9. Chemistry of the Atmosphere
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
State the length of time that the proportions of different gases in the atmosphere have been much the same as they are today
For 200 million years
2
New cards
Describe the components of the atmosphere and the relative proportions
80% nitrogen
20% oxygen
Small proportions of various other gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases.
20% oxygen
Small proportions of various other gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases.
3
New cards
Explain why evidence for the early atmosphere is limited
Because of the very long time scale of 4.6 billion years
4
New cards
Describe one theory for the formation of the early atmosphere during the first billion years of the Earth's existence .
There was intense volcanic activity that released gases that formed the early atmosphere and water vapour that condensed to form the oceans
5
New cards
State which planets have similar atmospheres to Earth's very early atmosphere
It may have been like the atmosphere of Mars and Venus today
6
New cards
Describe the current scientific ideas about the componentes of the early Earth's atmosphere
It may have consisted of mainly carbon dioxide with little or no oxygen gas.
Volcanoes also produced nitrogen which gradually built up in the atmosphere.
Three may have been small proportions of methane and ammonia.
Volcanoes also produced nitrogen which gradually built up in the atmosphere.
Three may have been small proportions of methane and ammonia.
7
New cards
What reduced the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Carbon dioxide dissolved in the oceans when they formed.
Carbonates were precipitated producing sediments.
Carbon dioxide was also decreased by the formation of sedimentary rock and fossil fuels that contain carbon.
Carbonates were precipitated producing sediments.
Carbon dioxide was also decreased by the formation of sedimentary rock and fossil fuels that contain carbon.
8
New cards
Describe the role of algae and plants in changing the Earth's atmosphere from 2.7 billion years - 200 million years ago
Algae and plants produced the oxygen that is now in the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
Algae and plants decreased the percentage of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
Algae and plants decreased the percentage of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere by photosynthesis.
9
New cards
State when oxygen first appeared in the atmosphere
About 2.7 billion years ago
10
New cards
State what had to happen before animals could evolve
Oxygen levels had to gradually increase to a level that enabled animals to evolve
11
New cards
Describe the role of greenhouse gases in supporting life on Earth
Greenhouse gases maintain temperatures on Earth high enough to support life
12
New cards
List three greenhouse gases
Water vapour, carbon dioxide and methane
13
New cards
Explain how carbon dioxide and methane have increased due to human activity
Carbon dioxide has increased due to combustion of fossil fuels and deforestation.
Methane has increased due to planting rice fields and cattle farming.
Deforestation reduces photosynthesis and increases carbon dioxide.
Destruction in peat bogs releases carbon dioxide.
Methane has increased due to planting rice fields and cattle farming.
Deforestation reduces photosynthesis and increases carbon dioxide.
Destruction in peat bogs releases carbon dioxide.
14
New cards
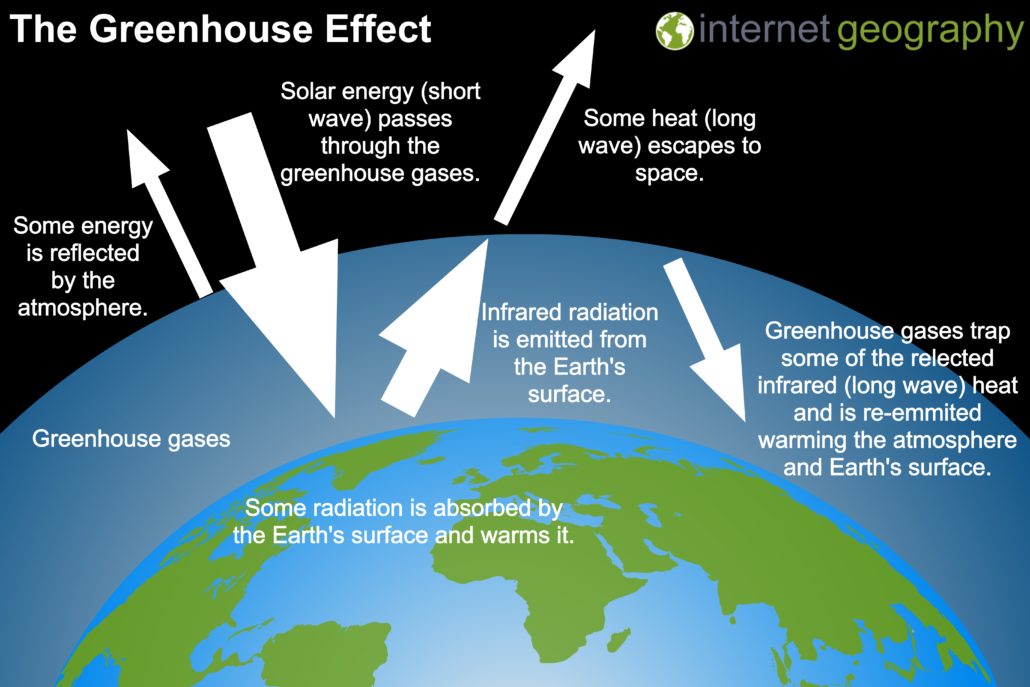
The greenhouse effect
Radiation from the sun has a short wavelength which passes through the atmosphere.
Radiation from objects on the Earth's surface emit a longer wavelength absorbed by greenhouse gases
The night time temperature on Earth is increased, allowing life to survive at night
Radiation from objects on the Earth's surface emit a longer wavelength absorbed by greenhouse gases
The night time temperature on Earth is increased, allowing life to survive at night
15
New cards
Explain why scientists believe that human activities will cause the temperature of the Earth's atmosphere to increase at the surface
They have peer reviewed evidence
16
New cards
Describe what causes global climate change
An increase in average global temperature is a major cause of climate change
17
New cards
Describe five effects of global climate change
Sea levels rising
Extreme weather events
Changes in the amount and time of rainfall
Changes to ecosystems and habitats
Polar ice caps melting
Extreme weather events
Changes in the amount and time of rainfall
Changes to ecosystems and habitats
Polar ice caps melting
18
New cards
Define carbon footprint
The carbon footprint is the total amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases emitted over the full life cycle of a product, service or event.
19
New cards
Describe how the carbon footprint can be reduced
The carbon footprint can be reduced by reducing emissions of carbon dioxide and methane. Going vegan, other transport alternatives to driving
20
New cards
State a major source of atmospheric plants
The combustion of fuels is a major source of atmospheric pollutants
21
New cards
State what most fuels contain
Carbon, hydrogen and may also contain sulphur
22
New cards
State what gases released into the atmosphere when a fuel is burned
Carbon dioxide, water vapour, carbon monoxide, sulphur dioxide, oxides of nitrogen
23
New cards
Describe how carbon monoxide is produced by burning fuels
Incomplete combustion of fuels
24
New cards
Describe how soot (carbon particles are produced by burning fuels
Incomplete combustion of fuels
25
New cards
Describe how soot (carbon particles are produced by burning fuels
Incomplete combustion of fuels especially in Diesel engines
26
New cards
Describe how sulphur dioxide is produced by burning fuels
Sulphur impurities in the fuel react with oxygen from the air
27
New cards
Describe how oxides of nitrogen are produced by burning fuels
Nitrogen in the air is heated near an engine and it reacts with ocygen
28
New cards
Describe carbon monoxide and explain why it is not easily detected
Carbon dioxide is a toxic gas. It is colourless and odourless and so is not easily detected
29
New cards
Describe what the effects of sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen cause
Sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen cause respiratory problems in humans and cause acid rain
30
New cards
Describe what particulates (soot and unburnt hydrocarbons) cause
Particulates cause global dimming, respiratory problems and have the potential to cause cancer.
31
New cards
Describe how sulphur dioxide emissions can be reduced
Using reduced sulphur fuels
Dissolving some of the sulphur dioxide in solutions before it's released into the atmosphere.
Dissolving some of the sulphur dioxide in solutions before it's released into the atmosphere.