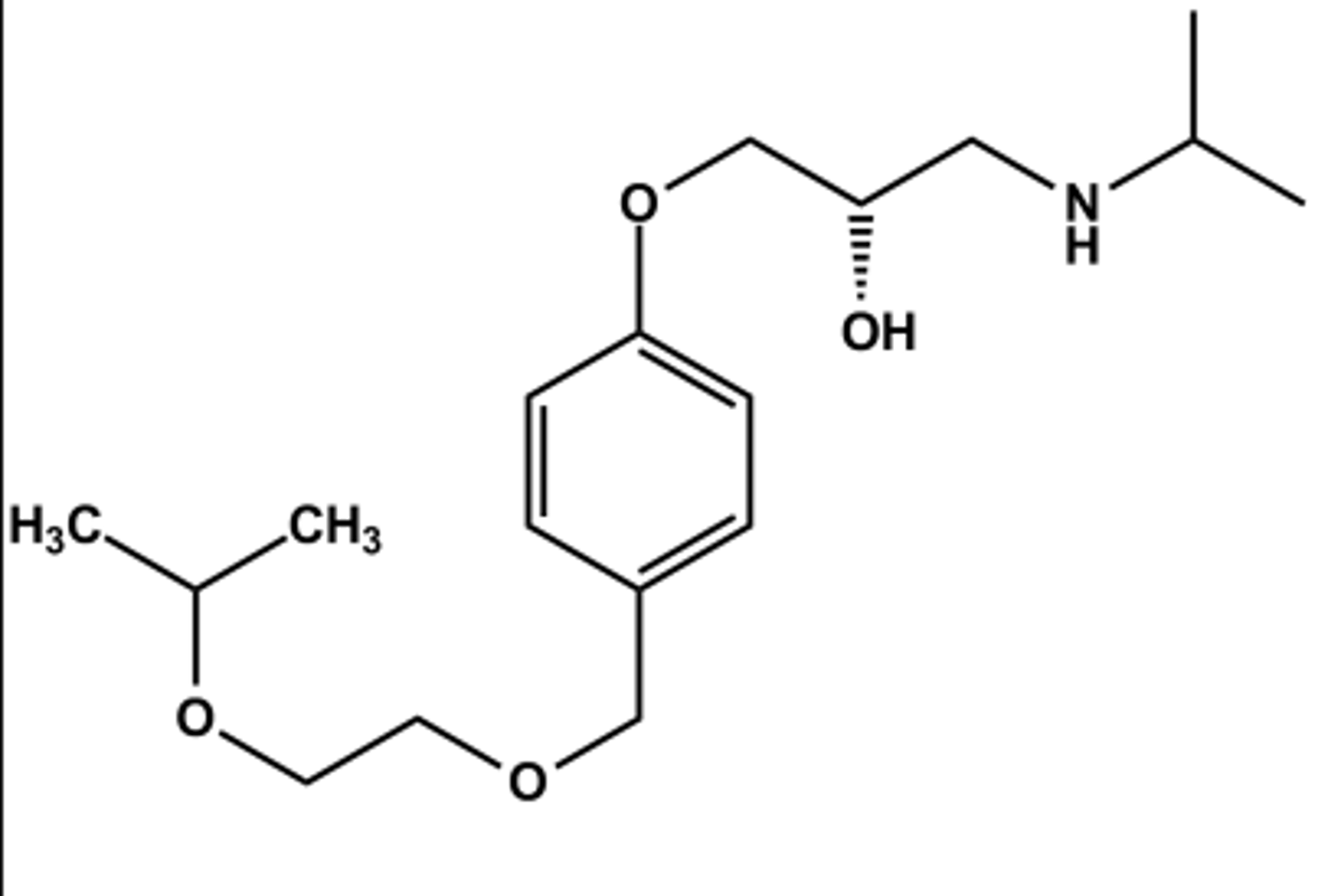
ATENOLOL (TENORMIN®)
LogP = 0.9; pKa = 9.2; T1/2 ca. 6 hr
Selective β1 -antagonist
One of the more potent members of the class
Lower lipophilicity, so cleared by kidney unchanged rather than liver
Lower LogP also reduces potential CNS effects
CHARACTERISTICS OF B -ANTAGONISTS
➢ Selectivity for β-receptor subtypes, especially β1
➢ Metabolic profile with respect to duration of action
➢ Location of metabolic events (liver, kidney, other)
➢ Lipophilicity (access to CNS, side effects)
➢ Clearance: More lipophilic drugs are cleared by the liver, whereas the more hydrophilic ones are cleared by the kidney: This may influence the choice of agents in cases of renal failure or liver disease
Nicotinic Receptors
❑ Receptors on skeletal muscle and nerve-nerve synapse
❑ Nicotine (tobacco) is the founder
Muscarinic Receptors
❑ Receptors on smooth muscle and cardiac muscle
❑ Muscarine in poisonous mushroom is the founder
Choline Acetyltransferase (ChAT)
enzyme that synthesizes ACh
Acetylcholine Esterase (AchE)
enzyme that breaks down ACh
ACh
non-selective endogenous agonist at ALL muscarinic & nicotinic receptors
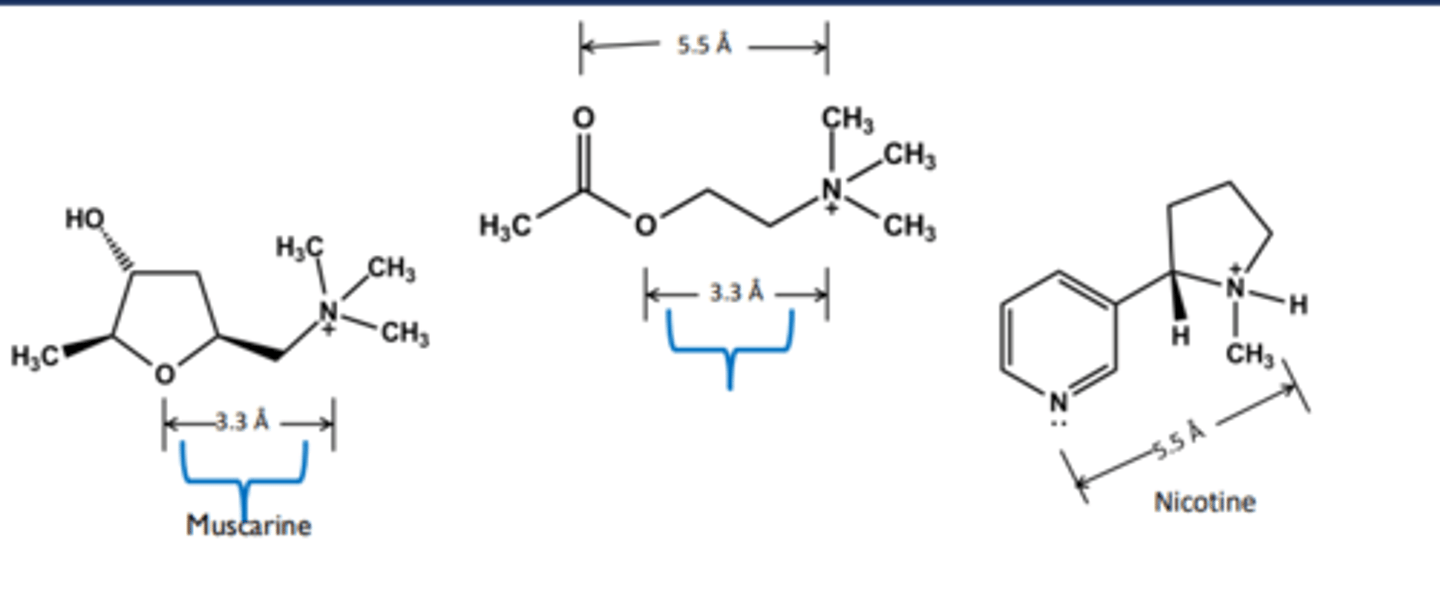
Muscarinic agonists
produce a SLUD response, especially in high doses
Nicotinic Agonists
have no great therapeutic use in the periphery but one centrally acting partial agonist has found use as a smoking cessation aid
Muscarinic antagonists
several therapeutic uses (anti-SLUD)
Nicotinic antagonists
mostly used as neuromuscular junction blockers to produce paralysis during surgery.
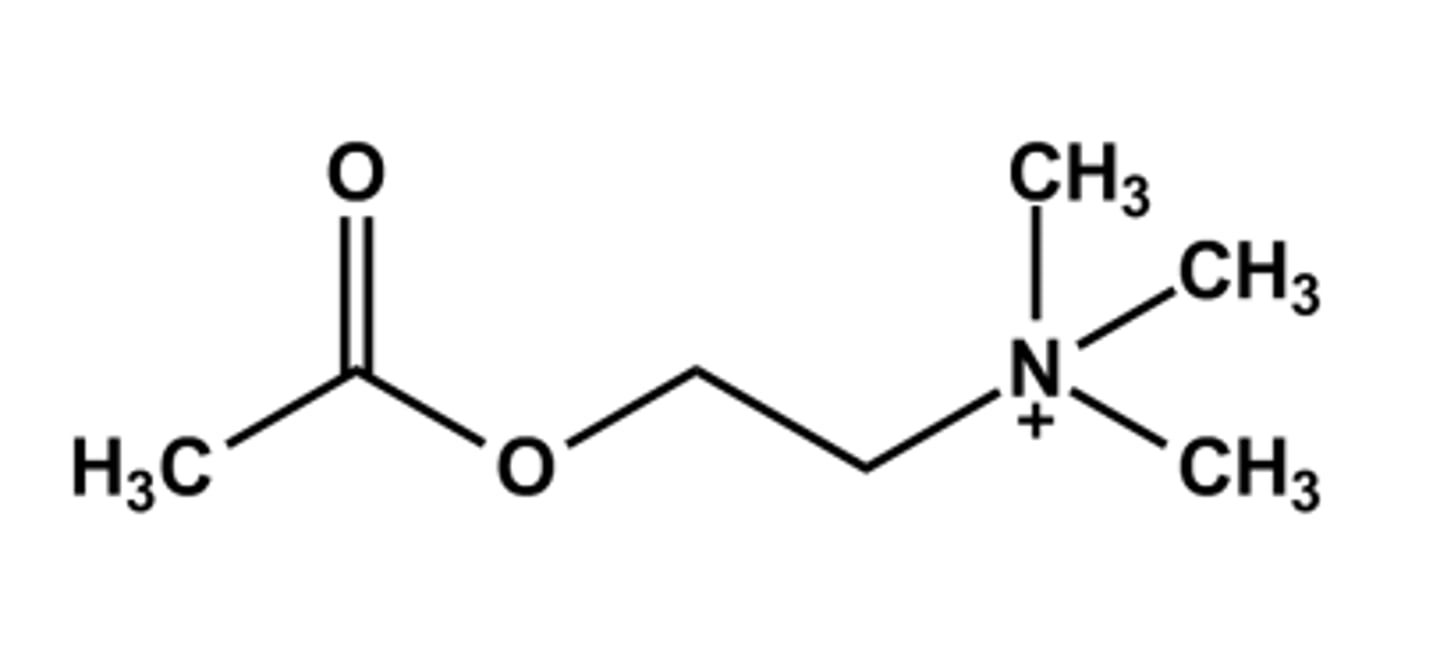
ACETYLCHOLINE (MIOCHOL®)
-Neurotransmitter
- Poor drug for general cholinergic agonist use due to
➢ High polarity
➢ Rapid hydrolysis by AChE
- Only use: Intraocular miotic agent in cataract surgery
➢ Also decrease the intraocular pressure.
- Mixed muscarinic/nicotinic action
- LogP = ca. -4.1
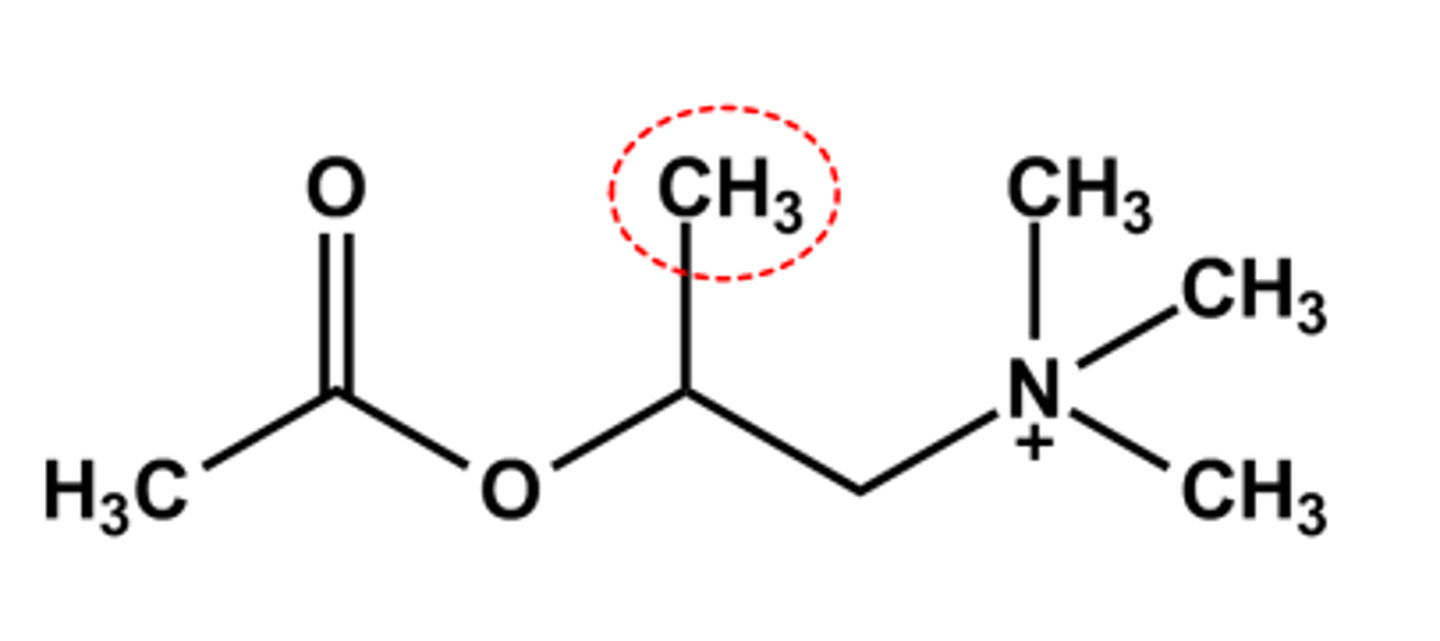
METHACHOLINE (PROVOCHOLINE®)
- β-Methyl favors muscarinic activity, extra binding opportunity with the receptor binding site
- S-(+) Isomer is 240x more potent than R-(-) isomer
- Hydrolyzed 50% slower by AChE
- LogP = ca. -3.8
- Use: Asthma diagnostic. Administered by inhalation with a nebulizer to test for asthma since the drug causes wheezing and shortness of breath
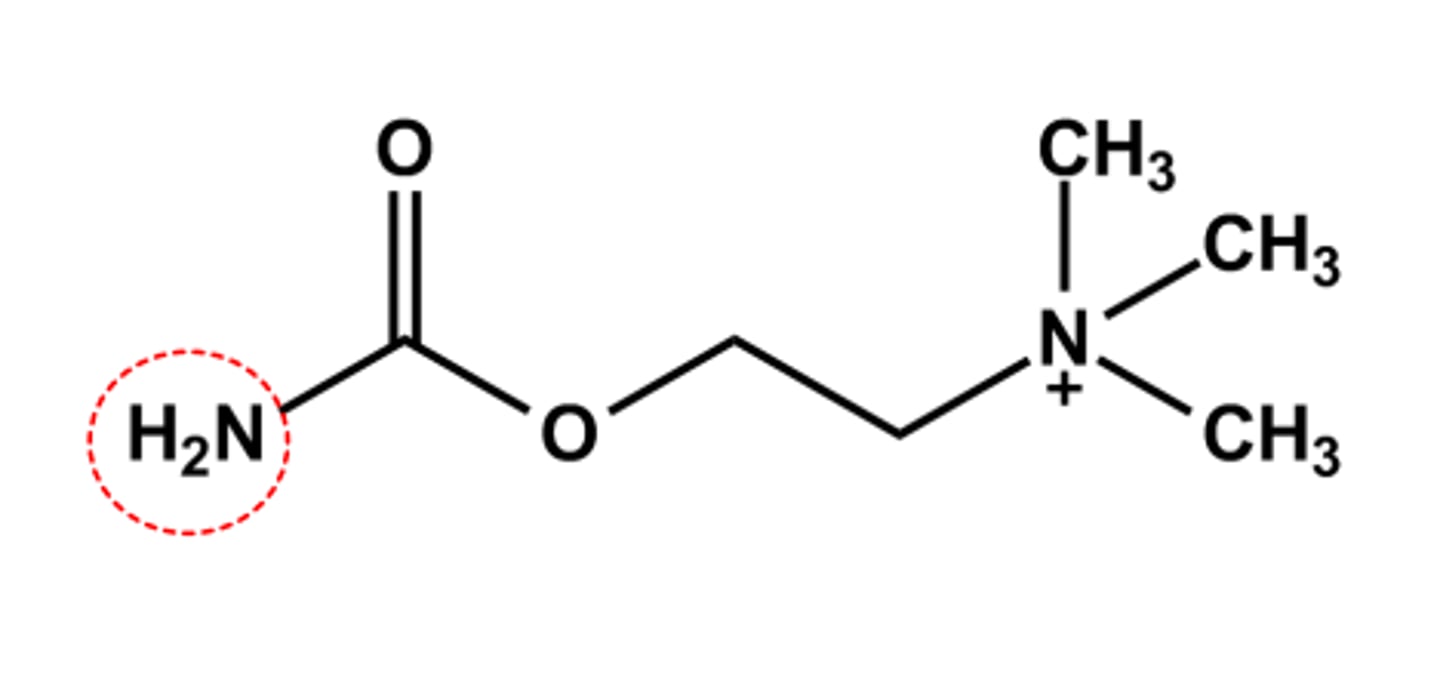
CARBACHOL (MIOSTAT®)
- Carbamate more resistant to AChE catalyzed hydrolysis
- Duration & stability are sufficient to produce some systemic SLUD effects
- Use: intraocular miotic drug during cataract surgery
- LogP = ca. -4.6
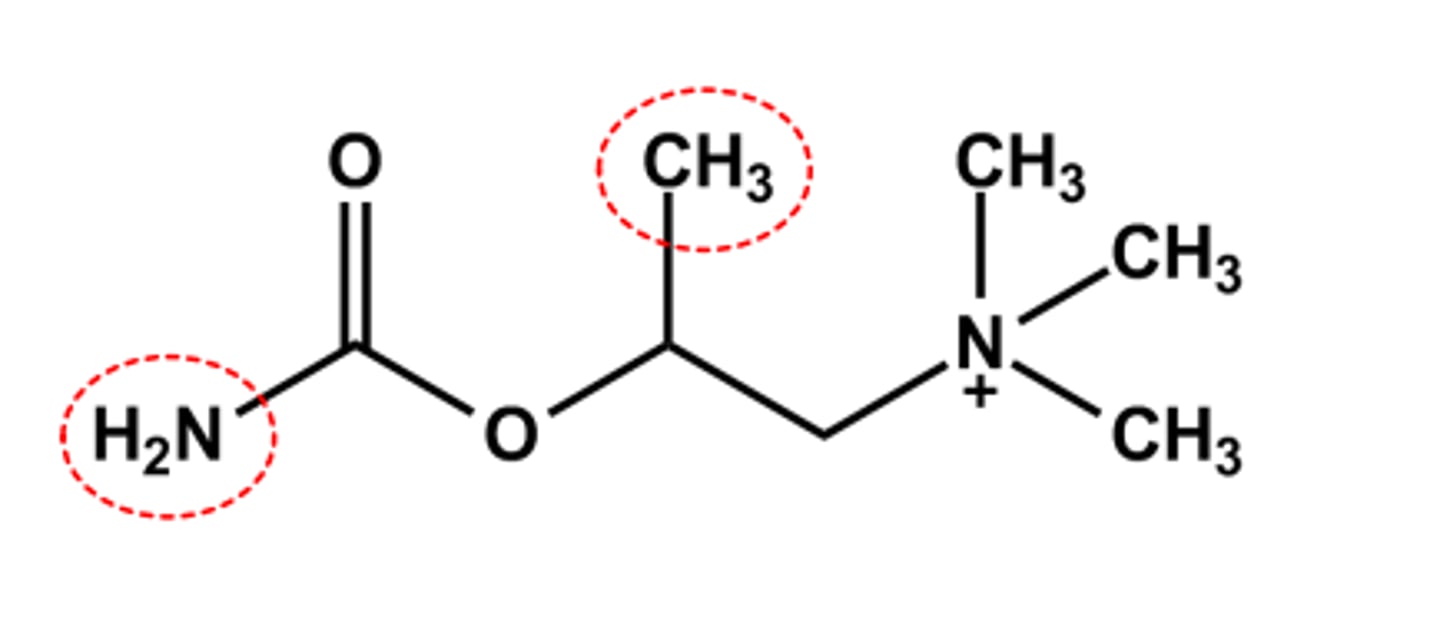
BETHANECHOL (URECHOLINE®)
- LogP = ca. -3.4, pKa = n/a
- Has both β-methyl and carbamate
- sufficient stability
- SLUD effects expected and observed
- Use: to reverse postoperative urinary retention
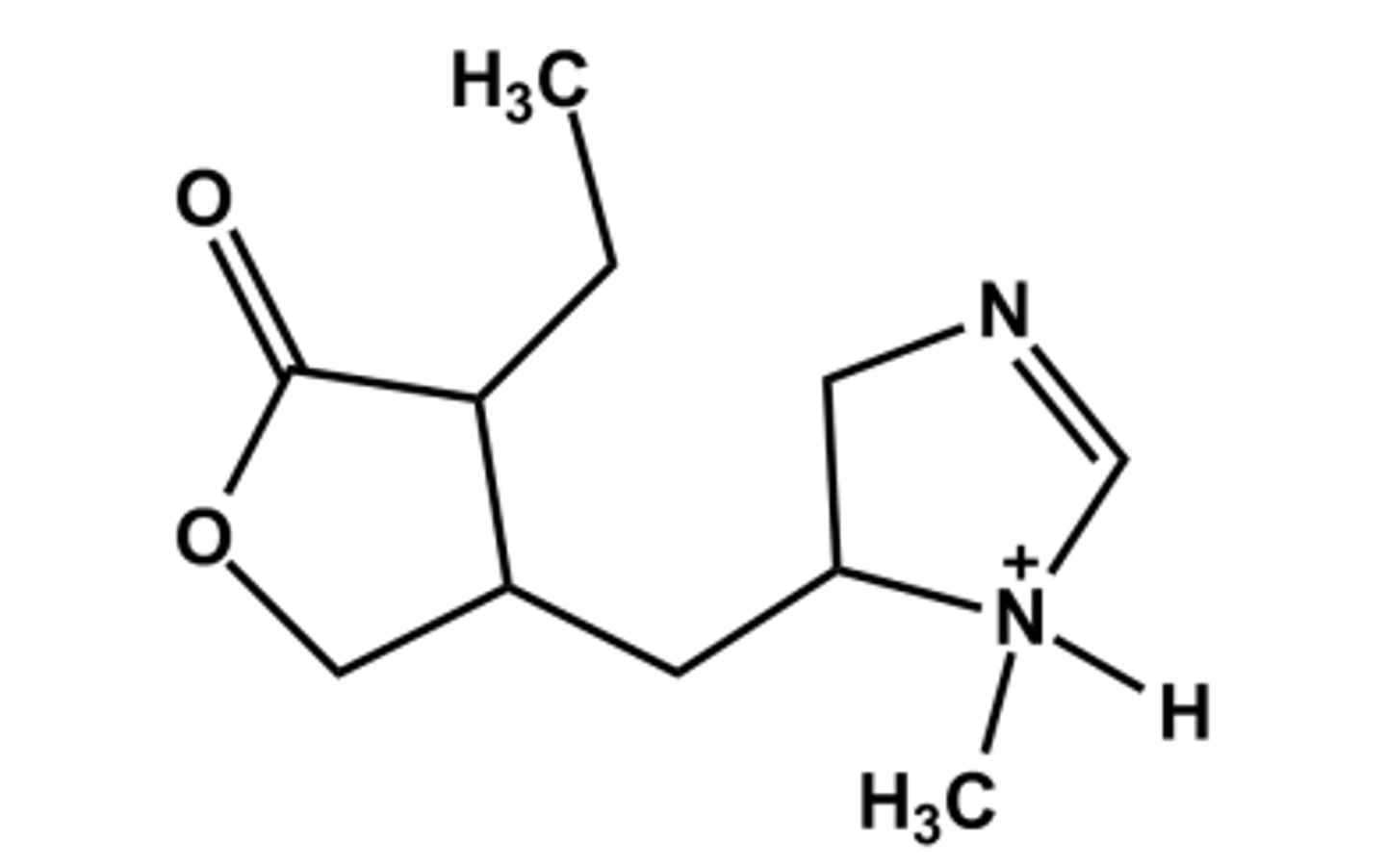
PILOCARPINE (PILOPINE®)
-Natural product from Pilocarpin microfelixis
- Nonclassical bioisostere of ACh; 3D structure shows approx. correct spacing
- LogP = 1.0; pKa = 6.8
- Use: miotic, treatment of dry mouth in Sjogren's syndrome
Therapeutic Uses of Muscarinic Agonists
Eye:
➢ Glaucoma (rarely used for this now)
➢ Use limited to initial treatment before Cataract surgery
GI and urinary tracts
➢ Post-operative ileus, post-operative urinary retention
➢ Treatment of dry mouth caused by radiation damage of salivary glands
➢ For patients with Sjögren's syndrome (immune system disorder characterized by dry eyes and dry mouth)
Adverse effects (SLUD)
Salivation, Lacrimation, Urinary urgency, Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, sweating, cutaneous vasodilation, and bronchial constriction
NICOTINE (NICOTROL®, NICORETTE®, OTHERS)
- Natural product; constituent of tobacco leaves
- LogP = 1.0; pKa = 10.9
- Selective agonist at peripheral nACh receptors and at sites in the CNS
- Highly habituating; or addicting
- Discontinuation produces physical and psychological symptoms of withdrawal
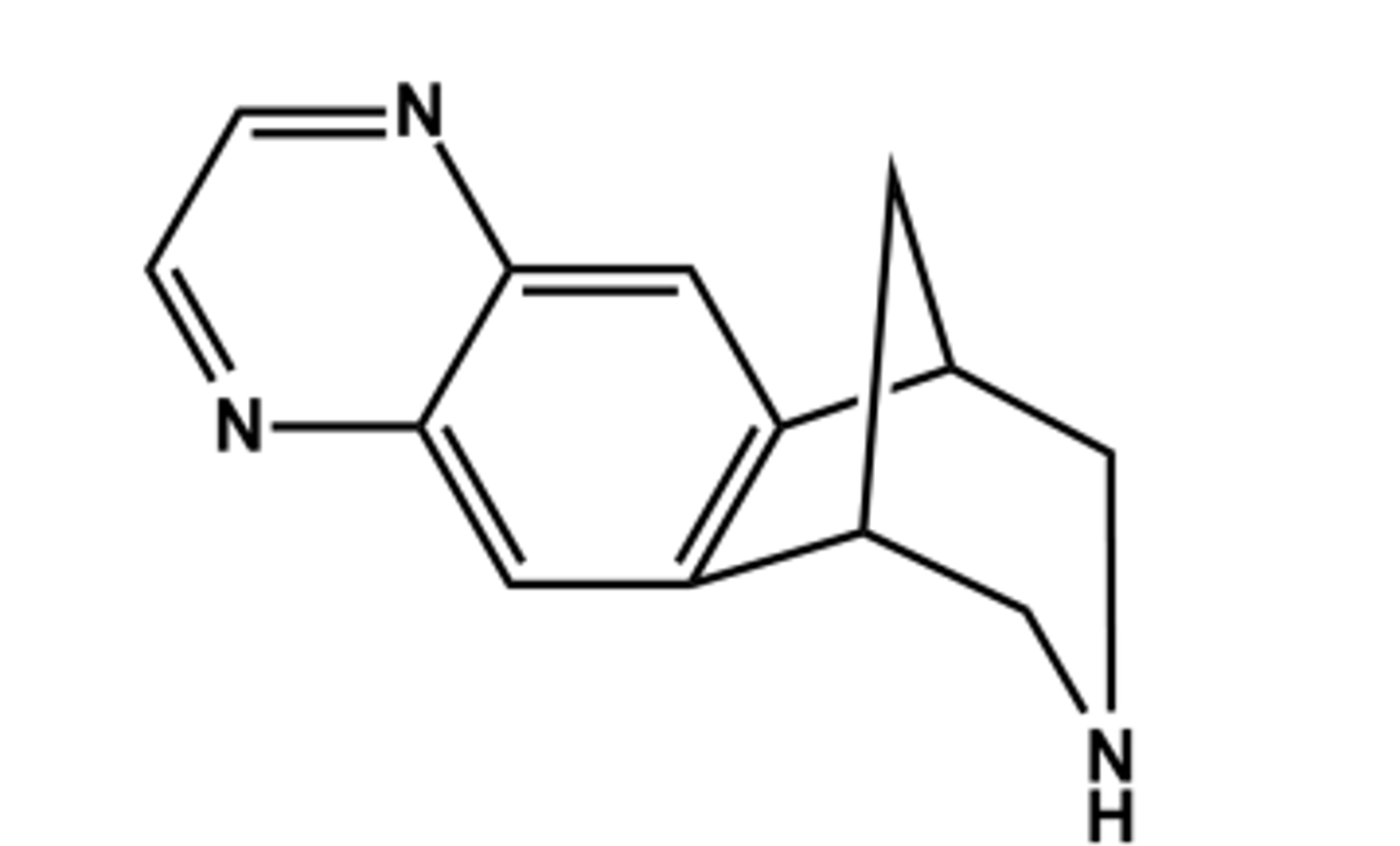
VARENICLINE (CHANTIX®)
- Partial agonist at the specific CNS nicotinic α4β2 acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs)
- No rewarding or addictive properties
- Only drug of its kind
- Use: reduce craving for nicotine and withdrawal symptoms in tobacco users
- Adverse effects: Nausea, vomiting, insomnia, vivid dreams, anxiety, depression, suicidal thoughts
therapeutic effects of nicotinic agonists
smoking cessation
adverse effects of nicotinic agonists
➢Central stimulant actions, convulsions, coma and respiratory arrest
➢Skeletal muscle end plate depolarization, which may lead to depolarization blockade and respiratory paralysis
➢Hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias
Therapeutic Uses of Muscarinic Antagonists
- Urinary disorders: Overactive bladder (urinary incontinence), urinary urgency
- Ophthalmologic disorders: Eye examinations (pupillary dilation)
-Respiratory disorders: Asthma and COPD
- GI disorders: Treat diarrhea (often combined with an opioid)
- CNS (if they cross BBB): Motion sickness and Adjunctive treatment in Parkinson's disease
adverse effects of muscarinic antagonists
Anti-SLUD
- Mydriasis, cycloplegia, Dry mouth, Amnesia, cognitive deficits, Hyperthermia-children are particularly sensitive- atropine fever
- Toxic overdose: Hyperthermia and flushing, agitation and delirium, decrease secretions from many glands (salivary, sweat, mucosal)
- "Blind as a bat, dry as a bone, full as a flask, hot as a hell, red as a beet, mad as a hatter"
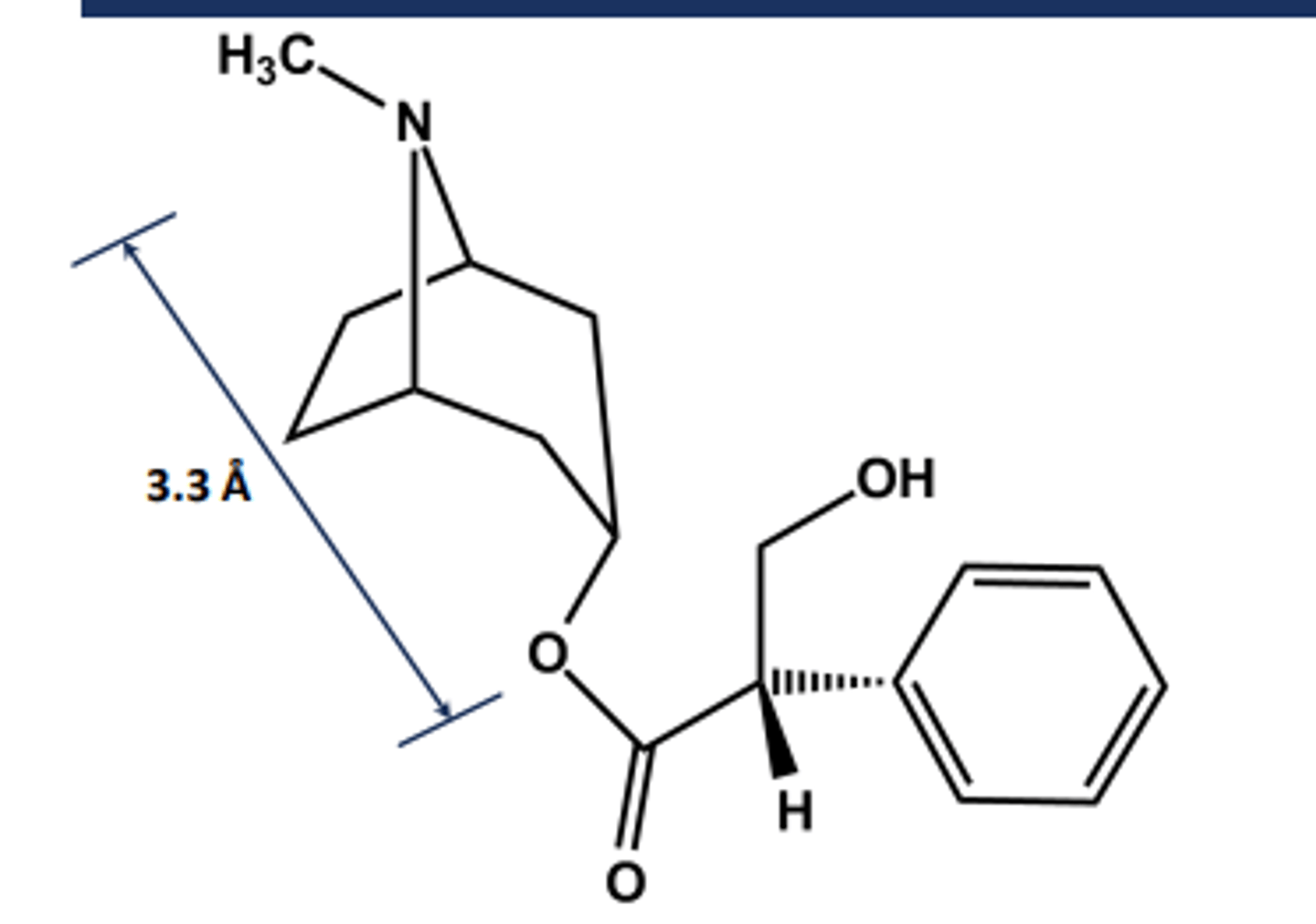
Atropine
-S-(-)-Hyoscyamine
- From Atropa Belladonna
- Chiral in its natural state
-called atropine when racemized upon isolation
- LogP = 1.6; pKa = 9.4
- Uses: Mydriatic agent (eye drops), organophosphate antidote
- Ester is hindered so not affected much by AChE, which accounts for 3 hours half life
- Long-acting systemic effects
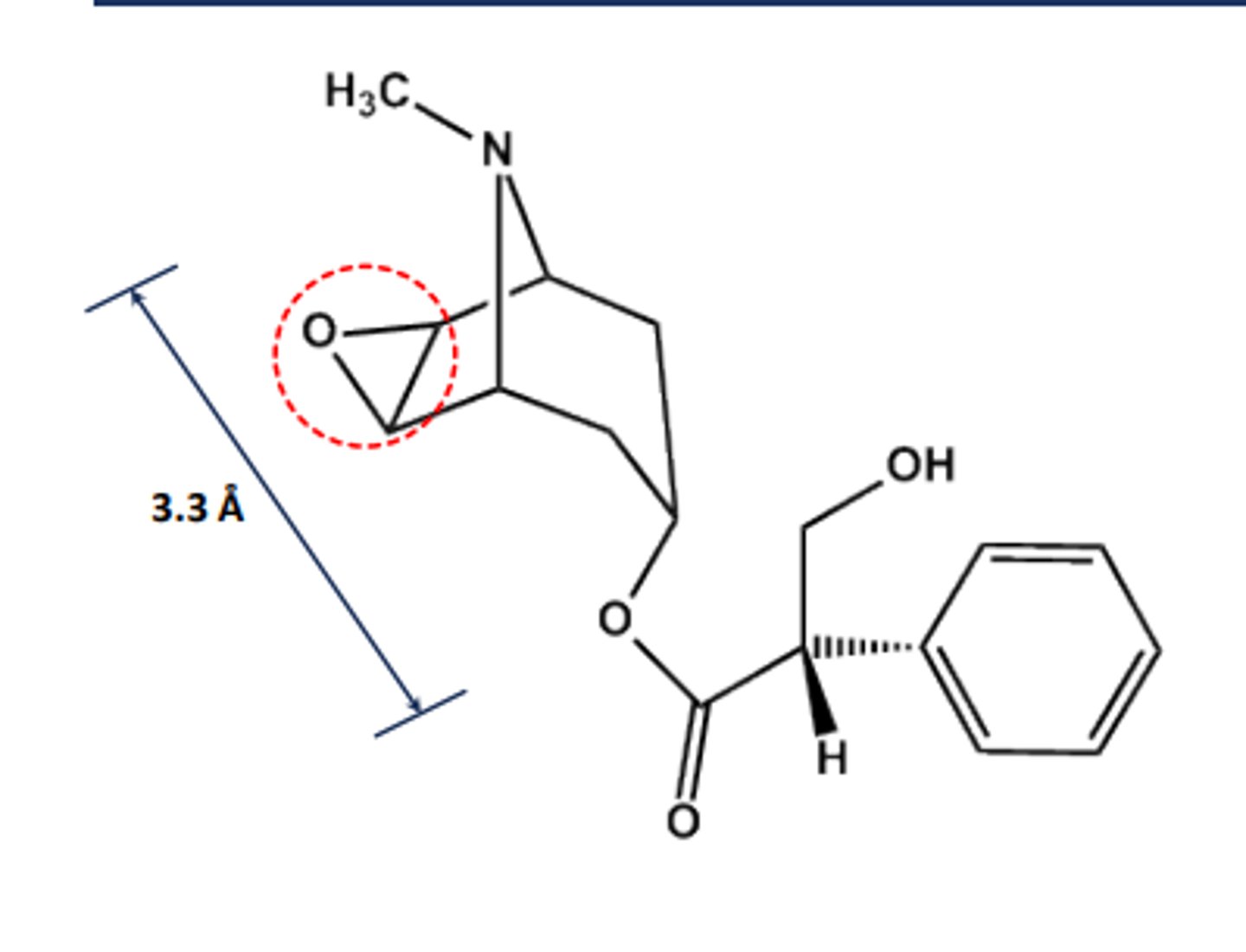
Scopolamine
- Chiral in its natural state
- Another Atropa Belladonna alkaloid
- LogP = 1.7; pKa = 7.6
- Long-acting systemic effects
- Uses: motion sickness
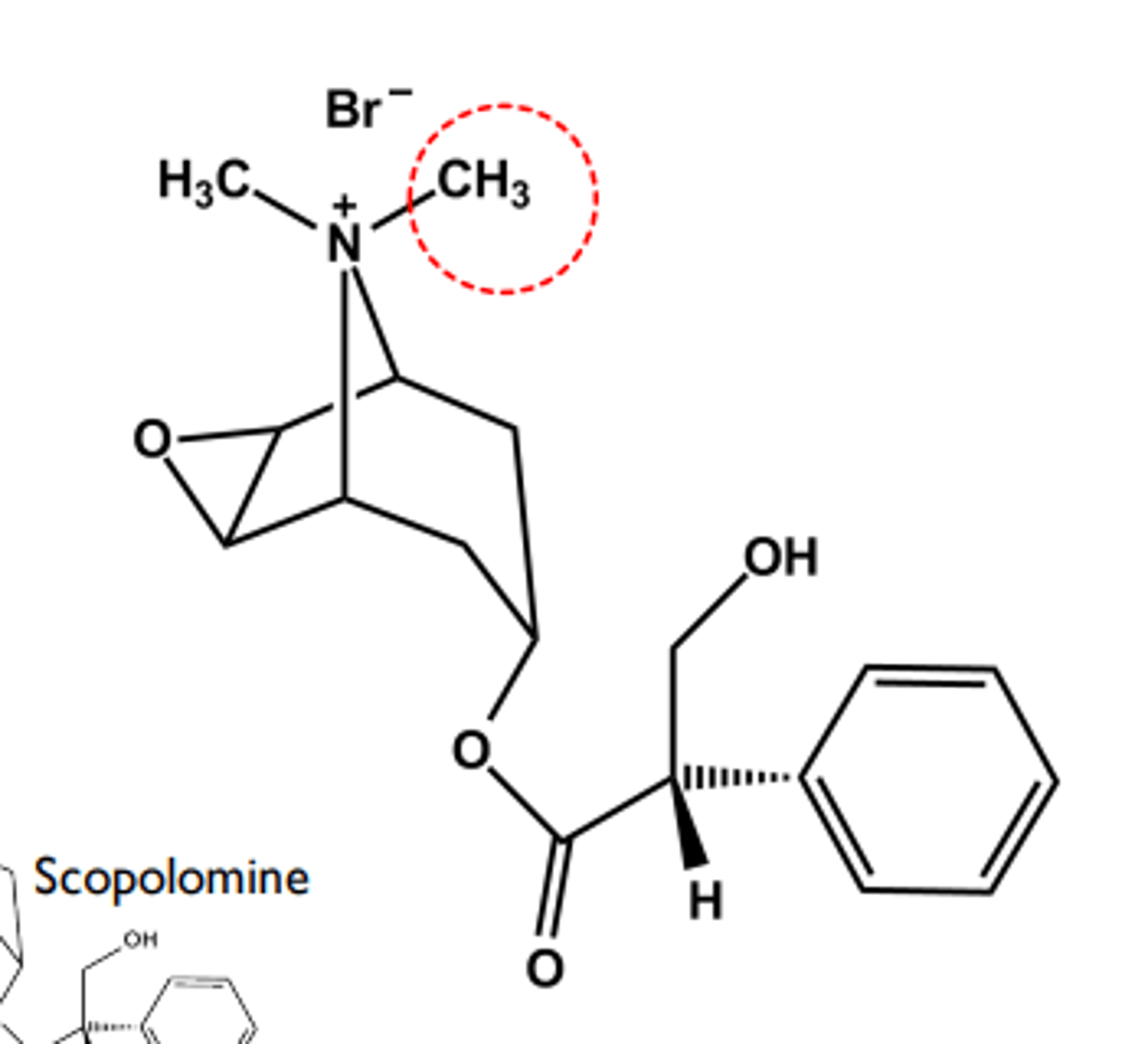
Methscopolamine bromide
- Quaternary Nitrogen limits transport to GI tract if given orally
- LogP = -1.5 Use: adjunctive treatment for peptic ulcer (antispasmotic)
- Relatively hindered ester resists hydrolysis
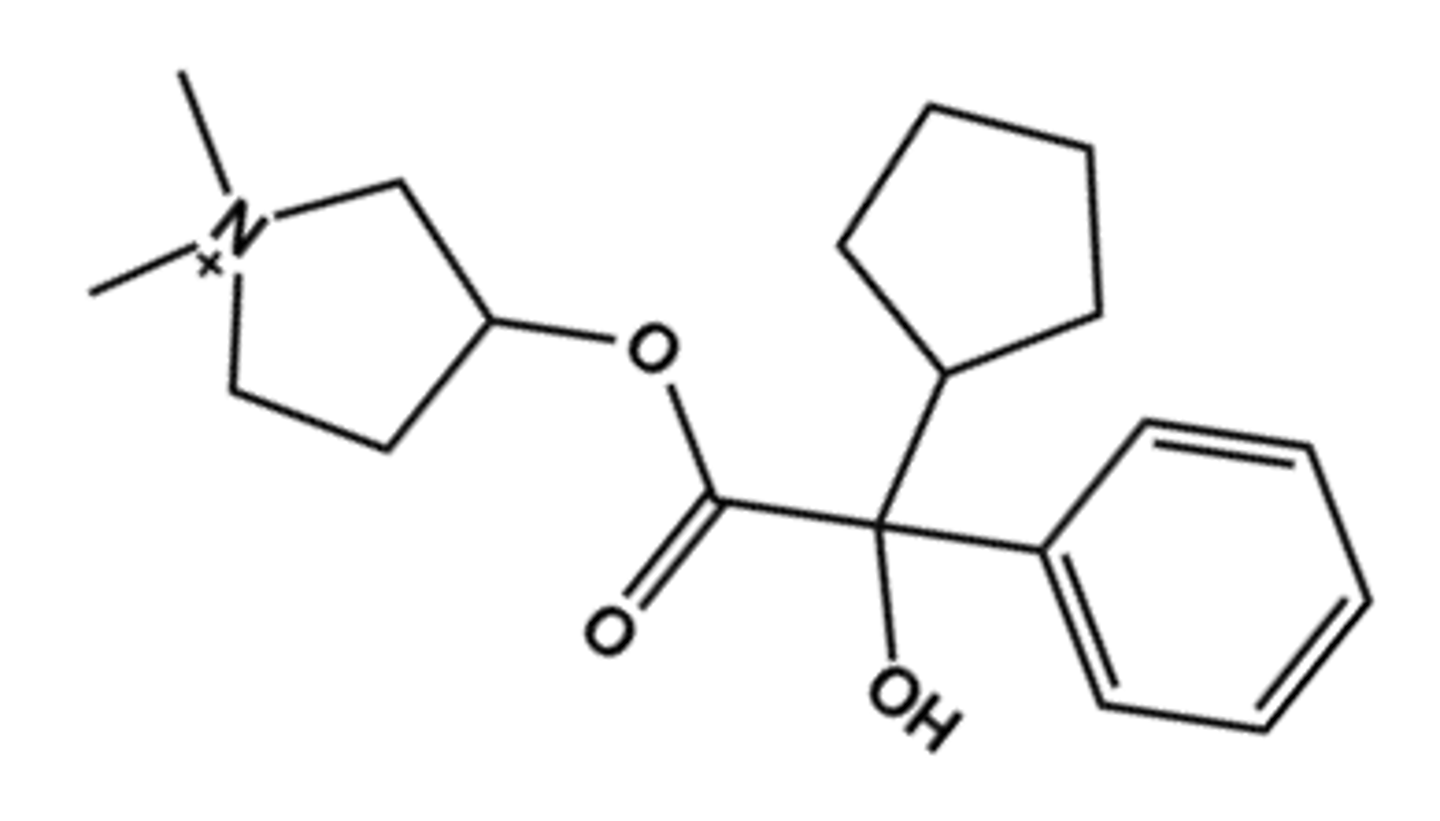
Glycopyrrolate (Robinul®)
- LogP = -1.0, T1/2 = "long"
- Uses: oral antispasmotic
- Ester is hindered so drug excreted mostly unchanged
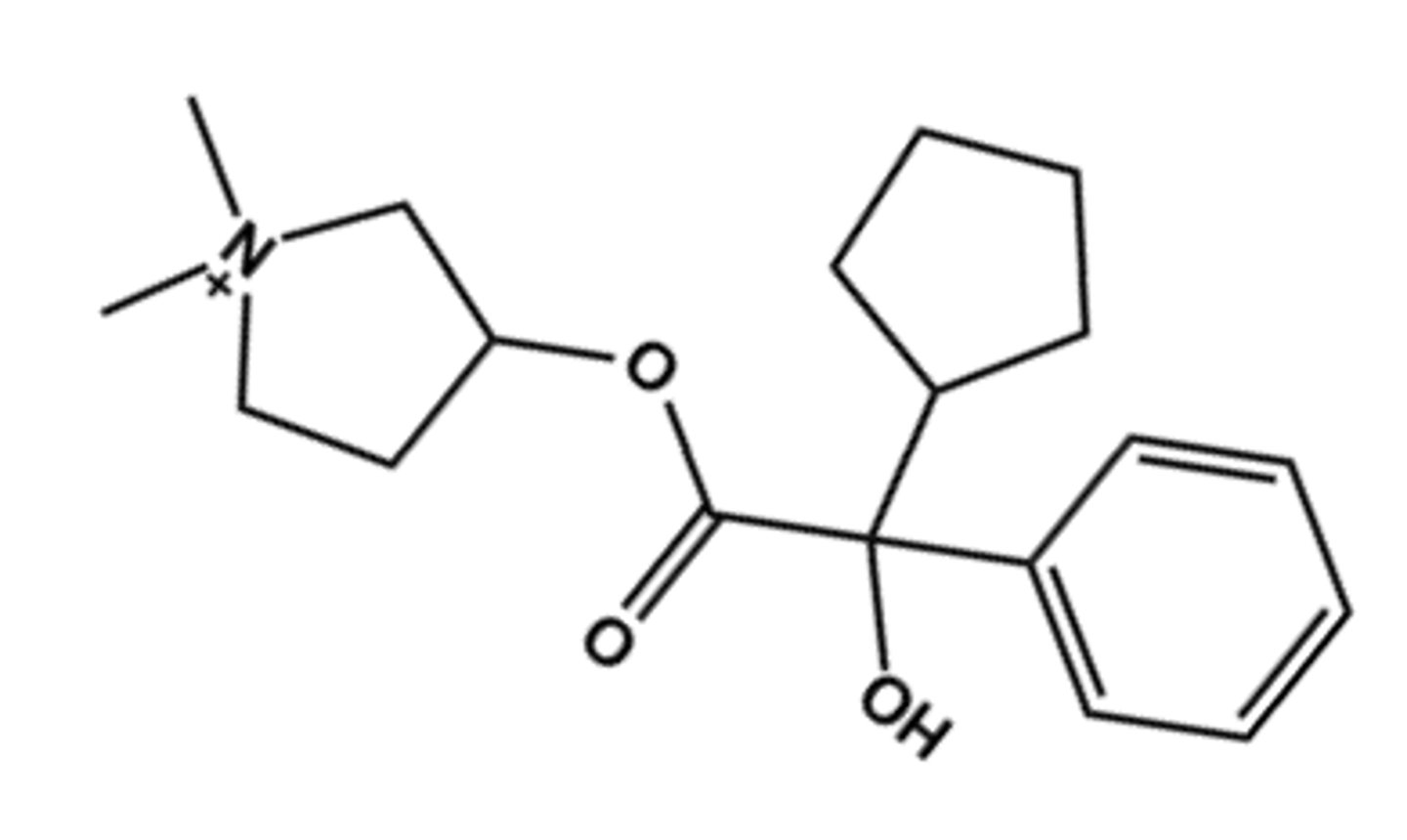
Glycopyrrolate (in Utibron® Neohaler®, and Seebri®)
- LogP = -1.0
- Uses: inhaled for anti-COPD
- Ester is hindered so drug excreted mostly unchanged
Ipratropium Bromide (Atrovent®)
- LogP = -1.8
- Relatively hindered ester resists hydrolysis
- Use: Prevent bronchospasm in bronchitis, COPD
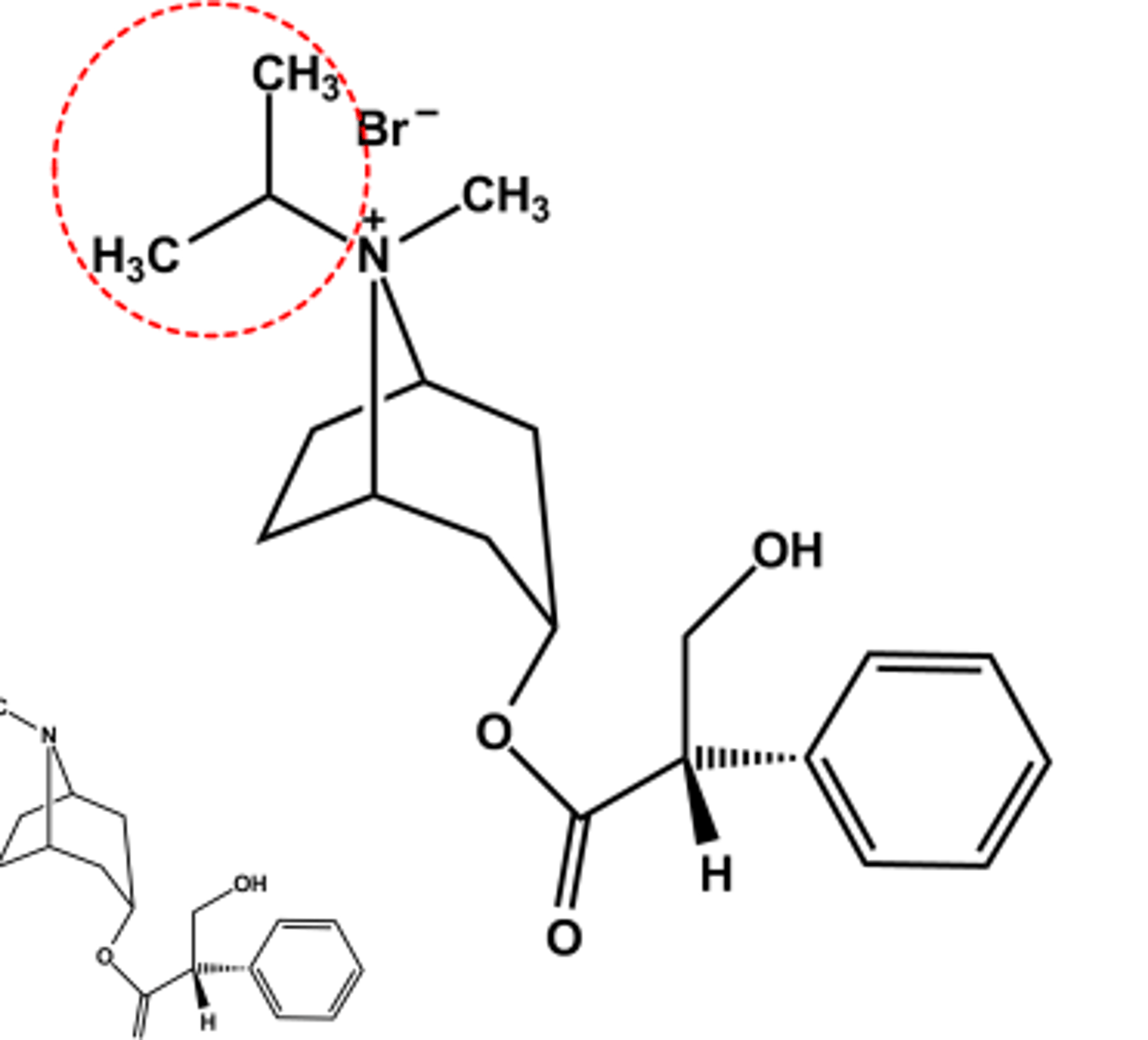
Tiotropium bromide (Spiriva®)
- LogP = -1.7
- M3 -receptor selective, but not clinically relevant
- Use: Prevent bronchospasm in COPD,
- Hindered ester resists hydrolysis; renal clearance is major elimination pathway
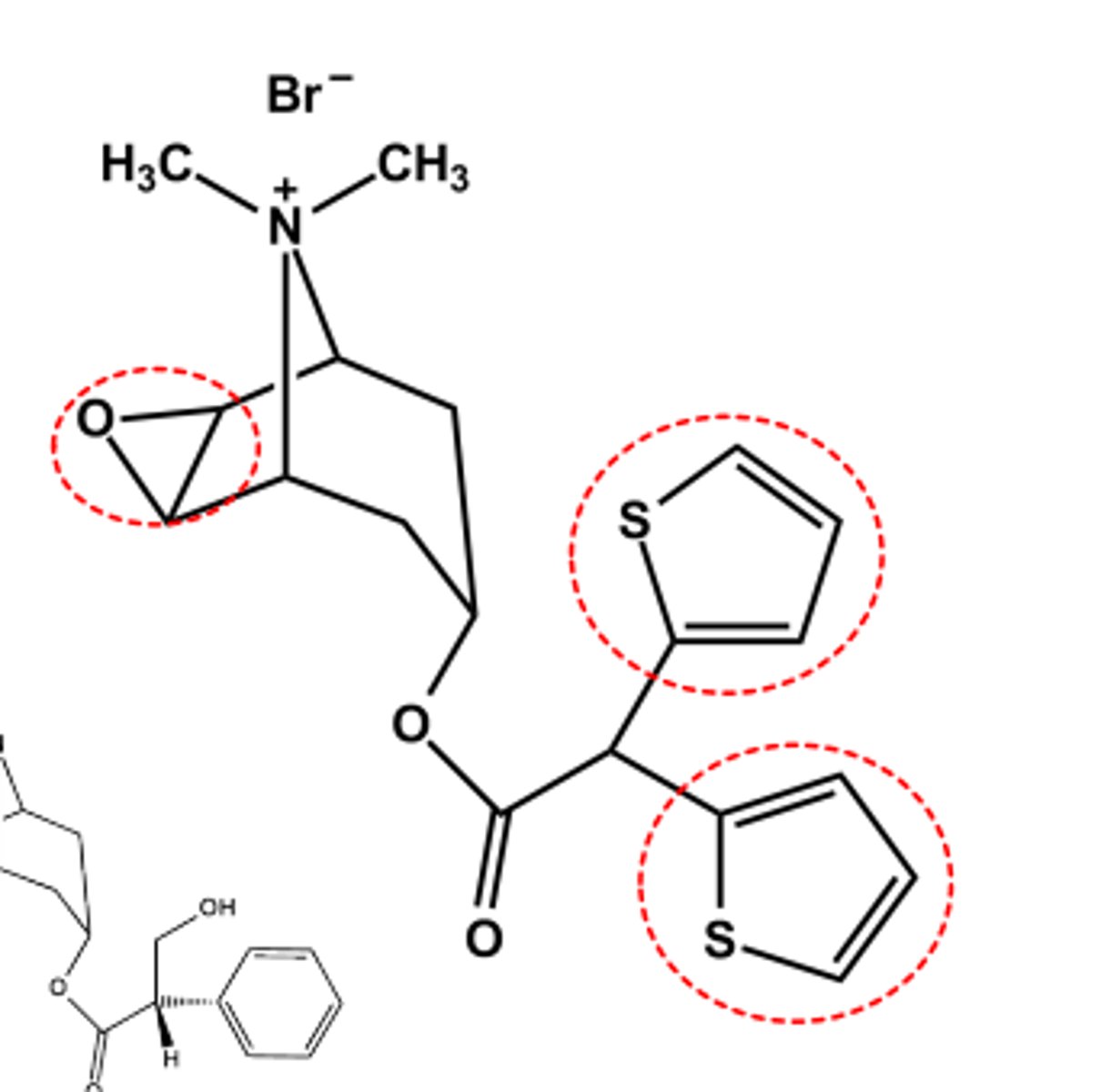
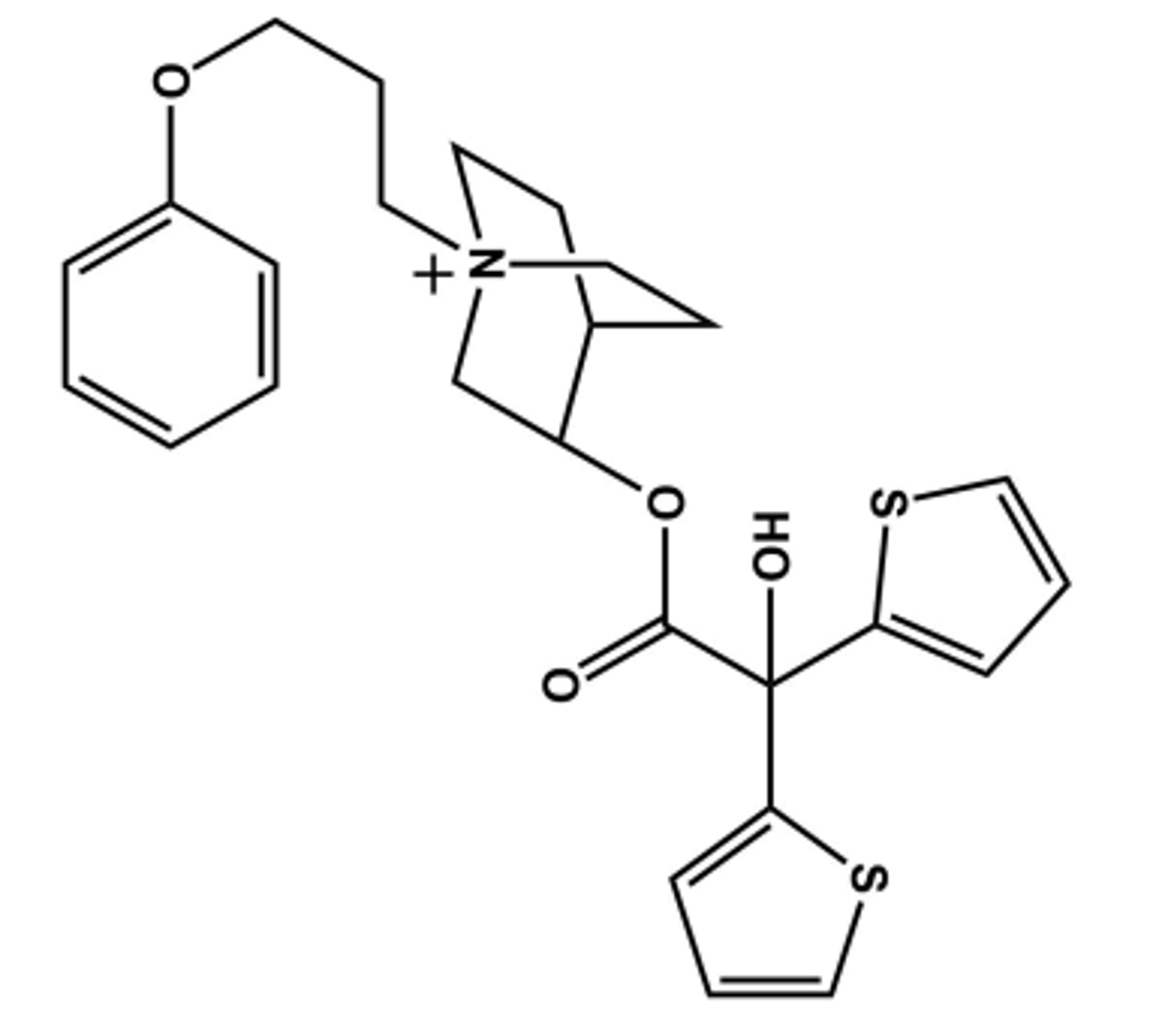
Aclidinium Bromide (Tudorza®)
- LogP = 0.45
- Long-Acting inhaled Muscarininc Antagonist (LAMA) (ca. 12 hrs)
- Use: Prevent bronchospasm in COPD
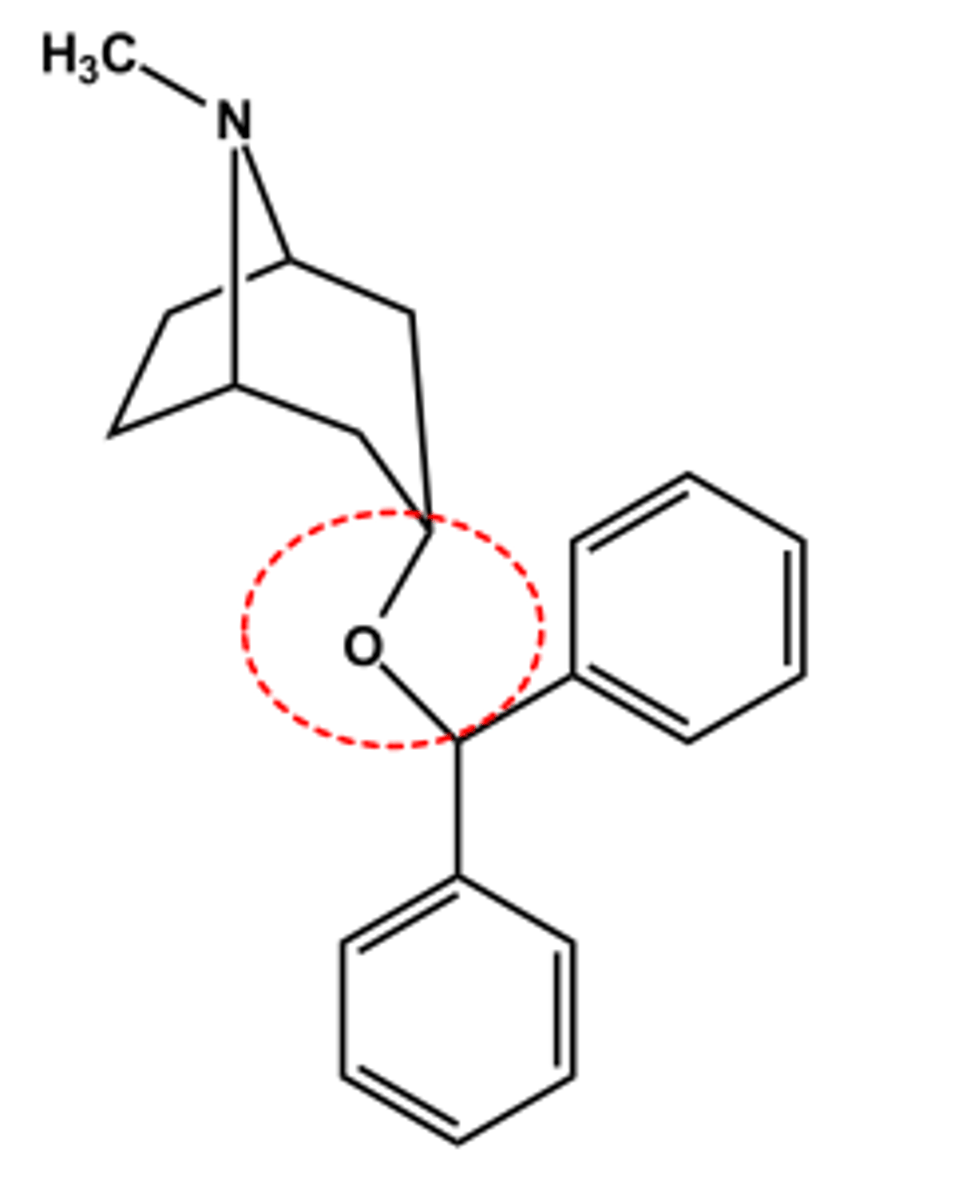
Benztropine (Cogentin®)
- Tertiary N permits systemic effects
- No ester, so longer duration LogP ~ 4.3; pKa ~10
- Use: adjunctive treatment of Parkinson's disease
Trihexyphenidyl (Artane®)
- Tertiary N permits systemic effects
- No ester, so longer duration
- LogP ca. 4.5; pKa ca. 9.9
- Use: adjunctive treatment of Parkinson's disease
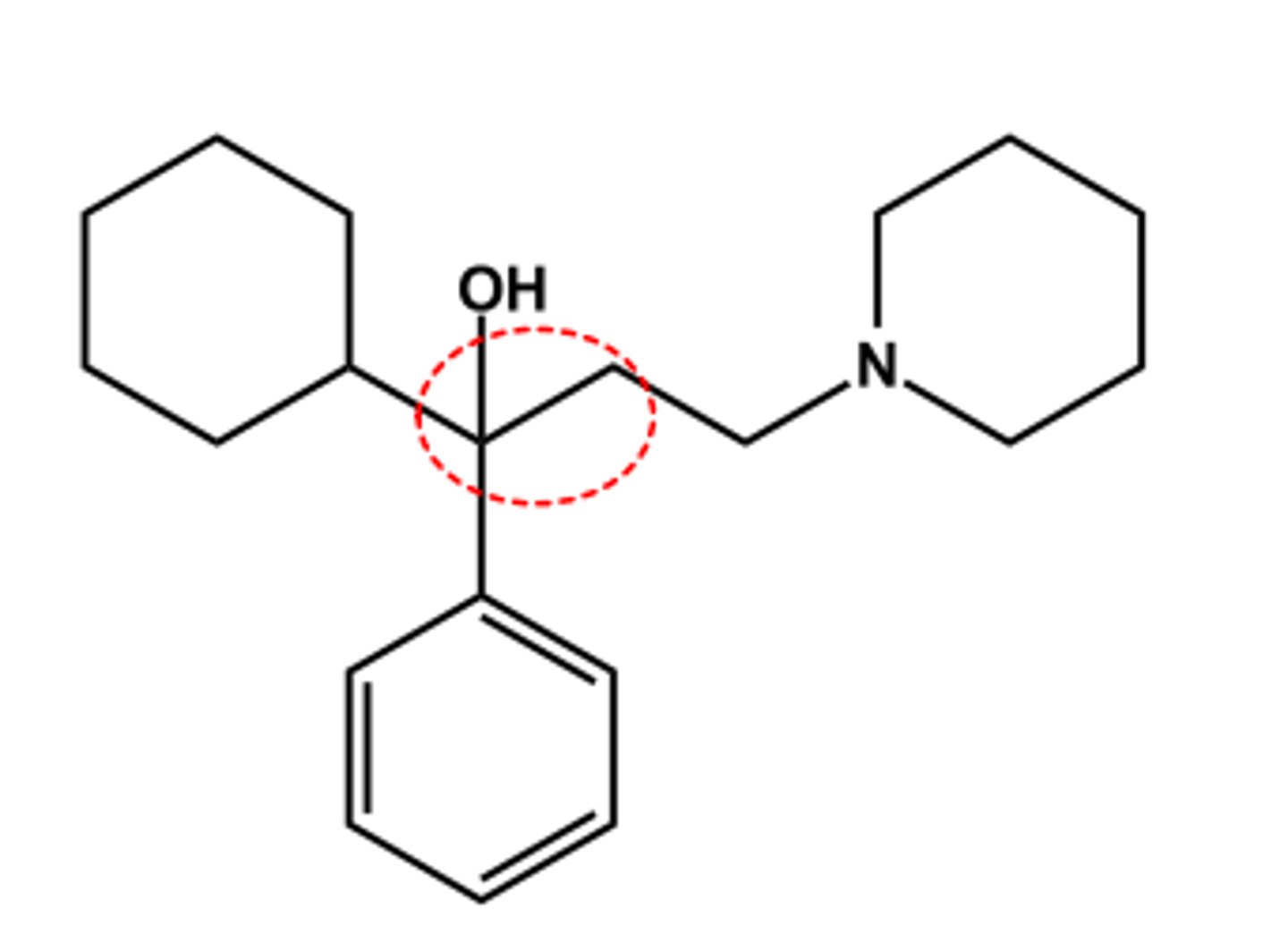
Diphenhydramine (Benadryl®)
- Tertiary N permits systemic effects
- No ester, so longer duration
- LogP ca. 4.5; pKa ca. 9.9
- Intended Use: Antihistamine and sleep aid
- Expected side effects: Antimuscarinic (anti SLUD)
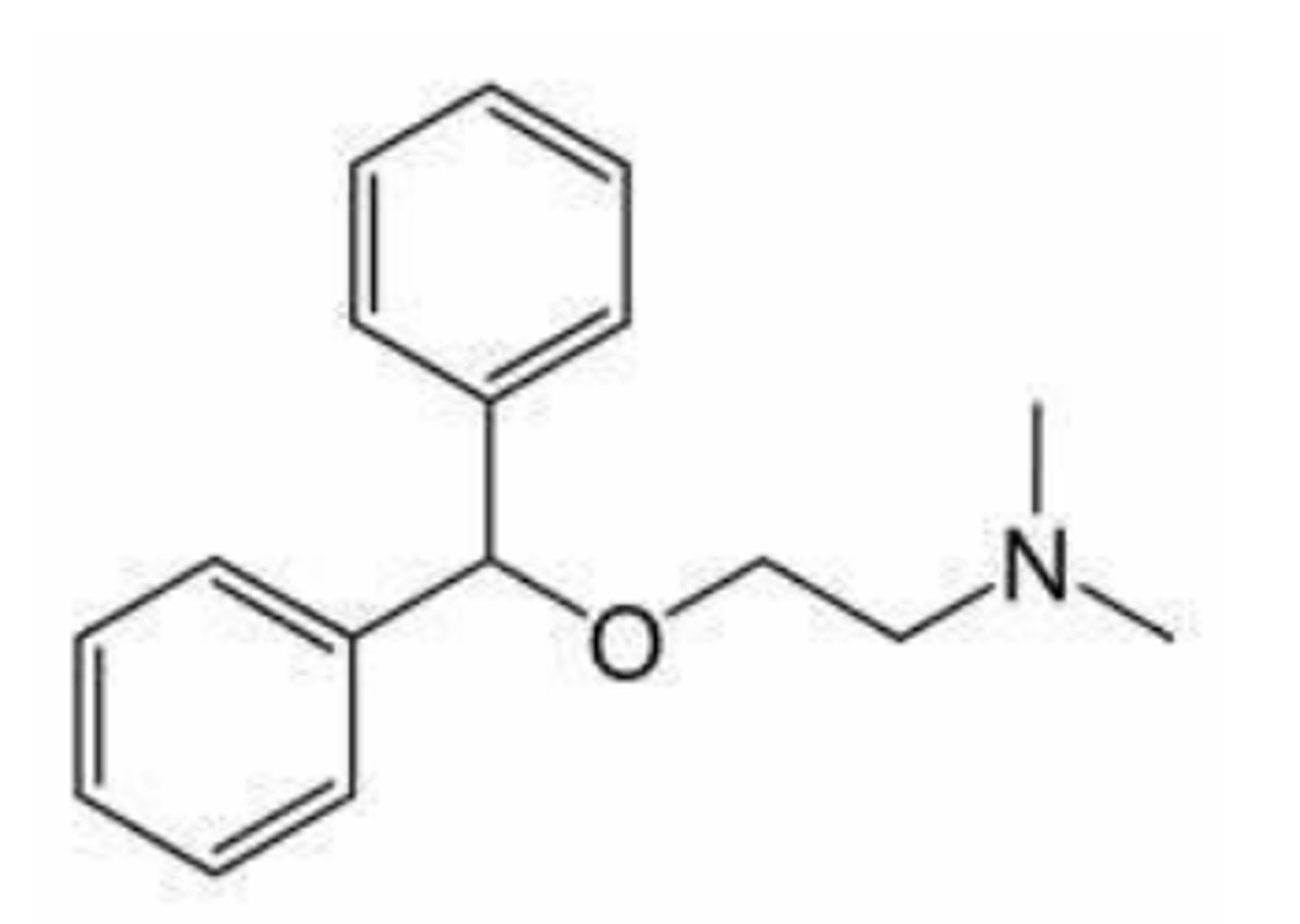
Tolterodine (Detrol®)
- LogP = 5.6; pKa = 9.9
- Nonselective
- Tertiary N causes systemic effects
- Benzylic OH metabolite equally active (CYP2D6-based)
- Half-life 2-4 hr vs. 9.6 hr in poor metabolizers
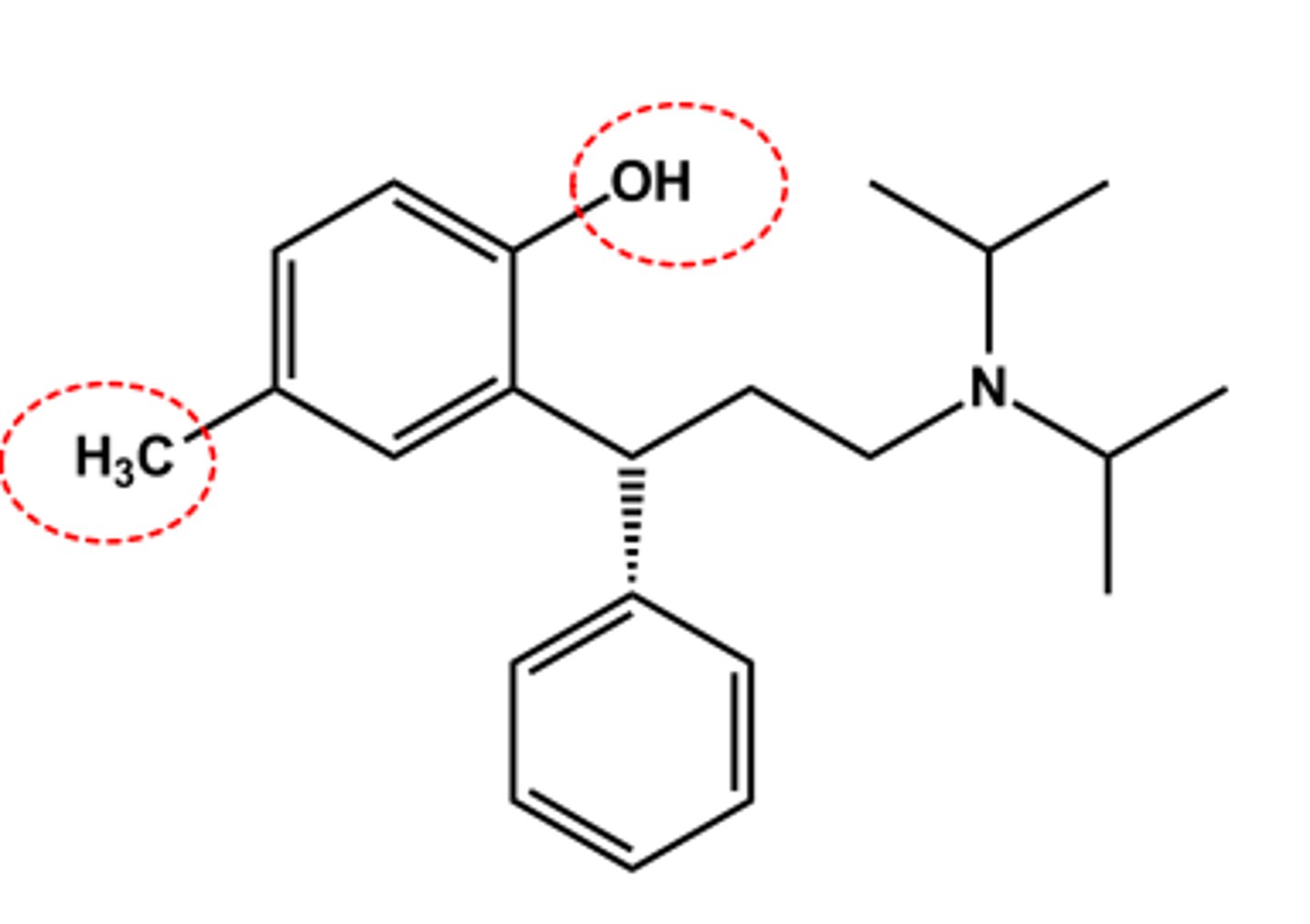
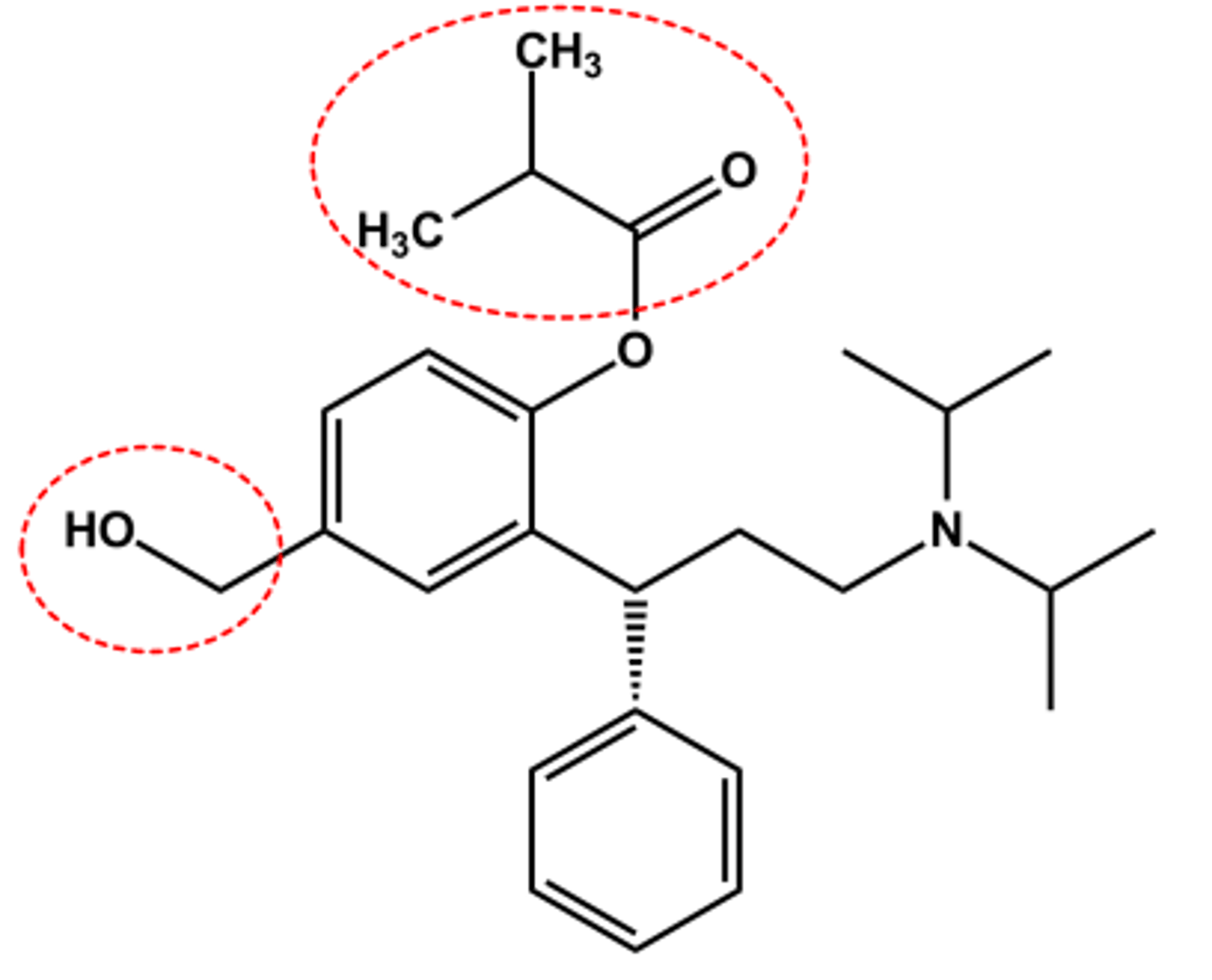
Fesoterodine (Toviaz®)
-Isobutyrate ester prodrug
- Adding CH2OH (major active metabolite of tolterodine) reduce metabolism
- LogP = 5.6; pKa = 9.3
- Half-life 7 hr
-bladder targeted
Nitrogen substitution and ester function determine ADME profile, targeted organs to some extent
Receptor selectivity produces cleaner profile
All possess the antimuscarinic pharmacophore
Indications are often based on the approval process as much as suitability for a particular use
Anti-SLUD side effects, even when targeted use
AChE Inhibitors
MOA: Indirect action by inhibition of ACh hydrolysis/breakdown
Produce nonselective response, both nicotinic & muscarinic, at many different sites of action
Therapeutically, reversible AChEIs are used to treat:
➢ Myasthenia Gravis (boost signals between nerves and muscles to improve muscle strength)
➢ Alzheimer's disease (compensate for the loss of cholinergic neurons)
➢ Treatment of antimuscarinic toxicity (such as atropine overdose)
Irreversible AChEIs
used as insecticides and chemical warfare agents
AChEI: CNS
➢ CNS-targeted drugs-treat cognitive dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease
-Adverse effects: convulsions, coma and respiratory collapse
AChEIs: Eye, respiratory tract, GI tract, urinary tract
➢ Effects of AChEIs mimic parasympathetic nervous stimulation
• Increased- Salivation, Lacrimation, Urination, Defecation etc. •
These are the primary adverse effects of all muscarinic receptor agonists, both direct and indirect
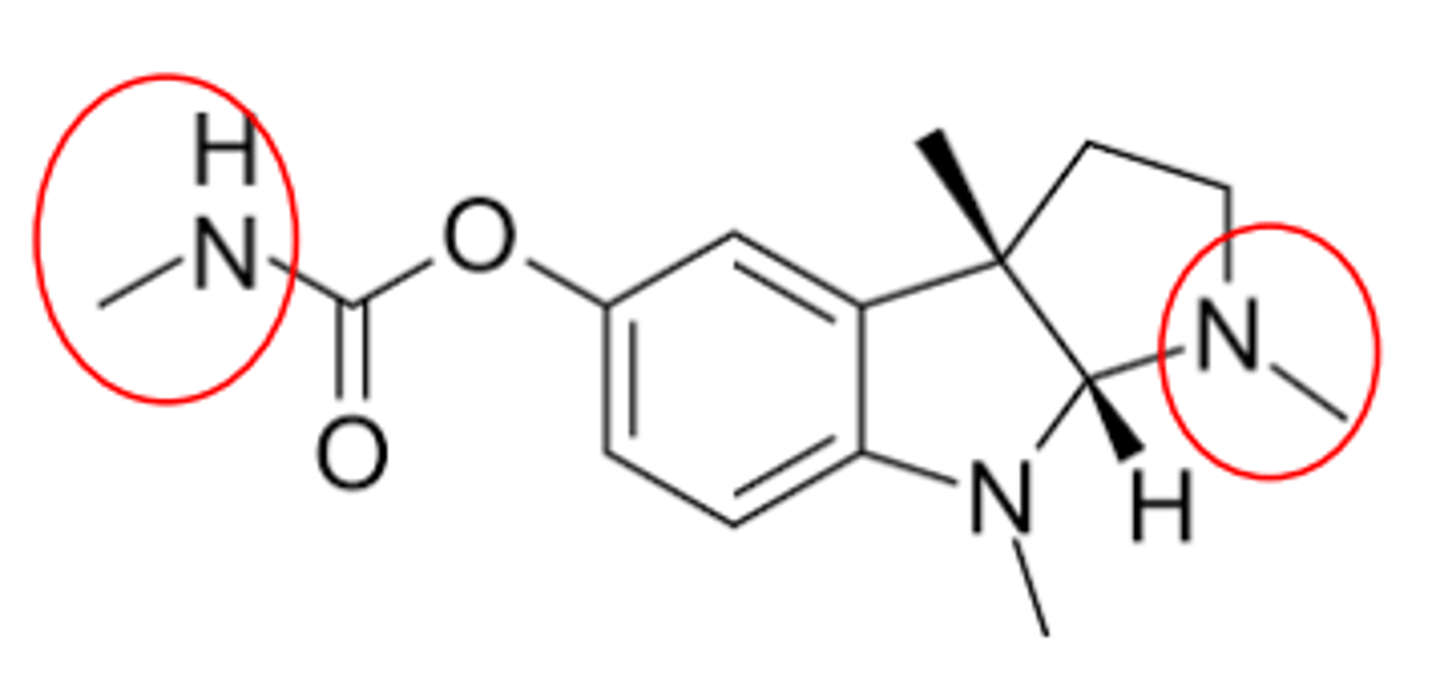
PHYSOSTIGMINE (GENERIC)
Natural product- Physostigma venenosum
Carbamate
LogP ca. 2.7, pKa ca. 8.2
Duration of action 3-4 Hrs
Shows CNS effects (why?)
Uses: Antidote for certain antimuscarinic overdoses
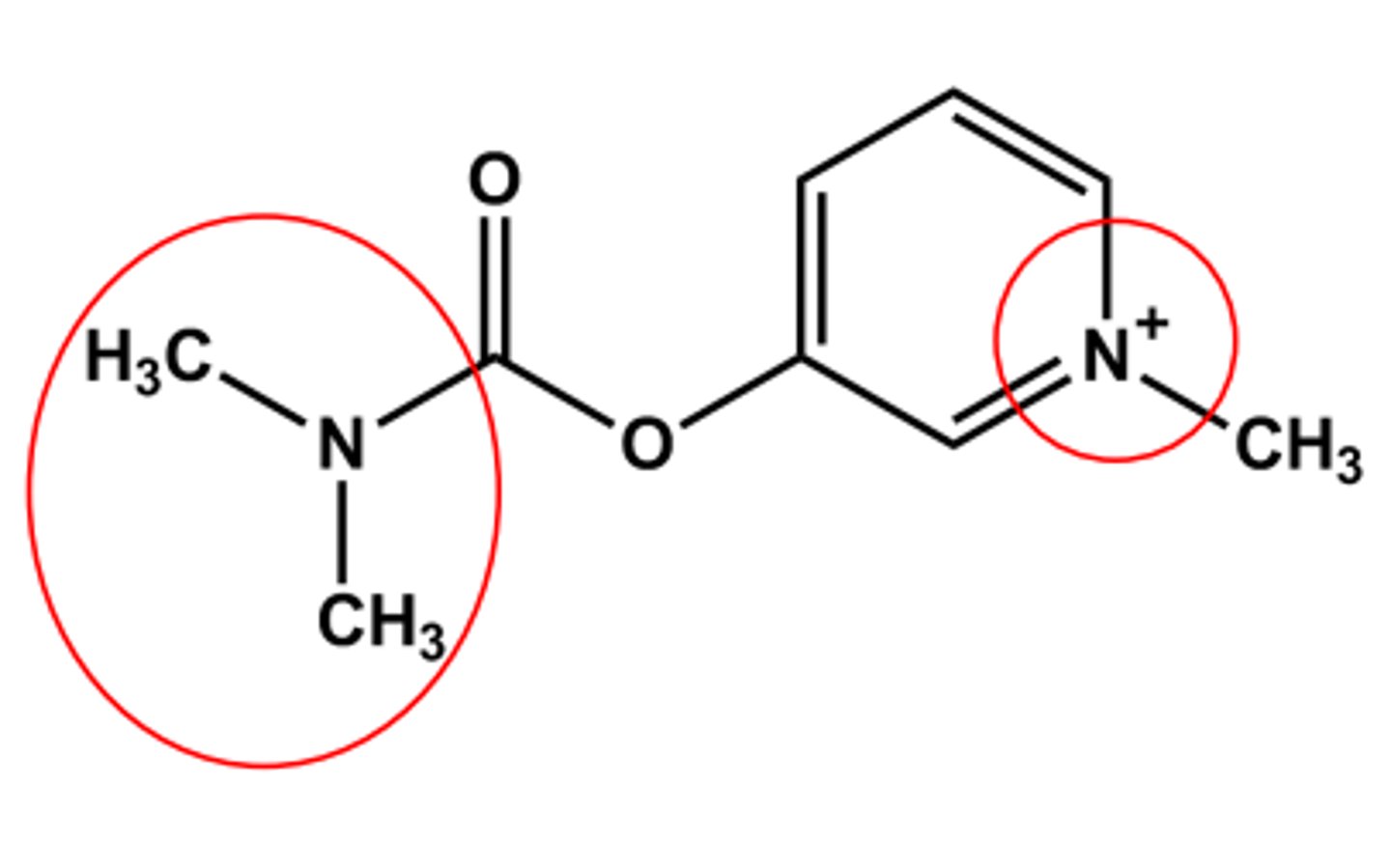
PYRIDOSTIGMINE (MESTINON®)
Bulkier carbamate
Duration of action 5-6 hours
LogP ca. -1.7
Quaternary amine
No CNS effects (why?)
Use: control of Myasthenia gravis; Antidote to some NMJ blockers
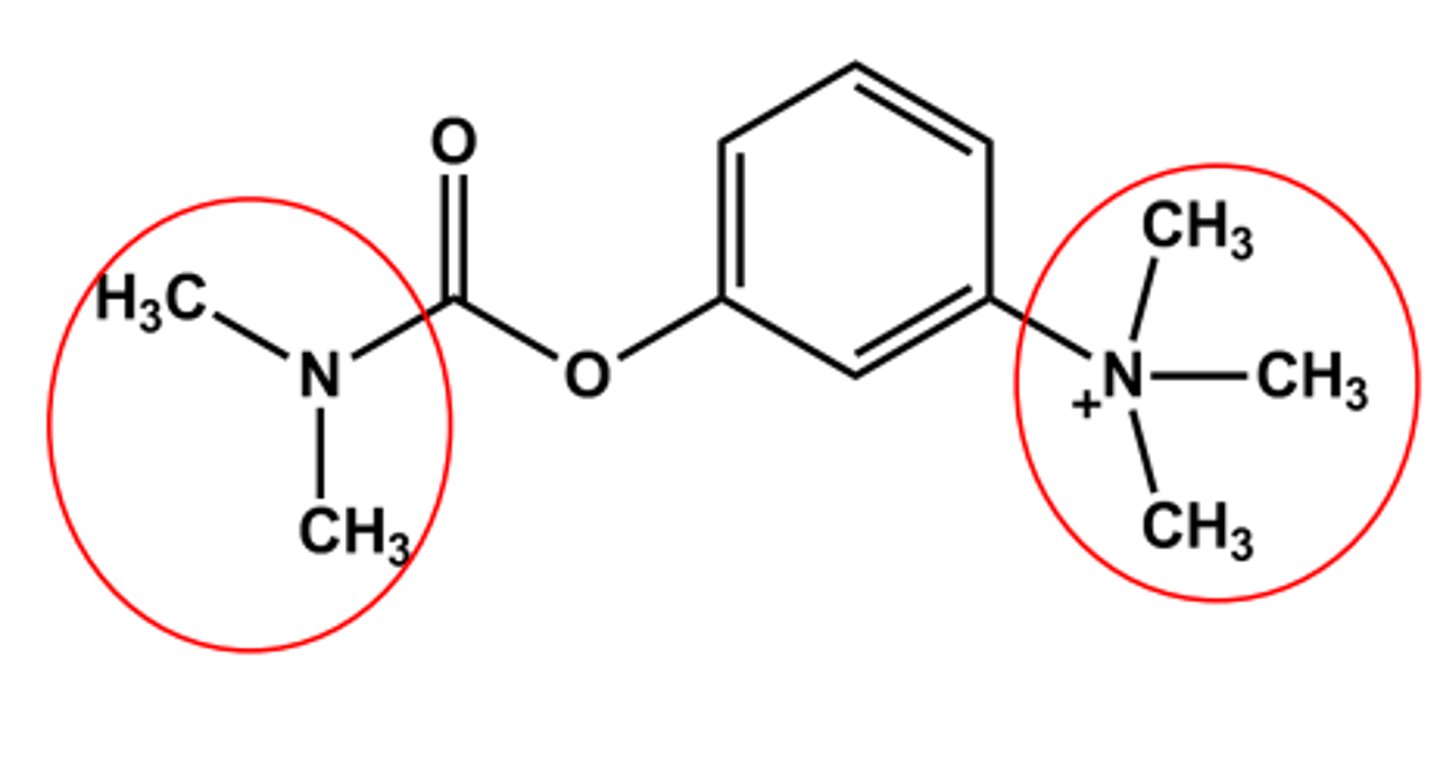
NEOSTIGMINE (PROSTIGMIN® , BLOXIVERZ®)
Bulkier carbamate
Duration of action 5-6 hours
Quaternary amine
No CNS effects (why)
Use: control of Myasthenia gravis; Antidote to some NMJ blockers
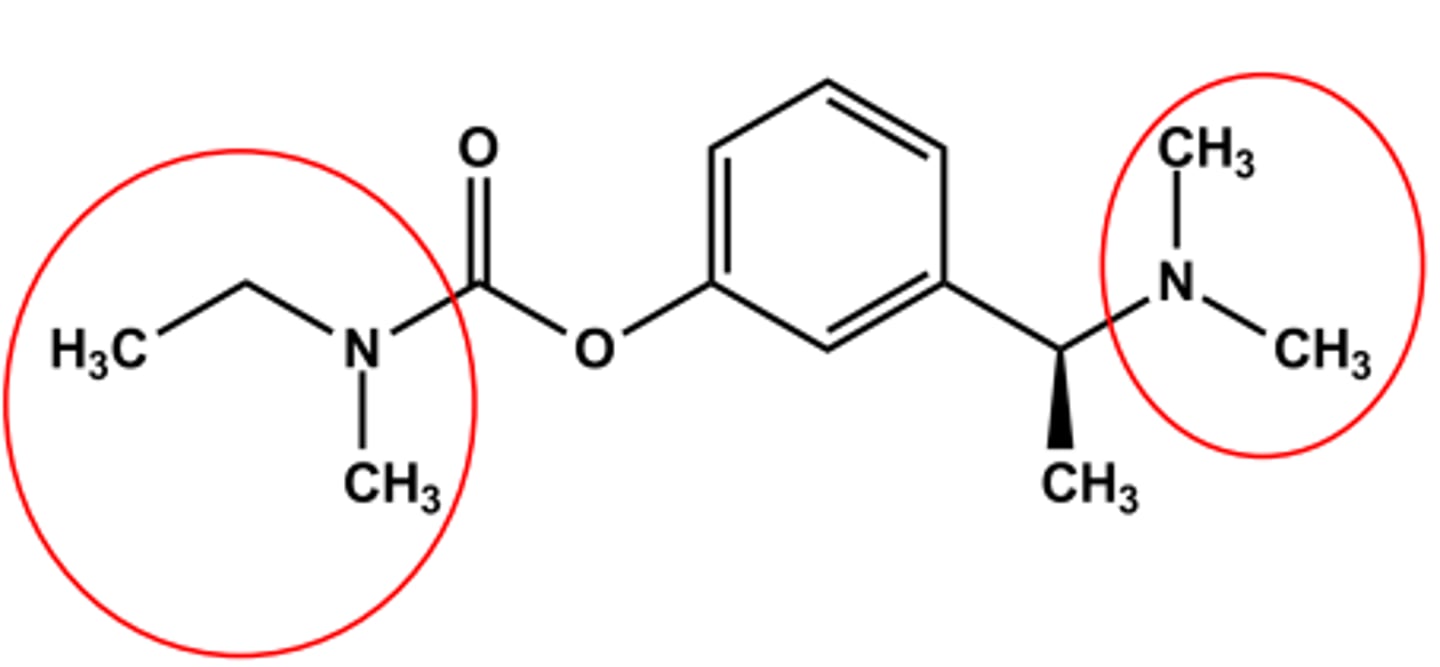
RIVASTIGMINE (EXELON®)
CNS-targeted AChEIs
Bulky carbamate
Tertiary amine
LogP ca. 2.3; pKa ca. 8.8
Use: symptomatic treatment of Alzheimer's disease
WHAT IF ACHE INHIBITION WERE IRREVERSIBLE?
-If the bond is covalent (irreversible), the only way to "reverse" the AChE inhibition is to synthesize new enzyme
➢ The effects of this AChEI will persist for days or longer
- Net effect: flood of ACh, stimulation of all cholinergic sites
-Modern use: insecticides and chemical warfare
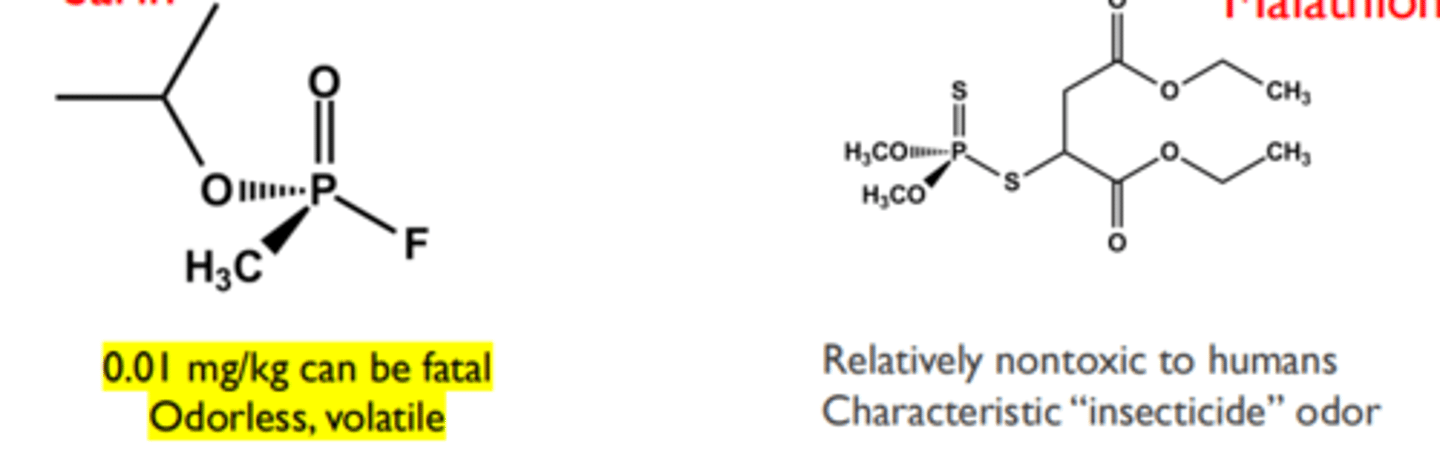
- Structurally: organophosphates and thiophosphates
Sarin and Malathion
➢ Phosphorylation can be reversed with a more potent nucleophile than water if done quickly (the phosphorus effect)
➢ The only drug to reverse inhibition is pralidoxime (next slide)
➢ Obvious military defense interest
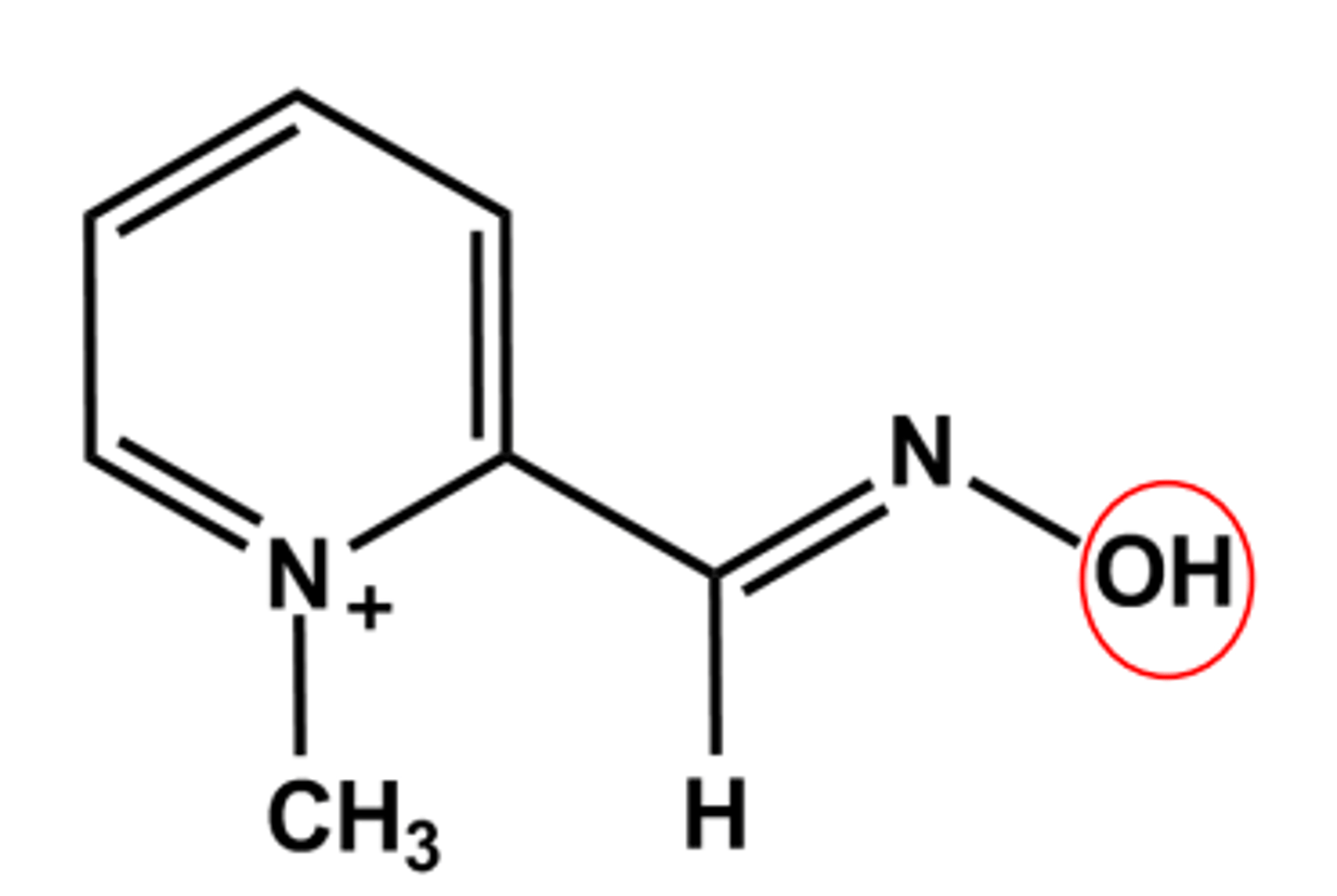
PRALIDOXIME (PROTOPAM®)
Relies on the high nucleophilicity of the oxime oxygen
Binds to the AChE active site with the oxime positioned to attack the phosphate ester.
Only works if used quickly in the first hour or two of exposure.