Biochemistry: Citric Acid Cycle
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Where does the citric acid cycle take place?
Mitochondria
How does pyruvate gain access to the mitochondrial matrix?
Via the pyruvate-H+ symport
Uses the electrochemical gradient created by the ETC
What are the advantages of using a multienzyme complex (pyruvate dehydrogenase) to convert pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
Diffusion distance
Minimize side reactions
Coordinated control of reactions
What are the 5 coenzymes of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
Lipoic Acid
Coenzyme A (CoA)
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD)
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
What is the function of TPP?
Decarboxylates pyruvate, yielding a hydroxyethyl-TPP carbanion
What is the function of lipoic acid?
Accepts the hydroxyethyl carbanion from TPP as an acetyl group
What is the function of CoA?
Accepts the acetyl group from lipoamide
What is the function of FAD?
An electron carrier
Reduced by lipoamide
What is the function of NAD+?
An electron carrier
Reduced by FADH2
Pyruvate => Acetyl-CoA
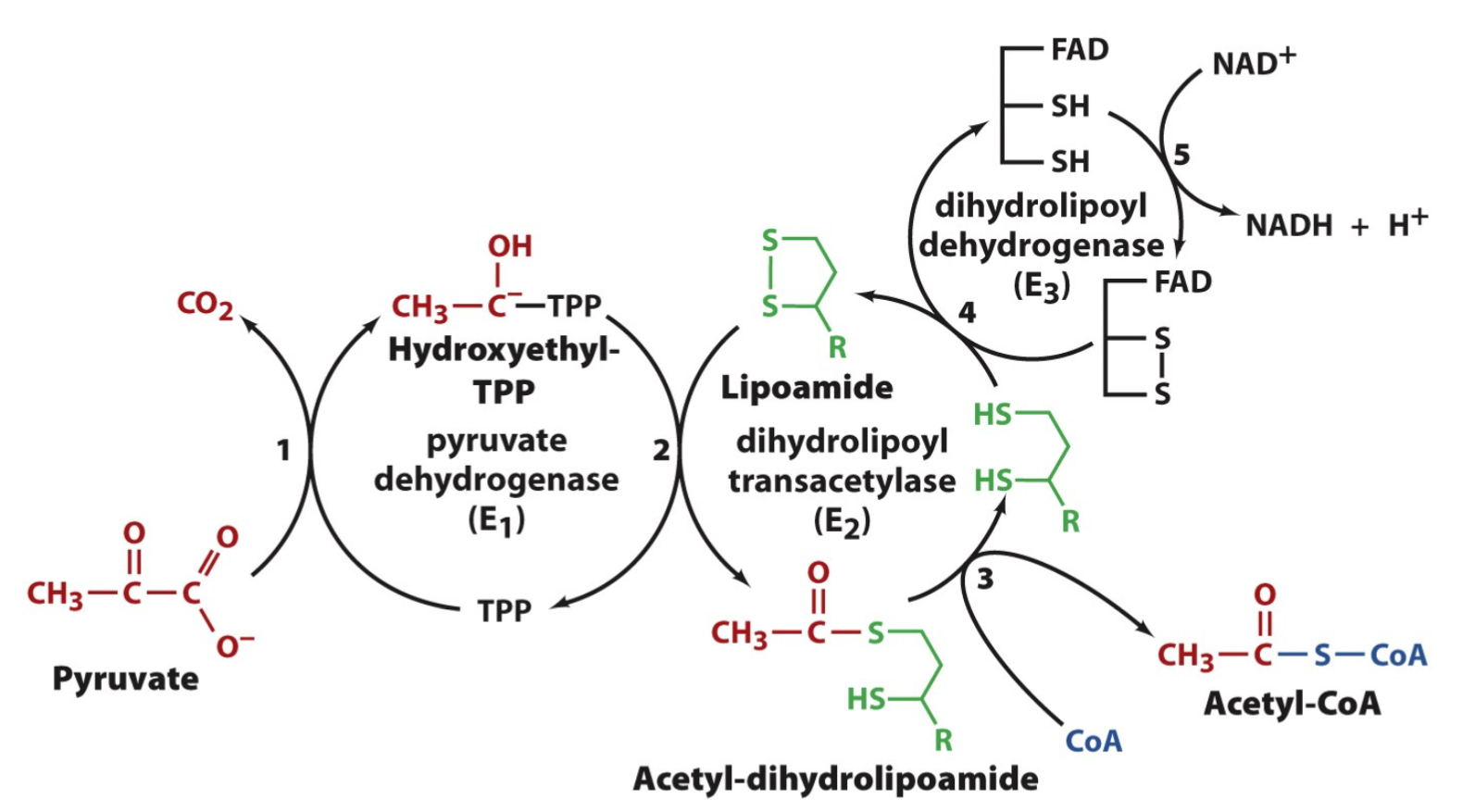
Step 1
Catalyzing Acetyl-CoA
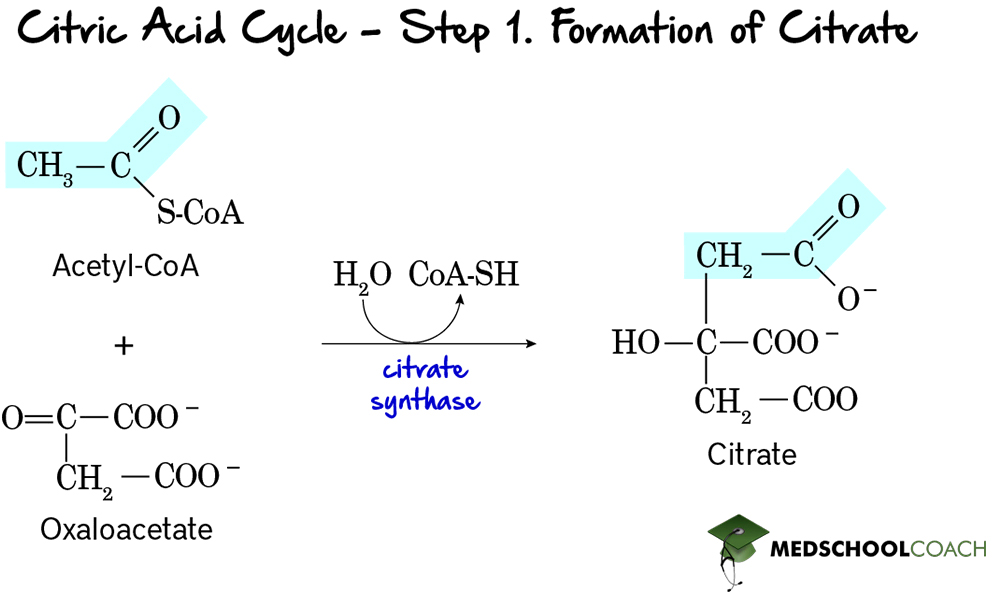
Step 1: Substrate
2 Acetyl-CoA
2 Oxaloacetate
2 H2O
Step 1: Product
2 Citrate
2 CoASH
Step 1: Enzyme
Citrate Synthase
For step 1 of the reaction, why is there a high amount of energy being used? (-32.2kJ/mol)
Allows for the condensation to take place even when the concentration of oxaloacetate is low
Step 2
Isomerization of Citrate
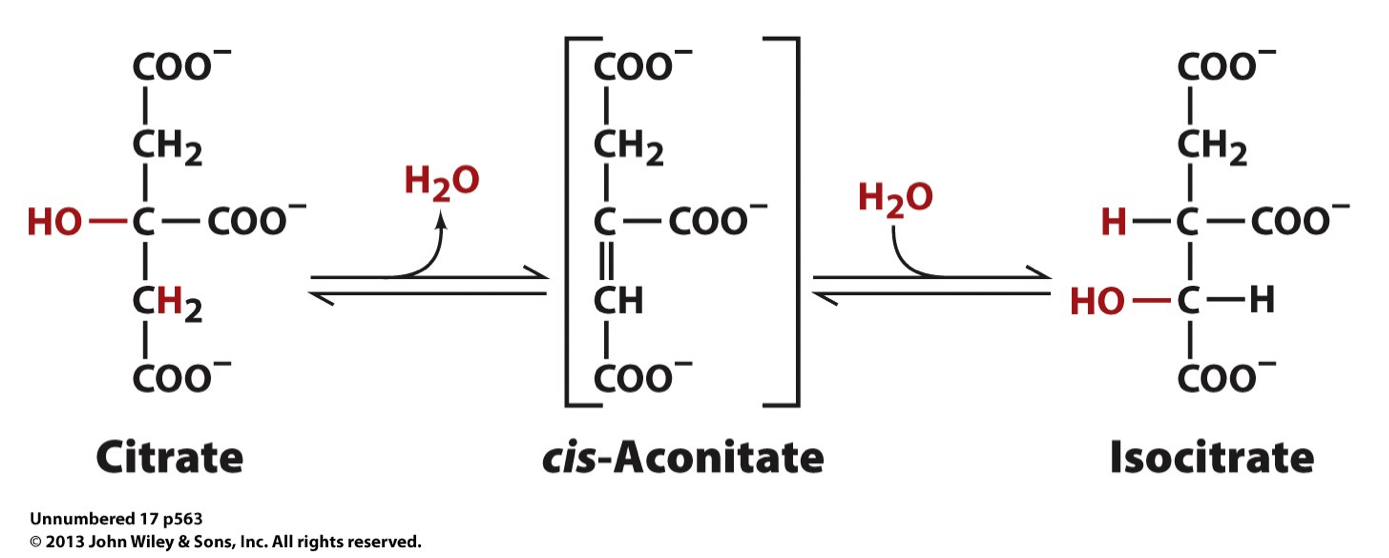
Step 2: Substrate
2 Citrate
Step 2: Product
2 Isocitrate
Step 2: Enzyme
Aconitase
Step 2: Purpose of chemical reaction
Isomerization facilitates future oxidation
Step 3
Oxidative Decarboxylation
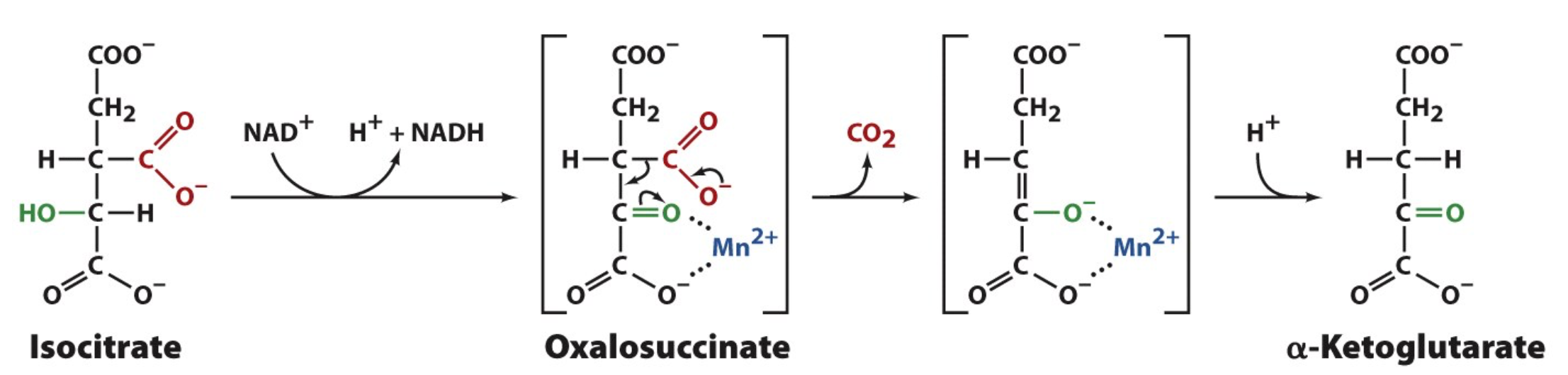
Step 3: Substrate
2 Isocitrate
2 NAD+
2 H+
Step 3: Product
2 a-Ketoglutarate
2 H+
2 NADH
2 CO2
Step 3: Cofactors
Mg2+ or Mn2+
NAD+
Step 3: Purpose for chemical reaction
Serves as an important site for regulation
Step 4
Oxidative Decarboxylation
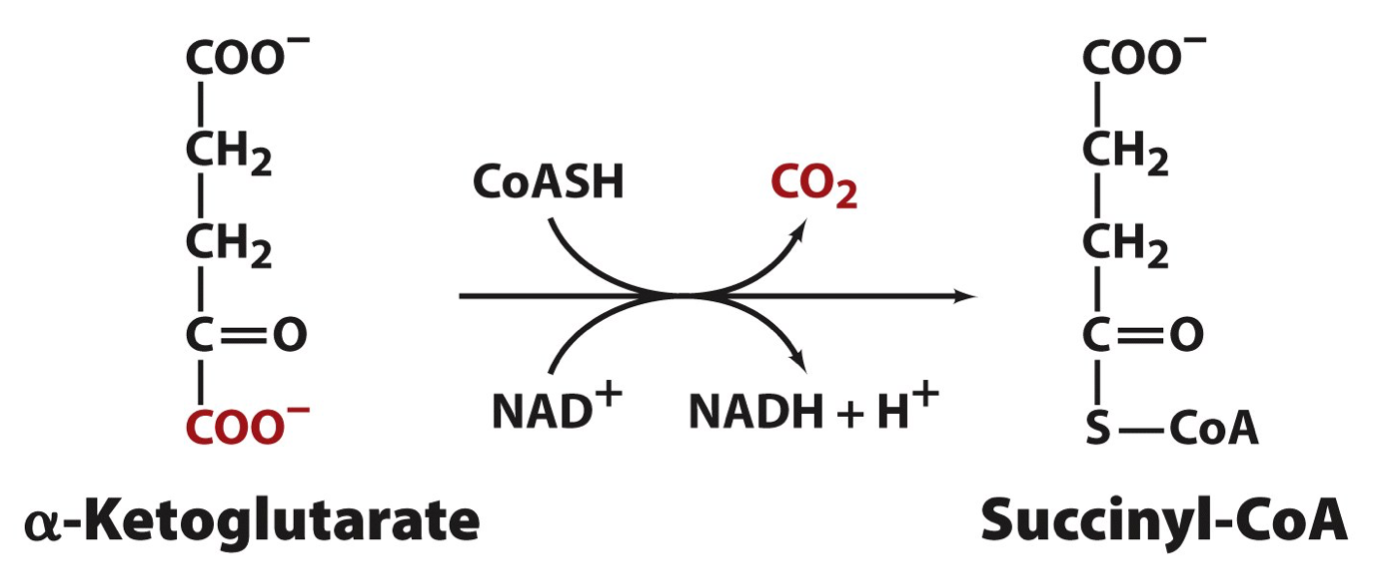
Step 4: Substrate
2 a-Ketoglutarae
2 CoASH
2 NAD+
Step 4: Product
2 Succinyl-CoA
2 CO2
2 NADH
2 H+
Step 5
Generation of GTP
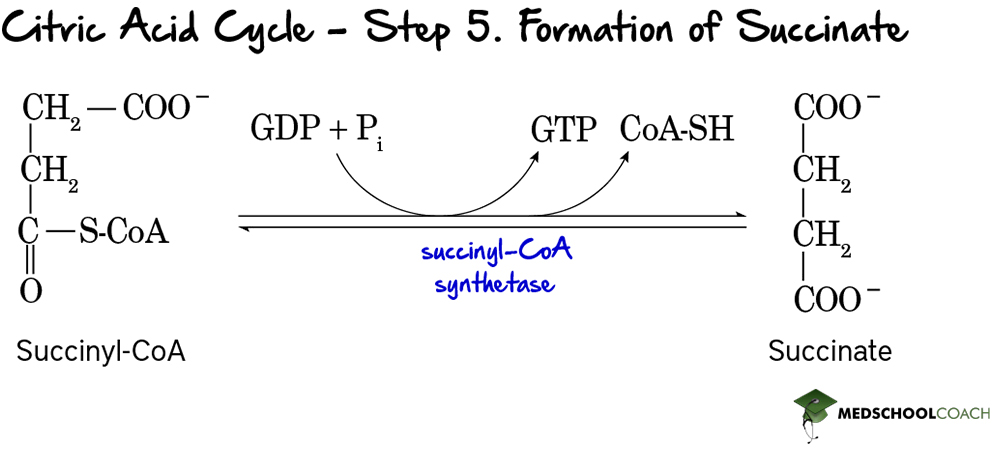
Step 5: Substrate
2 Succinyl-CoA
2 Pi
2 ADP or GDP (primarily GDP)
Step 5: Product
2 Succinate
2 GTP
2 CoASH
Step 5: Enzyme
Succinyl-CoA synthase
Step 6
Catalyzation of Succinate
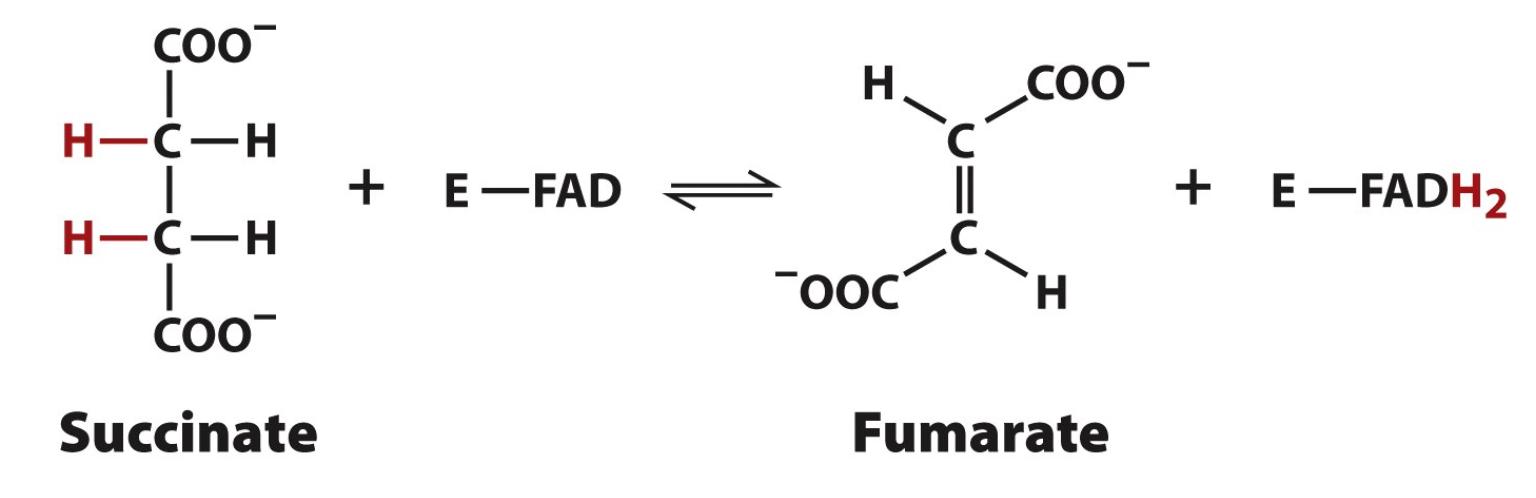
Step 6: Substrate
2 Succinate
2 E-FAD
Step 6: Product
2 Fumarate
2 E-FADH2
Step 6: Enzyme
Succinate Dehydrogenase
Step 7
Hydration of Fumarate
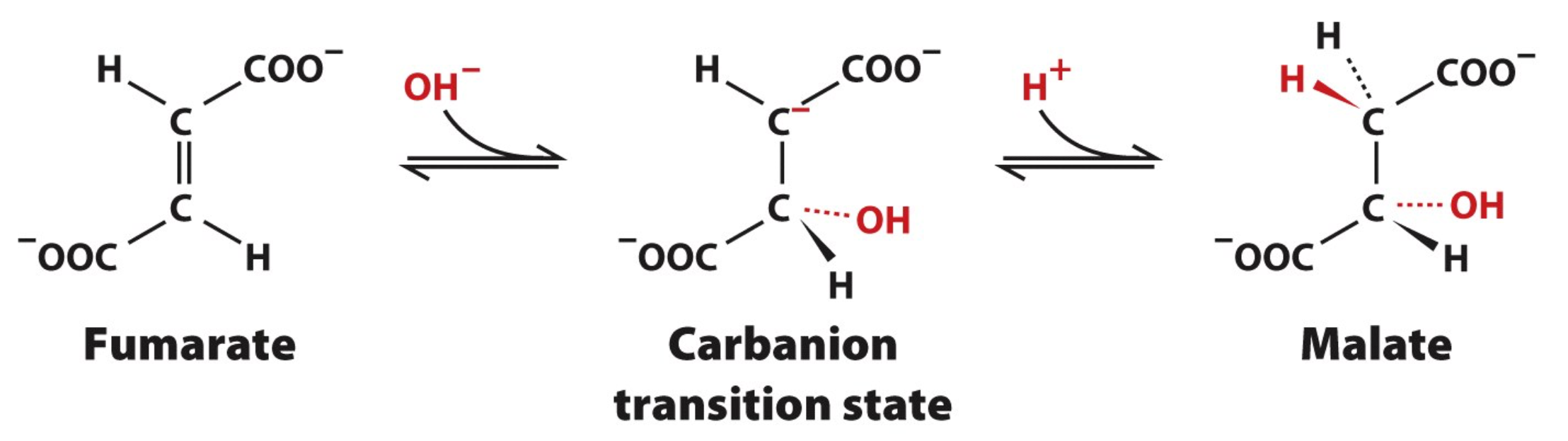
Step 7: Substrate
2 Fumarate
2 H2O
Step 7: Product
2 Malate
Step 7: Enzyme
Fumarase
Step 8
Catalyzing Malate
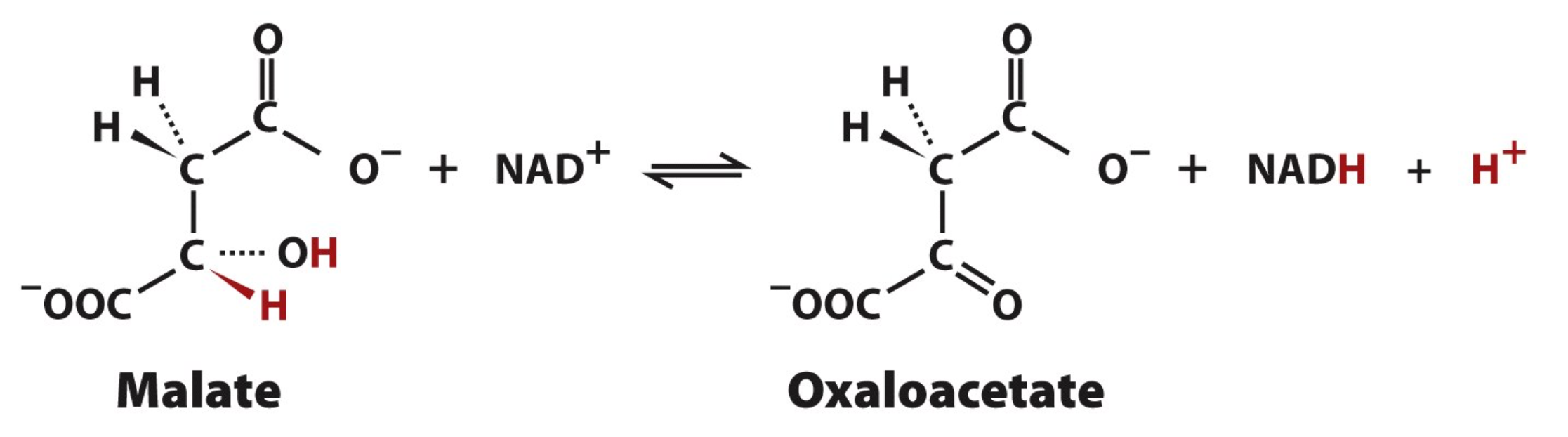
Step 8: Substrate
2 Malate
2 NAD+
Step 8: Product
2 Oxaloacetate
2 NADH
2 H+
Step 8: Enzyme
Malate Dehydrogenase
What are the regulatory steps for the citric acid cycle? How are they controlled?
Step 1 (substrate concentration)
Step 3 (product inhibition)
Step 4 (feedback inhibition)
Step 1: Importance of the reaction
To facilitate the oxidation of the carbons coming from Acetyl-CoA
Step 2: Importance of the reaction
It takes the tertiary alcohol and rearranges it to a secondary alcohol, which is more reactive, to prepare for the oxidation of the secondary alcohol in step 3
Step 3: Importance of the reaction
Oxidation of a carbon to make NADH
Step 4: Importance of the reaction
Generate NADH for the ETC
Step 5: Importance of the reaction
To generate the only 2 GTP to do work in other pathways
Step 6: Importance of the reaction
Prepares the molecule for the nucleophilic addition of water
Step 7: Importance of the reaction
The -OH will become the ketone in oxaloacetate
Step 8: Importance of the reaction
Regenerate oxaloacetate