12.3 Stems
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
What functions do plant stems fulfill the plant?
Stems are a place where water or carbohydrates can be stored, stems also raise and support the leaves and reproductive organs raising the leaves maximize their exposure to sunlight, so they are able to photosynthesize better. It can also help protect the plant from injury and herbivores.
2
New cards
What is cork cambium and what does it do?
Cork cambium is a meristematic layer in a woody plant that produces cork. It helps prevent water loss from the stem.
3
New cards
Do all plants have cork cambium?
No not all plants have cork cambium. It’s not found in non-woody plants such as grass and herbs
4
New cards
Do mature cells of xylem tissue have nuclei? Explain.
**Xylem cells that reach maturity become hollow and dead. In this case, it no longer contains cell organelles, such as nucleus**.
5
New cards
Do mature cells of phloem tissue in angiosperms have nuclei?
No, mature cells of phloem tissue in angiosperms do not have nuclei. They lose their nuclei as they mature, which allows for more space for the transportation of nutrients and sugars.
6
New cards
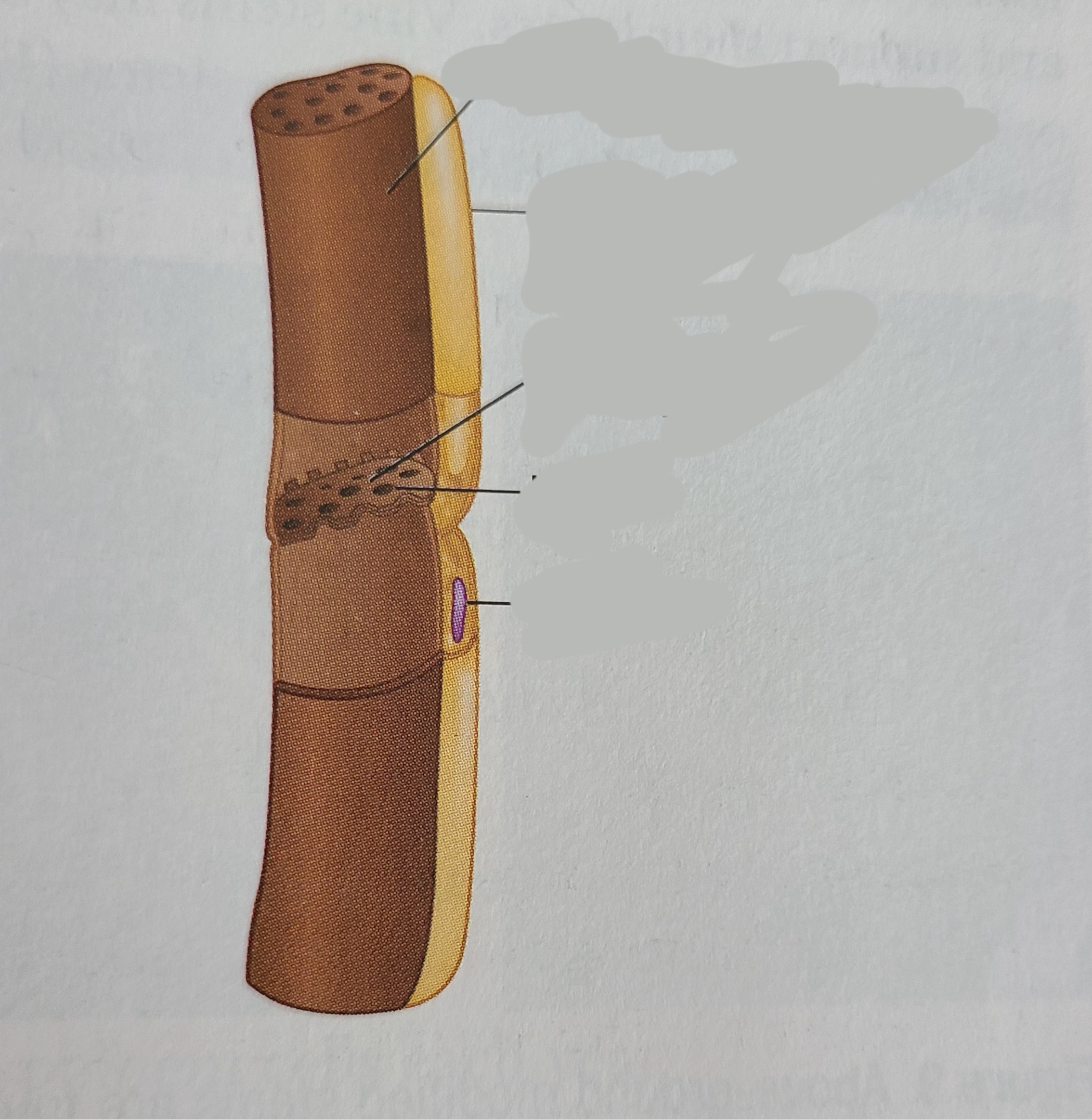
label the phloem cell
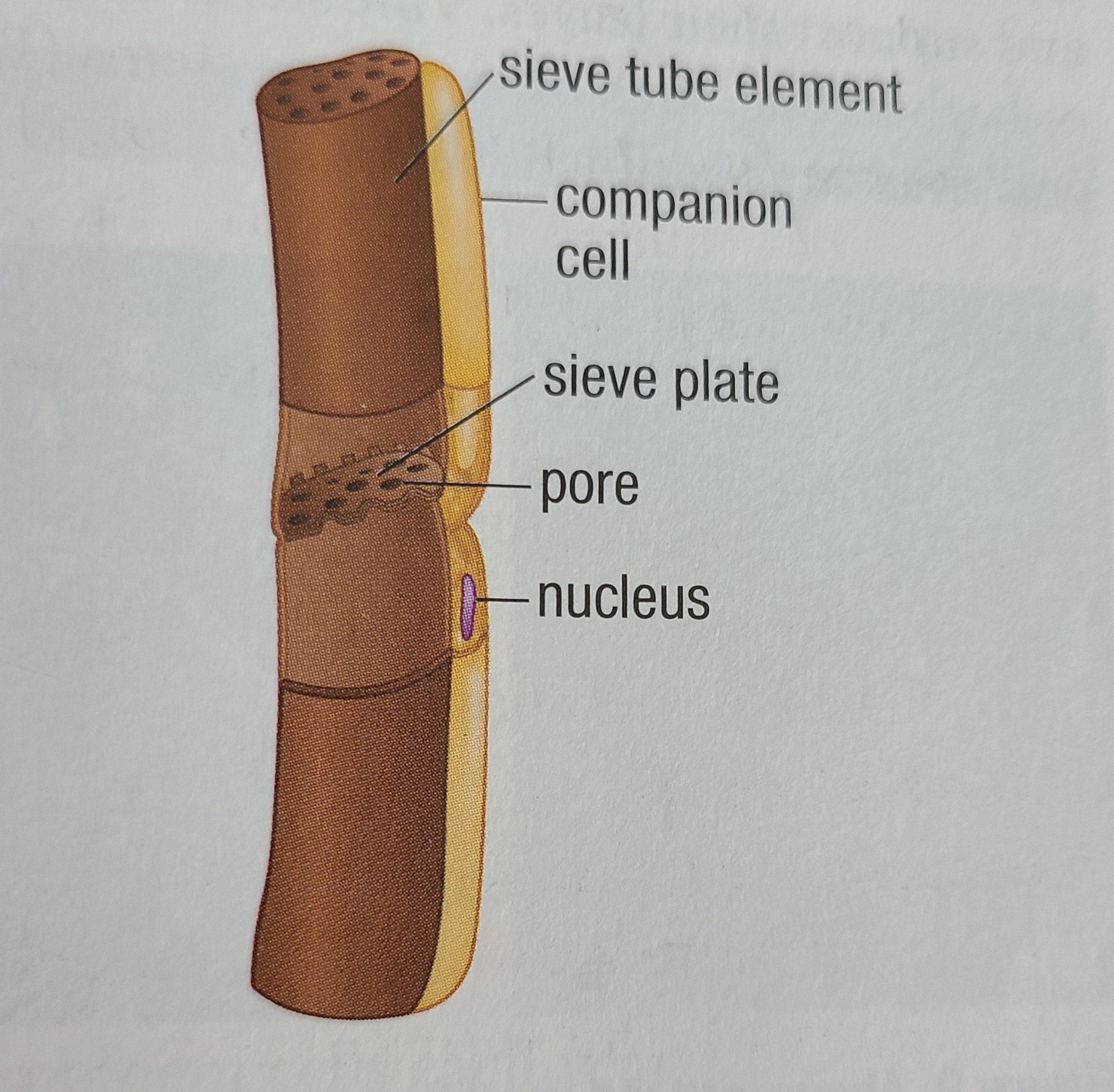
7
New cards
gymnosperms
xylem tissue cell types: tracheids phloem tissue cell types: sieve cells
8
New cards
angiosperms
xylem tissue cell type: **tracheids vessel elements** Phloem tissue cell types: **sieve tube elements companion cells**
9
New cards
Which plant group has a more diverse cellular makeup of xylem and phloem tissue?
Angiosperms have a more diverse cellular makeup of xylem and phloem tissue compared to other plant groups, such as gymnosperms and ferns. This diversity allows angiosperms to be more adaptable to different environments and to have a wider range of functions.
10
New cards
What are the xylem tissue cell types for each plant group?
In gymnosperms, the xylem tissue consists mainly of tracheids. In ferns and other seedless vascular plants, the xylem tissue consists of tracheids and sometimes also of sclerenchyma fibers.
11
New cards
Why can’t sieve tube elements stand alone as the main cell type for phloem tissue?
Sieve tube elements cannot stand alone as the main cell type for phloem tissue because they lack important organelles, such as nuclei and ribosomes, which are necessary for protein synthesis and other cellular functions. They also require the support of companion cells, which provide the necessary metabolic support for sieve tube elements to function properly. Without companion cells, sieve tube elements would not be able to transport nutrients and sugars effectively throughout the plant.
12
New cards
How is the location of vascular bundles in monocot stems different from the location of vascular bundles in eudicot stems.
The location of vascular bundles in monocot stems is scattered throughout the stem, whereas in eudicot stems, the vascular bundles are arranged in a ring around the pith. This difference in arrangement is due to the way in which the stem develops during embryogenesis.
13
New cards
How are vascular cambium and cork cambium similar? How are they different?
Vascular cambium and cork cambium are both lateral meristems that increase the girth of the stem or root. However, vascular cambium produces secondary xylem and phloem, while cork cambium produces cork cells.
14
New cards
Vascular cambium grows rapidly and produces large xylem cells with hin walls in the
spring
15
New cards
fewer xylem cells are produced in the_________and they thick celled walls
summer
16
New cards
Aspirin (used to relieve pain and reduce inflammation)
bark of the willow tree
17
New cards
Paclitaxel (used to treat cancer)
bark of the pacific yew tree
18
New cards
sieve cell
are plant cells that transport nutrients and sugars throughout the plant. They are elongated cells with sieve plates that allow for fluid movement between cells.
19
New cards
Herbaceous
are soft-stemmed plants that are not woody or hard. They die back to the ground at the end of the growing season and are often grown for their flowers.
20
New cards
Perforation plates
are structures in plant cells that allow water and nutrients to move freely between adjacent cells. They are found in xylem cells and are important for the efficient transport of water and nutrients throughout the plant.
21
New cards
sieve plate
allows the movement of nutrients and sugars between adjacent cells. It is found in phloem tissue and is important for the efficient transport of nutrients throughout the plant.
22
New cards
Sieve tube elements
are cells in plant phloem tissue that transport nutrients and sugars throughout the plant. They are long, thin cells without a nucleus and other organelles, which allows for efficient transport. They are usually accompanied by companion cells.
23
New cards
Vessel elements
in plant xylem tissue that transport water and minerals throughout the plant. They are long, tube-like cells that lack a nucleus and other organelles, which allows for efficient transport. They are usually stacked on top of each other to form a continuous column.