COMP GRAPHICS MIDTERMS
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
coordinate system
is defined by an origin point and the orientation and scale of a set of coordinate axes.
point 𝒑 = (𝒙, 𝒚)
refers to a location in space, specified relative to a coordinate system.
vector 𝒗 = 〈𝒎, 𝒏〉
refers to a displacement
are not associated with any particular location in space
may exist at different locations
displacement
an amount of change in each coordinate—and is typically drawn as an arrow pointing along the direction of displacement
Initial point or tail
the point where the arrow begins
Terminal point or head
the point where the arrow ends; indicates the result when the displacement has been applied to the initial point
Length or magnitude
the distance between the initial and terminal points of the vector; can be calculated from the components of the vector.
standard position.
A vector whose initial point is located at the origin (when a coordinate system is specified)
scalars
Individual numbers (that are not part of a point or vector)
matrix
a rectangular array of values called elements that are typically accessed by means of subscripts.
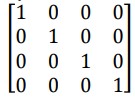
identity matrix
contains all zeros, with ones along the diagonal. Any point or matrix multiplied by the identity matrix is unchanged
transpose
matrix is computed by interchanging its rows and columns.
scalar multiplication.
multiply a scalar by each element of the matrix using the dot operator.
geometric transformation
refers to a change applied to an object in terms of size, orientation, or position.
Scaling
The object’s dimensions are either expanded or compressed to change its size.
Translation
The object is moved to another position or location on the screen.
Rotation
The object is moved around a fixed point at a given angle
2D rotation
a rotation transformation rotates vectors around the origin point
3D rotation
rotations are performed around a line rather than a point.
scaling factor
is used to determine whether the size of an object will be increased or reduced.
translation vector
also called a shift vector,
defines the distance to move an object’s coordinate
frustum or truncated pyramid
In a perspective projection, the shape of the viewable region is called _______ .
near and far distances
The shape of a frustum is defined by four (4) parameters
refer to distances from the viewer (along the z-axis).
These two set absolute bounds on what could potentially be seen by the viewer.
Any points beyond this range will not be rendered.
However, not everything between these bounds will be visible.
larger angles of view correspond to larger frustums.
angle of view
The shape of a frustum is defined by four (4) parameters
measures how much of the scene is visible to the viewer.
It is defined as the angle between the top and bottom planes of the frustum
aspect ratio
The shape of a frustum is defined by four (4) parameters
defined as width divided by height
is used to specify the shape of the frustum
projection window
a flat rectangular region in space corresponding to the rendered image that will be displayed on the computer screen