2.05 OCT of the optic nerve head
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
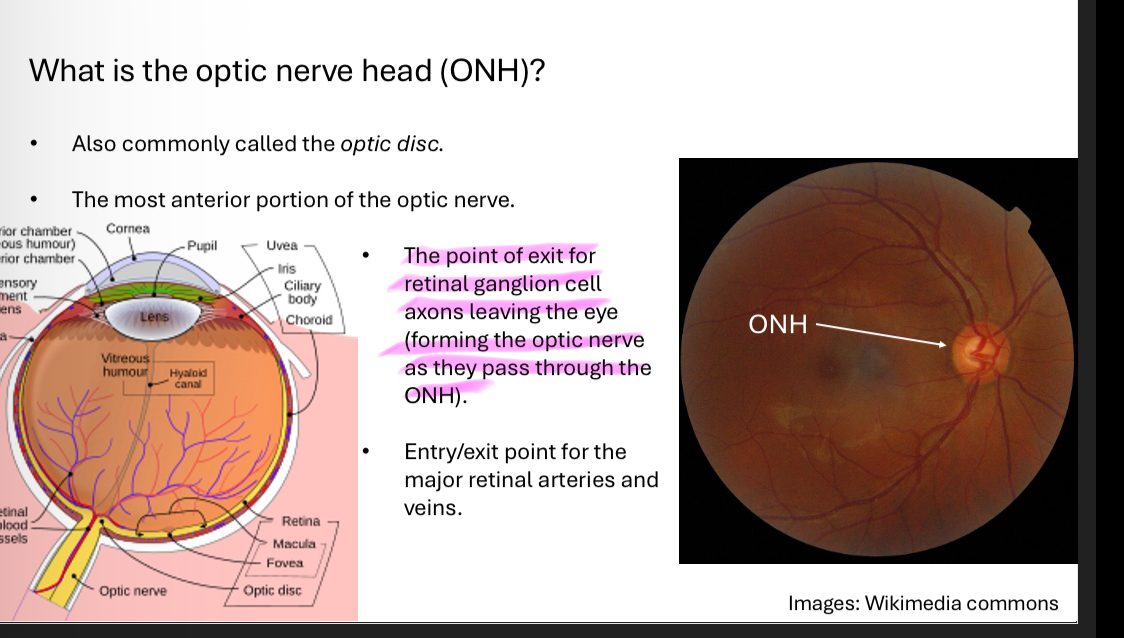
What is the optic nerve head
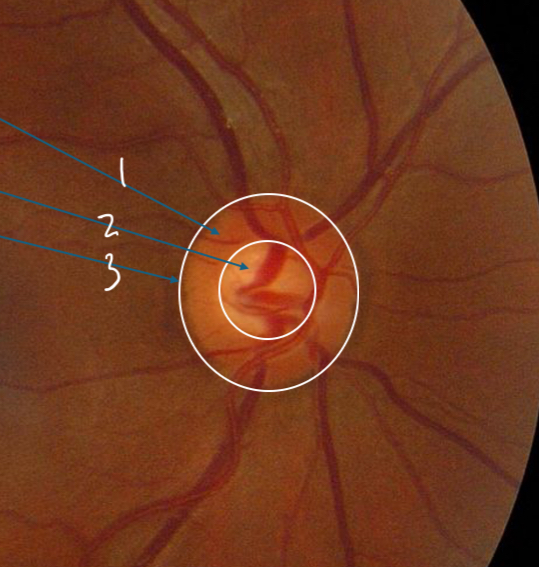
Label
Neuroretinal rim
Cup
Margin
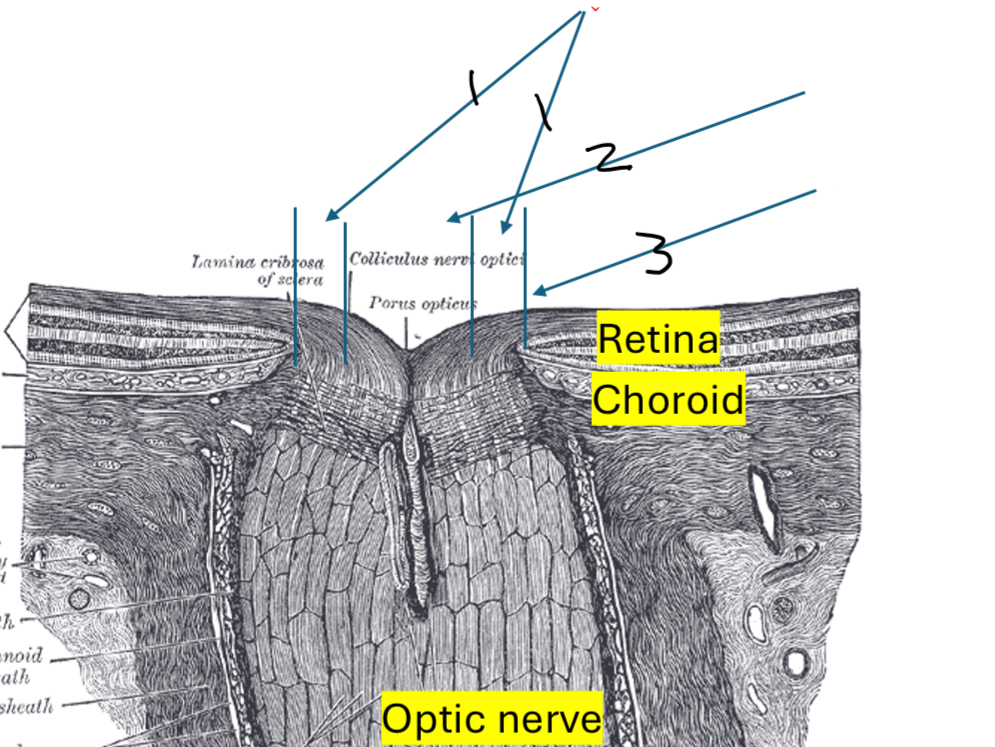
Label
NRR
Cup
Margin
What does ONH margin represent
A break in the retima
All layers stop, no photoreceptors = blind spot
What is the NRR
NRR is the retinal nerve fibre axon bundles passing from the retina into the optic nerve
What is the cup
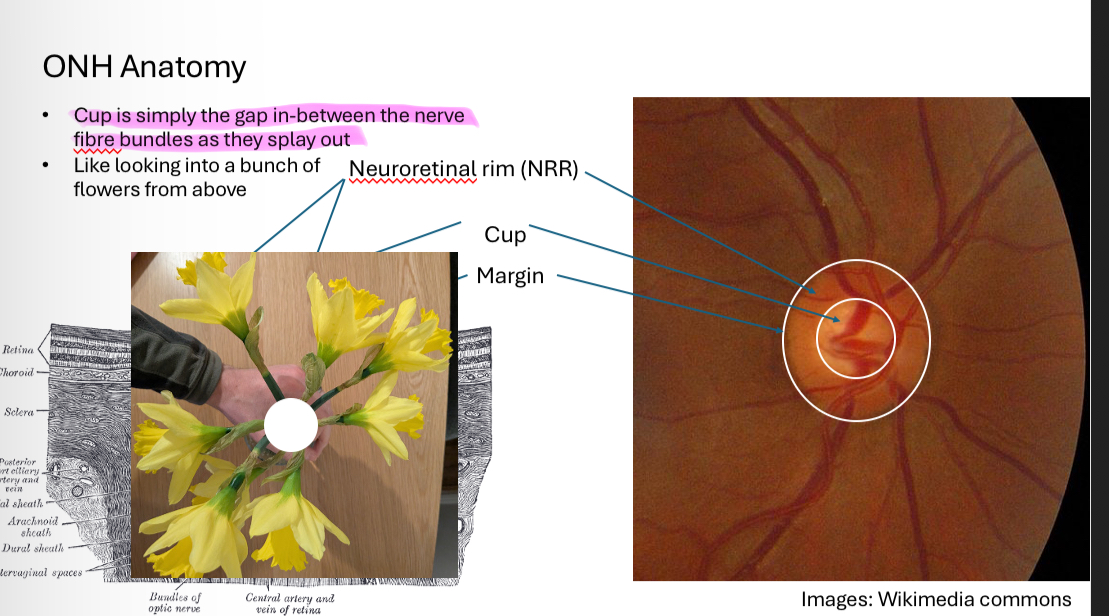
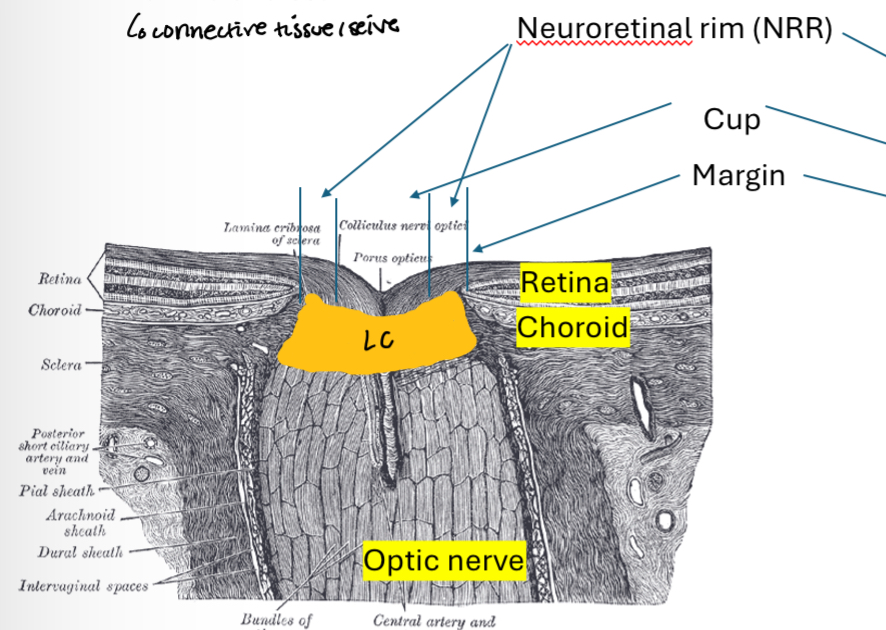
When the cup is large and deep you can see…
Lamina cribrosa (connective tissue/seive)
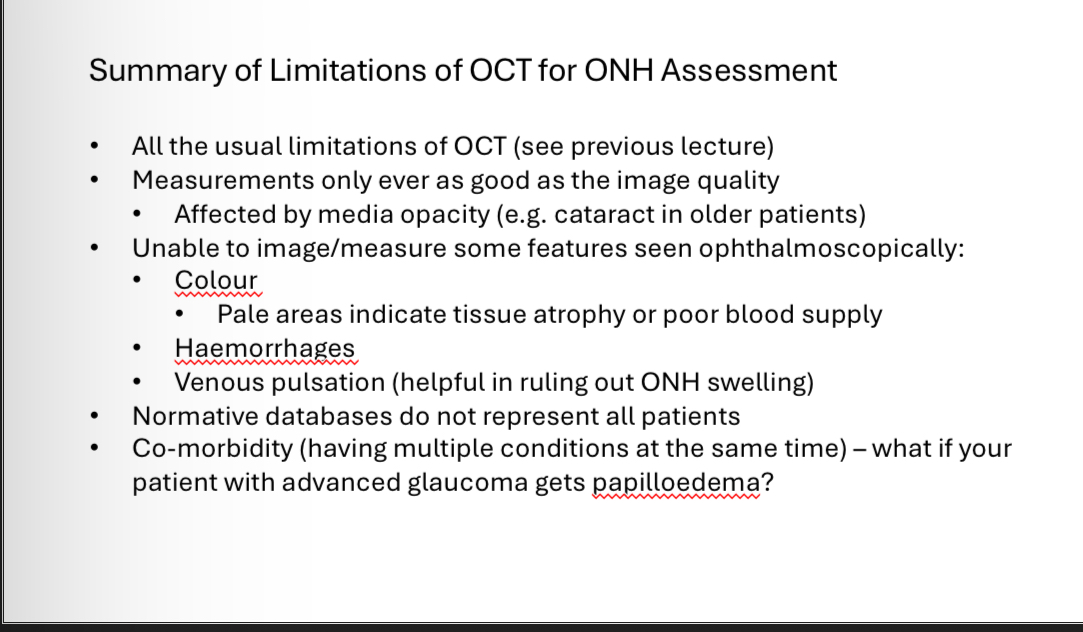
Sight threatening diseases associated with optic disc

Life threatening diseases associated with swelling of optic disc

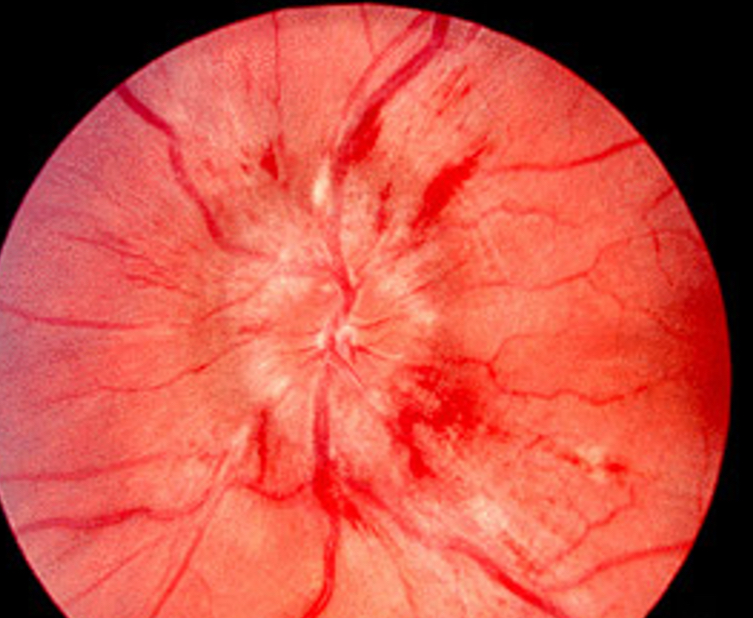
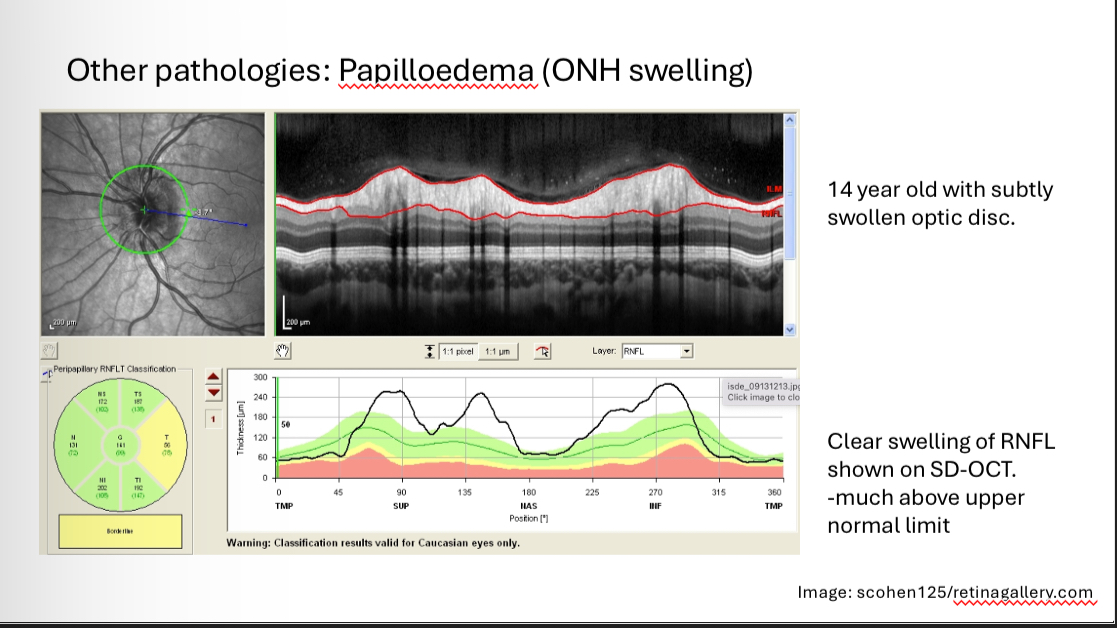
What is this
Papilloedema (swollen disc)
What to record when observing the ONH

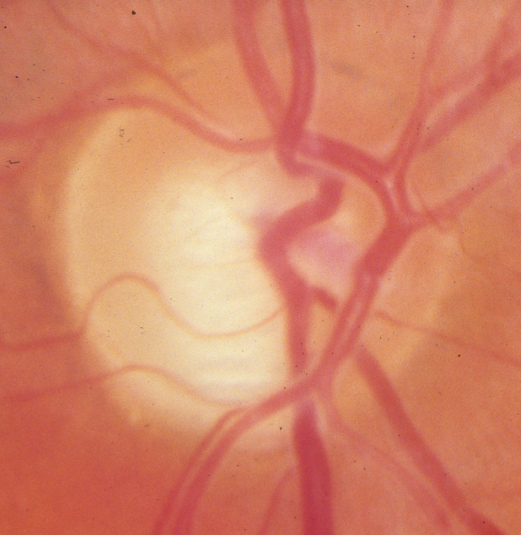
What is this
Glaucoma
Notching of ONH
How can we image the ONH

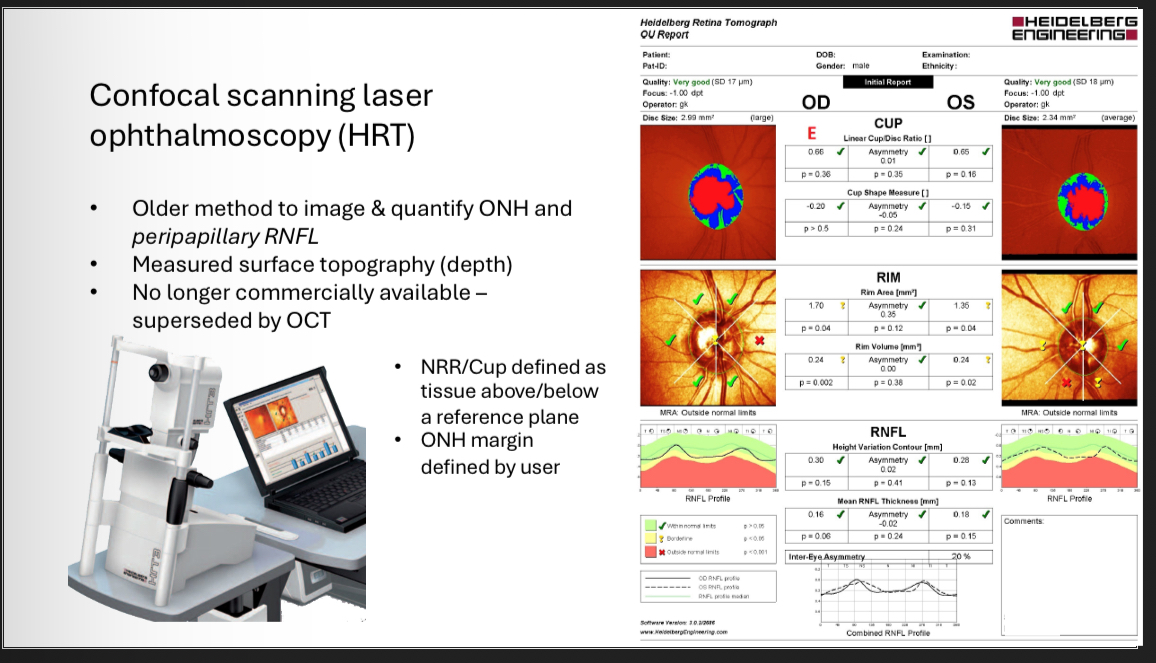
Confocal scanning laser opthalmoscopy
ONH margin is defined by…
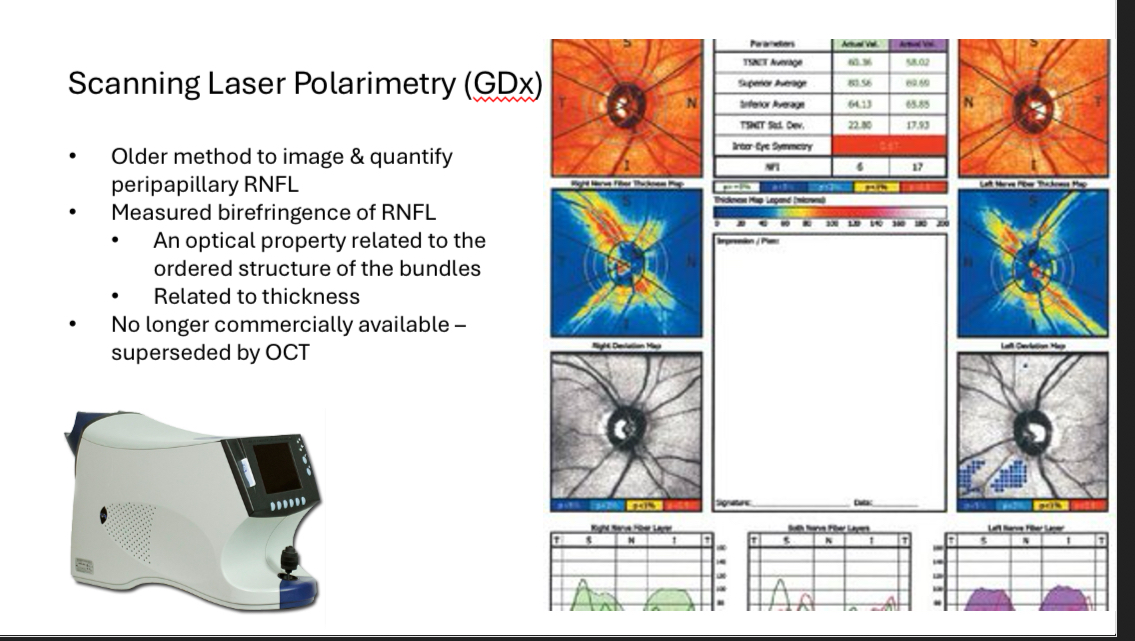
Scanning laser polarimetry (GDx)
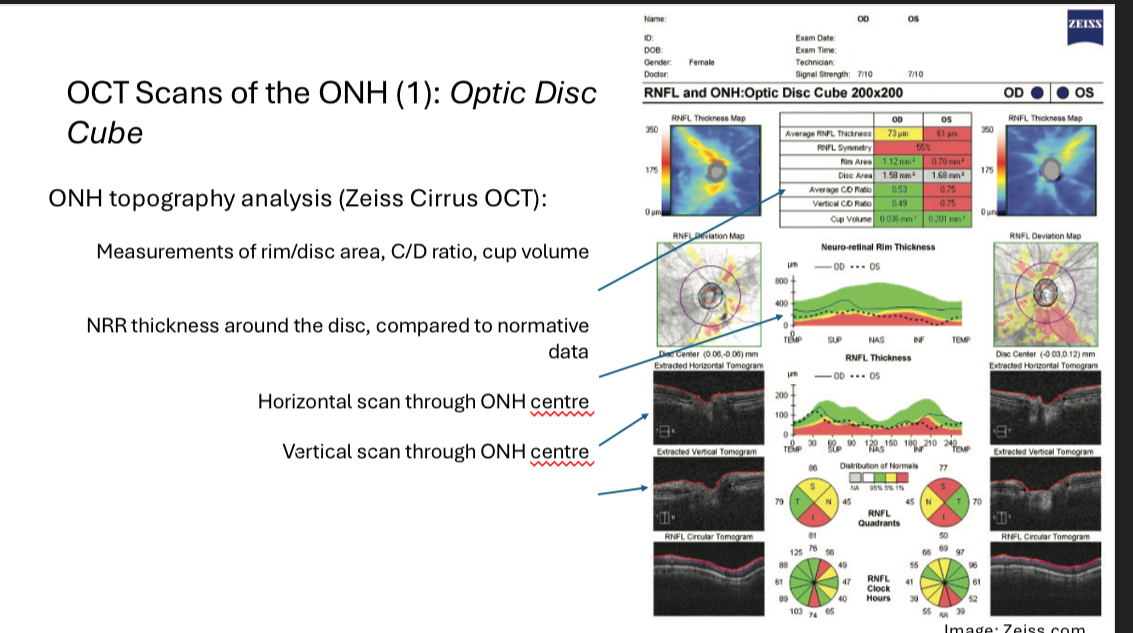
OCT scans of the ONH 1 - optic disc cube
•Raster scan approach capturing disc and peripapillary area
•Typically ~ 200 x 200 A-scans, 6mm x 6mm on the retina
Can be used to analyse disc topography and surrounding RNFL thickness
OCT scans of the ONH 1 - optic disc cube - ONH topography analysis
For analysis, the “cup” is defined as anything below a reference line
Reference line is set 150μm above the adjacent retinal pigment epithelium
-this is totally arbitrary!
This analysis mimics subjective ONH analysis
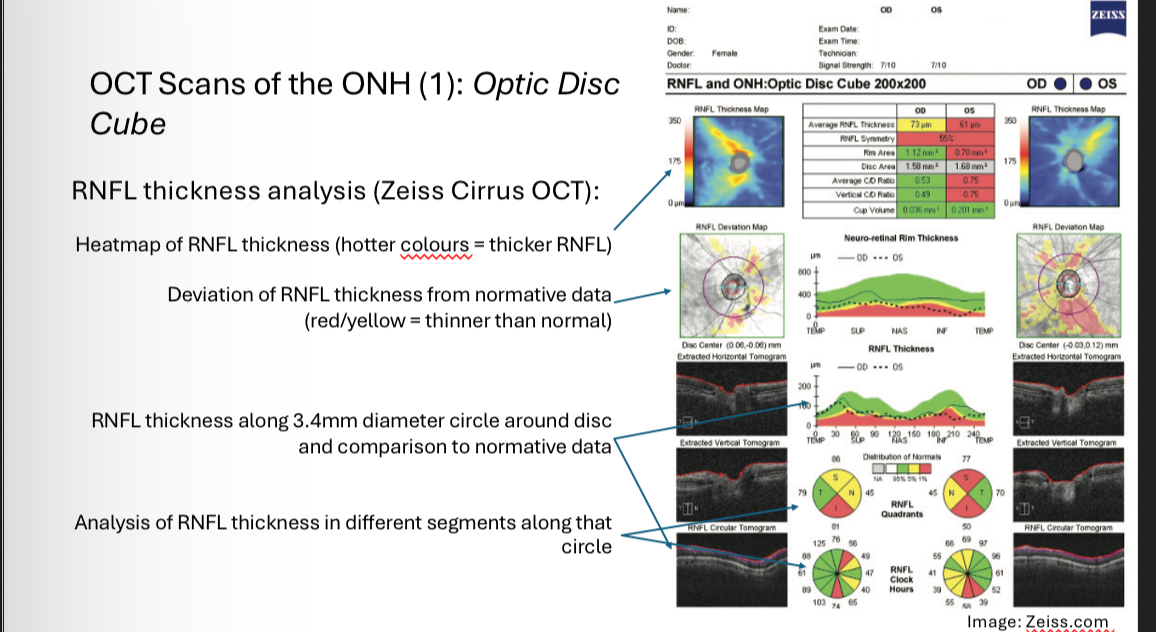
OCT scans of the ONH 1 - optic disc cube - RNFL thickness analysis
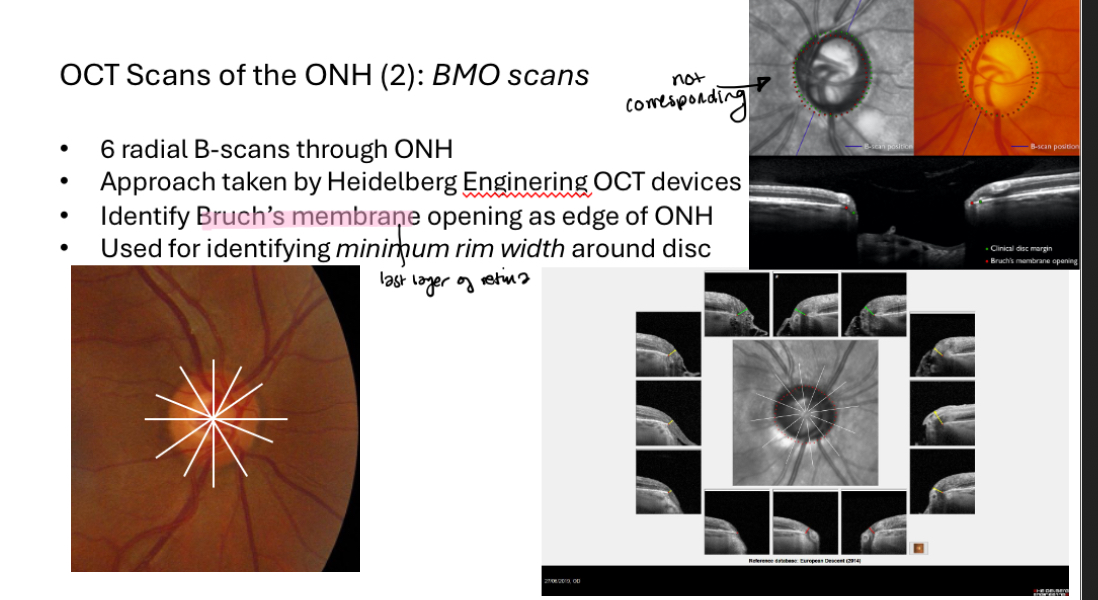
OCT scans of the ONH 2 - BMO scans
Sometimes the subjective disc margin (green dots)does not correspond to the actual opening in Bruch’s membrane (red dots).
This analysis can therefore sometimes identify areas of thinner rim than subjectively assessed (e.g. superior & inferior)
Useful in glaucoma
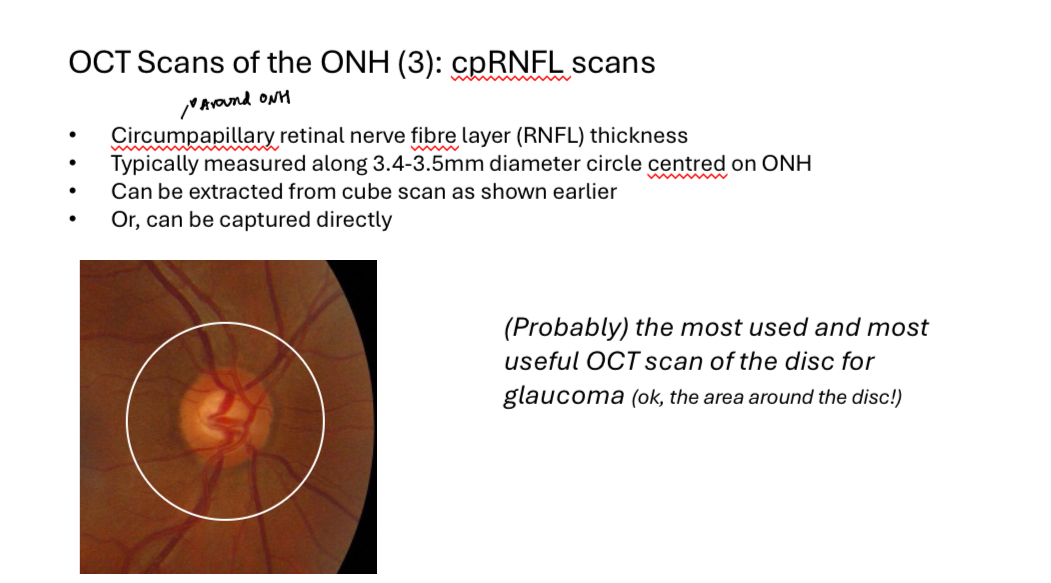
OCT Scans of the ONH 3 - cpRNFL scans
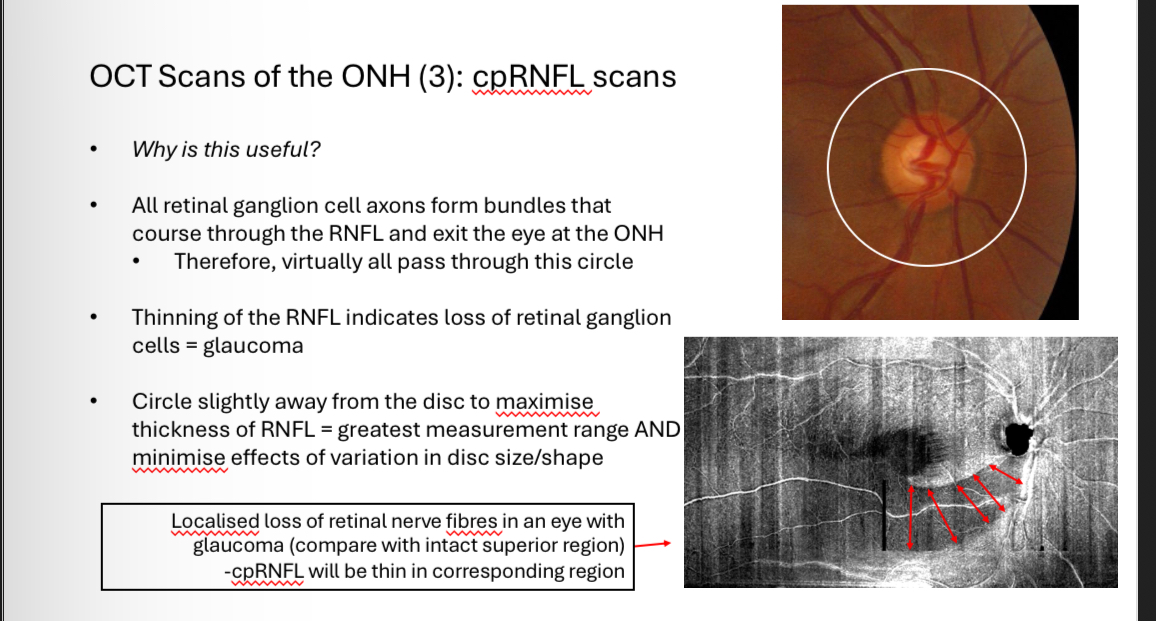
Why is cpRNFL scans useful
OCT Scans of the ONH 3 - cpRNFL scans - what layer thickness does it measure
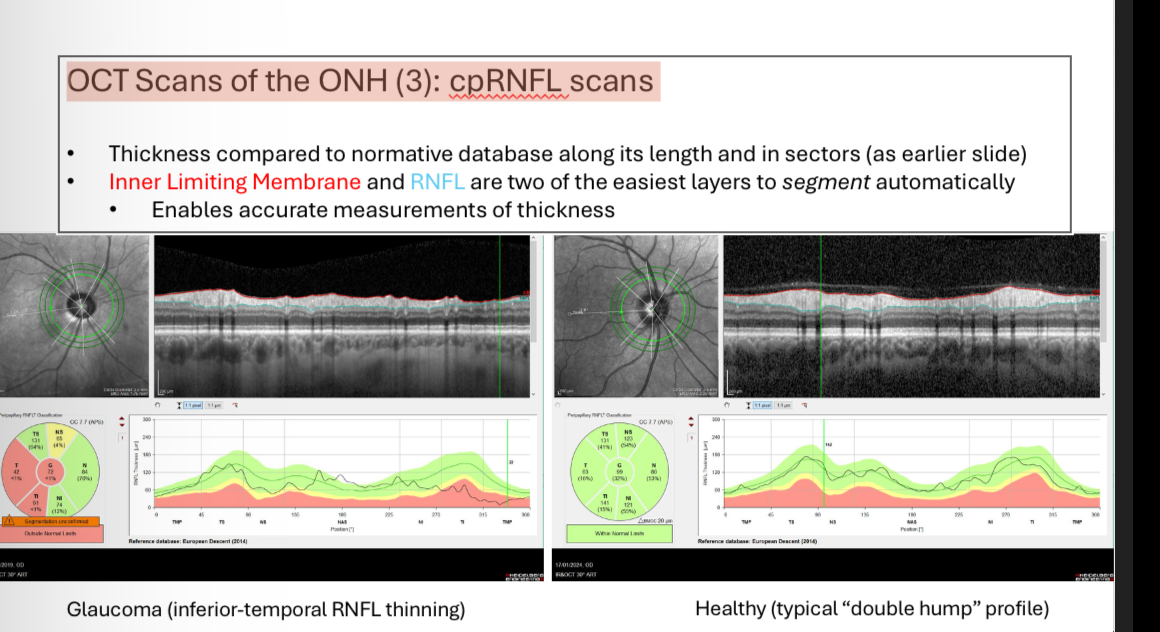
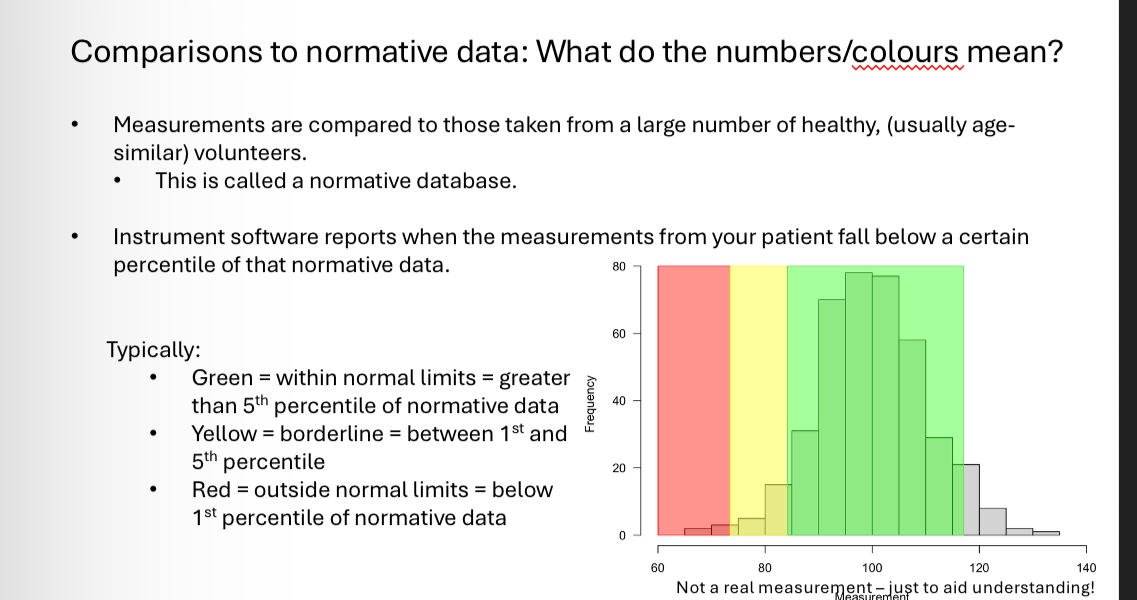
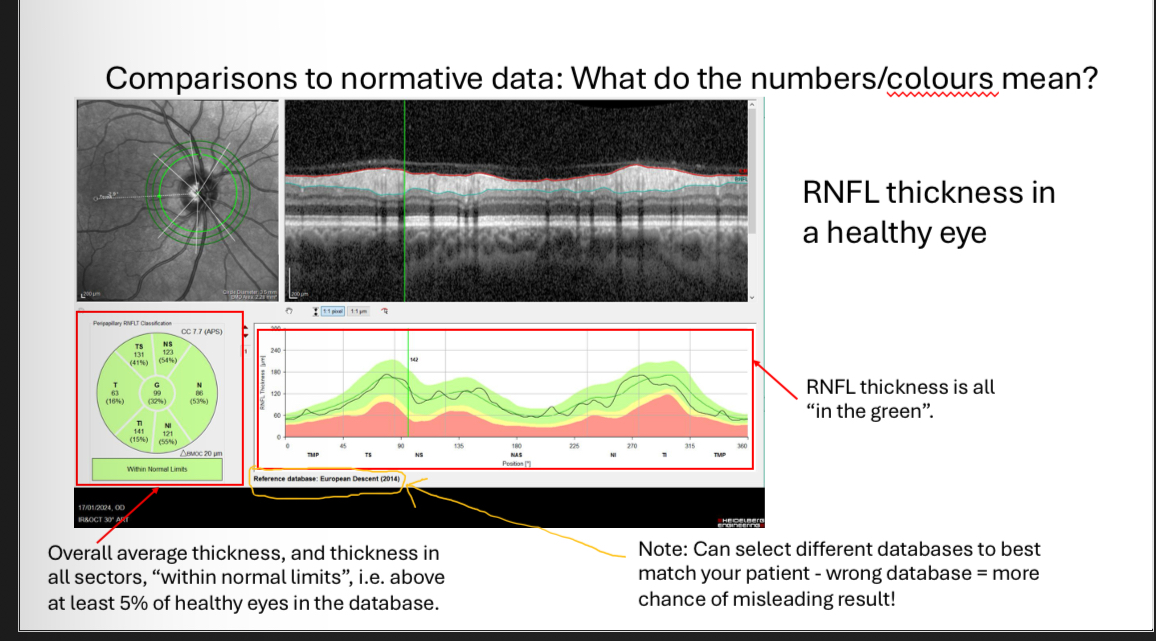
cpRNFL scans - what do the colours mean when comparing against database
A measurement falling “outside normal limits” means that it is smaller than that measurement for 99% of the healthy eyes in the normative database
It is an indication that disease may be present
•It DOES NOT mean that disease is present!
•Similarly, a measurement “in the green” doesnt mean a disease is not present
•Measurements must always be considered
in context with other clinical findings.
Can change database to match ethnicity
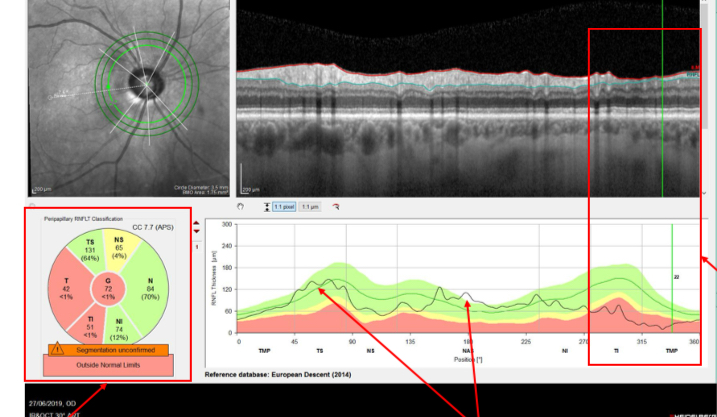
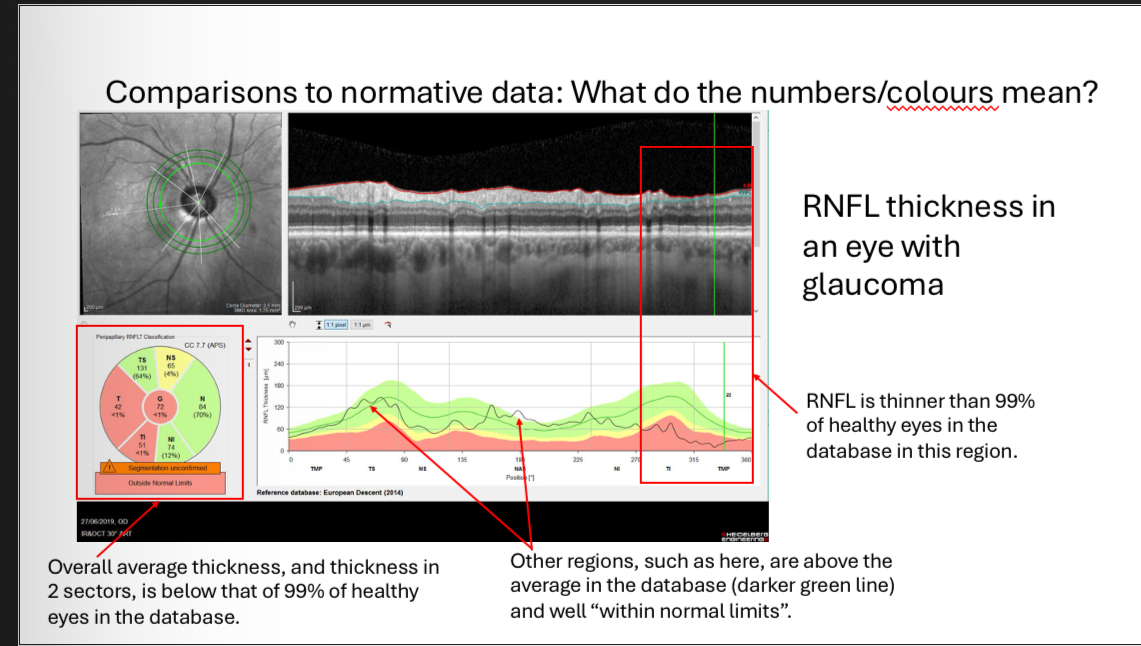
What does the RNFL of this eye show
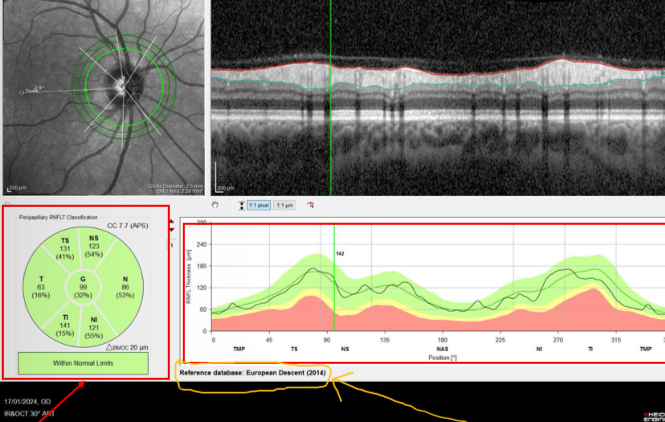
What does the RNFL of this eye show
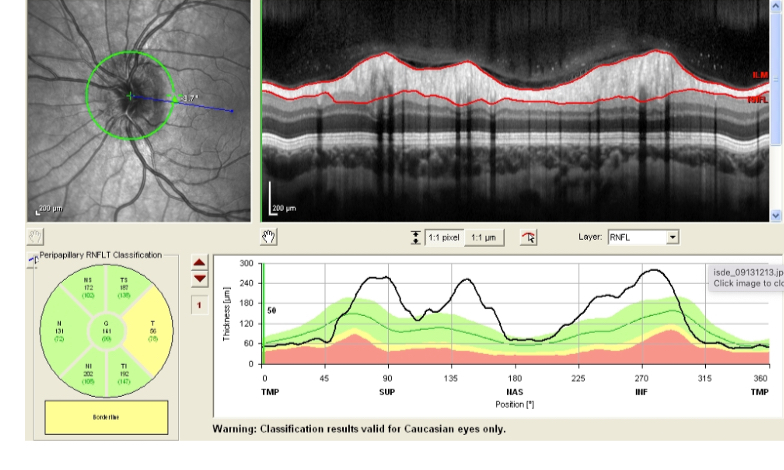
What does the RNFL of this eye show
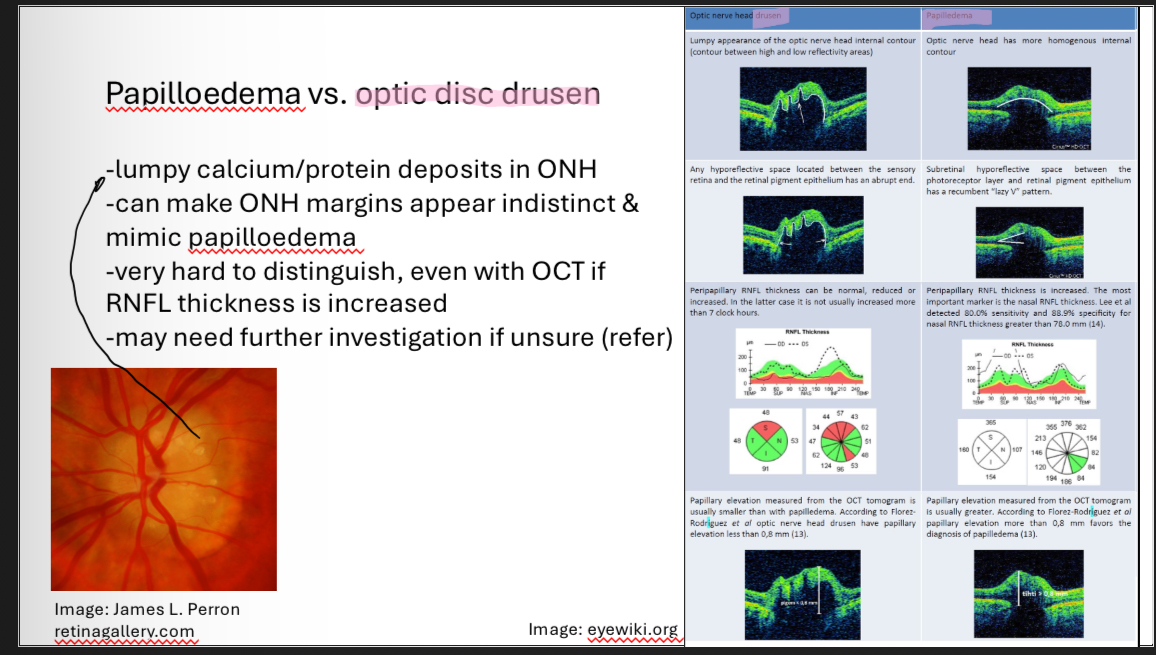
Papilloedema vs optic disc drusen
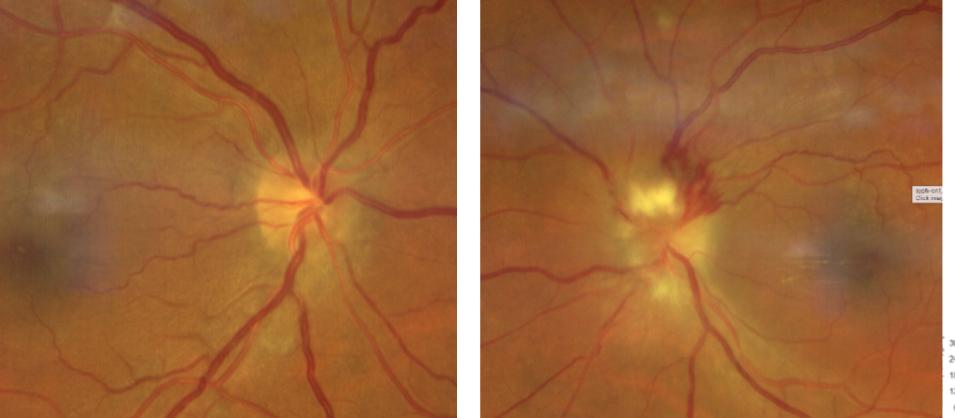
What is this
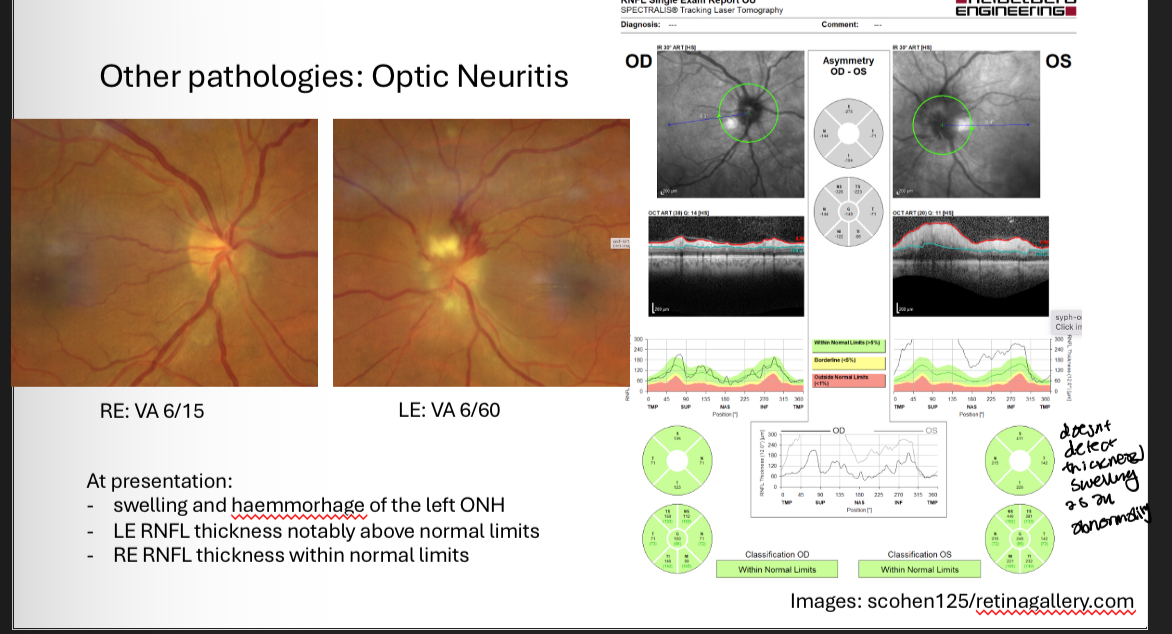
Optic neuritis
Optic neuritis appearance
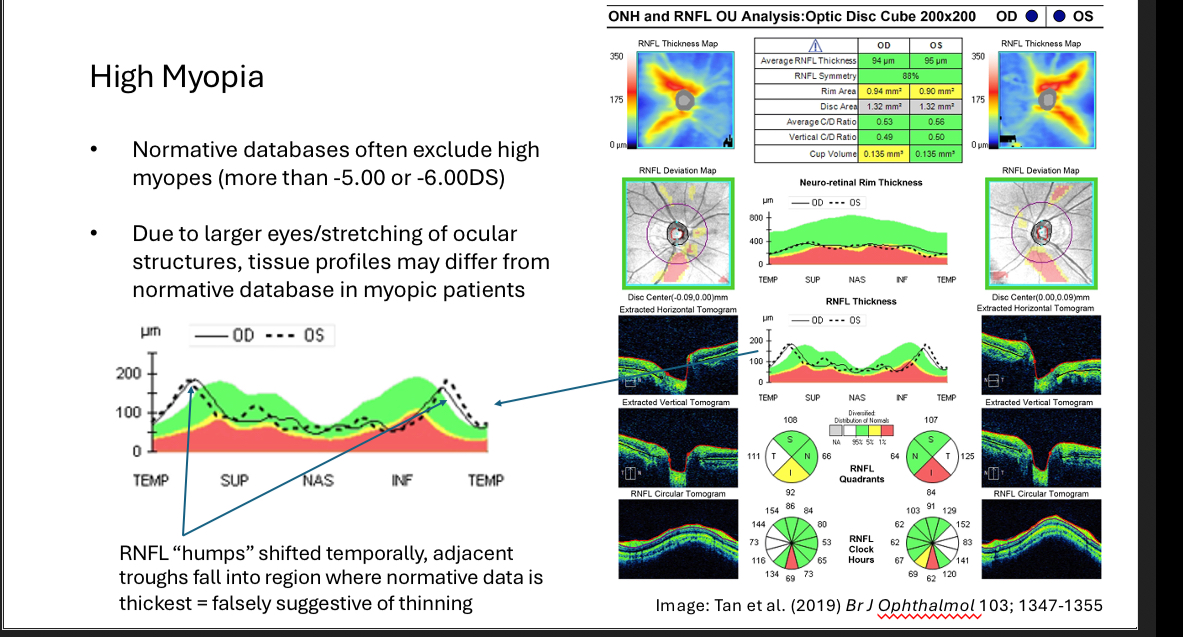
High myopia effect on disc

RNFL of eye with High myopia
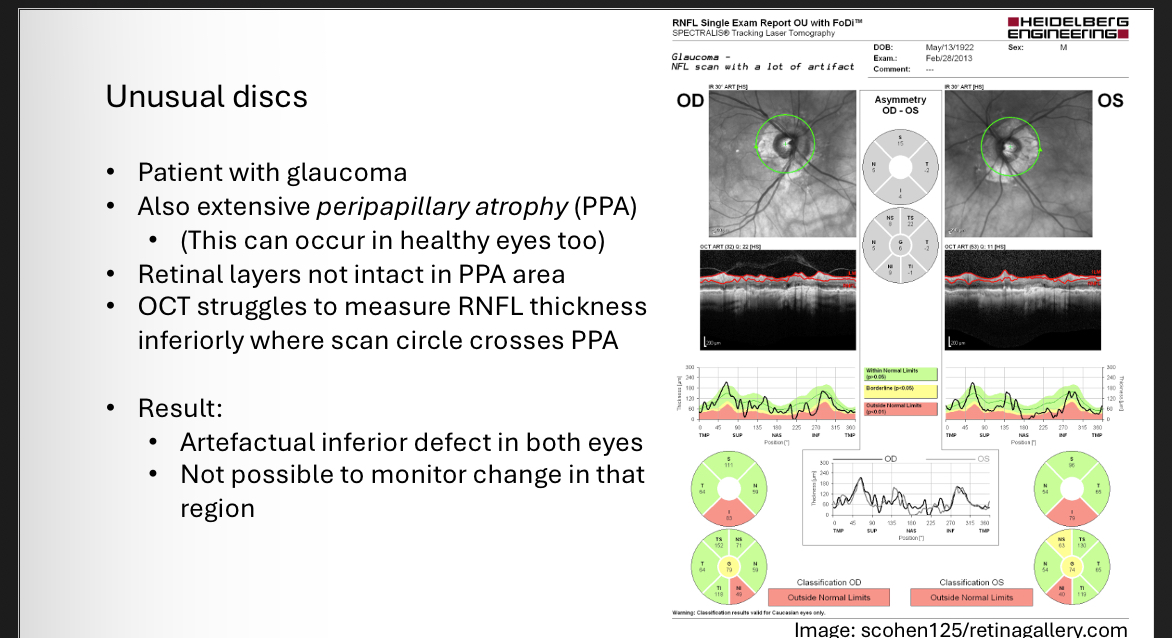
What gives misleading RNFL results

RNFL artefacts - unusual discs
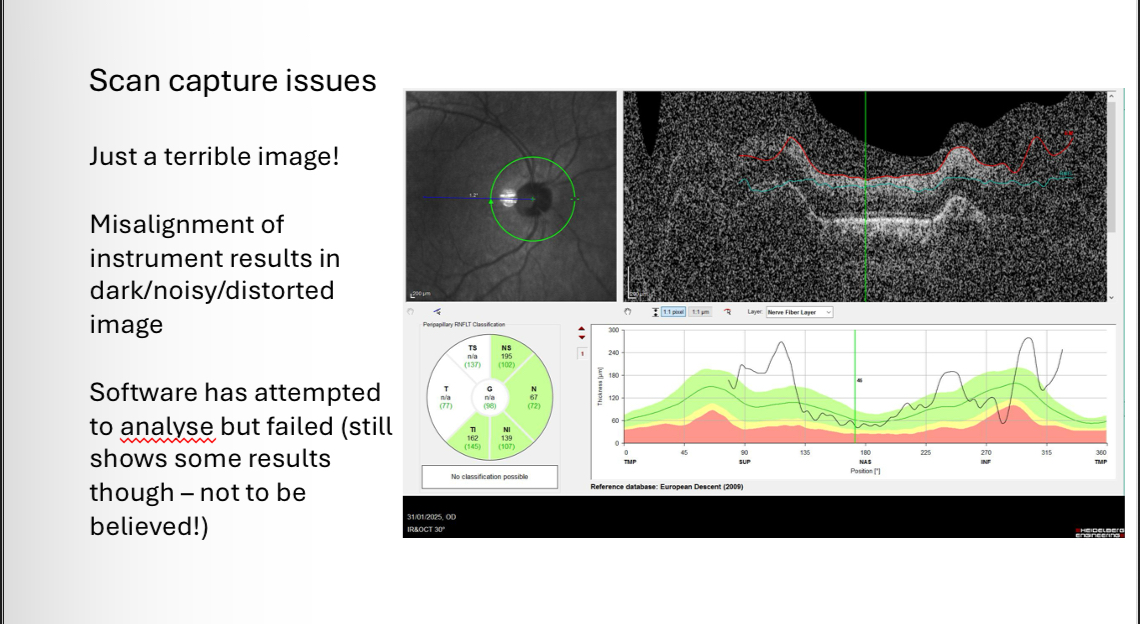
RNFL artefacts - Scan capture issues
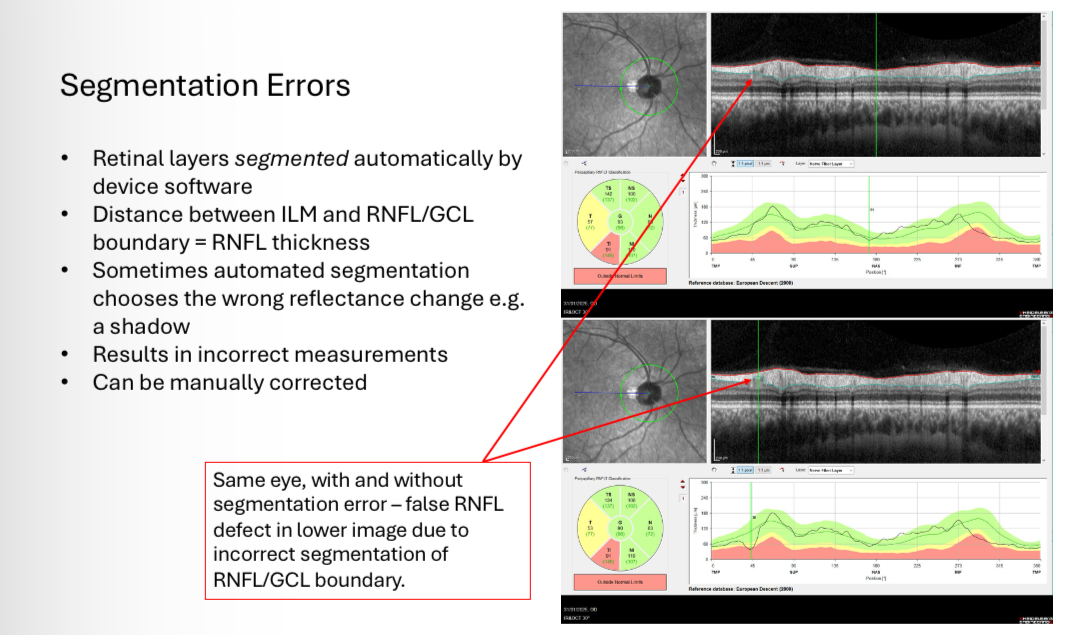
RNFL artefacts -Segmentation errors
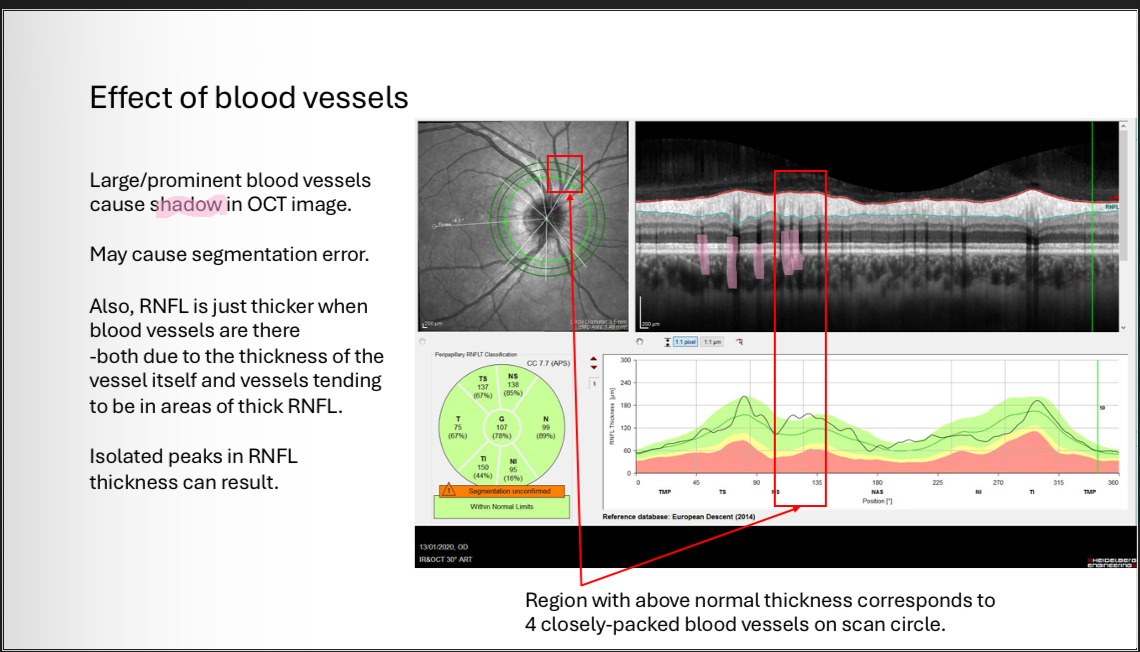
RNFL artefacts - Blood vessels
Monitoring change with OCT

Benefits of OCT

Limitations of OCT