Fundamentals of algorithms
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
searching, sorting lists
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
list the details describing a linear search
Does not have to be sorted.
Search only terminates when element is found or end of list is reached (meaning item is not in list)
Best case scenario: first item
Worst case scenario: last item
Uses while loop for increase in efficiency
how do linear searches work?

what is the time complexity of a linear search
O(n)
list the details describing a binary search
lists needs to be sorted
more efficient than linear search
Best case scenario: first midpoint
Worst case scenario: Log2(n)
how do binary searches work?

how to find worst case scenario: binary search

what is the least efficient and most efficient sorting algorithms?
LEAST: bubble
MOST: merge
list the types of algorithms we can use to sort lists data
bubble
merger
insertion
quick
describe process to carry out bubble sort
runs up list comparing each pair of data items
if they are the wrong way around, they are swapped over
the largest item ‘bubbles’ to the top
next time around, sort runs up list to second from top item
at same time, smallest moves down one place
carry out a bubble sort for this list of data:
9, 17, 6, 88, 28, 91, 12, 3, 95
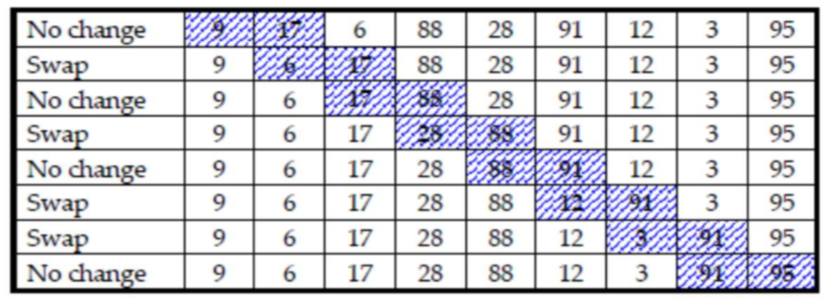
when does a bubble sort algorithm stop running? how does this happen?
stops when all items are in correct place
program makes note of whether or not variable was swapped over during last pass
to do this, variable swapped is set to TRUE every time swap is made but set to FALSE before new pass is made.
if swapped still equals false at end of passthrough, data is in order so sort can finish
as we make pass, we get one further element into correct place. so for n elements, we know after n-1 passes, all elements should be in correct space
time complexity for bubble sort
O(n2) as it uses a nested loop
how to complete insertion sort

time complexity for insertion sort
O(n2)
how to complete merge sort

complete merge sort for this list of data:
22, 7, 26, 11, 9, 37, 1, 6
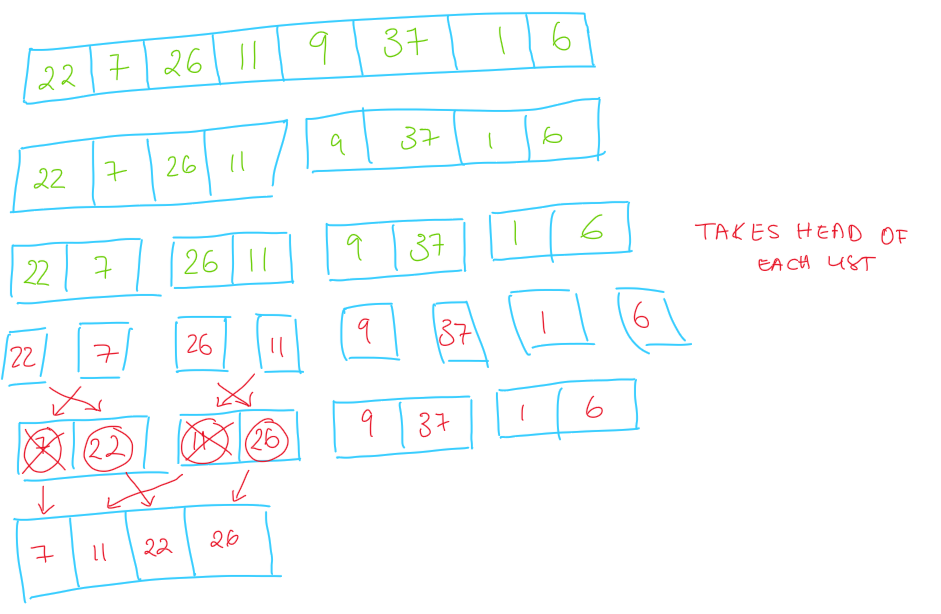
time complexity of merge sort
average: O(nlog n)
best case: O(n) - if input lists are pre sorted
how to carry out quick sort
uses a partition and a sort phase
divide list into 2
set a pivot
arrange all the items lower than pivot in lower part
arrange all the items higher than pivot in greater part
recursively sort two partitions

time complexity for quick sort algorithm
average: O(n2)
worst: O(nlog n)
best: O(nlog n)