General Biology II: Circulation
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
Flatworms, cnidarians, nematodes
Can you list some animals without a circulatory system?
Circulatory fluid, interconnected vessel network, heart (muscular pump)
What are the 3 components for the circulatory system?
Open Circulatory System
These contain hemolymphs that act as your circulatory fluid → found in Mollusca & arthropods that is in charge of bathing tissues
It is pumped through vessels to reach interconnected sinuses in contractions
When the central heart organ undergoes contractions, what happens to the hemolymph?
Hemolymph sucked back to heart via pores
When the central heart organ undergoes relaxation, what happens to the hemolymph?
Low Pressure
This forces the hemolymph throughout body and spread out (less costly, but more effective)
Closed Circulatory fluid
Fond in annelids, cephlapods and vertebrates that has blood as circulated fluid that moves within vessels (different compared to intestinal fluid) and contains a heart → has an advantage of higher BP which means it is more efficient with bigger, active animals
Hemolymph
Your circulatory fluid in the open circulatory system that is an interstial fluid bathing tissues
Blood
Circulated fluid that moves within vessels that is different than intestinal fluid
Capillaries, veins, arteries
3 Blood vessels found in closed circulatory system
Arteries
Bring blood away from heart to organs of body that soon divide into arterioles that deliver blood to capillaries
Veins
These receive blood from your venules, which is sandwiched between muscles for muscle movement
Capillaries
Microscopic blood vessels that infiltrate organs
Valves
Open/close in order to prevent backflow of blood towards the heart
Capillary Beds
Network of capillaries that will infiltrate tissues (exchange material between blood)
Venules
Capillaries merged with each other
Arteries → Arterioles → Capillaries → Tissues → Venules → Veins
SEQ blood flow
Heart
Acts as your muscular pump that will pump blood into large vessels which branch into smaller vessels that gets to the organs (2 or more muscular chambers)
Atria
Receives blood returning to tissues (1-2 depending on species)
Ventricles
Pumps blood away from heart to arteries (1-2 depending on species)
Pericardium
Enclosing sac for heart that supports muscles
Fish Circulatory Patterns
This organism undergoes single circulation with only 2 chambers (1 atrium and 1 ventricle) → blood flow is a single circuit (low metabolism rate, slow system)
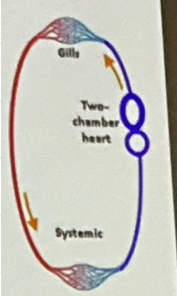
1) Atrium will pump blood into ventricle (heart)
2) Ventricle contracts, pumps blood to arteries (heart)
3) Blood to capillary beds in gills (O2 poor) (Gills)
4) Net diffusion of O2 in blood (CO2) and now O2 rich (Gills)
5) Capillaries will converge into vessels that carry blood to capillary beds in rest of body (body)
6) Blood will return to atrium (heart)
SEQ the blood flow of a fish
1) Atrium will pump blood into ventricle (heart)
1st step of blood flow of a fish
2) Ventricle contracts, pumps blood to arteries (heart)
2nd step of blood flow of a fish
3) Blood to capillary beds in gills (O2 poor) (Gills)
3rd step of blood flow in a fish
4) Net diffusion of O2 in blood (CO2) and now O2 rich (Gills)
4th step of blood flow in a fish
5) Capillaries will converge into vessels that carry blood to capillary beds in rest of body (body)
5th step of blood flow in a fish
BP will drop in capillary beds in gills (blood has a hard time traveling) as O2 rich blood reaches organs slowly, but they can combat that by swimming (heart)
Why isn’t single circulation as effective?
Amphibian Circulatory Pattern
This animal has double circulation and blood flow is double circuit where the heart has 3 chambers (1 ventricle + 2 atria) where the ventricle will pump blood into forked artery in 2 circuits → low metabolic rate/slow system
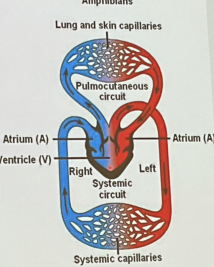
Systematic
Will transport O2 rich blood to organs which will return to the heart’s right atrium
Pulmocutaneous
Will transport blood from lung/skin → where blood picks up O2 to become O2 rich as the circuit returns to left atrium via veins
Systemic
Will transport O2 (rich) to body then returns to the right atrium
1) Ridge in ventricles
2) Diverts most of the rich blood to systematic and poor blood to pulmocutaneous circuit
3) Mixes a little and can go to either lungs or skin
SEQ amphibian atria (R/L) pumping into a single ventricle
Human Circulatory Pattern
Double circulation with more vigorous blood flow with a 4 chambered heart (2 atria + 2 ventricles) where the 2 circuits are seperate
Arteries
These bring blood away from heart
Veins
These bring blood to the herat
Cardiac Output
Volume of blood pumped by left ventricle by systematic circulation
Heart Rate x Stroke Volume
How can you calculate cardiac output?
Stroke Volume
Amount of blood pumped in a single contraction
Right Atrioventricular (tricuspid), Left Atrioventricular (mitral), Semilunar valves (Pulmonary Valves and Aortic Valves)
What are the 4 valves found to prevent backflow?
Right Atrioventricular Valve (Tricuspid)
This is the valve where it will allow the blood to enter into the right ventricle
Left Atrioventricular Valve (Mitral)
This is the valve where it will allow the blood to enter into the left ventricle
Semilunar
Ventricles to heart exit
Pulmonary valve
This valve has deoxygenated blood that leads to heart exit
Aortic Valve
This valve has oxygenated blood that leads to heart exit
1) Blood enters the atria
2) Gets through a valve
3) Ventricles will contract it
4) Another valve will close once blood fully flows and exits to prevent backflow
SEQ the human heart pathway
The lungs
Where does the right ventricle send the blood to (deoxygenated)?
The body
Where does the left ventricle send the blood to (oxygenated)?
Lub
A low pitched heart beat that is long lasting, which signifies the atrioventricular valves closing
Dup
Your high pitched heartbeat that is shorter lasting, which signifies semilunar valves closing
Lub-smnh
This means a heart murmur has happened and there is backflow in the semilunar valves
Sinoatrial Node
The pacemaker that will initiate the heartbeat
1) Mass of cardiac muscle atrium which autorhymically initiates heartbeat
2) Generates action potentials on their own
3) Triggers Ca2+ channels opening (depolarization)
4) Will create an action potential as the impulse will spread rapidly through atrial walls
5) Both atria contracts simultaneously
6) SA node will reach AV node
7) Will be purposefully delayed 1/10 second to prevent 4 chambers from squeezing at once and complete contractions before ventricles contract
8) Ventricles can fill completely
9) Bundle branches conduct signals from AV nodes to heart apex
10) Signal continues to Purkinje Fibers → ventricles contract
SEQ the initiation of a heartbeat
Autorhythmic
This means self contracting where AP is generated by Ca2+ channels that causes impulse to spread rapidly where both atria contract stimultaneously
Bundle Branches
This will conduct signal to heart apex (tip)
Purkinje Fibers
Signal spreads throughout ventricle where it contracts from blood to body/lungs
1) Mass of cardiac muscle atrium which autorhymically initiates heartbeat
1st step to initiating heartbeat
2) Generates action potentials on their own
2nd step to initiating heartbeat
3) Triggers Ca2+ channels opening (depolarization)
3rd step to initiating heartbeat
4) Will create an action potential as the impulse will spread rapidly through atrial walls
4th step to initiating heartbeat
5) Both atria contracts simultaneously
5th step to initiating heartbeat
6) SA node will reach AV node
6th step to initiating heartbeat
7) Will be purposefully delayed 1/10 second to prevent 4 chambers from squeezing at once and complete contractions before ventricles contract
7th step of initiating heartbeat
8) Ventricles can fill completely
8th step of initiating heartbeat
9) Bundle branches conduct signals from AV nodes to heart apex
9th step of initiating heartbeat
10) Signal continues to Purkinje Fibers → ventricles contracts
10th step of initiating heartbeat
Artificial Pacemakers
What can also be a replacement if the sinoatrial node stops working at some point?
To prevent 4 chambers from squeezing at once and complete contractions before ventricles contract
Why is the impulse delayed 1/10th of a second before ventricle gets signal to move blood away?
Nervous System
One of the main regulators for the heartbeat (controls your systems)
Baroreceptors
In blood vessels + chambers that sense Blood Pressure change and talk to the medulla by sending the messages afferently
Cardiac Centers
Controls 2 sets of autonomic nerves going to the SA node
Sympathetic
This part of the nervous system speeds up your contraction due to the fight and flight nature
Parasympathetic
This part of the nervous system slow down your contraction due to the rest and digest nature
Endocrine System
The adrenal medulla will be stimulated by sympathetic nerves in response to stress, which increases your heartrate
Temperature
This will increase as heartrate increases, decrease as heartrate decreases
Endothelium
Innermost that lines lumen, provides smooth surface, sliding to minimize resistance to blood flow
Smooth Muscle
Thick in arteries, elastic and involuntary (in arteries than veins)
Connective Tissue
Outer coat with elastic and collagen fibers providing support
Capillaries
This contains the endothelium with basal lamina & only location of gas exchange between blood and ISF
Diffusion, gas exchange, waste removal, nutrient arrival
How are substances moved between blood and tissue?
Plasma
Fluid compartment of blood with no cells → will be under high pressure in closed circulatory system where it might eventually be forced out into tissues
Interstitial Fluid
Plasma forced out into tissues that will bathe tissues, no cells but some proteins (25%) and hypotonic to Red Blood Cells
Fluid Movement
This is the back and forth between capillaries and tissues via opposing forces
Blood Pressure
Pressure exerted on capillary wall due to heart pumping, which will push plasma out of capillary
Osmotic Pressure
Antagonistic to Blood Pressure where blood is hypertonic to the interstitial fluid so ISF wants to flow back into blood
Blood pressure > Osmotic pressure where blood wants to move out of capillary
When you are at the arterial end of capillary, what is greater?
Osmotic Pressure > Blood pressure, where we want to go back into the capillary
When you are at the venous end of capillary, what is greater?
15%
How much fluid remains even after some of them return?
Lymphatic System
This will collect and return interstial fluid to maintain fluid balance, absorbs lipids from digestive system, immunity
Lymph
lymphatic system fluid WBCs, bacteria and other filtrates
Lymph vessels
Where throughout the body, almost all tissues extended
Lymph nodes
Connective tissues with lots of WBCs where pathogens filtered out
Edema
Blocked nodes, swelling due to ISFs, poor circulation