Animal Behavior Exam II
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Communication
Information transfer from a sender to a receiver that, on average benefits the sender in some way
Channels (modalities)
Vision, audition, chemical, touch, electrical
Communication is shaped by
characteristics of sender, receiver, and environment
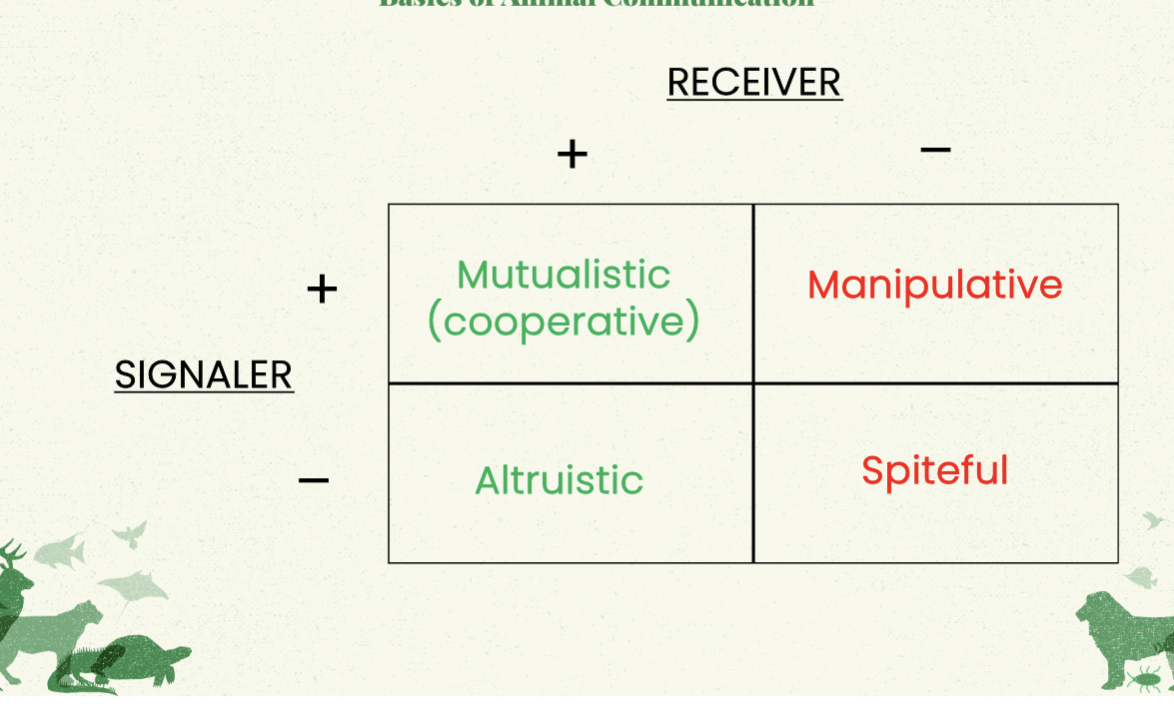
Communication types in terms of positive or negative outcome for signalers and recievers
Equation for amount of information transferred/ amount the uncertainty is reduces
H= log2 n, where n = # of equally probably alternatives
2H = n
Widespread message types
Attack, escape, sex, indecisiveness, attentiveness
Arbitrary signal
Signal ‘removed’ from information (most signals)
Iconic signal
Signal related to, or representing something, about information
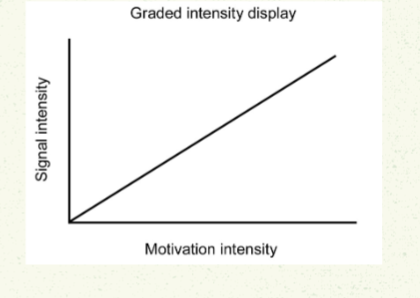
Graded signal intensity
Continuous. Can potentially convey more info. e.g facial expressions
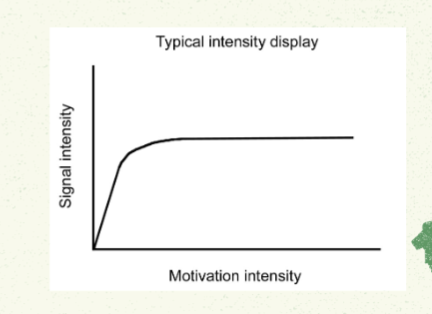
Typical Intensity
Discrete. Less subject to misinterpretations. Less limited in range. e.g. ritualized displays
Ritualization steps
Simplification, exaggeration of remaining components, stereotype, repetition of signal