Lecture 23 - Secondary Cancers in RT patients and Heritable Effects of Radiation
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ONCOL 335 - Radiobiology. University of Alberta
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
what are secondary malignancies?
new cancers that occur in individuals as a result of previous treatment
not a relapse of the first cancer
what is the most common secondary cancer after radiation treatment?
skin cancers
in order to estimate the risk of secondary cancers, what is needed?
the general risk in the population due to background radiation
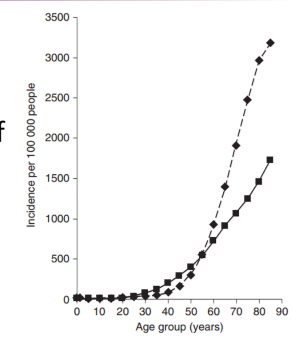
what does this graph tell us?
Most cancers arise later in life
- Women rises earlier, men increases later
Prostate cancer appears later in life than breast cancer
the longer the patient lives after radiation therapy …
the higher the risk of getting a secondary cancer
the cure for the first cancer causes the second cancer
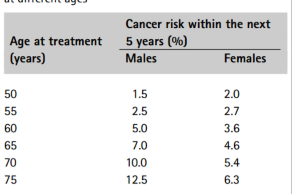
what three factors increse risk of secondary cancers
age
genetic predisposition
carcinogen exposure
why is it hard to estimate risk of secondary cancers from radiation therapy?
due to genetics and carcinogen exposure
what two cancers occur as a result in Rb mutation
retinoblastoma
osteosarcoma
what two cancers occur as a result of BRCA1 mutations
breast cancer
ovarian cancer
what types of secondary cancers do chemotherapies mostly lead to?
leukemias
especially AML
what type of secondary cancers does radiation therapy mostly lead to?
solid cancers
what is relative risk
the risk comparing the number of persons in exposed population showing a late effect against the number of persons who develop the same effect in an unexposed population
how is relative risk calculated
RR = observed cases/expected cases

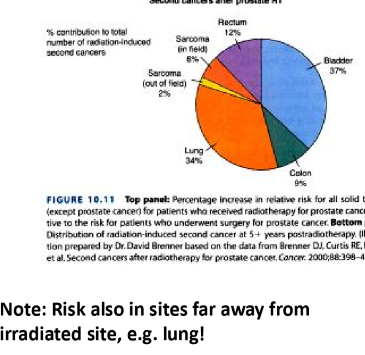
which two organs are most likely to gain a secondary cancer after radiation therapy to the prostate
bladder and then lung
how does the relative risk of secondary cancers increase after RT to prostate
increases over time
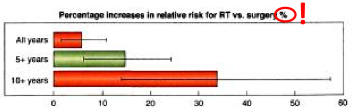
how does the risk for sarcomas near the treatment field increase after RT to the prostate
increases vastly over time
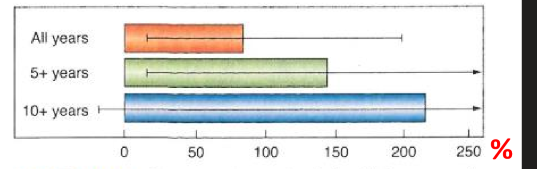
what is a sarcoma
A type of cancer that arises from connective tissues such as bones, fat, muscles, and cartilage.
what is a carcinoma
a type of cancer that originates in the epithelial cells, which line the surfaces of organs and structures throughout the body.
what organs show an increase in secondary cancers after radiation therapy to cervix
surprisingly, not many showed an increased risk, even close organs
what percent of the target dose is received by the contralateral breast (without cancer)
5%
where do secondary cancers occur after radiation therapy in breast cancer
on the other breast!
not sure why
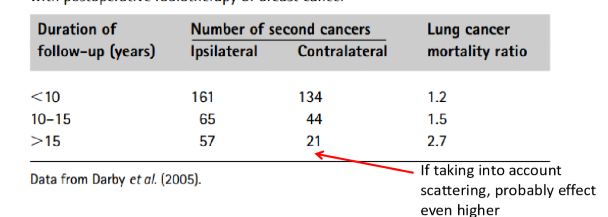
what two secondary tumors occur in children after treatment for leukemia
meningioma
glioma
what age group is most sensitive to radiation induced carcinogenesis
patients receiving radiation during puberty
increases triple negative breast cancers in women
for most elderly patients risks of radiation are far outweighted by the risk of ….
recurrence
more than 90% of secondary cancers occurring after radiotherapy are the consequence of what?
increased life expectancy because of cure from the first cancer
secondary cancers key points
how long does it take to go from spermatogonia to spermatozoa
around 10 weeks in humans
differences in gonadal kinetics between men and women
refers to the varying rates and timelines of development and maturation of gametes, with men producing sperm continuously while women have a finite number of eggs developed over a lifetime.

what dose causes permanent sterility in men
6 Gy single dose
2.5-3 Gy fractionated
what dose causes permanent sterility in prepubescent females
12 Gy
what dose causes permanent sterility in premenopausal females
2 Gy
how does radiation effect hormone balance in men
no effect, doesnt change hormone balance, libido, and physical capability in men
how does radiation effect hormone balance in women
produces hormonal changes like those seen in menopause
what are heritable effects
adverse health effects due to mutations in germ cells
does radiation produce new heritable effects?
no, but it increases the indicence of the same effects that occur spontaneously
where does information on genetic effects by irradiation come from?
animal studies
what do Hermann Muller prove?
a quantitative connection between radiation and mutations on fruit flies
observed changes in eye color, wings, lethality
what are the three categories heritable effects can be classified as
mendelian effects
chromosomal effects
multifactorial effects
mendelian effects
caused by mutations on single genes on the autosomes or sex chromosomes
chromosomal effects
caused by gross abnormalities in either the architecture or number of chromosomes
multifactorial effects
disease known to have a genetic component but whose transmission pattern cannot be described as mendelian
examples of mendelian effects
‘dominant, recessive, or sex-linked’ diseases
Huntington’s disease (dominant)
sickle cell anemia (recessive)
hemophilia (sex-linked male)
examples of chromosomal effects
abnormal number or aberrations of chromosomes
downsyndrome (trisomy 21)
embryonic death
examples of multifactorial diseases
manifestation at birth or chronic disease with late onset
cleft lip (manifestation at birth)
diabetes
mutate vs. mutant
mutate = gained through external means, not inherent at birth
mutant = genetic mutation inherent at birth
what is the radiation doubling dose
the amount of radiaion required to produce twice as many mutations that occur spontaneously in a generation
what is the relative mutation risk
relative mutation risk per unit dose
reciprocal of doubling dose
low relative mutation risk implies a ____ doubling dose
high
what was the megamouse project
a project used to determine mutation rates in mice under various irradiation conditions
three conclusions of megamouse project
Different mutations have different radiosensitivity.
Dose rate effect reduces mutation risk if exposure is spread out.
Longer gap between radiation exposure and conception reduces genetic risk.
estimated doubling dose time from A bomb survivors
1.56 Sv

what are epigenetics
gene expression with DNA sequence alterations
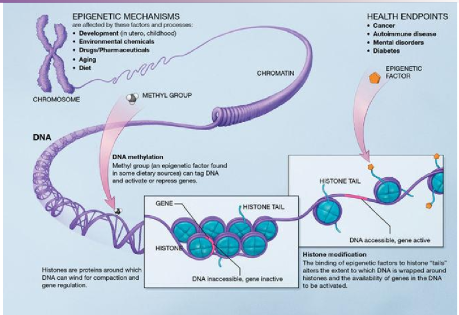
what is imprinting
certain genes are expressed are only expressed from one parent’s allele
if father’s genes are imprinted, only mother’s allele is expressed
rare in mammals
diseases caused by epigenetics
cancer
schizophrenia
angelman syndrome
prader-willi syndrome