vectors and libraries
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Why couldn’t scientists purify genes like they did proteins?
They purified proteins by charge and size, but dna is made up of a c t and g which are very similar in terms of size and charge. Genes are also in chromosomes, which break super randomly and easily often in the middle of genes.
How did they purify individual genes?
By inserting dna fragments of interest into vectors, then cloning the vectors by replicating the bacteria
What is the vector type used in Waksman
Plasmid
What is the name of the plasmid used in Waksman
pTriplEx2
How did they insert the gene of interest into ptripleex2 (digest then ligate)
They used restriction enzymes (sfil) to cleave both the insert and vectors at a (sfila and sfilb sites)
Then added dna Ligase to Ligate the insert and vector
How did they transform and amolify
When a bacteria replicates, its plasmid is replicated regardless if it is its own dna.
Plasmid structure of manmade ones
Origin of replication (pUC ori) the replication proteins in bacteria bind to ori, and initiate replication of plasmid.
Selection marker (ampr and lacz genes) that encode proteins that allow us to see which bacteria have the plasmid
Cloning site (MCS) which is a stretch of dna between the lacz gene, acting as a site to put our insert and disrupt the lacz gene.
Why can’t plasmids be directly put into the bacteria?
Plasmid dna has a negative charge (phosphate in backbone) and repels the negative charge of the bacteria membrane (phosphate group in phospholipids)
How do we make bacteria more permeable to plasmids
Treat it with cacl2, and the ca2+ will bind to the membrane and make it more positively charged, allowing it to attract to the plasmid
How do u identify the cells with the plasmid?
The ampr gene makes it immune to ampicillin, so the ones w plasmid will live and grow.
How do u identify cells w the insert
If an insert is present in the mcs, the lacz gene will be distrupted. The lacz gene usually codes for beta galactosidase enzyme which cleaves the substrate xgal (present on agar), leaving the substrate blue. If disrupted, the lacz gene will code for a truncated beta galactosidase enzyme, and therefore the xgal will stay intact and be white.
Landolita punctata
Duckweed, the goal of Waksman is to identify expressed genes in duckweed.
DNA library
A random collection of dna fragments from an organism with ideally one copy of every dna sequence
The dna fragments in libraries are cloned into vectors
They are easily maintained in a lab
Can be manipulated to isolate dna fragments of interest (just isolate plasmid with the fragment)
Genomic library
Contains all randomly generated dna fragments from genome: all genetic material, coding and noncoding, promoters, introns, intergenic
cDNA library
Contains only expressed dna that codes for proteins
Cdna is complimentary dna (copy of mRNA in the form of dna)
U can’t use mRNA as libraries because they are single stranded, unstable, and cannot clone and are difficult to sequence.
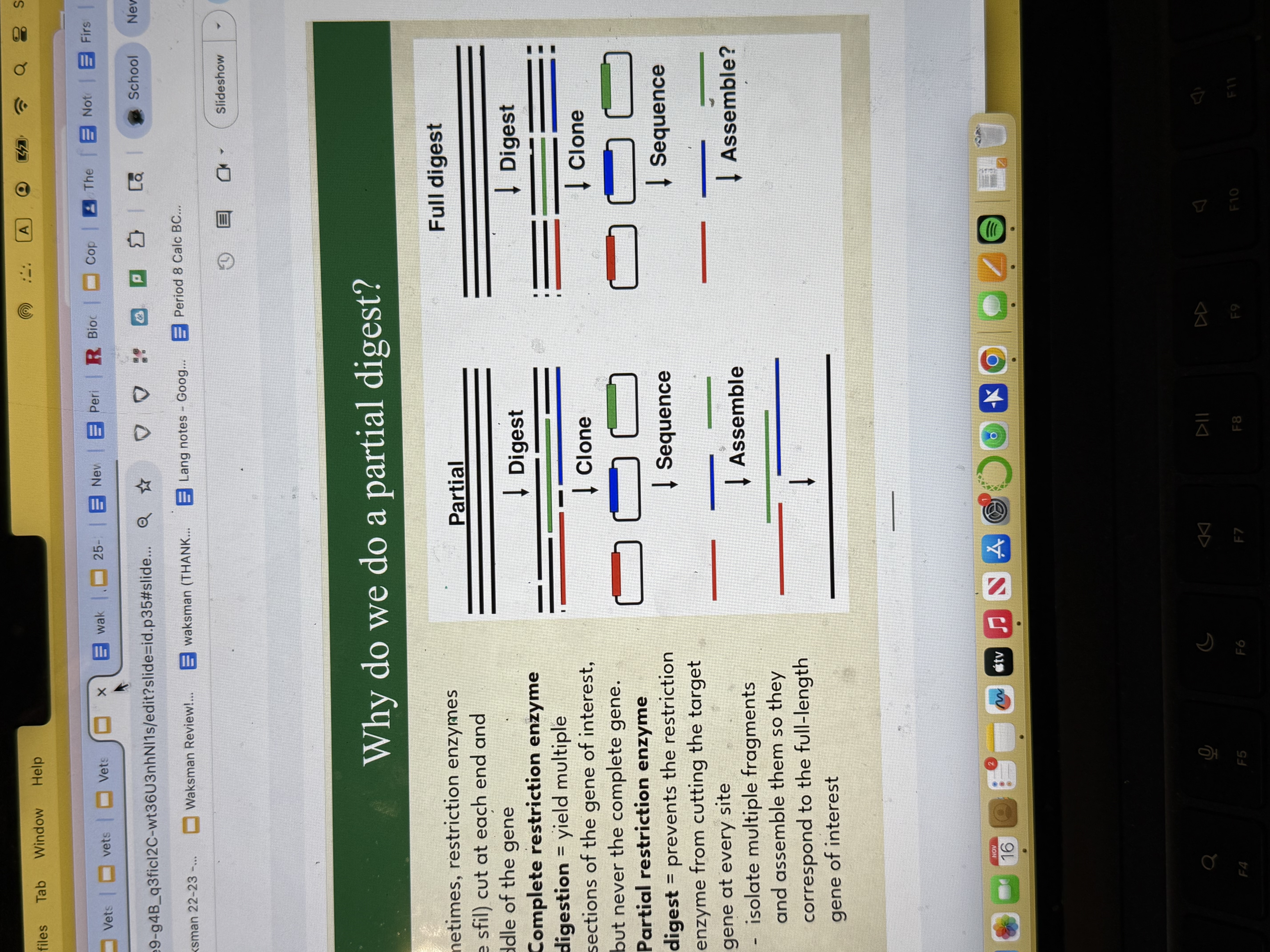
Partial digest
Partial restriction enzyme digest prevents the enzyme from cutting the target gene at every site, then u isolate multiple fragments that may have overlap so u can get the full gene.
Isolate the rna
Freeze cells in liquid nitrogen, grind using a mortar to release cell contents, centrifuge to pellet debris, use ethanol and licl To precipitate rnas
Purify the mRNA
Pass the rna over an oligo dT column, the poly a tails in mRNA will hybridize the mRNA to the column, then wash away the unwanted rna, then elite the mRNA to get pure mRNA
Reverse transcribe mRNA
Use reverse transcriptase, uses the T tail as a primer, synthesizes complimentary dna strand, then adds c to very end through terminal transferase activity, results in dna rna hybrid
Remove rna from rna dna hybrids
Add a strong base like Naoh to hydroloze the rna strand (it’s more susceptible than dna due to its OH at 2 prime carbon)
Perform second strand dna synthesis
Anneal oligonucleotide to the string of c at end of dna, dna polymerase uses that to synthesize dna
Ligate double strand cdna into pTriplEx2 vector
Use sfil to cut vector and cdna, cdna allows the plasmid to circularize
Transform bacteria
Add cacl2 to bacteria, add to plasmids, then incubate to let them in. Place bacteria in lb agar to replicate ( then use selectable markers to choose colonies)