electromagnetic induction.
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is electromagnetic induction?
The process of generating an emf in a conductor by changing the magnetic field around it.
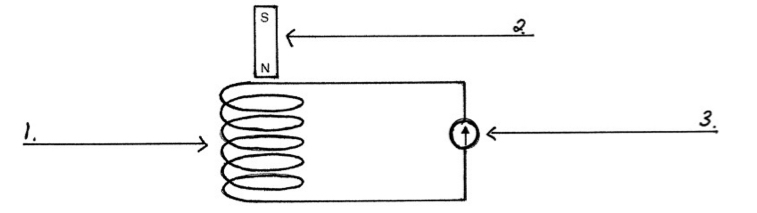
Demonstration of electromagnetic induction:
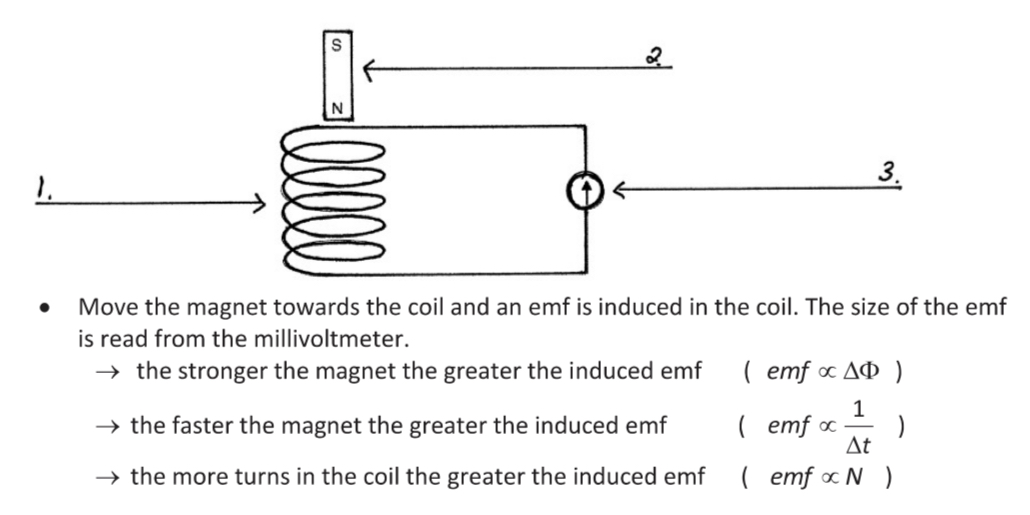
Move the magnet towards or away from the coil or move the coil relative to the magnet The needle on the millivoltmeter will deflect indicating a voltage has been made.
The change in the magnetic flux passing through the coil made a voltage in the coil which caused a current to flow in the circuit.
Magnetic flux formula

Faradays law
If the magnetic flux lines passing through a circuit change then an emf is induced.
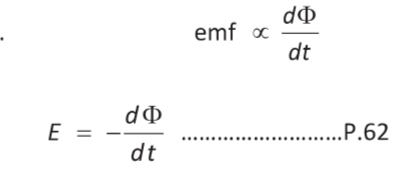
The induced electromotive force (EMF) is equal to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit.
Lenz’s Law
The induced EMF will generate a current whose magnetic field opposes the change in magnetic flux.
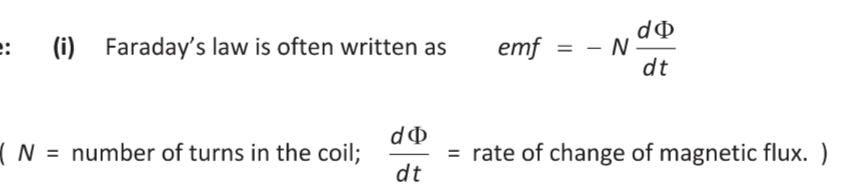
Demonstration of Faradays law:
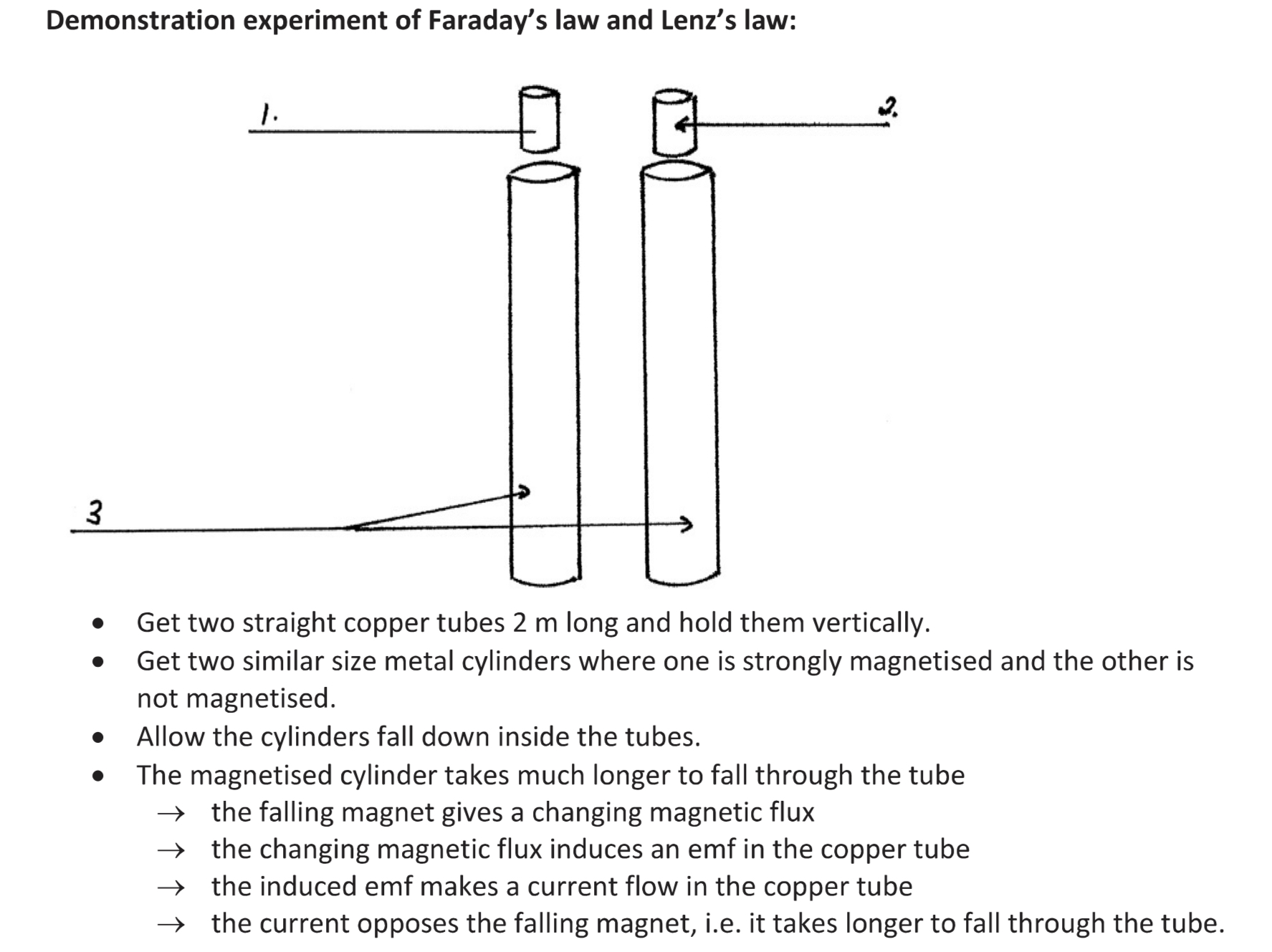
Demonstration of Lenz’s law.
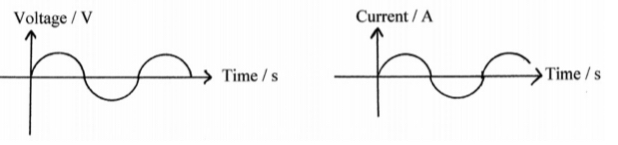
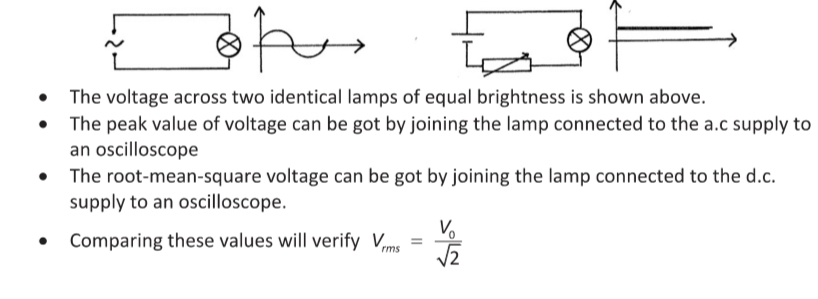
Magnitude of a.c. Current and Voltage
Both current and voltage start at 0, rises rapidly to a peak value then decreases to 0.
Direction changes and magnitude of current and voltage rises rapidly from 0 to a peak value and then decreases to 0. This process repeats while the current
Formula for the root mean voltage/current given the peak voltage/current.
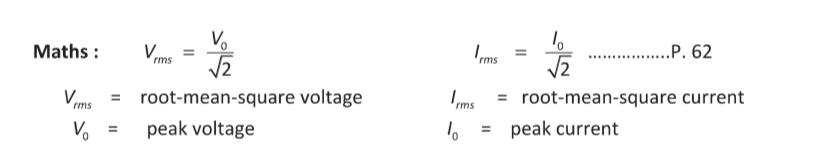
Demonstration experiment to show the relationship between a.c and d.c
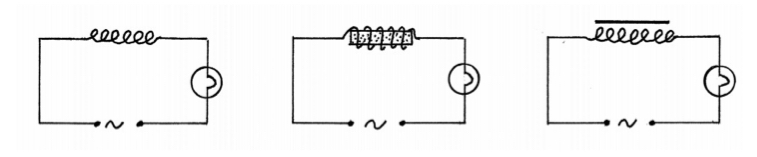
Self induction of an a.c. source.
With an a.c. source the current is constantly changing direction through the solenoid
This gives a changing magnetic flux in the region around the solenoidThis changing magnetic flux induces an emf (voltage ) in the same solenoid
This induced voltage opposes the voltage of the source resulting in a lower overall voltage
Resultant voltage = source voltage - induced voltage
A lower resultant voltage causes a smaller current to flow in the circuit, i.e. the bulb lights less brightly
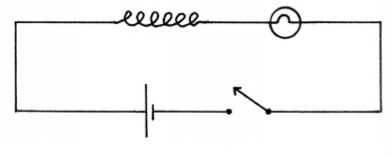
Self Induction of a d.c. source.
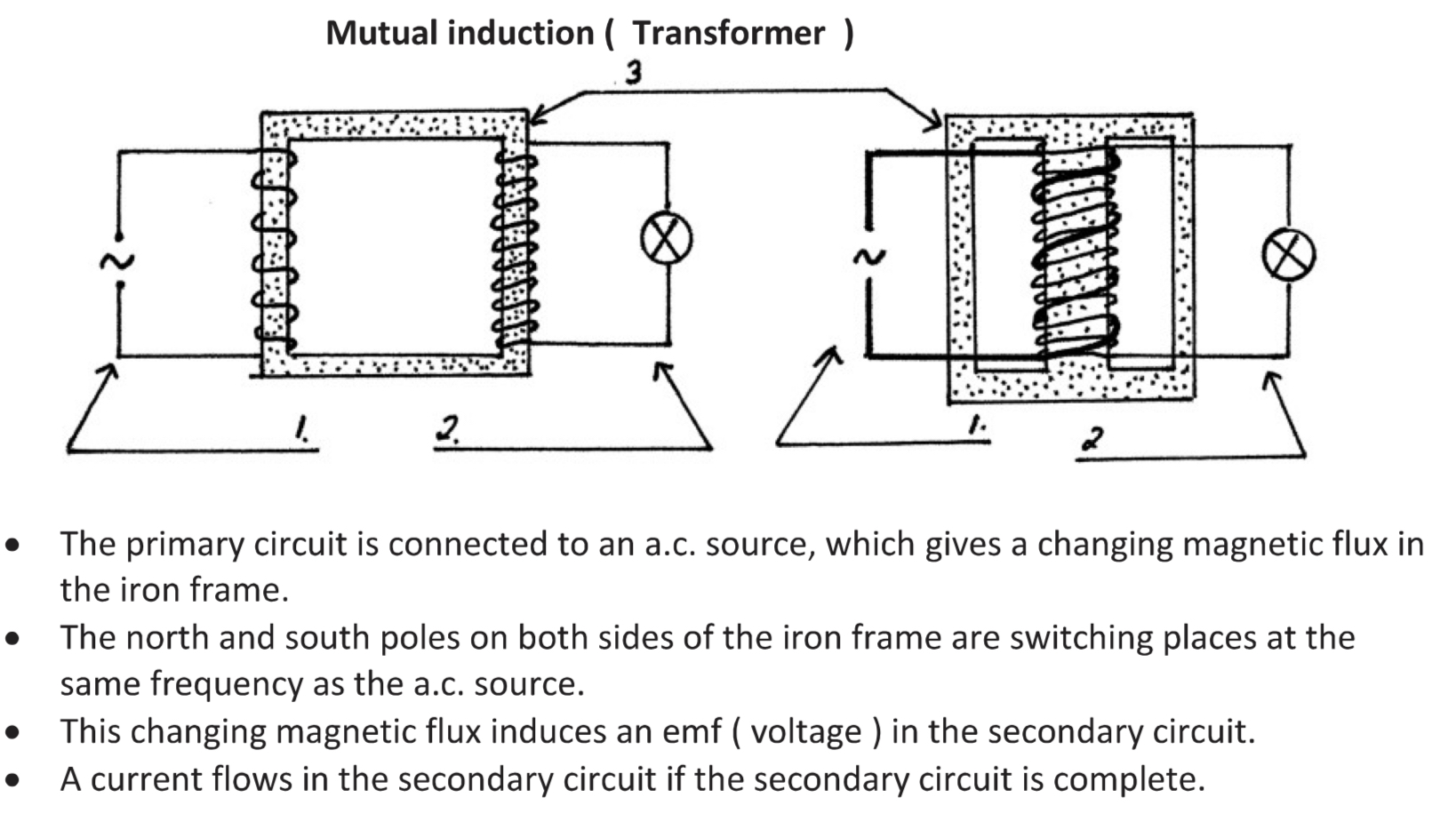
Mutual induction (transformer)