Lecture 6-Transcrption ll + Translation
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is RNA splicing ?
It’s the removal of the introns (non-coding RNA) from the pre-mRNA.
What is the splicing machinery called and made up of ? What is the removed intron called ?
The complex is called the spliceosome. It’s made up of 5 snRNAs which are each complexed with at least 7 proteins to form snRNPs (small nuclear RNAs).
The removed intron is called a lariat.
How does the spliceosome work ?
It needs to recognize three sequences : the 5’ splice site, the 3’ splice site and the branch point.
The splice sites contain both intron and exon sequence as it’s the junction.
Sequence recognition happens through base-pairing with the snRNAs.
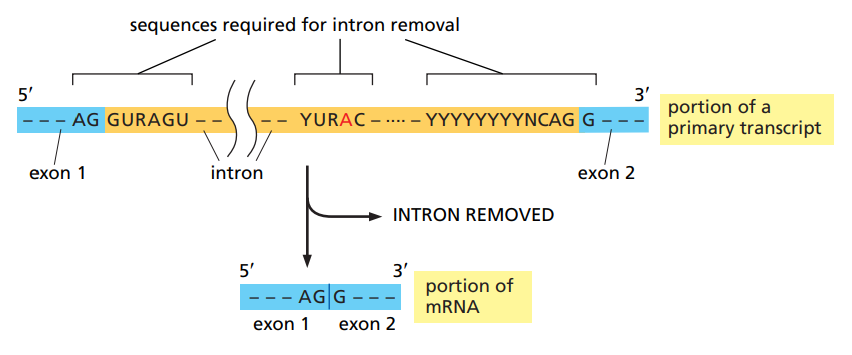
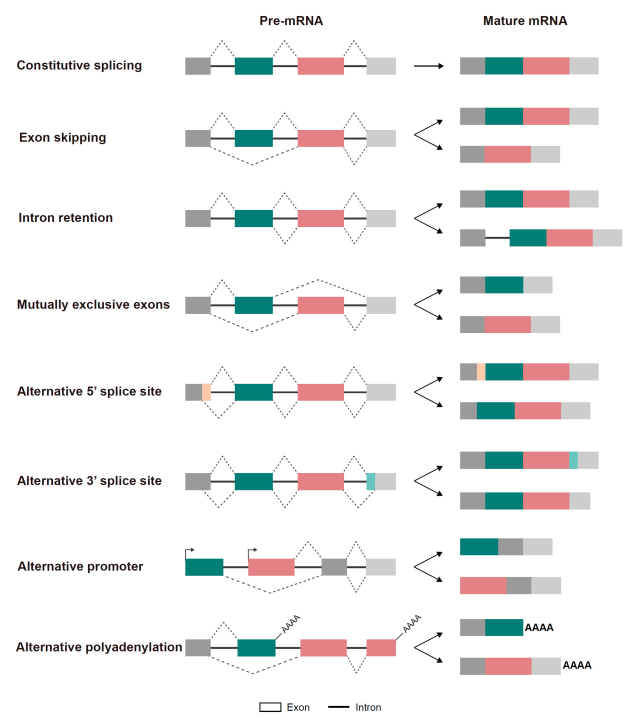
What is alternative splicing ?
It allows the synthesis of different proteins form the same gene, as it keeps or changes different exons of the gene.
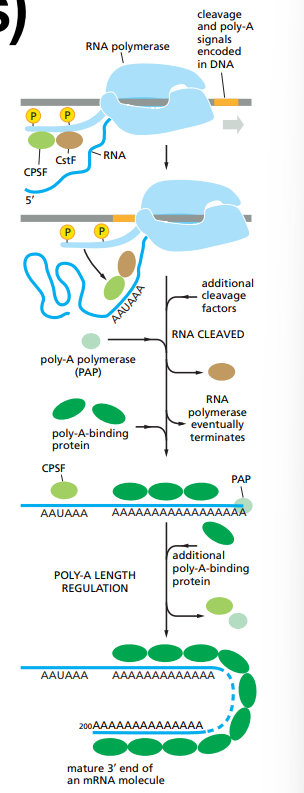
How is RNA polyadenylated ?
There are signals encoded in the genome which get recognised by RNA-binding-proteins and RNA-processing enzymes.
CstF and CPSF, 2 enzymes, bind their recognition sequence on the RNA molecule.
The RNA is cleaved, the Poly-A polymerase binds to the signals and CstF leaves.
Poly-A polymerase adds ~200 Adenine nucleotides ate the end of the sequence and at the same time poly-A binding proteins bind to the poly-A sequence.
What is translation ?
It’s the conversion from RNA to protein.
How many reading frames does a sequence have ?
3 reading frames.
How many amino acids are there ?
20
What do tRNAs do ?
They recognize the codons and bring the correspnding amino-acid.
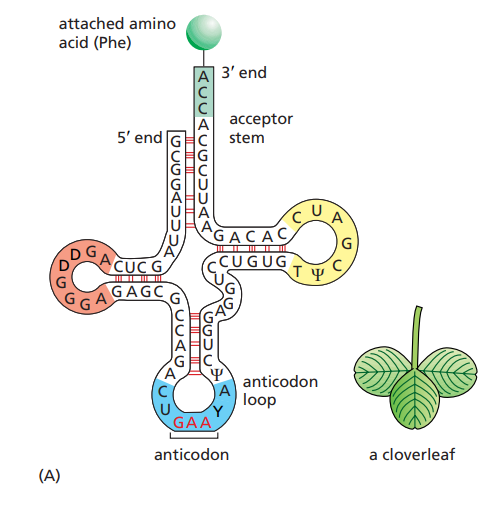
What are the important elements of tRNAs ?
~80 nucleotides long.
The anticodon region : 3 nucleotides that pair with the complementary codon on the mRNA.
The 3’ end region : Region that binds the corresponding amino-acid.
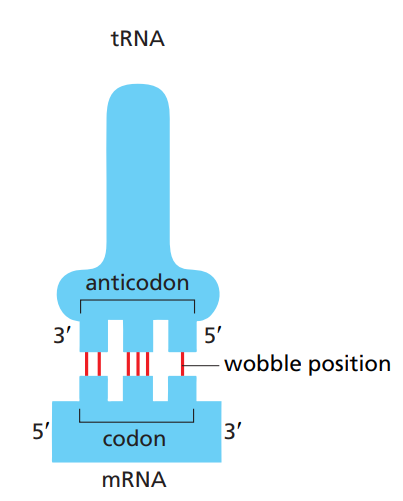
What is the wobble position ?
Some amino-acids have more than one corresponding tRNA. This is because some tRNAs allow for a mismatch at the 3’ end of a codon and the 5’ of the anticodon. In this position, base-pairing is less strict which allows the tRNA to recognize more than one codon.
This allows all codons (61 combinations) to be recognized with fewer tRNAs.
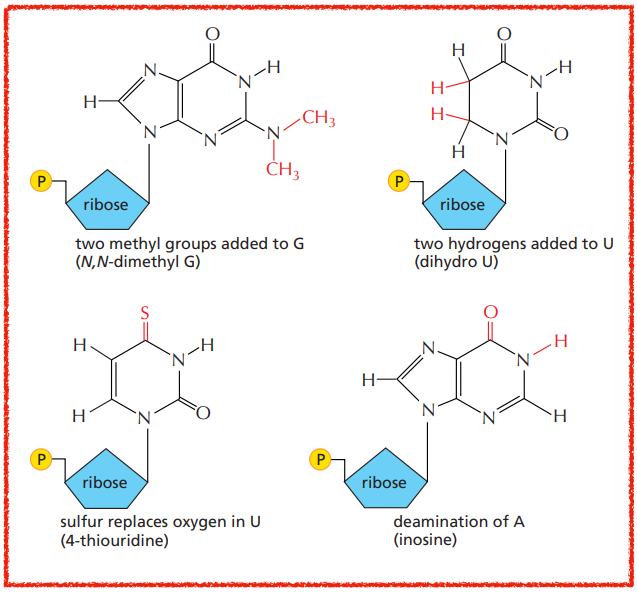
By which RNA polymerase are tRNAs made and what gives them their particular shape ?
They are made by RNA polymerase lll and some of the ribonucleotides need to be chemically modified (~1 out of 10).
What are some chemical modifications that the ribonucleotides of tRNAs undergo ?
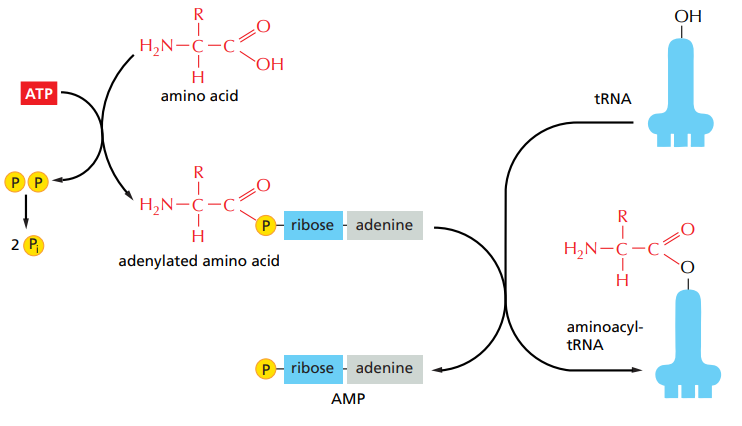
What do amino-acyl-tRNA synthesases do ? And what reaction takes place ?
They covalently bind each amino-acid to their respective tRNA. It is an energy-releasing hydrolysis of ATP reaction.
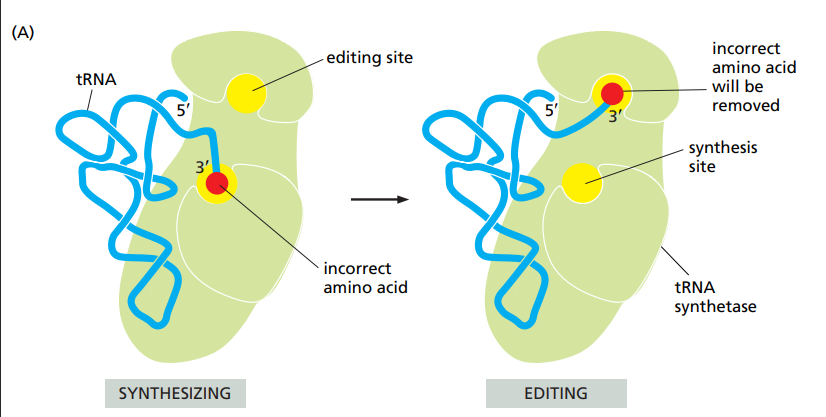
How do amino-acyl-tRNA synthesases make sure the right amino-acid is bound to the right tRNA ?
The correct amino-acid has higher affinity.
Larger amino-acids than the one that should be added can’t enter the catalytic site.
For similar sized amin-acids, there is an editing site that checks if it fits or not. If it does it isn’t the right amino-acid and it isn’t linked.
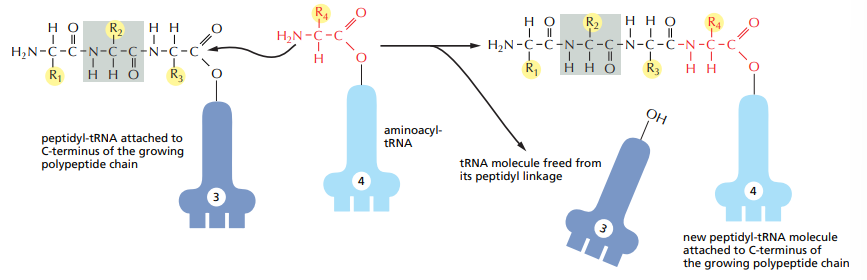
How are amino-acids added to the polypeptide chain ?
A peptide bond forms between the carboxyl group of the previous polypeptide chain to the N-terminal of the new amin-acid connected to the respective tRNA. The previous tRNA is let go.
What are ribosomes for ?
They perform the protein synthesis by managing thee tRNAs and their linked amin-acids.
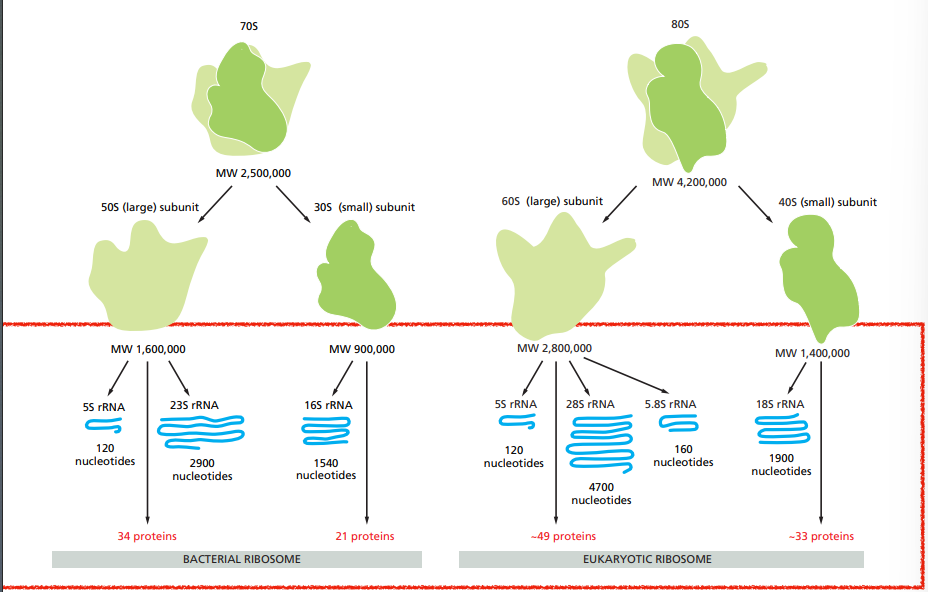
What are ribosomes made of ? Are they the same in every organism ?
They have a large and a small subunit which are assembled in the nucleus from ribosomal RNAs and >50 proteins.
Bacterial ribosomes aren’t the same as eukaryotic ribosomes.
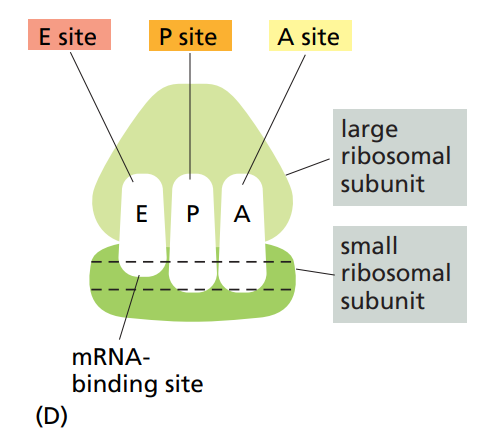
How many binding sites do ribosomes have and what are they for ?
4 binding sites :
For mRNA.
A site : Site for the new tRNA.
P site : Site for the previous tRNA.
E site : Site where previous tRNA exits.
What are the steps to protein synthesis ?
Step 1 : tRNA binding in A site.
Step 2 : peptide bond formation in the large subunit.
Step 3 : Large subunit translocation.
Step 4 : Small subunit translocation.
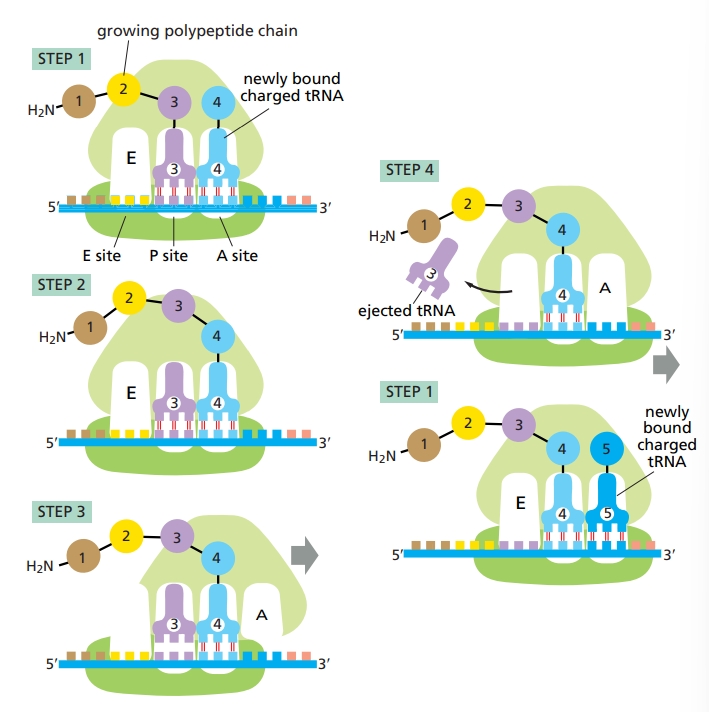
What do elongation factors do in translation and what are their names for both eukaryotes and prokaryotes ?
They helps the ribosome add amino-acids to a growing polypeptide chain.
For eukaryotes : EF1 and EF2
For Prokaryotes : EF-Tu and EF-G
How to start translation ?
All proteins start with methionine which is the AUG codon. The specific tRNA is recognized by initiation factors. This determines the reading frame.
What is an open reading frame (ORF) ?
It’s a continuous stretch of codons in DNA or mRNA that can potentially be translated. It starts with an AUG codon and ends with a stop codon.
On one strand there are 3 possible reading frames, which means that on double-stranded DNA there is a total of 6 possible reading frames.
Wat is the Shine-Dalgarno sequence ?
It’s a specific ribosomal binding site in bacteria which is recognized by the 16S rRNA to position the ribosomes to read the first AUG.
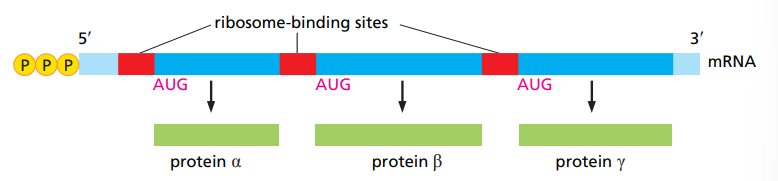
What is special about bacterial mRNA ?
They are often polycistronic, meaning they contain multiple genes that produce different proteins.
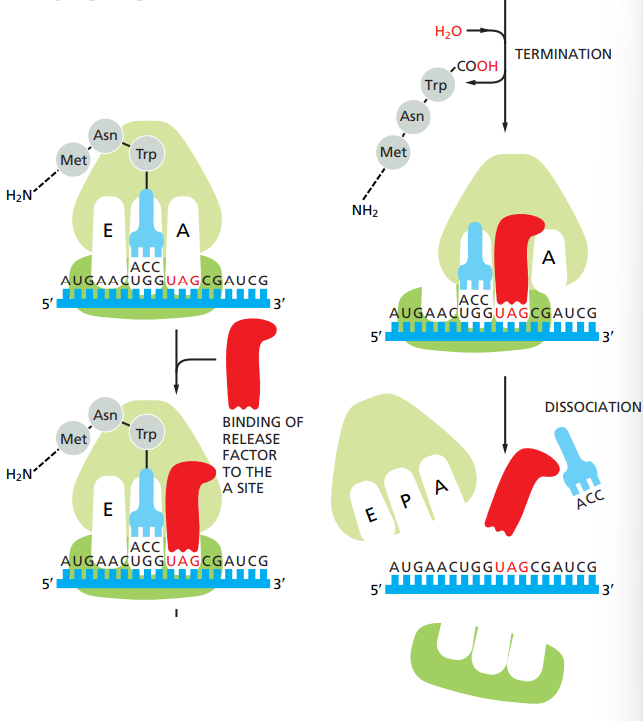
How does the translation stop ?
Stop codons are UAA, UAG and UGA.
When STOP codon is reached, it’s a signal that bind to the A site and not a tRNA.
Other release factors bind to the site to help.
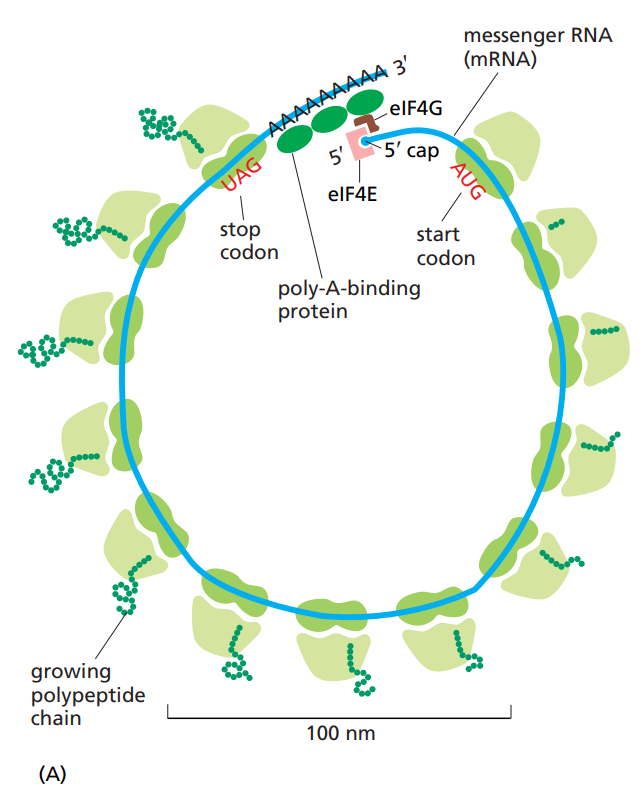
What are polyribosomes ?
A structure consisting of a mRNA molecule and many ribosomes, all making proteins at the same time.
What are the different steps for protein folding ?

What typically helps proteins to fold if needed and how does it work ?
Molecular chaperones also called heat shock proteins help by recognizing the exposed hydrophobic surfaces of proteins to fold them properly.
What are the two main families of chaperones ?
Hsp70 and Hsp60
How do Hsp70 chaperones work ?
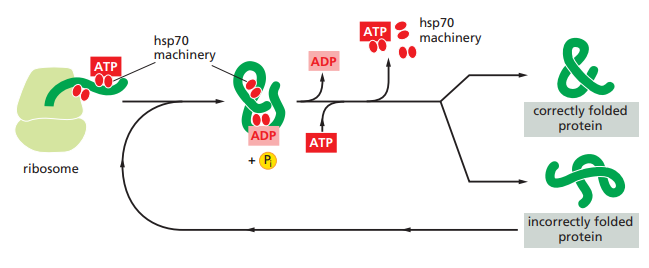
How do Hsp60 chaperones work ?
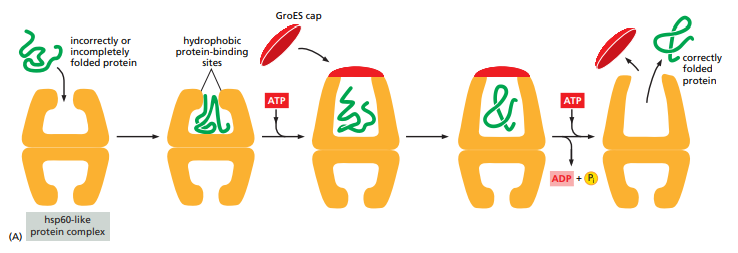
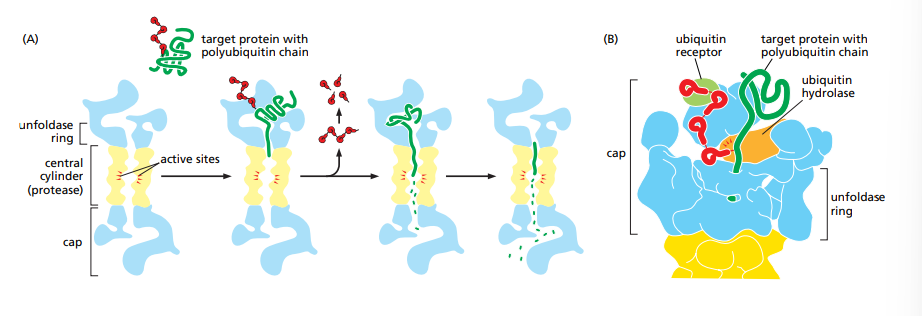
What do proteasomes do ?
They are large protein complexes that destroy aberrant proteins. As the protein is unfolded and move through the cap, they are exposed to the proteases in the central cylinder and destroyed. These proteins are marked for destruction by the covalently attached molecule called ubiquitin.
What are the possibilities for proteins after they are synthesized ?
Correctly folded protein without help and ready to use.
Correctly folded protein with the help of chaperones and ready to use.
Incompletely folded and digested by proteosome.
If nothing works, protein aggregate forms.