Chapter 1: How People Use Computers
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
What does IoT stand for?
Internet of Things
Where do you find computers?
Game Systems
Tablets
Digital Cameras
Entertainment Hardware
Clocks
Motorcycles
Cars
Refrigerators / Washing Machine
Cash Register
ATMs
Manufacturing Equipment in Factories
Inventory Management Systems in the warehouse
IoT Devices
What are Iot Devices?
are special gadgets that can connect to the internet and share information, but they’re not regular computers like desktops, laptops, servers, or smartphones.
What are some examples IoT devices?
smart cars
baby monitoring
amazon echo
home appliances
residential commercial security cameras including doorbell cameras
What’s a programmer?
a person who writes application or operating system software for computing devices.
What’s software?
is the set of instructions or programs that tell a computer or device what to do.
What’s hardware?
a physical computer component
What’s an Operating System?
it lets people interact with the computing machine
What’s an application?
specialized programming, that lets the computer accomplish specific tasks
What’s Data Storage?
The ability to store huge programs and save vast amounts of data for later use
Data is typically organized into ______
files
What’s a file?
collection of any form of data that is stored beyond the time of execution of a single job.
What data has unique or artistic properties?
Intellectual Property
What can a computing device do?
does math incredibly fast
Authors can protect their artistic expressions with ________.
copyright
Inventions can be protected with _________.
patents
What’s a con of Iot Devices?
Sending data from an IoT devices can present security challenges, a remote attacker can take control of an IoT device.
What does CPU stand for?
Central Processing Unit
What are processors (CPUs)?
are fast, powerful electronic components that perform calculations and follow instructions to run programs and complete tasks.
What does OS stand for?
Operating System
What does an operating system enable us to do?
it lets us communicate with the computing machine.
What’s data?
raw facts or information that can be processed and presented in meaningful ways.
What does IP stand for?
Intellectual Property or Internet Protocol
What does Internet Protocol mean?
It’s like a home address — but for a device (like a phone, computer, or IoT device) connected to the internet.
Identify the device
Send and receive data to the right place (like sending a letter to a house)
What does Intellectual Property mean?
ownership of ideas and creative work — and others can’t copy or use it without permission
What’s programming?
writing instructions that a computer can follow to do a task.
What’s a multi user computer?
A computer that can serve more than one person at a time
Examples of multi user computers
mainframes, minicomputers, and supercomputers.
What’s a mainframe?
a powerful computer, specialized in multitasking, supporting dozens or even thousands of user sessions at the same time.
What are minicomputers?
smaller versions of mainframes
What do supercomputers focus on?
focus the power of a mainframe computer on a single task, making them arguably the most powerful computers on the planet.
What’s a dedicated computer?
A computer meant for one user at a time.
What are peripherals?
devices that enable you to interact with the machine, such as a keyboard, mouse and monitor.
What’s a file server?
a special computer that stores files (like documents, pictures, videos, etc.) in one central place, so other computers can access and share them over a network
What are PC’s that aren’t easily transportable?
Desktop computers or desktop PCs
What are PCs that are transportable called?
Laptops
Yes or No: Can every PC run every operating system?
No
The hardware on which an OS runs is known as the _______.
platform
What does GUI stand for?
Graphical User Interface
What’s a GUI?
is the visual part of a device that lets you click and tap your way through it — instead of typing code.
What does CLI stand for?
Command Line Interface
How do users interact with a CLI?
By typing commands at a text-based on-screen prompt.
True or False: Linux is a variant of a much older OS, Unix, which started as a command-line OS used on servers.
True
What’s Linux?
A free, open source operating system, meaning that anyone can download and modify the source code.
True or False: Chrome OS is a Linux variant designed by Google
True
Why is Chrome OS not a viable replacement for a full-featured operating system like Microsoft Windows?
It lacks the ability to run desktop applications such as Microsoft Office.
What are smartphones?
Smartphones are not just mobile phones; they’re tiny computers that help you stay connected by enabling you to access the Internet on the go.
What’s a tablet?
A digital slate with a touchscreen, it resembles an extra-large smartphone, but most don’t have cell phone functionality.
A tablet that does have cell phone capability is called a
phablet
Devices with global positioning system (GPS) receivers enable
you to pinpoint your physical location and help you find your way around.
List OS for Mobile Devices
Apple iOS, Android, Windows Phone, and BlackBerry OS
A network occurs when?
whenever two or more computers communicate
What does LAN stand for?
Local Area Network
What does WAN stand for?
Wide Area Network
What’s a LAN?
connects computers in a single physical location, such as school, office, or home.
What’s a WAN?
two or more LANs connect
Computers in a wired LAN connect through network cabling and connection boxes called
switches
Wireless LANs use _______ instead of physical network ______ to connect PCs.
radio waves
cables
What’s a wireless access point (WAP)?
a device that lets wireless devices connect to the internet or a network without using cables.
A WAN connects many LANs over a big area (like across cities or countries), and it’s called "______" because the networks are far apart.
remote networks
The best example of a remote network is the
Internet
What is the Internet?
A worldwide network of remote networks connected by a series of high-speed communication lines.
What’s a switch?
a device that filters and forwards traffic based on some criteria.
A switch is like a traffic director within a single neighborhood. It helps devices within the same network (like your computer or printer) communicate with each other.
What’s a router?
a device that connects your local network (like the computers, phones, and devices in your house or office) to other networks, such as the internet or other distant networks
A router is like the gatekeeper or post office. It allows your local network (the neighborhood) to communicate with other networks outside (like connecting to the internet or to a remote office in another city).
What’s a server?
A server is a special computer that provides services or resources to other computers on a network.
It’s like the central hub or manager that shares things like files, printers, or websites with other computers.
Imagine you have a library. The server is the librarian who manages the books (resources) and lets others (computers) borrow them.
So when you want to print something, the server lets your computer connect to a printer that's shared by others on the network.
If you want to access a file, the server has those files stored and sends them to your computer.
PCs that receive services from server systems are called
clients
What happens when you download a music or video clip?
the file transfers permanently to your local computing device and you can play it back even when your device isn’t connected to the Internet.
What’s streaming?
Its when your system plays the clip back immediately as the data transfers without bothering to save it for later.
What’s cloud computing?
describes applications and data you can access online rather than on a local PC.
True or False: Web apps are an example of cloud computing.
True
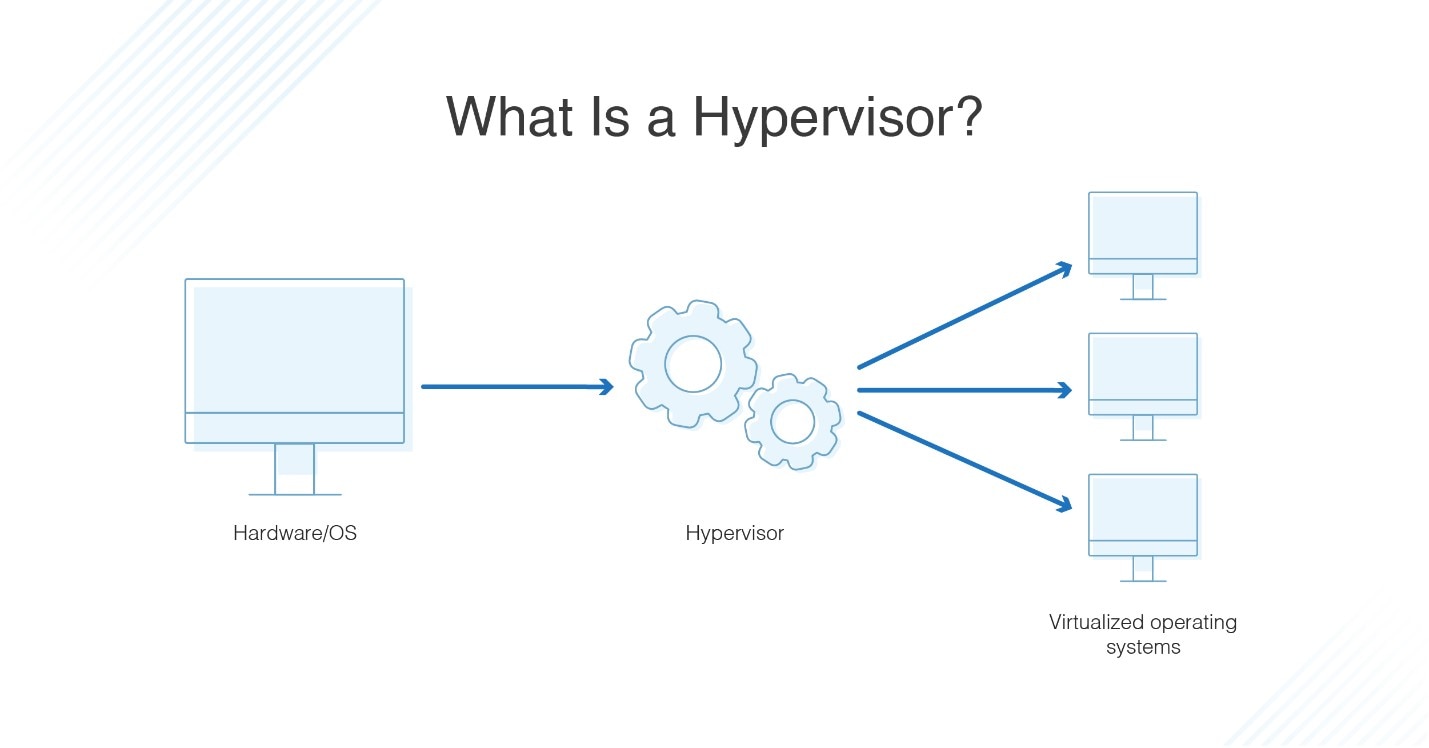
What’s virtualization?
is the process of creating virtual versions of things like computers, operating systems, or storage devices, so one physical machine can run multiple virtual machines
Imagine your physical computer is like a big apartment building.
you can divide that building into separate apartments (VMs).
Each apartment (VM) has its own entrance (os), furniture (apps), and rooms (files), but they all share the same building (the physical computer’s hardware).
What’s the computer’s “real” OS ?
host OS
The computer itself is
the host PC
The secondary operating system installed inside the host OS is called
the guest OS
Hypervisors come in how many flavors?
Two Flavors: Type 1 and Type 2
What’s Type 1 hypervisors?
is a special type of software that runs directly on the physical hardware of a computer, without needing an existing operating system (OS).
Type 1 Hypervisor is like building a house directly on land (the physical hardware) — no need for an existing house (OS) to be there first.
The hypervisor takes control of the machine’s resources (CPU, memory, storage) and then creates virtual machines (VMs) on top of them.
What’s Type 2 hypervisors?
is software that runs on top of an existing operating system. It allows you to create and manage virtual machines (VMs), but it requires a regular OS to be installed first.