UAMS HEMATOLOGY EXAM 6
1/250
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
251 Terms
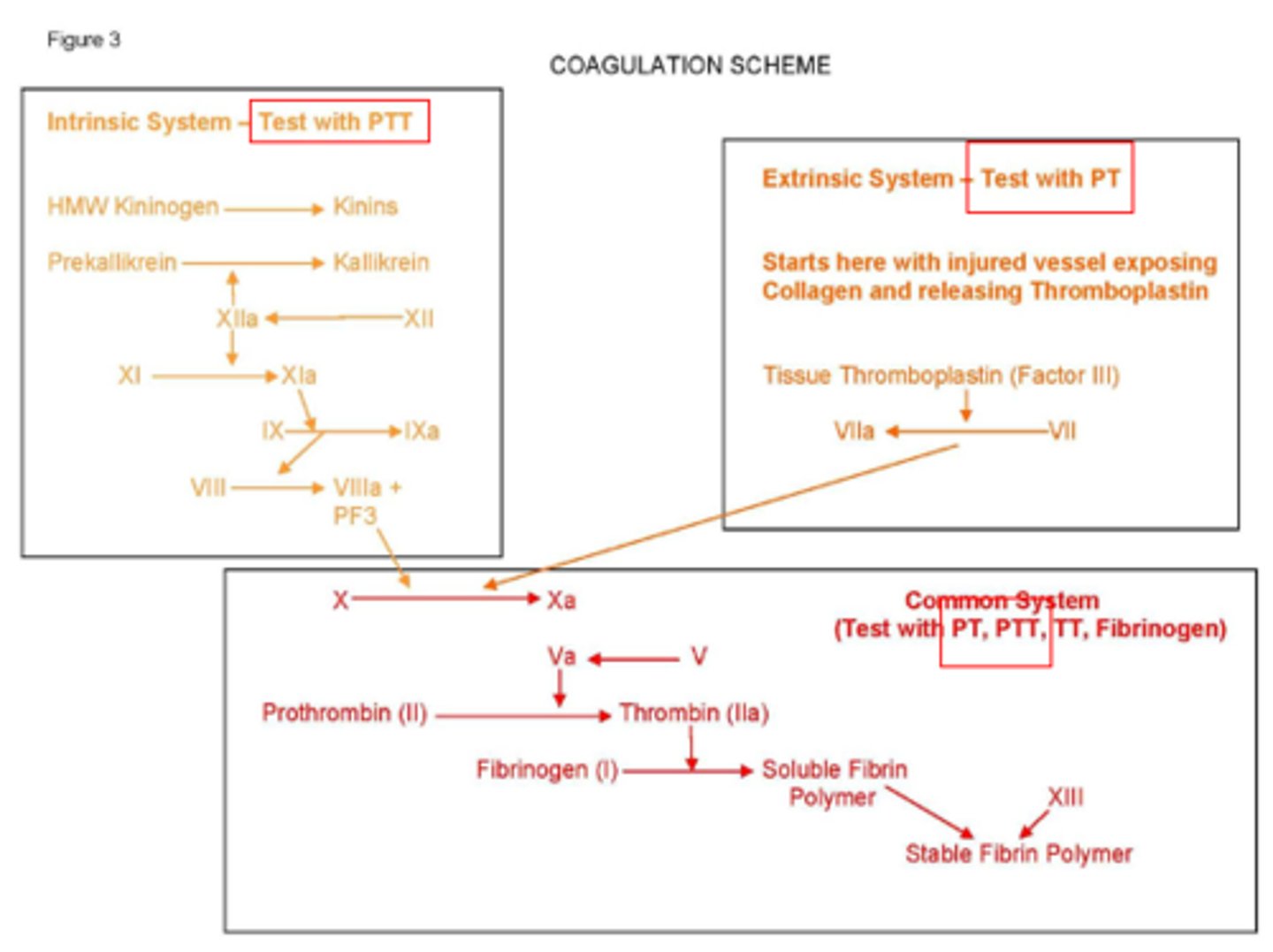
Write out the coagulation cascade.
Define hemostasis.
Process of keeping blood in the fluid state unless clotting occurs due to vascular injury
What does hemostasis involve?
Vessels, platelets, plasma coagulation factors and fibrinolysis
What is primary hemostasis?
The platelet plug formed on damaged vessels
What is secondary hemostasis?
Fibrin formation from plasma factors
True or false: The vascular system will normally allow red cells through the endothelial layer.
False: Normally will NOT allow red cells through the endothelial layer
What is the role of the vascular system?
- Release of exposed substances: VWF and collagen
- Vasoconstriction or stoppage of blood flow
What are symptoms of a vascular disorder?
Bruising, petechiae, mucous membrane bleeding
Name an inherited vascular disorder.
Hereditary telangiectasia
Drugs (steroids or estrogen) and age can cause what type of disorders?
Acquired disorders
Where is a megakaryocyte developed?
Bone marrow
What influences the number and size of megakaryocytes produced?
Thrombopoietin influences size of megakaryocytes with CSF-Meg
Define endomitosis. What is it responsible for?
Doubling of DNA without cell division; reason for megakaryocyte's large size
How do platelets enter into the peripheral blood?
Platelets get into the blood when the filament extends through the endothelial cells and fragments into cells.
How many platelets are within the blood? Where are the rest of them stored?
2/3 of platelets circulate in the blood; the rest are stored in the spleen
What is the lifespan of a platelet?
8-12 days
What does the platelet plasma membrane (peripheral zone) contain?
Glycocalyx that is a receptor for various glycoproteins and phospholipids
What is involved in platelet adhesion and binds vWF?
Glycoprotein Ib/IV/V
What is involved within platelet aggregation and binds to fibrinogen?
Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
__________ are necessary for the activation of the intrinsic system and keeps the reactions localized.
Phospholipids
What does the platelet cytoskeleton (structural zone or sol-gel zone) contain?
Cytoskeletal and microtubules
Name what is contained within dense granules.
ADP, Ca++, and serotonin
Which granules migrate to plasma membrane and release contents directly into plasma upon activation?
Dense granules
Name what is contained within alpha granules.
Coagulation factors I, V, and VWF
When activated, the granules fuse the SCCS, and their contents are released.
Alpha granules
What is the function of platelets?
Aids in healing endothelial cells through growth factors that are produced by megakaryocyte
What is a reversible characteristic in which platelets roll and cling to non-platelet surfaces?
Adhesion
Exposed collagen reacts with vWF that activates __________ on the platelet surface.
Glycoprotein Ib
Shape change whereby the platelet goes from discoid to spherical with pseudopods occurs in what process? Also, what causes it?
Adhesion; caused by ADP from endothelial cells
Platelet to platelet interactions are called?
Aggregation
True or false: Aggregation is irreversible.
True
Initial interaction fibrinogen binds to __________ on the platelet surface, forming bridges between the platelets. Also, name what process this occurs in.
Glycoprotein IIb
Aggregation
In platelet aggregation tests, what causes arachidonic acid to form thromboxane A2?
ADP
__________ promotes release of Ca, which promotes secondary aggregation
Thrombaxane A2
What is the process of secretion concerning platelets?
Thromboxane activates contractile waves causing release or secretion of granules
PF3 (platelet factor 3), a phospholipid, activates a portion of which pathway?
Intrinsic pathway
What is needed for secondary aggregation that solidifies the platelet plug?
ADP
What are the 3 platelet tests?
1. Count
2. Bleeding time
3. Aggregation studies
What test detects both primary and secondary waves?
Aggregation studies
Is platelet rich or poor plasma required for platelet aggregation studies?
Platelet rich plasma
What type of plasma is turbid?
Platelet rich
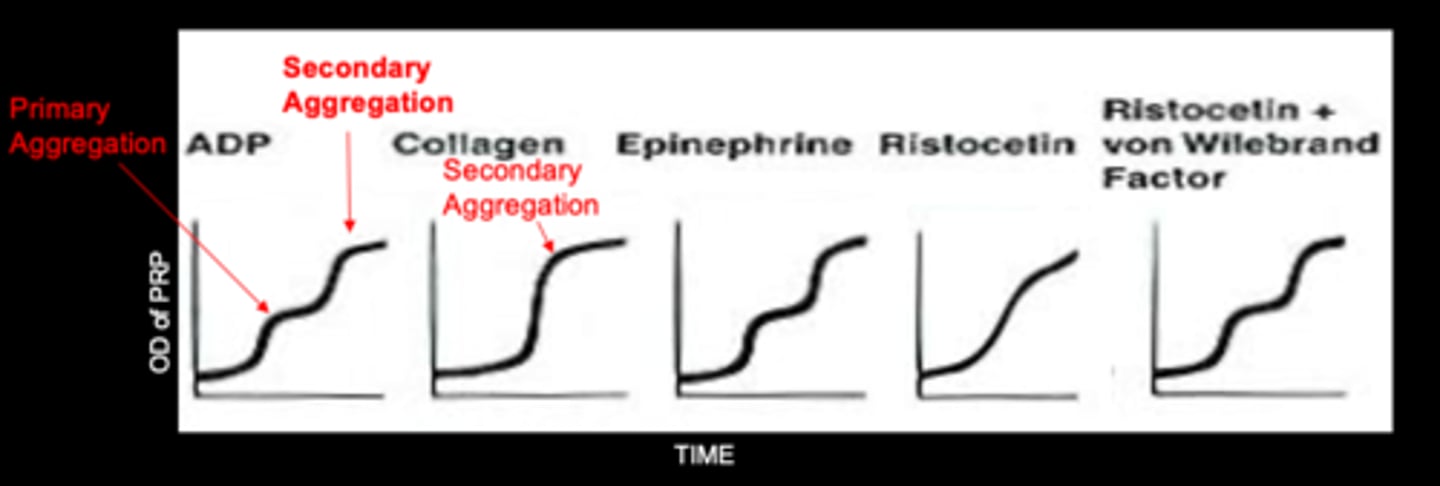
As platelet aggregation occurs, the amount of light transmitted through the sample is measured. As platelets aggregate, the turbidity _________, allowing for what to occur?
Decreases; allowing for increased light transmittance
What is plotted for aggregation patterns of primary and secondary aggregation?
The amount of light transmitted is plotted against time
What measures vascular integrity as well as platelets?
Bleeding time
What is the most common bleeding disorder due to?
Decreased platelet count is most common bleeding disorder
Know the normal platelet aggregation pattern.
Know the platelet aggregation results.
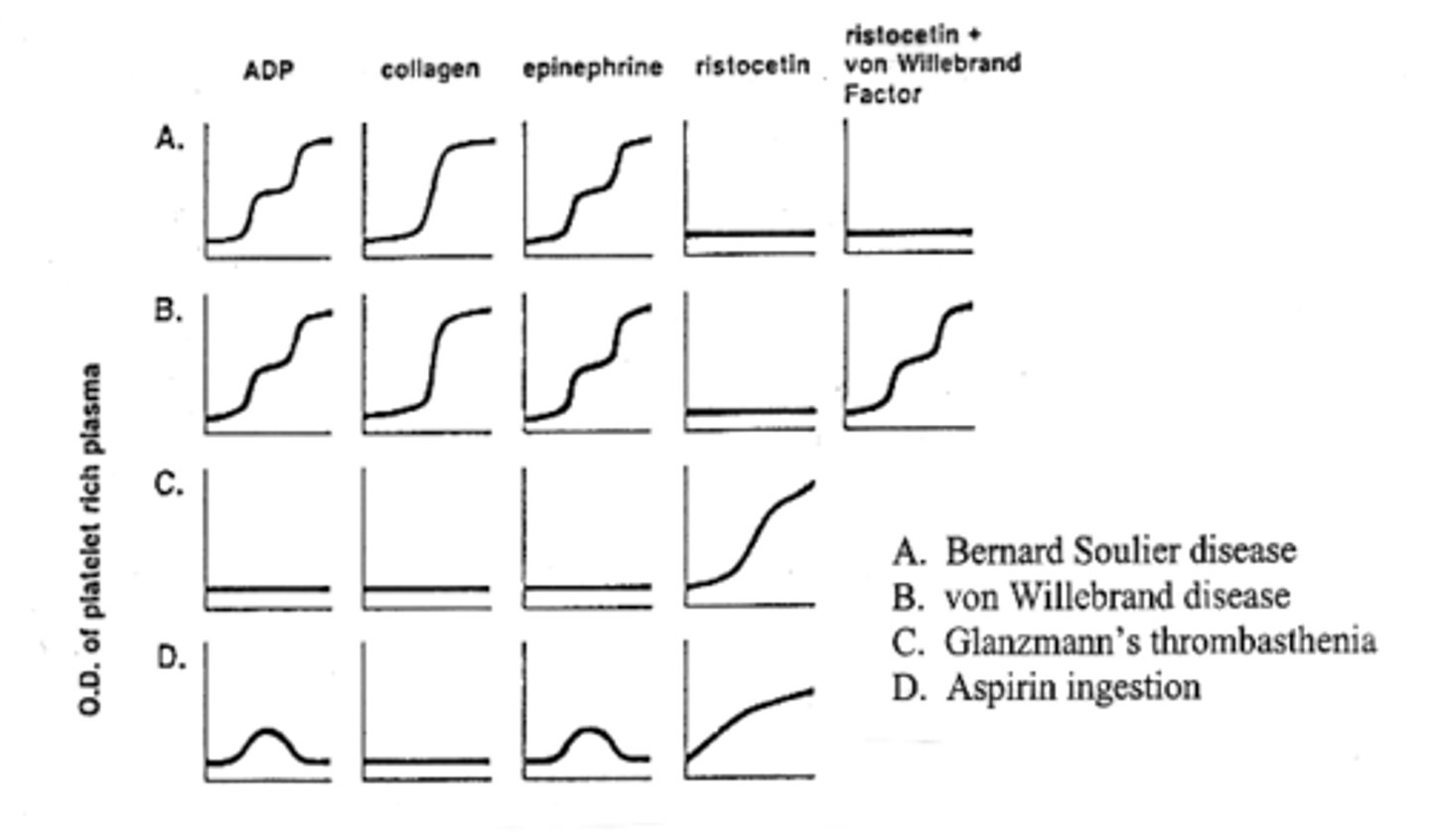
What are the 3 inherited diseases with abnormal bleeding time and platelet aggregation?
- Bernard-Soulier
- Von Willebrand's
- Galnzmann's Thrombasthenia
What is caused as a result of defective GPIb, the binding site for vWF?
Bernard Soulier disease
What has low or absent VIII:vWF and increased bleeding time with defective adhesion (qualitative disorder)?
Von Willebrand's
What is caused as a result of defective platelet membrane GP IIb which causes the inability to bind fibrinogen?
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia
True or false: Acquired abnormal platelet counts are always low.
False; can be low or high
What are acquired low platelet counts due to?
- May be due to increased destruction
- Decreased production in bone marrow
- Leukemia, aplastic anemia, megaloblastic leukemia
What are acquired high platelet (thrombocytosis) counts due to?
- May be secondary following splenectomy
- Thrombocythemia: primary malignancy
What has immune autoantibody to platelets and causes vessel occlusion with very low platelet count?
ITP
What tests are abnormal for ITP?
PAIgG is positive
(CBC and other coag tests are normal)
What are the treatment options for ITP?
Administer steroids and perform splenectomy
For DIC, indicate the following test results:
- Blood smear findings
- PT, PTT, TT, FSP
- Fibrinogen, Platelet count
- D-Dimer
- Schistocytes on blood smear
- ↑ PT, PTT, TT, FSP
- ↓ Fibrinogen, Platelet count
- + D-Dimer
Indicate what the following results are consistent with.
- Thrombocytopenia with RBC fragments
- Found predominantly in women and children
- Neurologic symptoms
TTP
What is a possibility for the etiology of TTP?
Formation of Ultra Large vWF
What normally cleaves ULVWF into smaller fragments?
ADAMTS-13
In the absence of ADAMTS-13, ULVWF bind to what? What does this cause the formation of?
GP Ib and GP IIa/IIIb
Formation of hyaline thrombi
What are neurological symptoms and renal disease of TTP caused by?
Caused by micro thrombi of platelets
How should TTP be treated?
Treat with plasma exchange
Coag tests are normal except for platelet count and shistocytes are found on peripheral blood smear in which disease?
TTP
What is similar to TTP but only found in children following an infection like Salmonella or E coli?
HUS
How does HUS manifest in the body?
Toxins enter bloodstream, attach to renal endothelial cells, which become damaged...
- Release ULVWF multimers
- Hyaline thrombi in renal vaculature
How many plasma proteins are there?
12... I-XIII (no VI)
Where are most of the coagulation factors produced?
Most are produced in the liver
Which coagulation factors are not produced by the liver?
Exception is III, Ca++, VIII:vWF
Name the vitamin K dependent factors.
II, VII, IX, X
What factors are absorbed by BaSo4 and impaired by coumadin?
Vitamin K dependent factors
Name the factors in the consumable group.
I, II, V, VIII, XIII
Which factors are absent in serum?
Consumable group
Name the factors in the contact group.
XII, XI, prekallikrein, HMWK
Which factors are labile?
Factors V and VIII
The coagulation reaction is a cascade that begins with the activation of XII to XIIa by contact with __________ and __________.
Phospholipid and calcium
What helps to activate the intrinsic pathway?
Platelet factor 3
Each factor acts as a __________ until activation. It then acts as an __________ after activation.
substrate
enzyme
What factors does the intrinsic pathway include?
XII, XI, IX, VIII, X, V, II, I
What is the intrinsic pathway activated by?
Activated by collagen and PF3
PTT is used to detect which pathway?
Intrinsic pathway
The extrinsic pathway includes which factors?
VII, V, X, II, I
What is the extrinsic pathway activated by?
Activated by tissue thromboplastin
PT is used to detect which pathway?
Extrinsic
Name the common factors.
I, II, V, X
What cleaves peptide A and B from fibrinogen to form fibrin?
Proteolytic thrombin
Fibrin monomers polymerize through hydrogen bonding to form a clot. This clot is stabilized by which factor?
Factor XIII
What must be added to the platelet plug to form a clot?
Fibrin
Barium sulfate absorbs which factors?
II, VII, IX, X
At every step of coagulation, there must be what?
A balance to prevent too much clotting
What must be present in order for heparin to work?
ATIII
What are the two most common coagulation inhibitors?
Protein C and S
What binds to thrombomodulin, activating the Protein C pathway?
Thrombin
When the protein C pathway is activated, what happens?
Stops the action of V and VIII
Deficiencies in inhibitors will cause what issue?
Thrombosis
Define fibrinolysis.
Enzyme dissolution of fibrin clot after healing
In fibrinolysis, __________ is converted to __________ by activators such as __________ and __________.
In fibrinolysis, plasminogen is converted to plasmin by activators such as TPA and streptokinase.
What is incorporated into the clot in fibrinolysis?
Plasminogen
What attacks fibrinogen or fibrin and dissolves the clot?
Plasmin