lecture 12 until second order isomorphism
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Object, spatial
The old model states that there is a separation between the ventra, and dorsal pathways. However, neuron aging evidence show that sims oars in the dorsal can decode the ___ while some part in the ventra, can decode ___ info.
Cortical region, how many fibers, bidirectional,
When you see boxes and connections, the bigger the boxes, the bigger the ___. Thickness indicates ___ are connected, lines are ___: there is info going from V 1 to V4 but also feedback processes doing the opposite.
Non linear, circular
Cells in V4 respond to ___ shapes. Ex: ___ shapes.
V1, IT
V4 seems to be the intermediate step between ___ and ___
posterior IT , inferior temporal lobe
After V4, info goes from the ___ to the ___.
Object parts, shape, full, specificity
Posterior IT responds best to ___. It integrates multiple ___ features but not the ___ object. Not far from the IT, some regions will show ___. There, you will need the full complete object.
Lateral occipital cortex, LOC, objects
The ___ (___): the first area with specificity after V4. It seems this region responds more to ___. It integrates information into a coherent whole, even when color or texture properties are removed, it will respond to the object.
Invariant representations, general shape
How do you call representations that do not depend on the viewpoint ? It seems the LOC responds to these. It doesn’t respond to a specific image but to the ___ of an object.
V4, PIT, IT, PPA, FFA
The LOC is important because it bridges mid level feature processing (___, ___) with high level object recognition (___ cortex, ___, ___). It also provides whole object representations, making it a key step in the ___ visual stream. It is a major hub for object recognition.
Fusiform gyrus, ventral temporal, right, invariance, prosopagnosia
The fuse form face area is located in the ___ of the ___ lobe in the ___ hemisphere. Category selectivity: highly tuned to faces. Up ut also responds to expert level recognition. More of an expertise area. It is not exactly category selective but more category preferential. It also shows ___ to face recognition. Damage to it is linked to ___.
Spatial layout
The parahippocampal place area: responds to the visual environment. Highlights the important of ___ scene perception.
A
These areas do this. Please look at the table. Answer is a
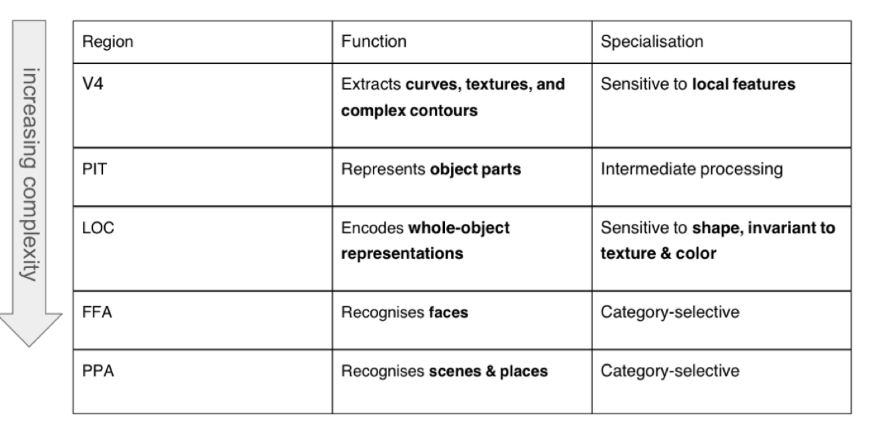
Smaller, bigger, fusiform gyrus
If you take real world sized objects and you contrast using invariant analysis, you see a division between ___ and ___ objects, the area that processes that is not far from the ___. Also extends to the dorsal part, providing evidence that the dorsal pathways is more than simply for spatial location.
IT, invariance, abstract, sensory, rotate
Many ___ neurons demonstrate ___, meaning they continue to respond to an object regardless of its size, position, or viewpoint. This suggest that these neurons encode more ___ representations of objects rather than raw ___ features. You can ___ the object and the neurons will still fire. But if you rotate it too much, they won’t recognize it.
Unseen
You can train a computer model to recognize the brain pattern activity associated with each object category, then you can show it a brain scanning of another source and ask if can still recognize to see if it learned. Text the model to see if it can correctly identify an ___ image based on learned brain activity patterns
New unseen, estimation, identification
Once trained, encoding models can predict responses to ___, ___ stimuli. Voxelized models ? Step 1: model ___. Step 2: image ___.
Similar
Second order isomorphism: similar objects in the world must have ¥_¥ representations in the mind.