biochem quiz preparation
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
What are the three main functions of metabolism?
Conversion of energy in food to energy for cells, conversion of food to building blocks of macromolecules, elimination of metabolic waste
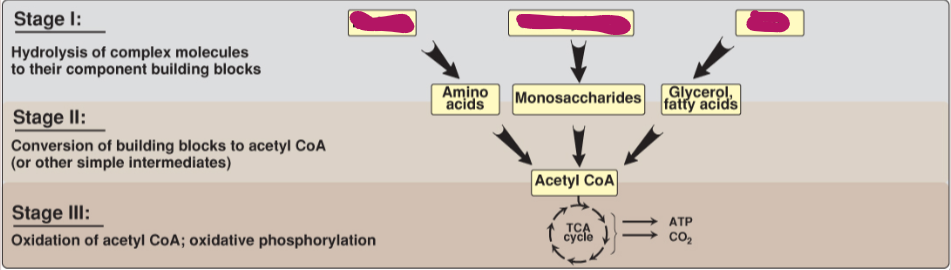
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
Proteins, carbohydrates, fats
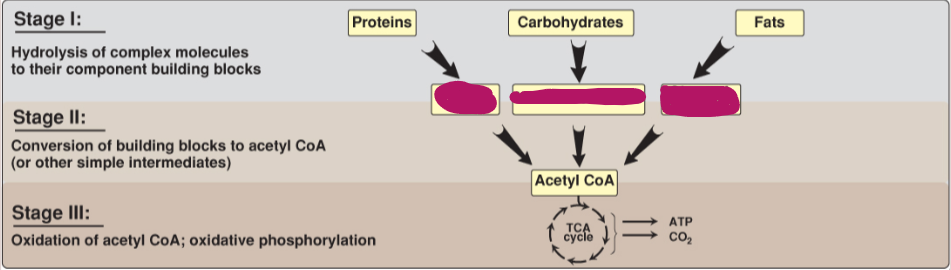
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
Amino acids, monosaccharides, glycerol and fatty acids
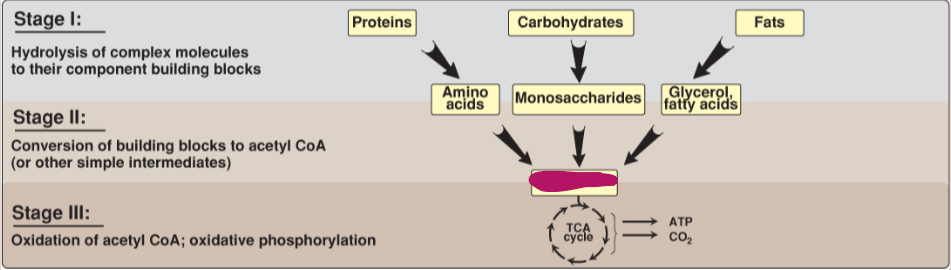
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
Acetyl CoA
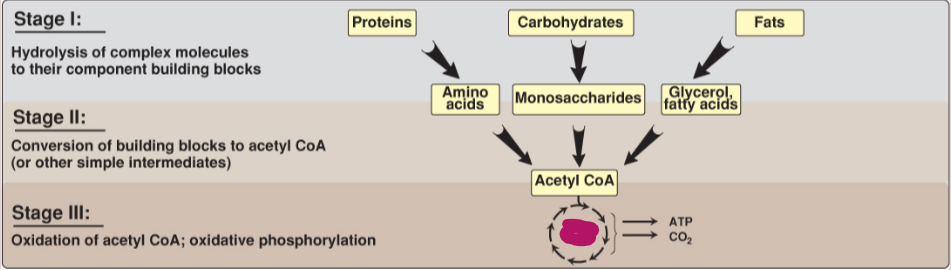
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
TCA cycle
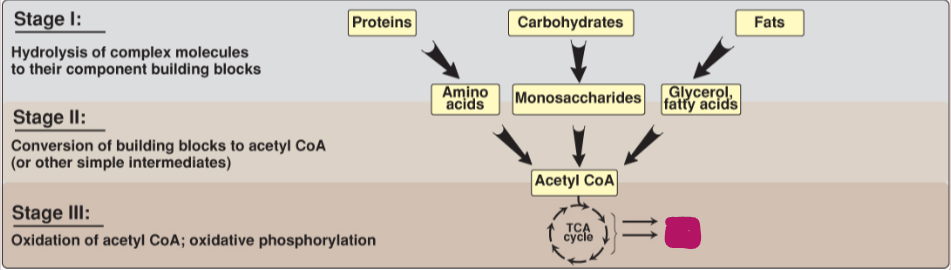
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
ATP and CO2
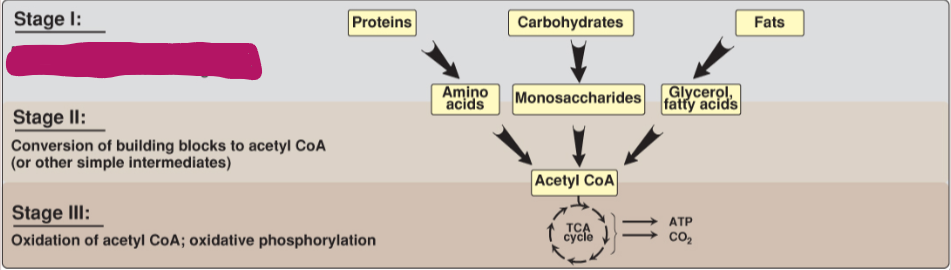
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
Hydrolysis of complex molecules to their component building blocks
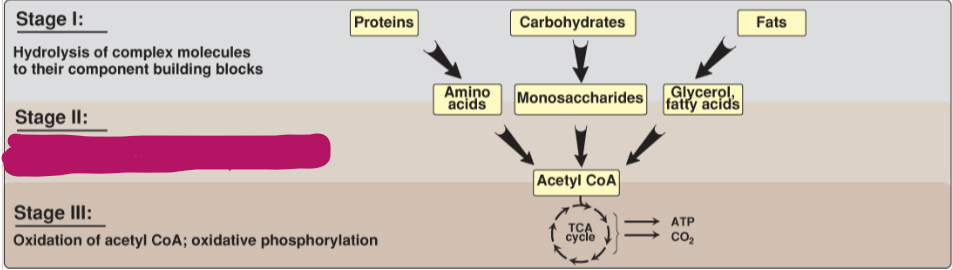
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
Conversion of building blocks to acetyl CoA or other simple intermediates
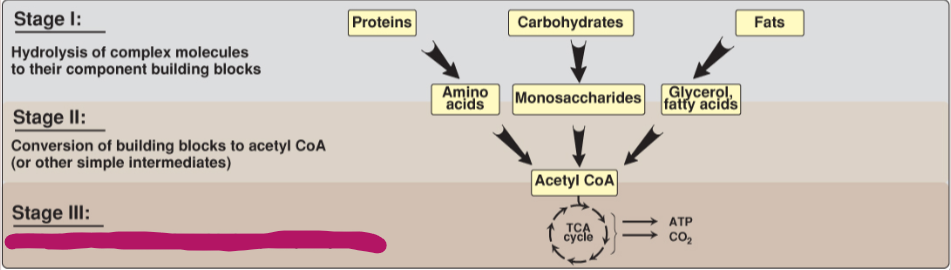
Fill in the stages of metabolism.
Oxidation of acetyl CoA; oxidative phosphorylation
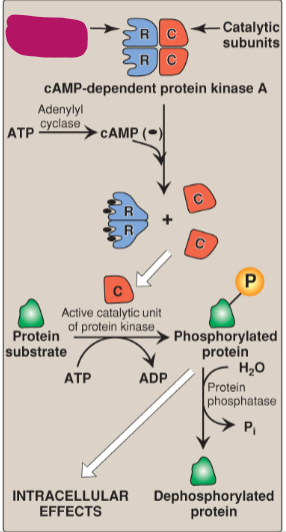
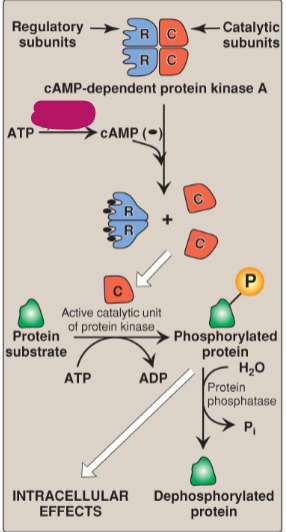
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Regulatory subunits
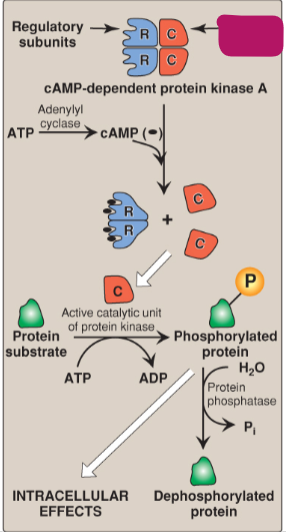
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Catalytic subunits
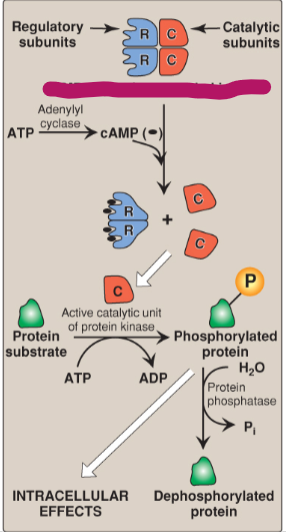
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
cAMP-dependent protein kinase A
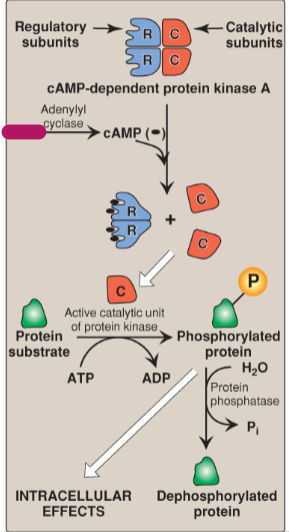
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
ATP
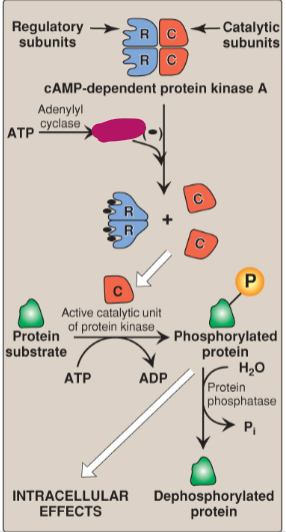
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Adenylyl cyclase
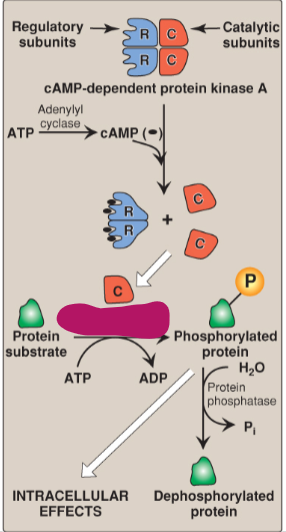
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
cAMP
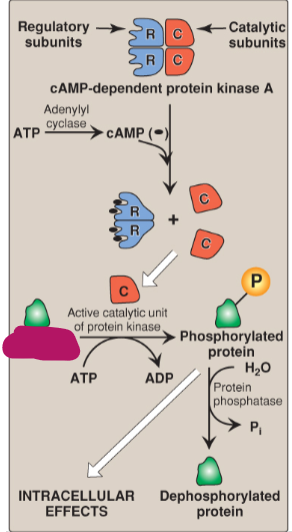
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Active catalytic unit of protein kinase
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Protein substrate
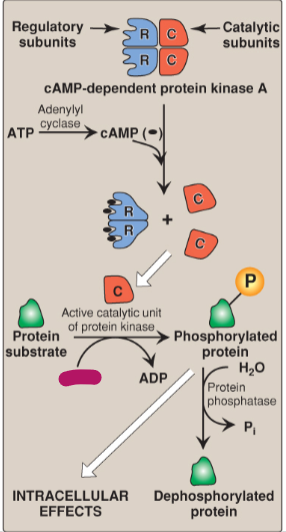
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
ATP
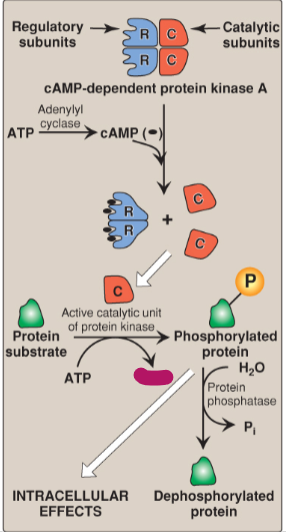
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
ADP
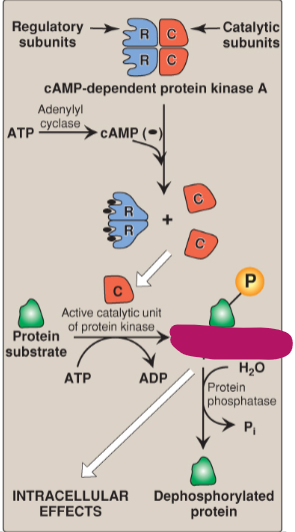
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Phosphorylated protein
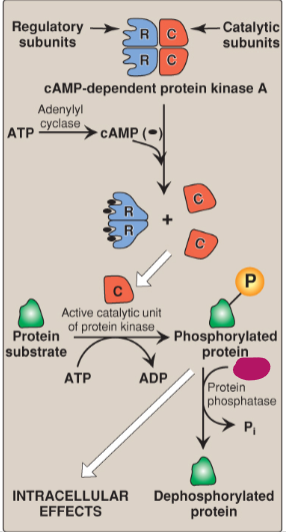
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
H2O
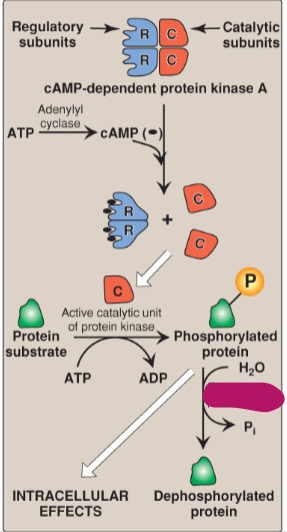
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Protein phosphatase
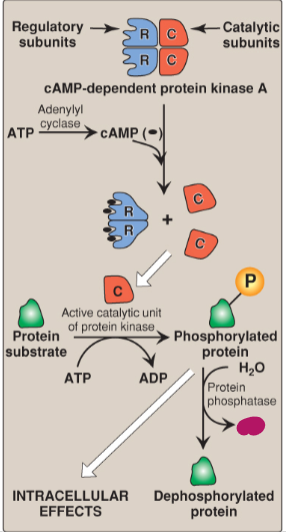
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Pi
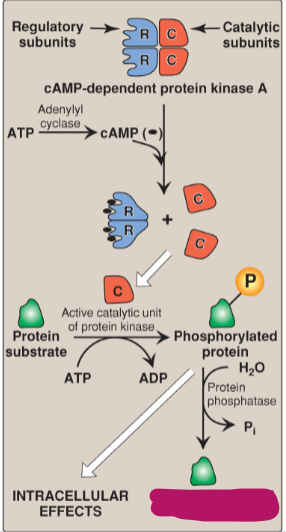
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Dephosphorylated protein
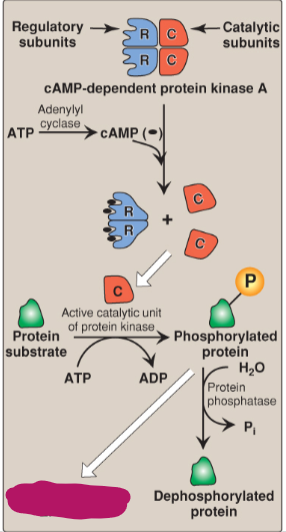
Label the actions of cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Intracellular effects
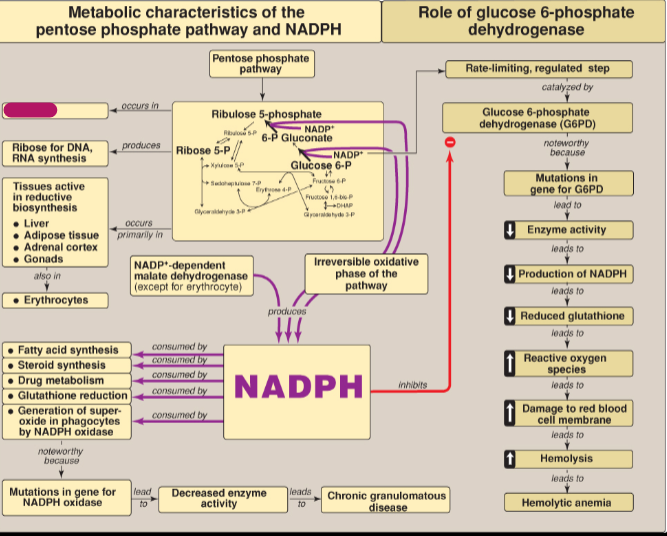
Where does the Pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) occur?
Cytosol
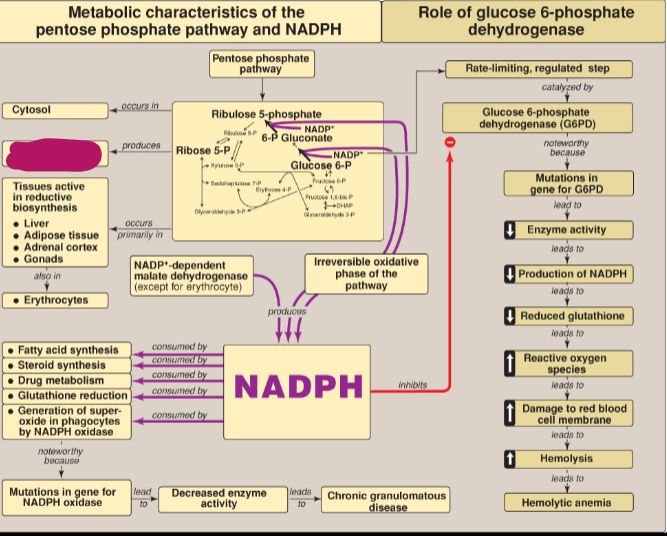
What does ribose 5-P produce?
Ribose for DNA and RNA synthesis
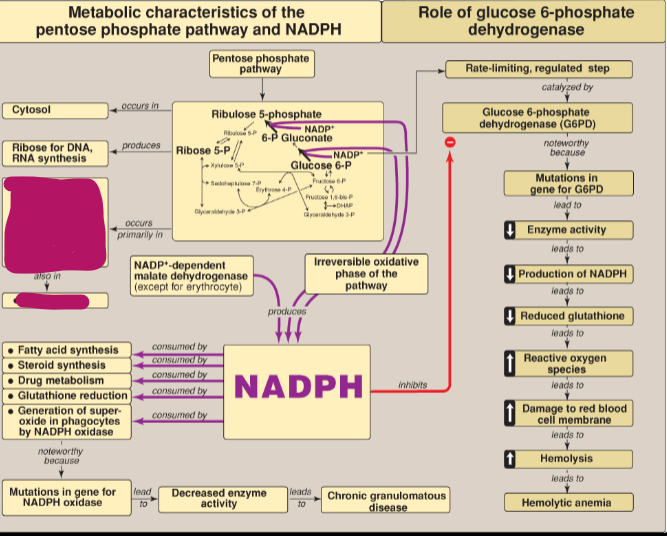
In what tissues does the PPP occur?
Tissues active in reductive biosynthesis: liver, adipose tissue, adrenal cortex, gonads, as well as erythrocytes
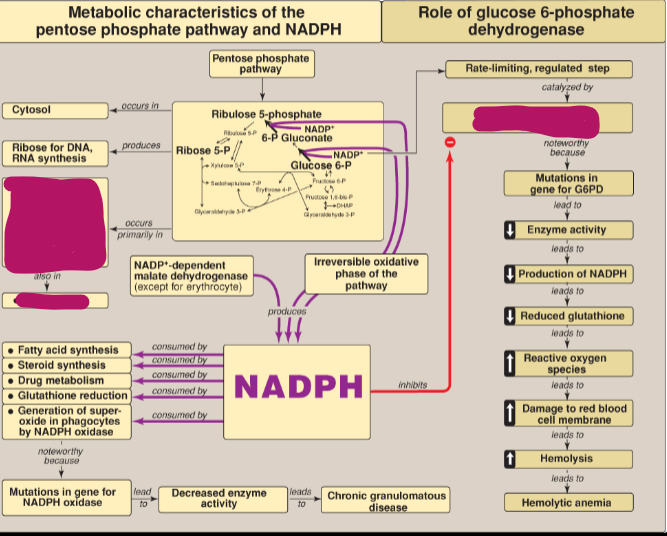
What does NADPH inhibit?
Glucose 6-P dehydrogenase
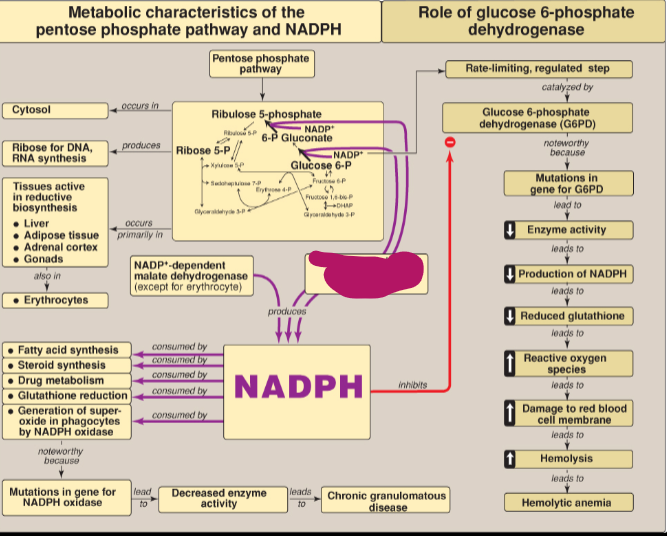
What step of the PPP produces NADPH?
Irreversible oxidative phase
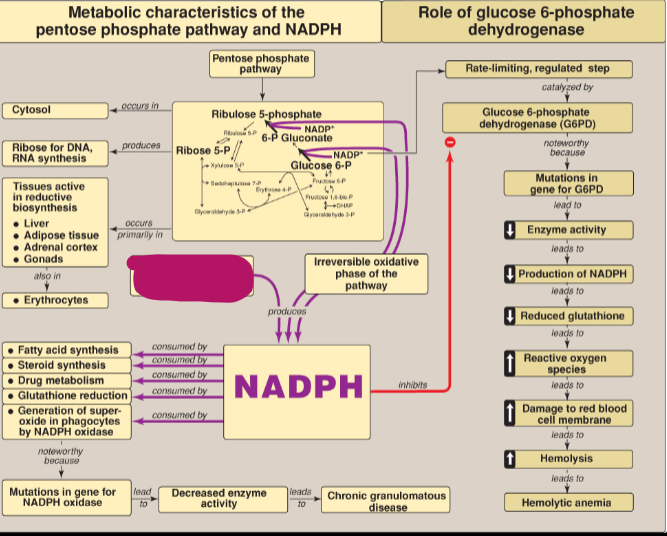
Other than the PPP, what else produces NADPH?
NADP+-dependent malate dehydrogenase (except for erythrocyte)
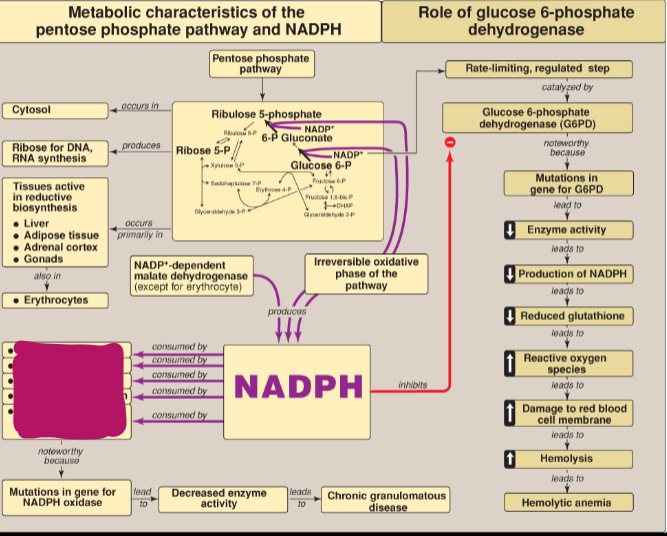
What consumes NADPH?
Fatty acid synthesis, steroid synthesis, drug metabolism, glutathione reduction, generation of superoxide in phagocytes by NADPH oxidase
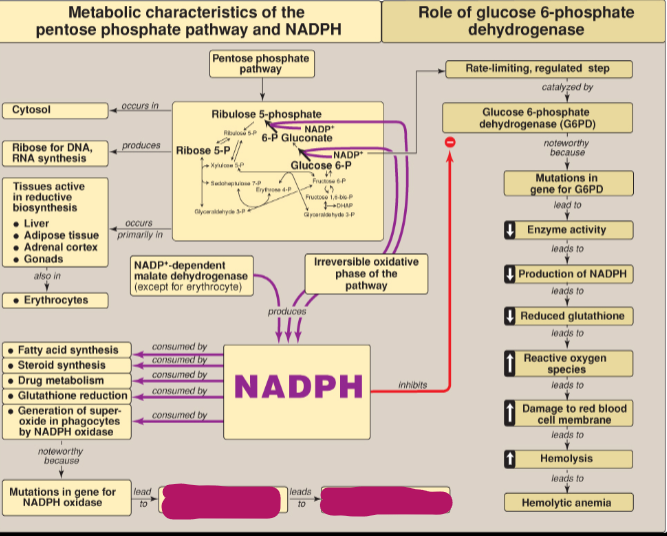
What happens as a result of mutations in the gene for NADPH oxidase?
Decreased enzyme activity which leads to chronic granulomatous disease
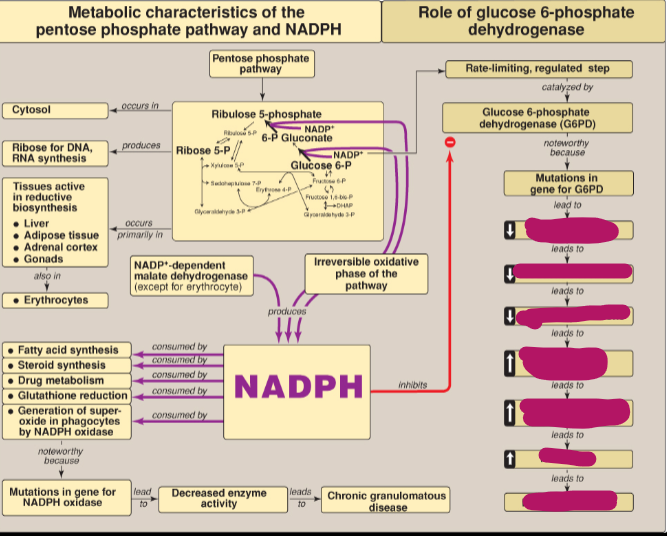
What happens as a result of mutations in the gene for G6PD?
Decreased enzyme activity, decreased production of NADPH, reduced glutathione, increased reactive oxygen species, which leads to damage to RBC membrane which causes hemolytic anemia
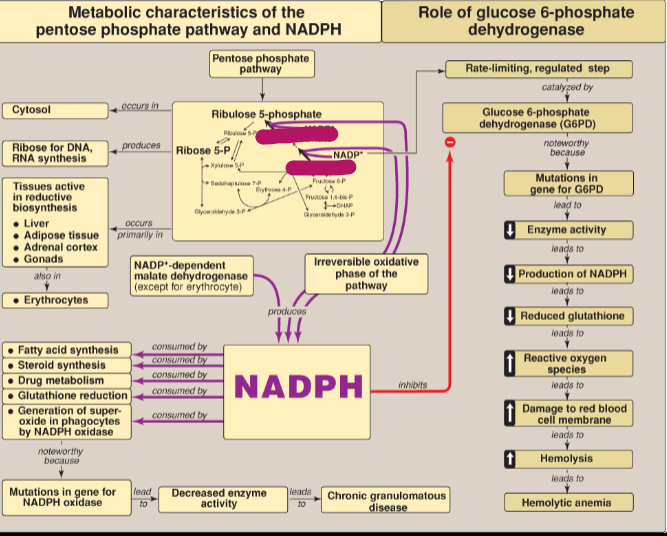
What is the rate-limiting step in the PPP?
Conversion of glucose 6-P to 6-P gluconate
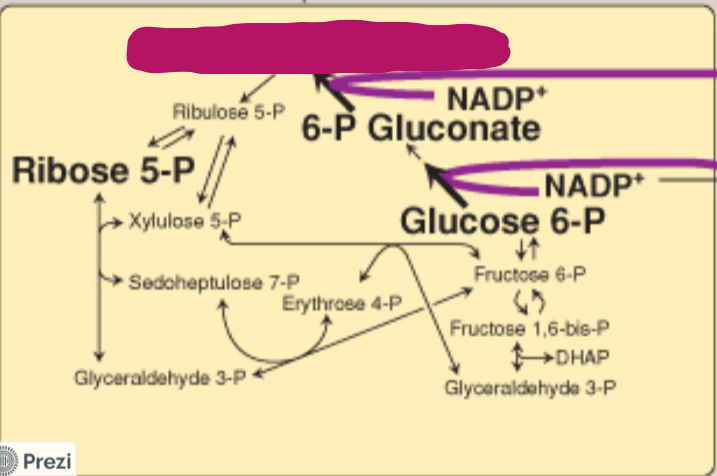
Label this step of the PPP.
Ribulose 5-phosphate
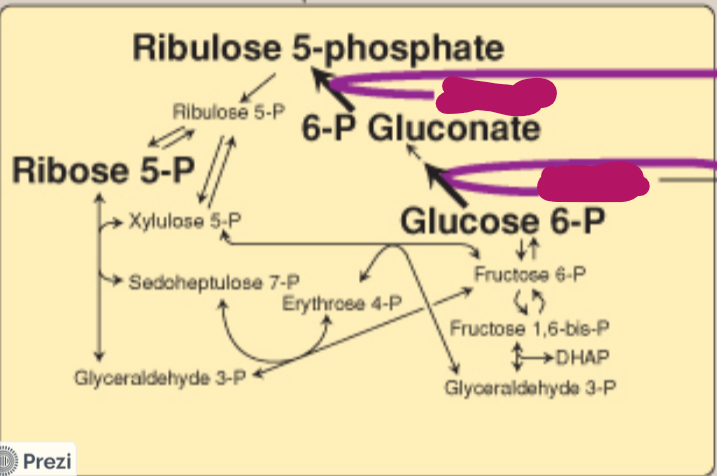
Label this step of the PPP.
NADP+
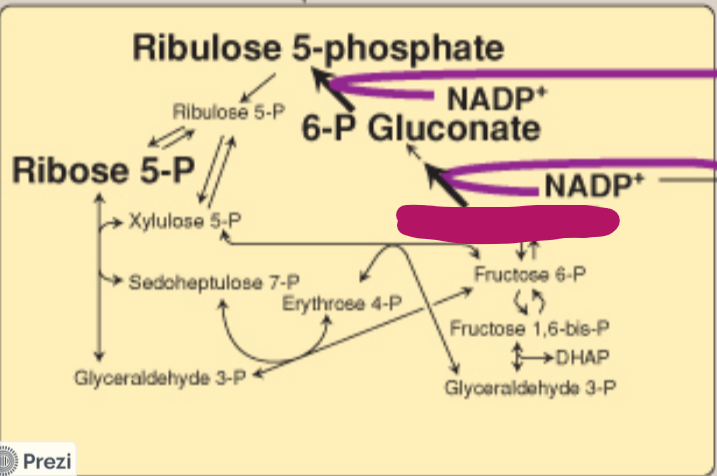
Label this step of the PPP.
Glucose 6-P
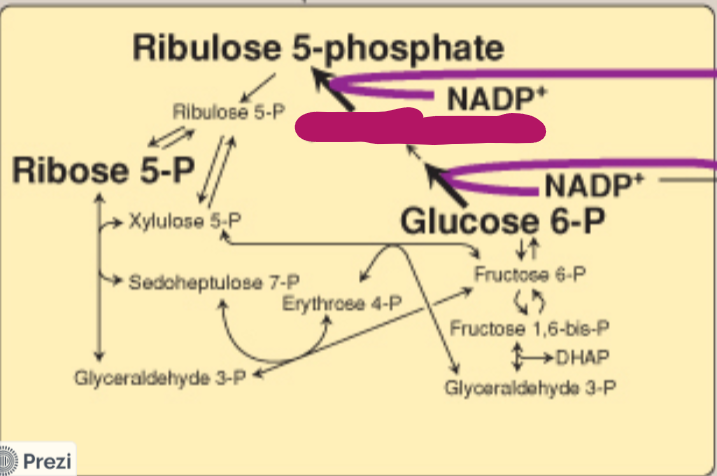
Label this step of the PPP.
6-P gluconate
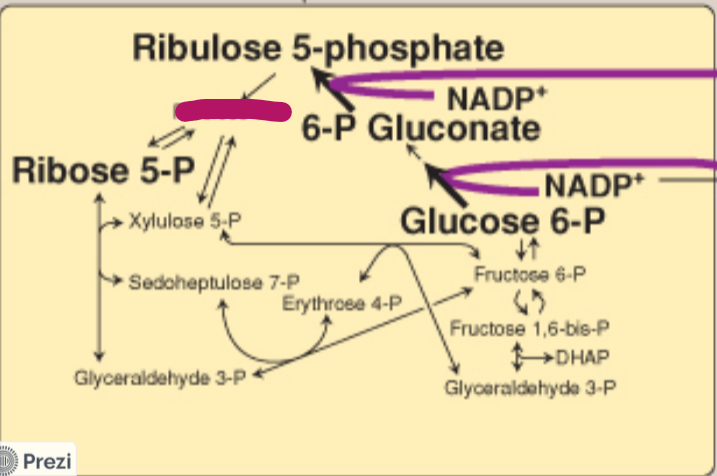
Label this step of the PPP.
Ribulose 5-P
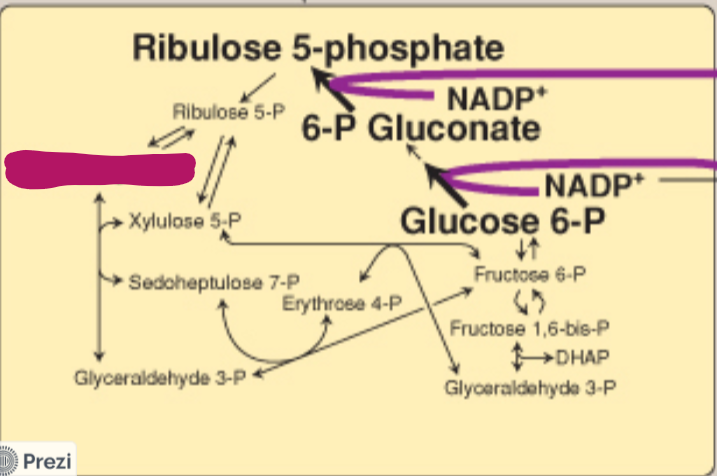
Label this step of the PPP.
Ribose 5-P
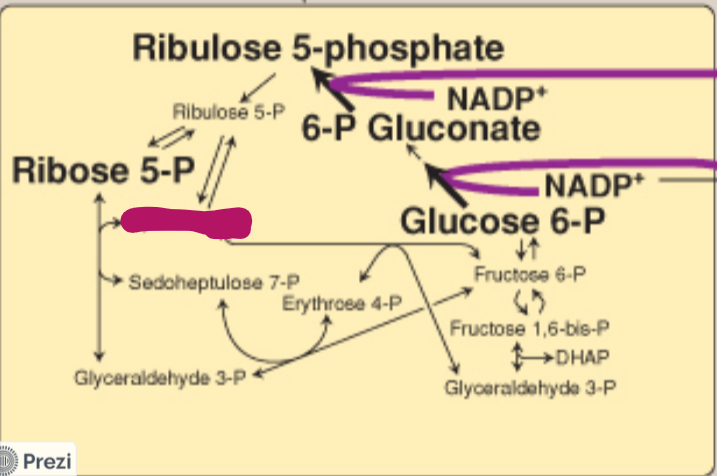
Label this step of the PPP.
Xylulose 5-P
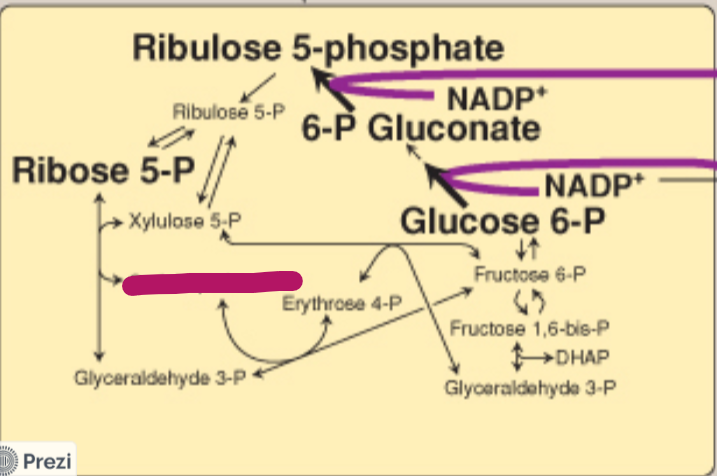
Label this step of the PPP.
Sedoheptulose 7-P
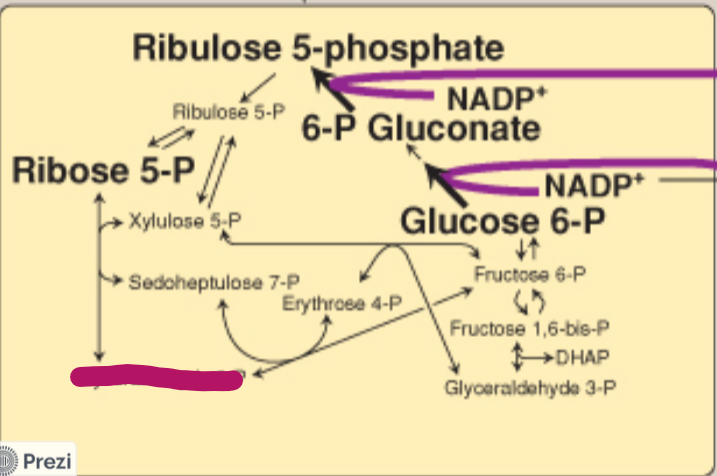
Label this step of the PPP.
Glyceraldehyde 3-P
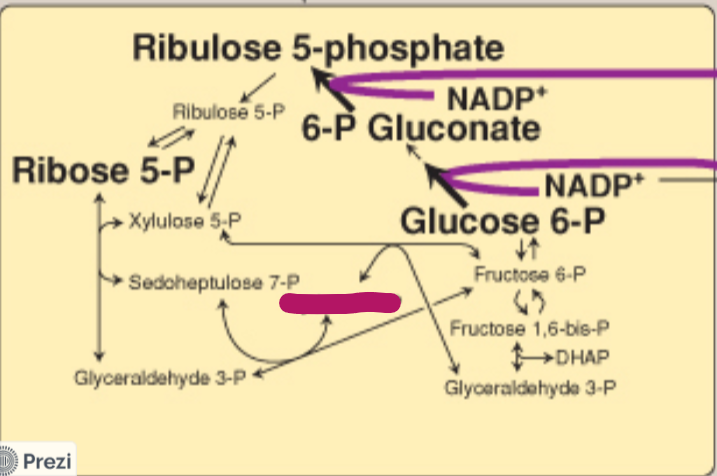
Label this step of the PPP.
Erythrose 4-P
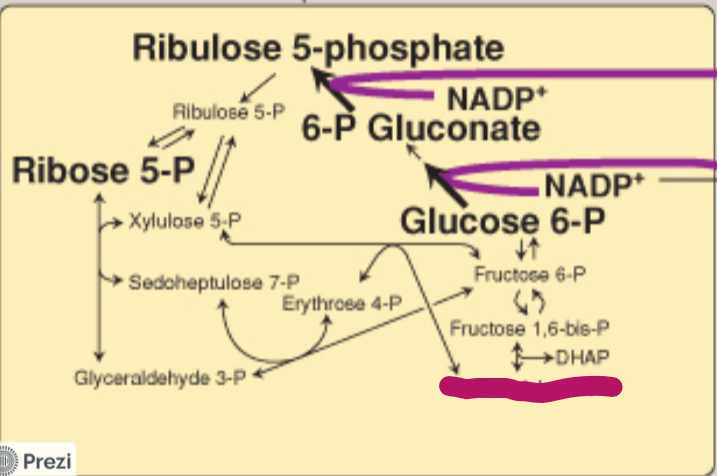
Label this step of the PPP.
Glyceraldehyde 3-P
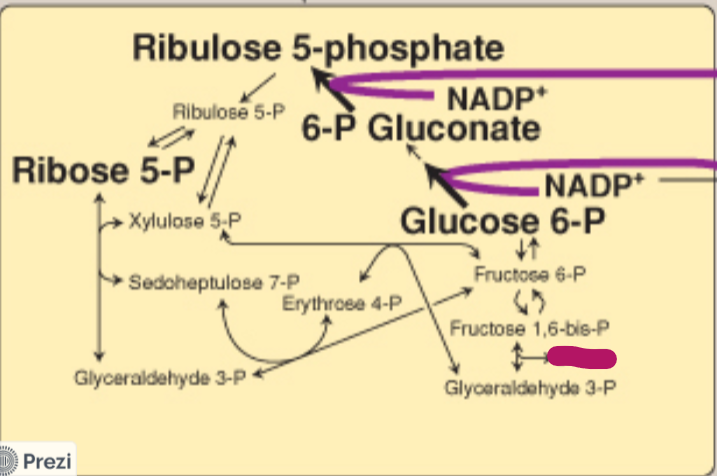
Label this step of the PPP.
DHAP
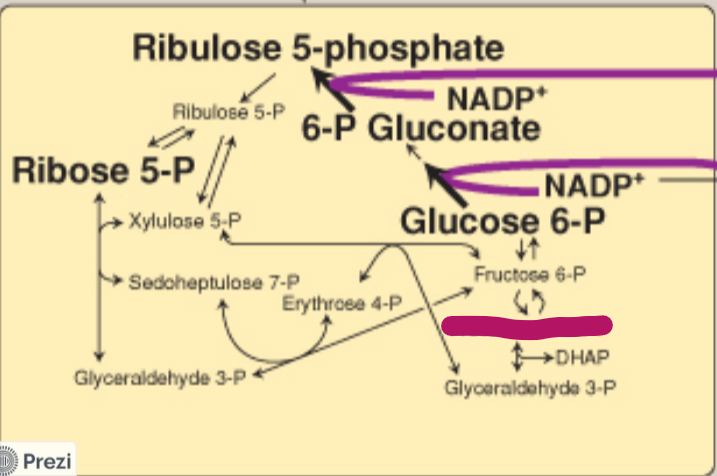
Label this step of the PPP.
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate
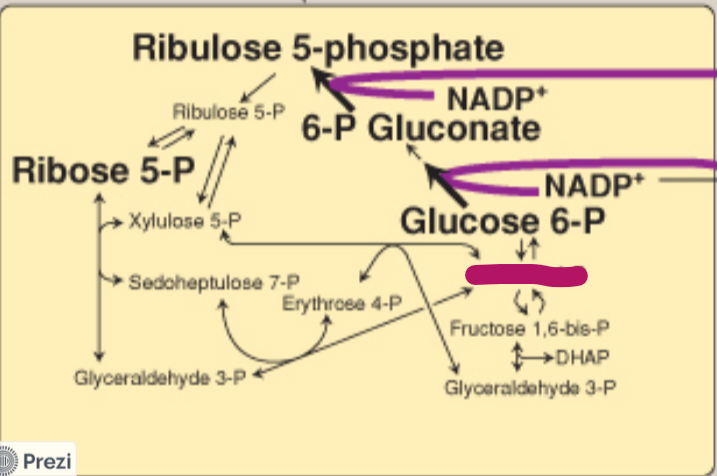
Label this step of the PPP.
Fructose 6-P
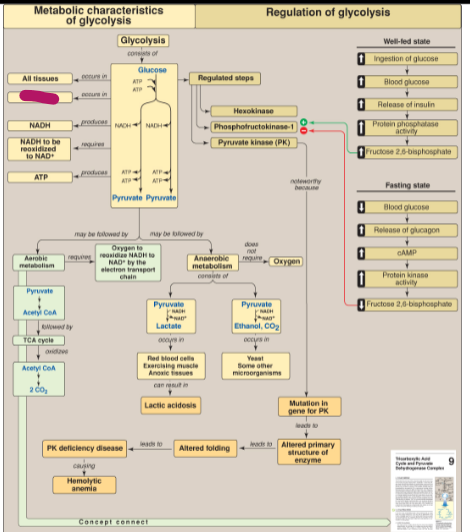
Where in the cell does glycolysis occur?
Cytosol
In what tissues does glycolysis occur?
All tissues
What does glycolysis produce?
2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, 4 ATP (Net 2 ATP)
Aerobically, what happens after glycolysis?
pyruvate forms acetyl CoA, then the TCA cycle oxidizes acetyl CoA into 2 CO2
Anaerobically, what happens after glycolysis?
In RBCs, exercising muscles, and anoxic tissues, lactate is formed. In yeast and some other microorganisms, ethanol and CO2 is formed
What can lactate buildup lead to?
Lactic acidosis
What does a mutation in the gene for pyruvate kinase lead to?
PK deficiency disease which causes hemolytic anemia
What happens during a well fed state?
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels increase, activating phosphofructokinase-1
What happens during a fasting state?
Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate levels decrease, inhibiting phosphofructokinase-1
What inhibits glycogen phosphorylase?
ATP, glucose 6-P, glucose (in the liver), increased protein phosphatase activity
What activates glycogen phosphorylase?
Increase in protein kinase activity
What stimulates glycogen synthase?
Increased protein phosphatase activity and glucose 6-P
When is increased protein phosphatase activity seen?
In a well-fed state
What does glycogen phosphorylase activation lead to?
An increase in the conversion of glycogen to glucose
What does an increase in glycogen synthase activity lead to?
A decrease in the conversion of glycogen to glucose
What does the creation of glycogen require?
UTP
What tissues does glycogen synthesis occur in?
The liver and muscle
What part of the cell does glycogen synthesis occur in?
Cytosol
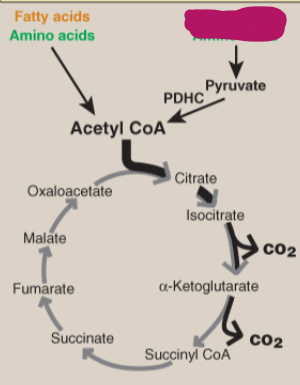
Label the TCA cycle.
Carbohydrates and amino acids
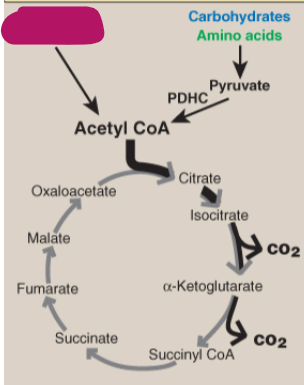
Label the TCA cycle.
Fatty acids and amino acids
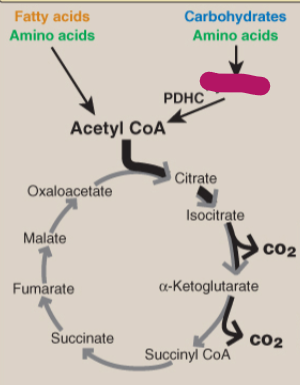
Label the TCA cycle.
Pyruvate
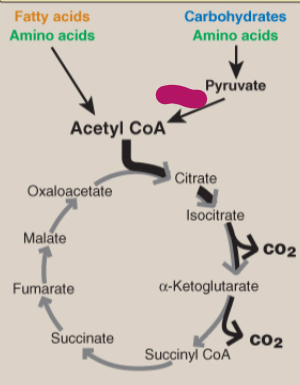
Label the TCA cycle.
PDHC
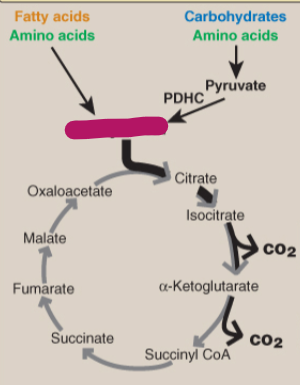
Label the TCA cycle.
Acetyl CoA
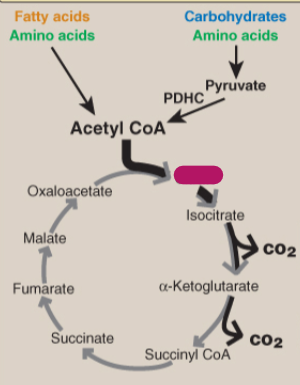
Label the TCA cycle.
Citrate
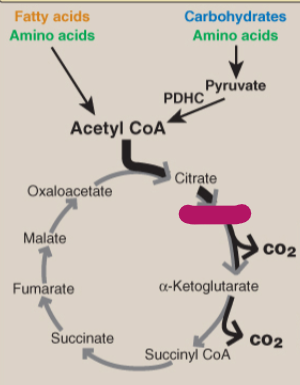
Label the TCA cycle.
Isocitrate
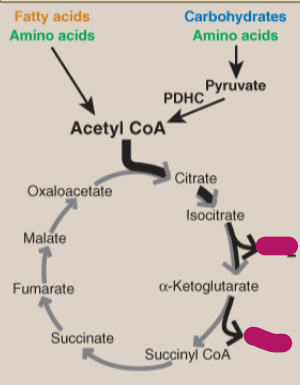
Label the TCA cycle.
CO2
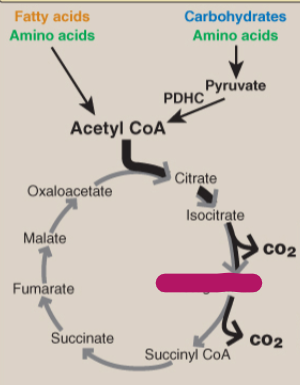
Label the TCA cycle.
Alpha-ketoglutarate
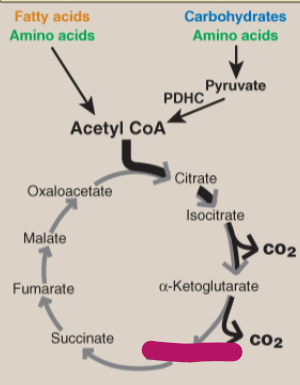
Label the TCA cycle.
Succinyl CoA
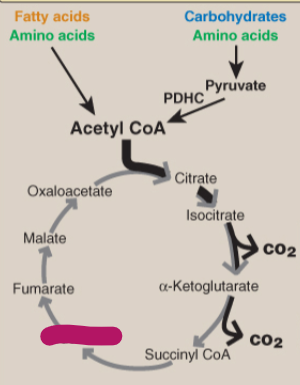
Label the TCA cycle.
Succinate
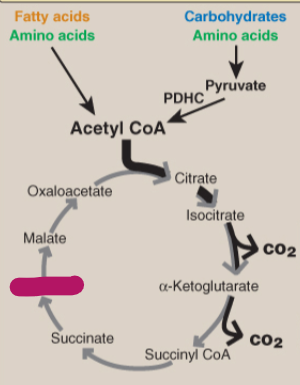
Label the TCA cycle.
Fumarate
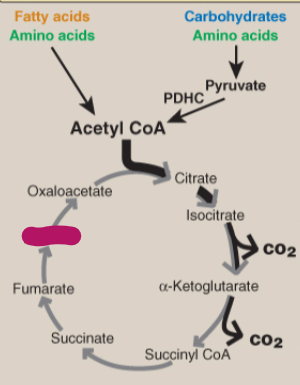
Label the TCA cycle.
Malate
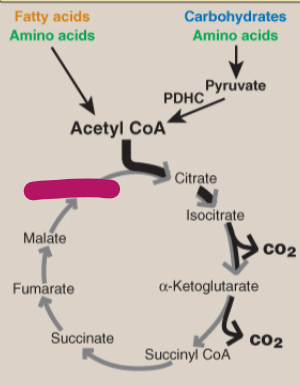
Label the TCA cycle.
Oxaloacetate
What enzymes regulate conversion of glucose to glucose 6-P?
hexokinase and glucokinase
What activates glucokinase?
Increased glucose levels
What activates glucokinase attaching to GKRP?
Increase in fructose 6-P
What activates the active pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
Ca2+
What inhibits the active PDHC?
NADH and acetyl CoA
What activates the inactive PDHC?
ATP, acetyl CoA, NADH
What inhibits the inactive PDHC?
Pyruvate