Ch 42 Urinary
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
excretory
urinary system also called the ____ system
180L
how much water per day do kidneys filter
water, nutrients, ions
kidneys remove waste while retaining what 3 things
kidneys
what organ is primary filter system for body
1. regulation of blood ionic composition
2. regulation of blood pH
3. regulation of blood volume/BP
4. regulation of blood glucose
5. excretes waste/foreign substances
5 functions of urinary system
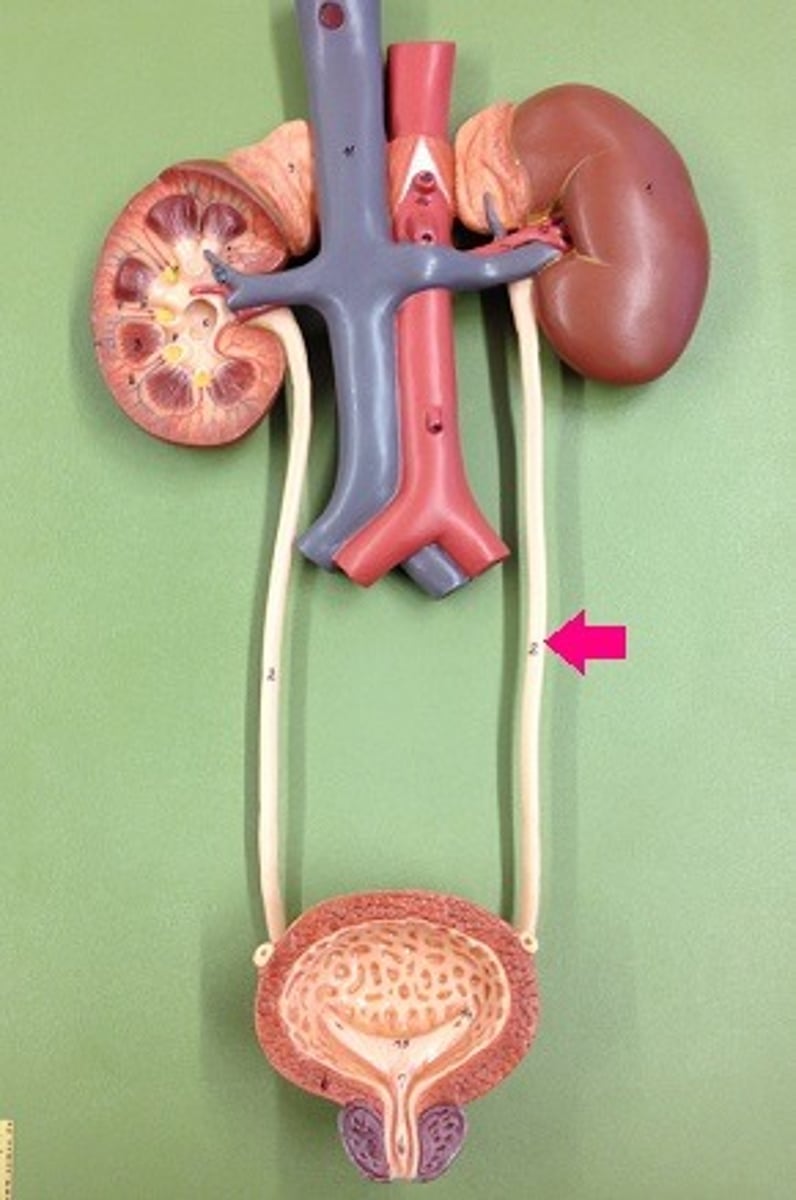
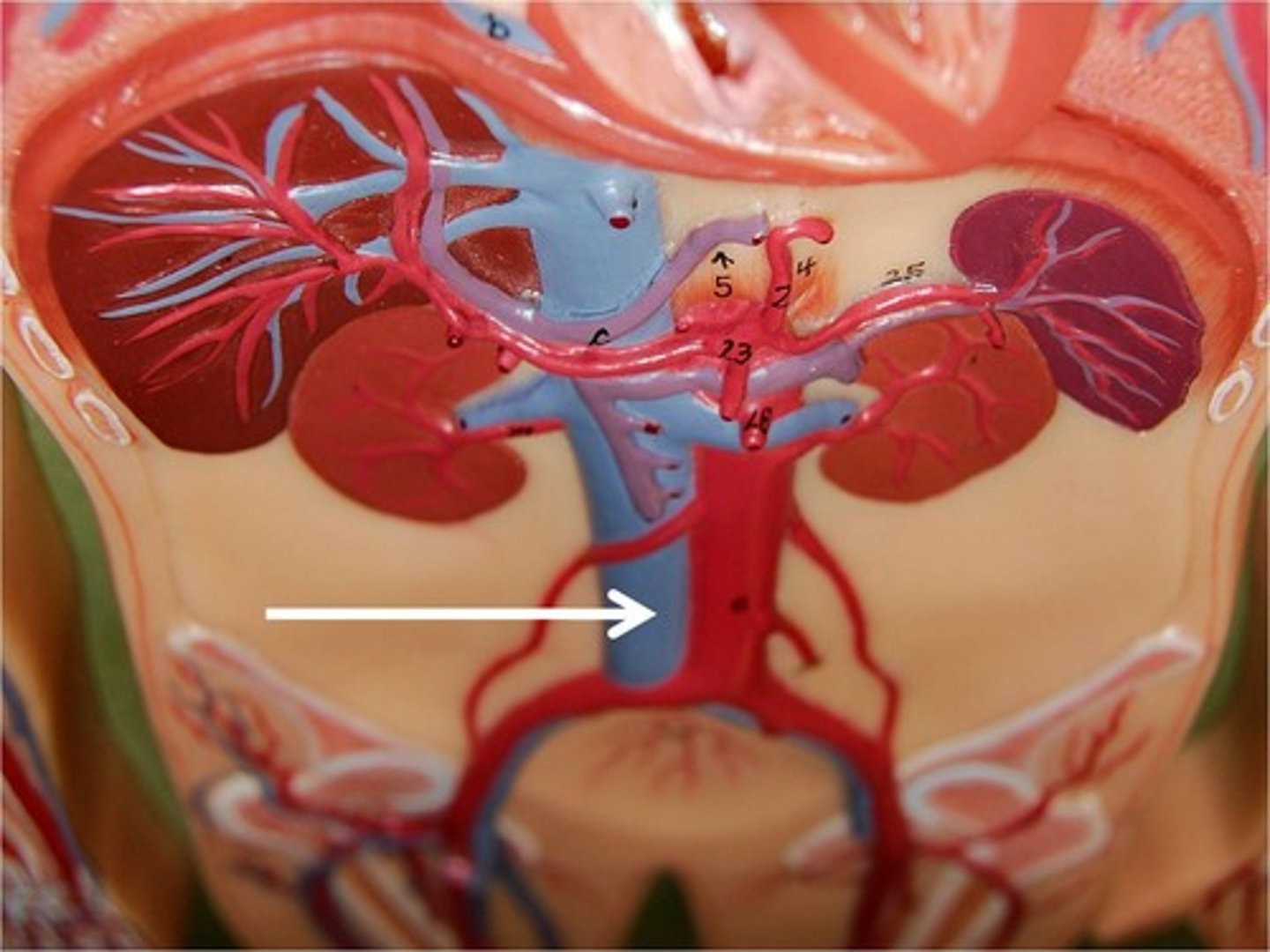
ureters
what structures drain urine from kidneys to bladder
muscular
rugae
bladder is a ____ structure with distensable ____ to help it expand
external
urethra gets urine from bladder to ____ environment
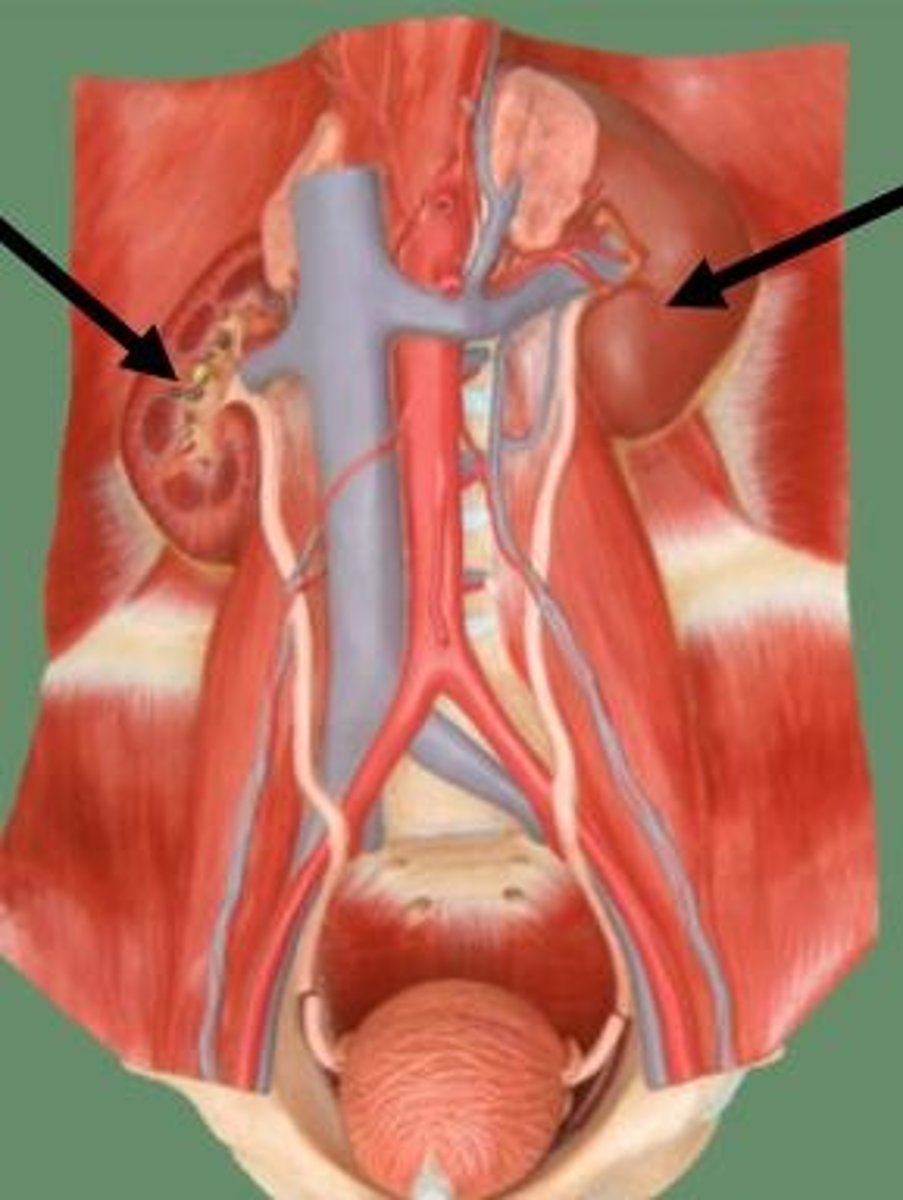
liver lies on top of it
why is R kidney lower than the L
kidneys
what are these
ureters
what are these
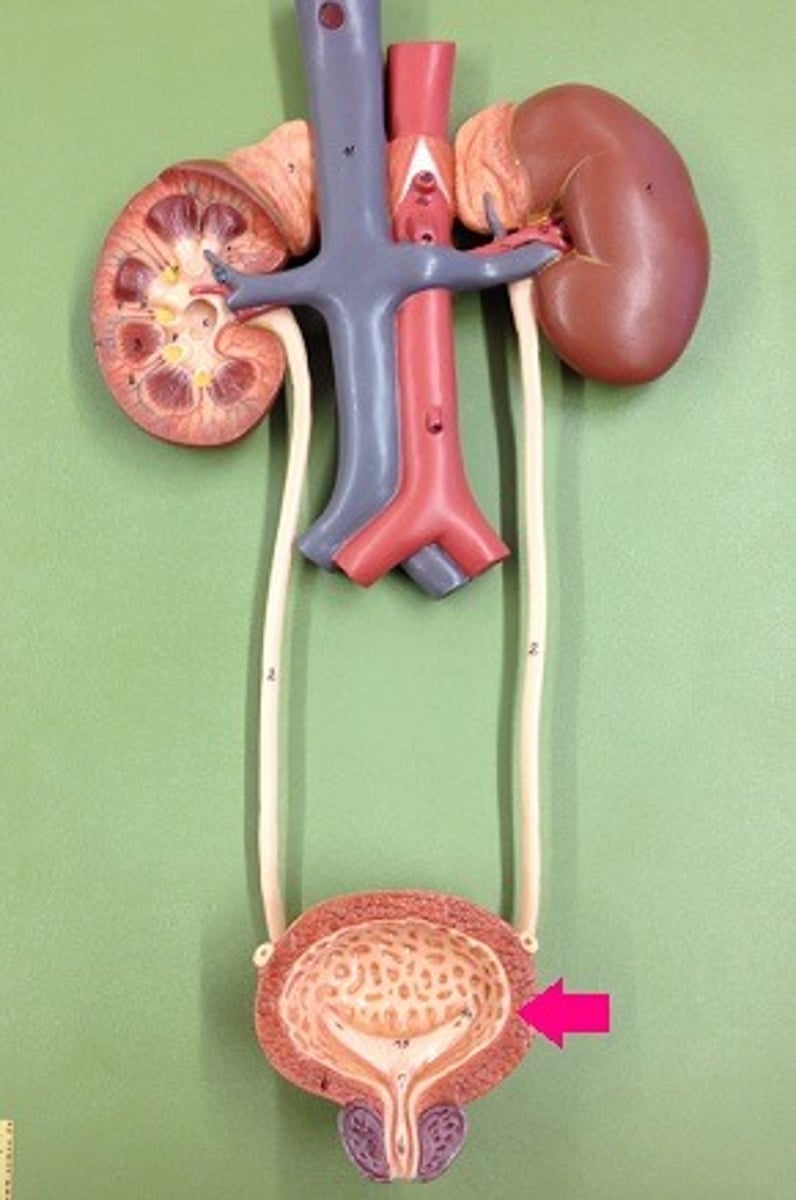
bladder
what is this
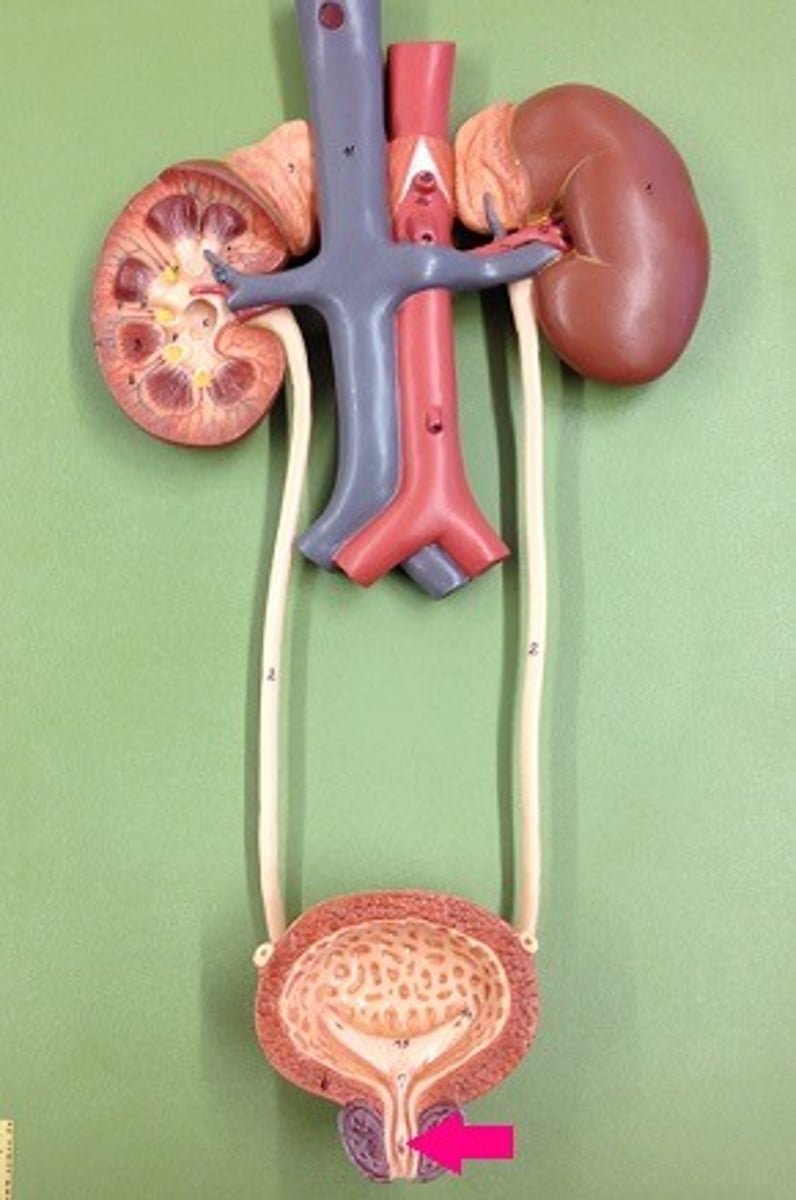
urethra
what is this
peritoneal
(behind the peritoneum/intestines)
kidneys are retro________
fascia
the kidneys are not free floating and are anchored via renal ______
hillus
what is this concave curve
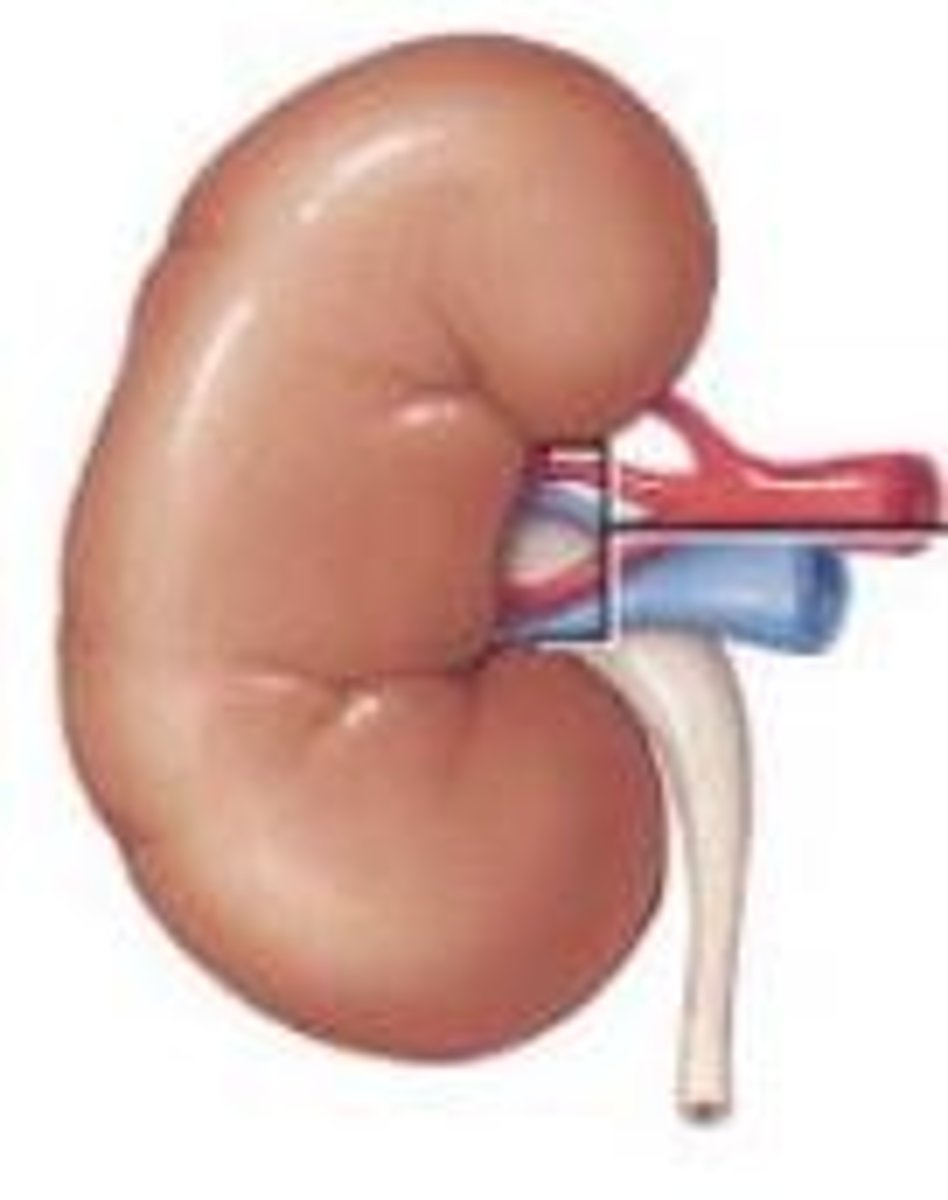
renal vessels
what are these
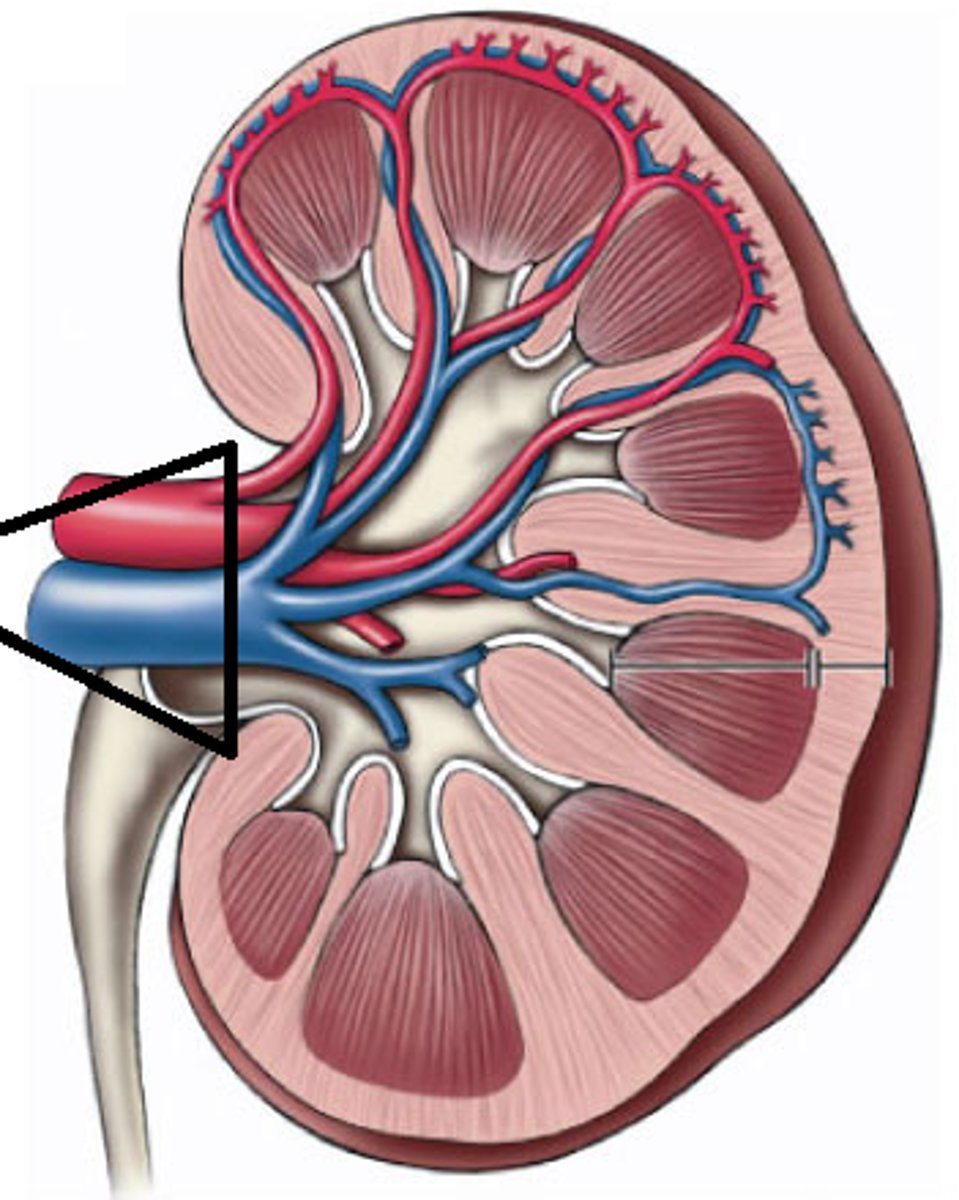
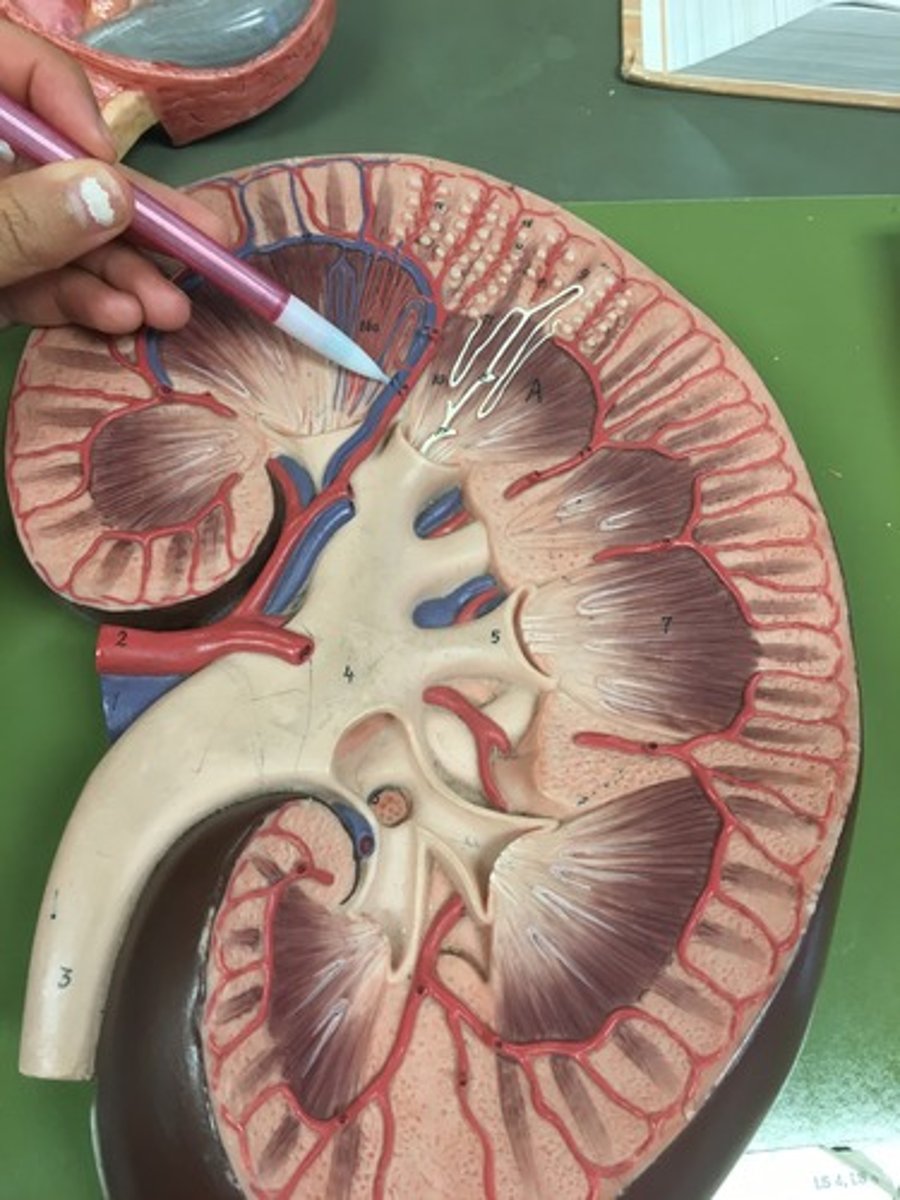
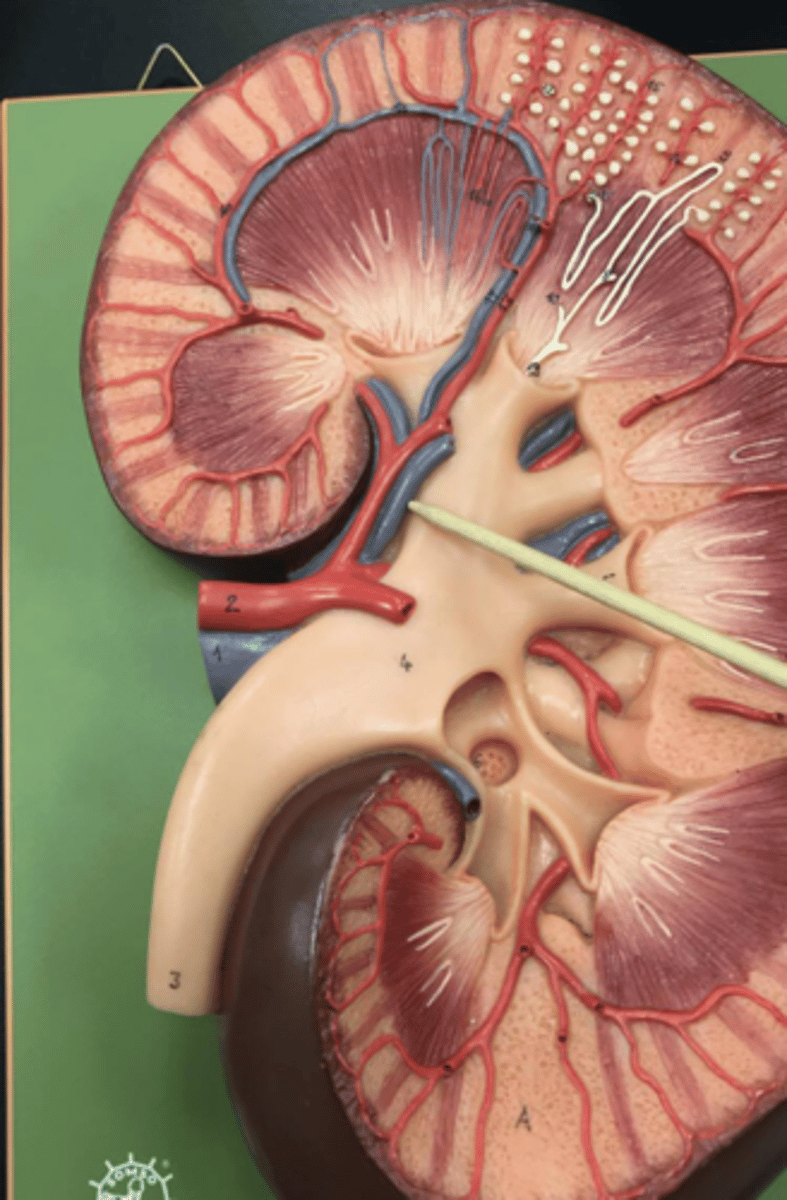
major calyx
what is this (collecting duct for urine)
minor calyx
what is this (feeds into major calyx)
renal pyramids
what are these (projections off the calyx)
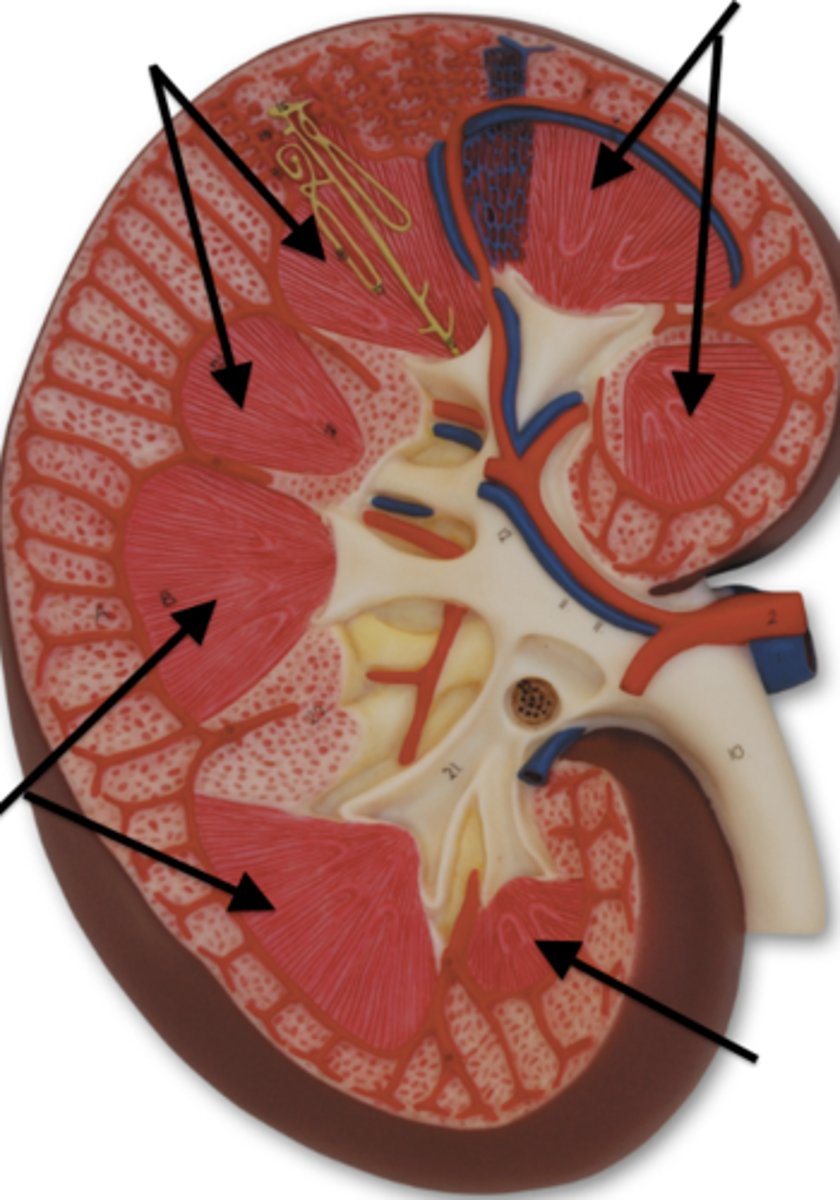
renal columns
what are these (areas between renal pyramids)
pelvis of kidney
what is this
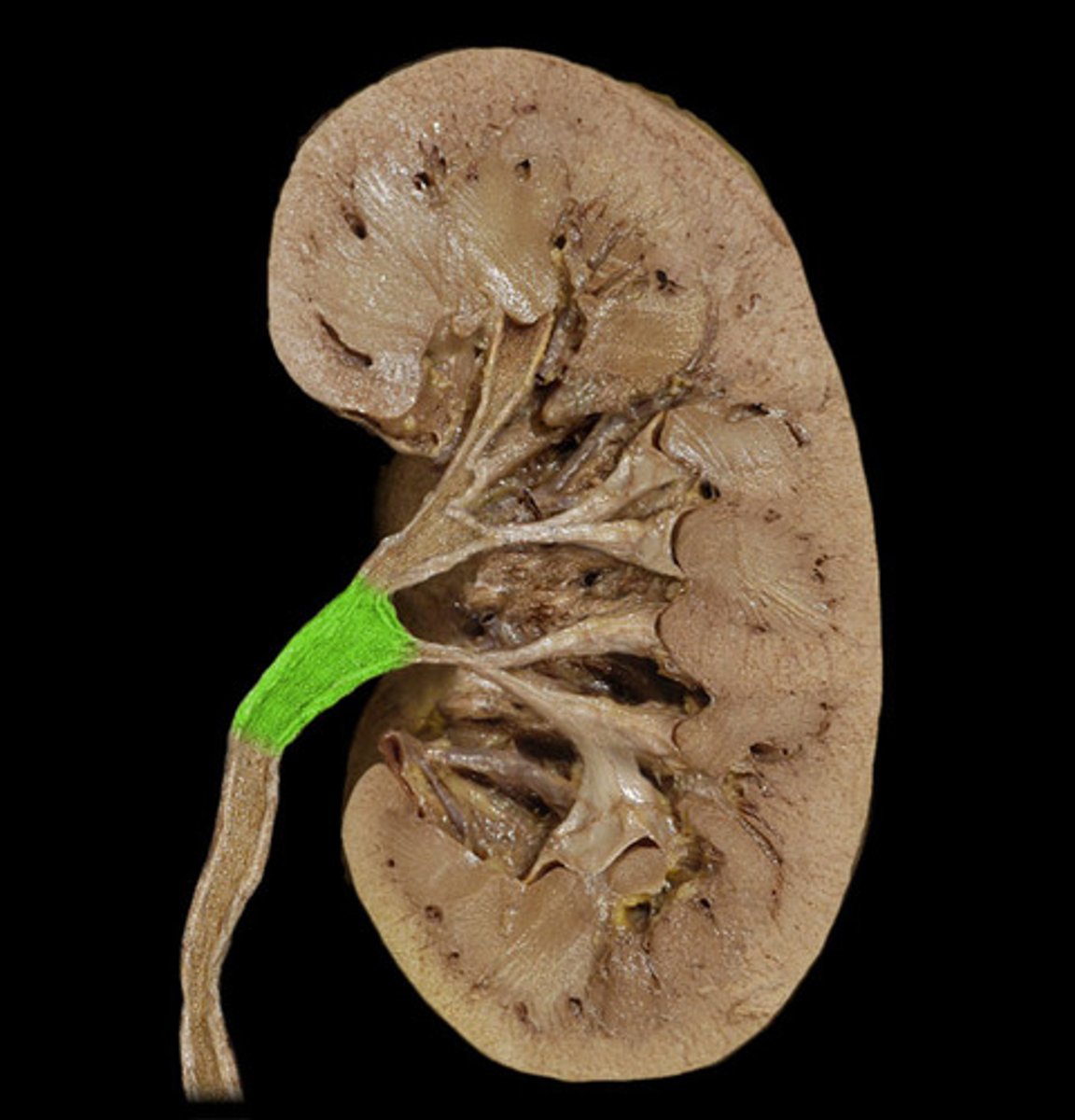
ureter
the pelvis of kidney then becomes the
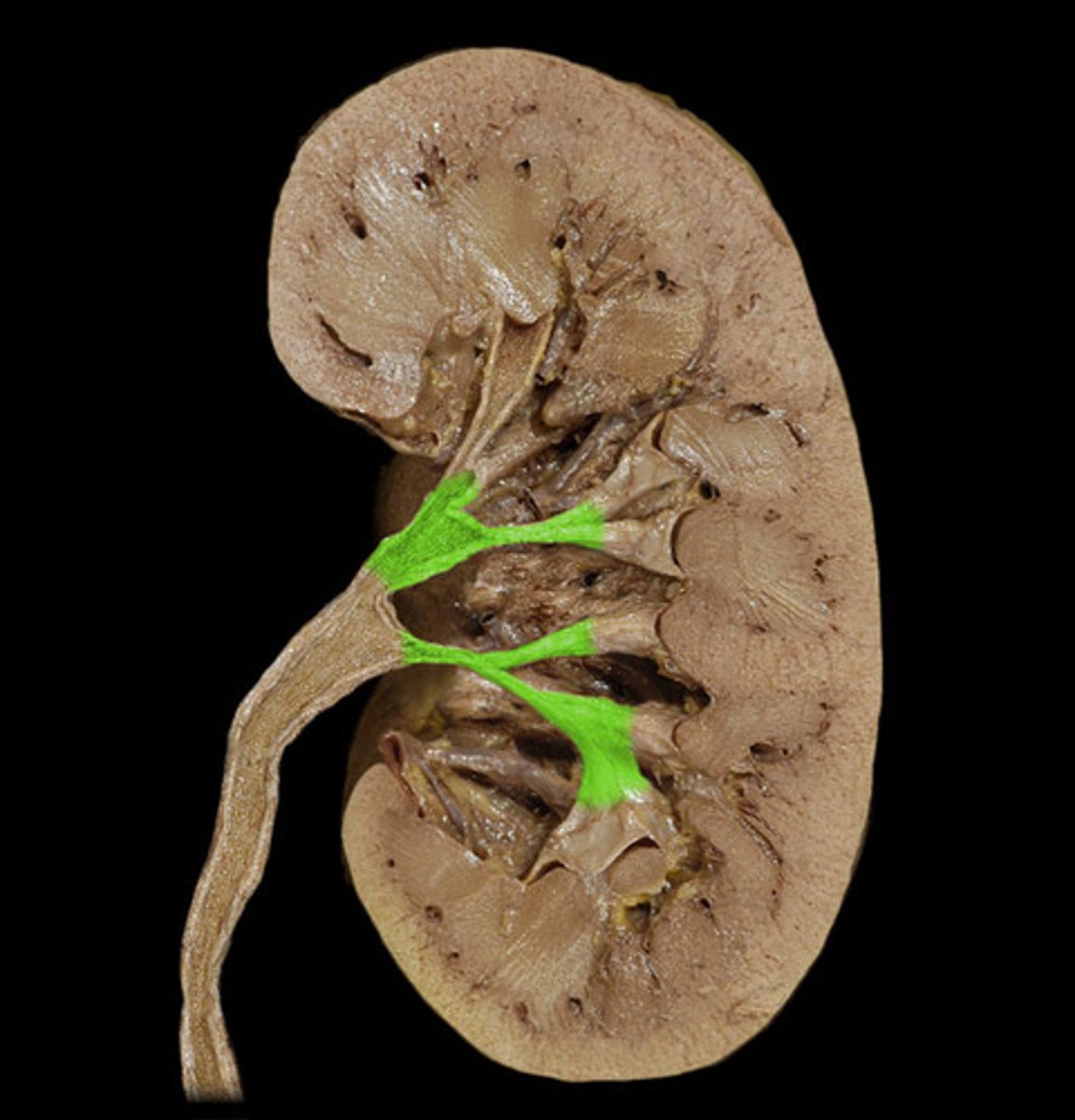
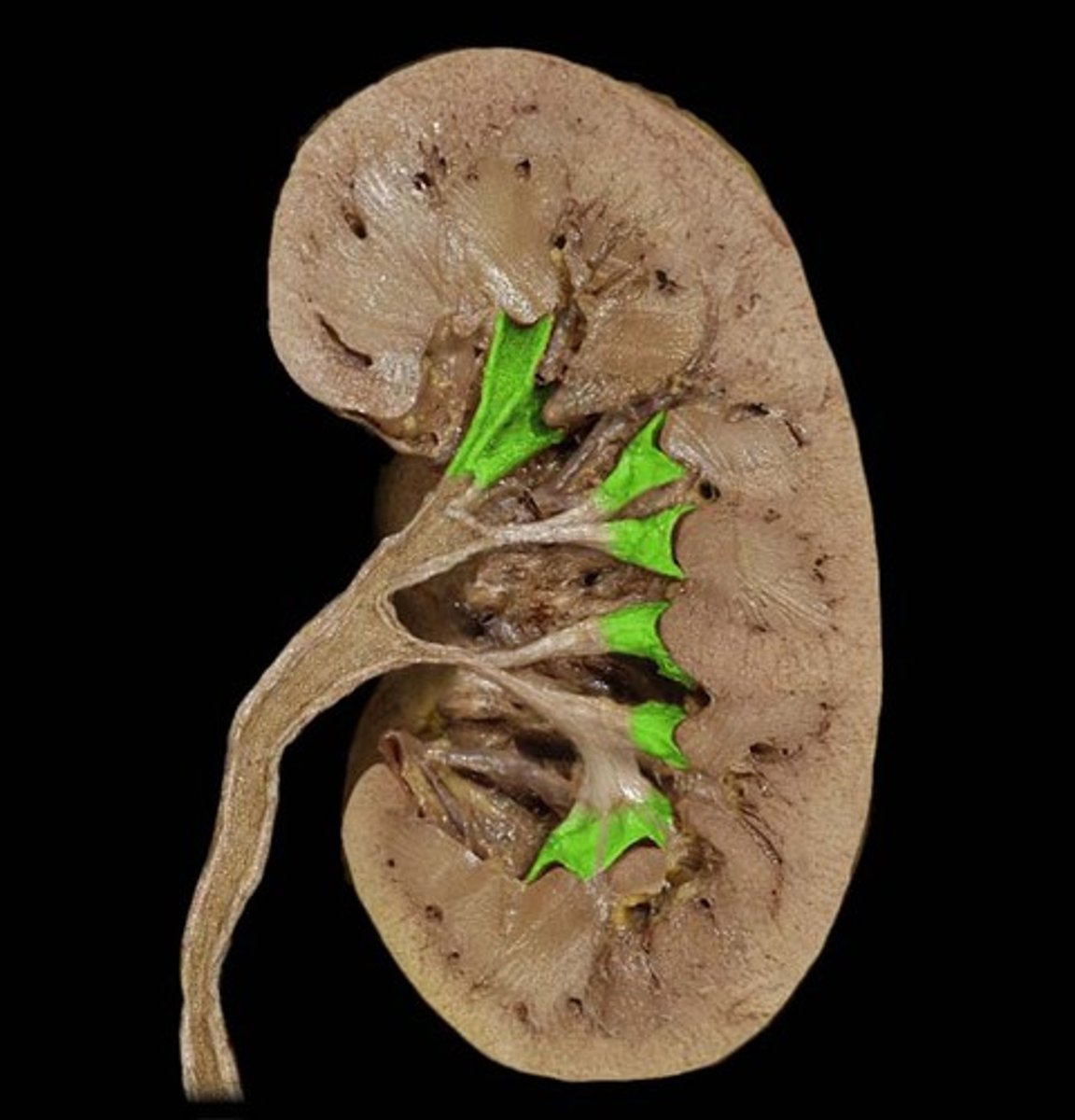
calyces
calyx/calyces
pelvis
ureter
bladder
1. blood gets filtered through pyramids, comes out as urine
2. drops into minor _____
3. collects into major _____
4. then drops into _____ of kidney which becomes the _____
5. then goes to _____
renal cortex
the outer layer of kidney (urine formation begins here)
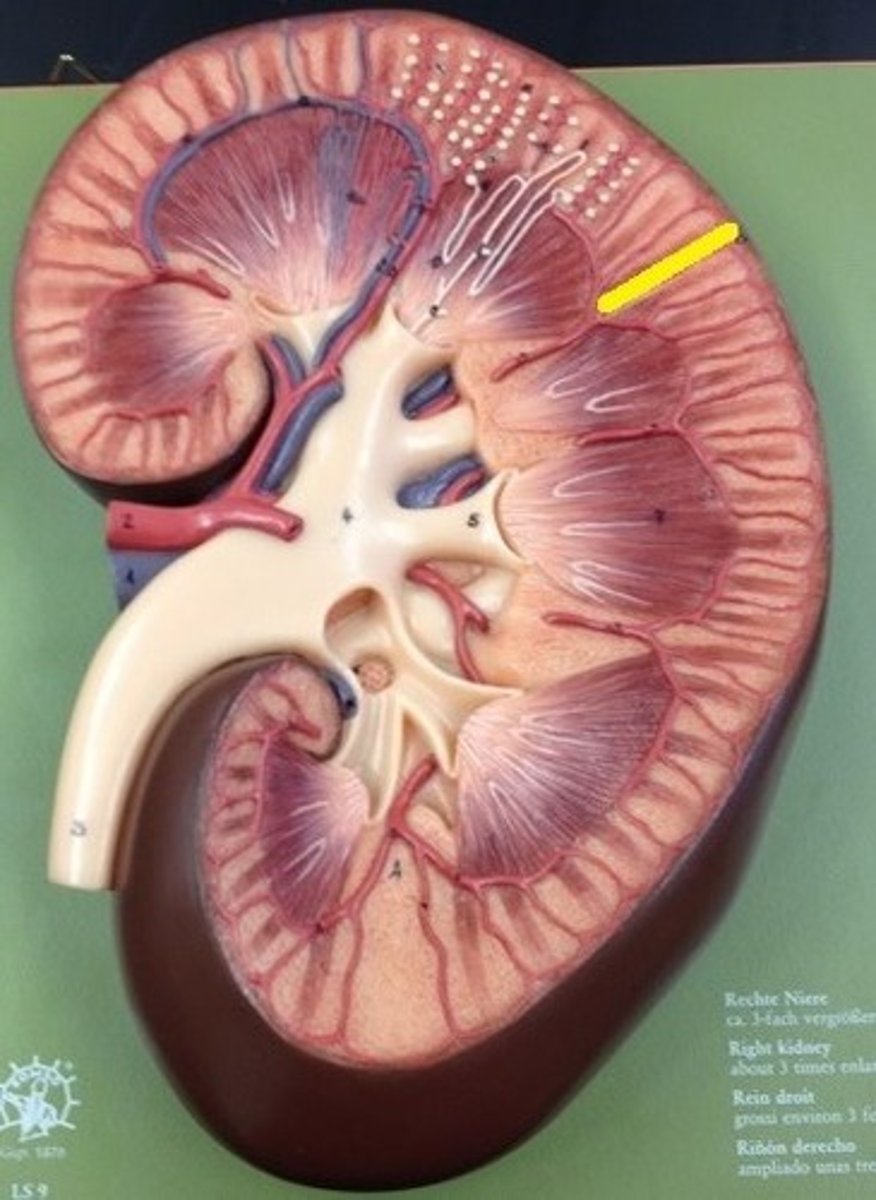
renal medulla
the area that makes up the pyramids
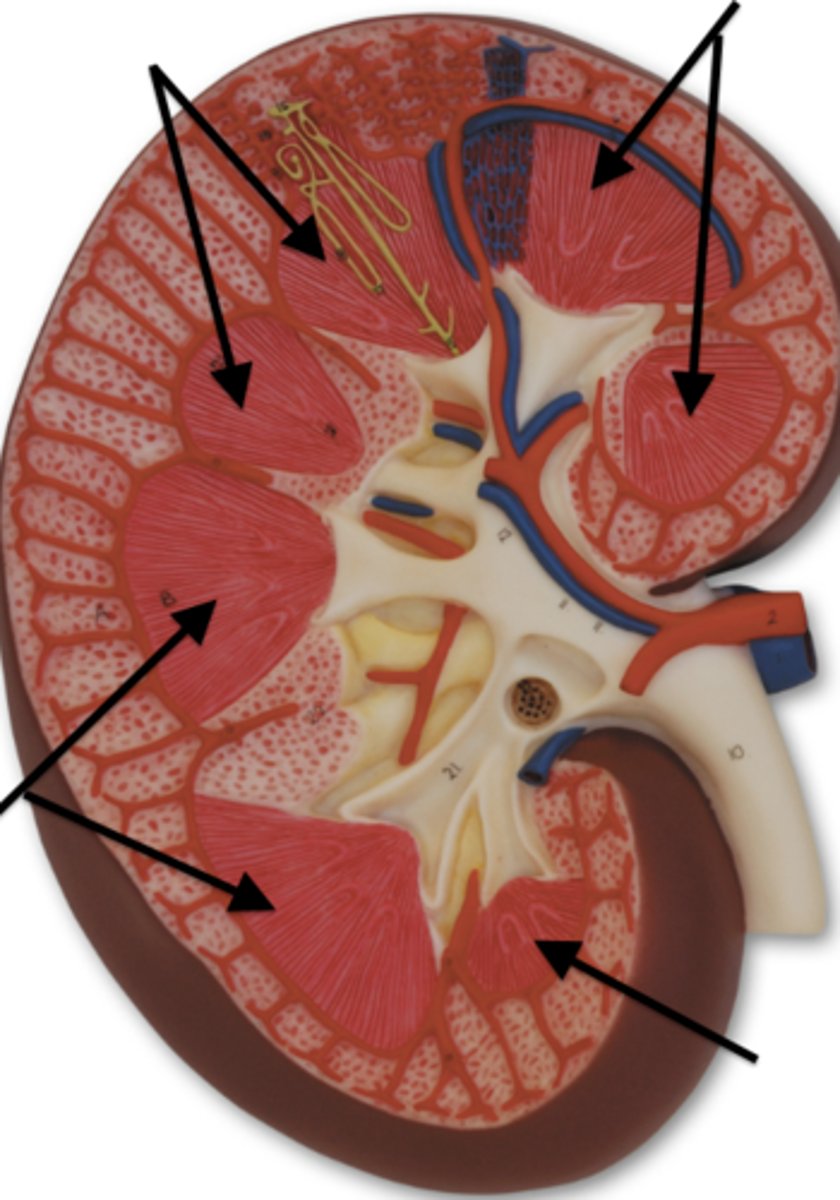
renal arteries
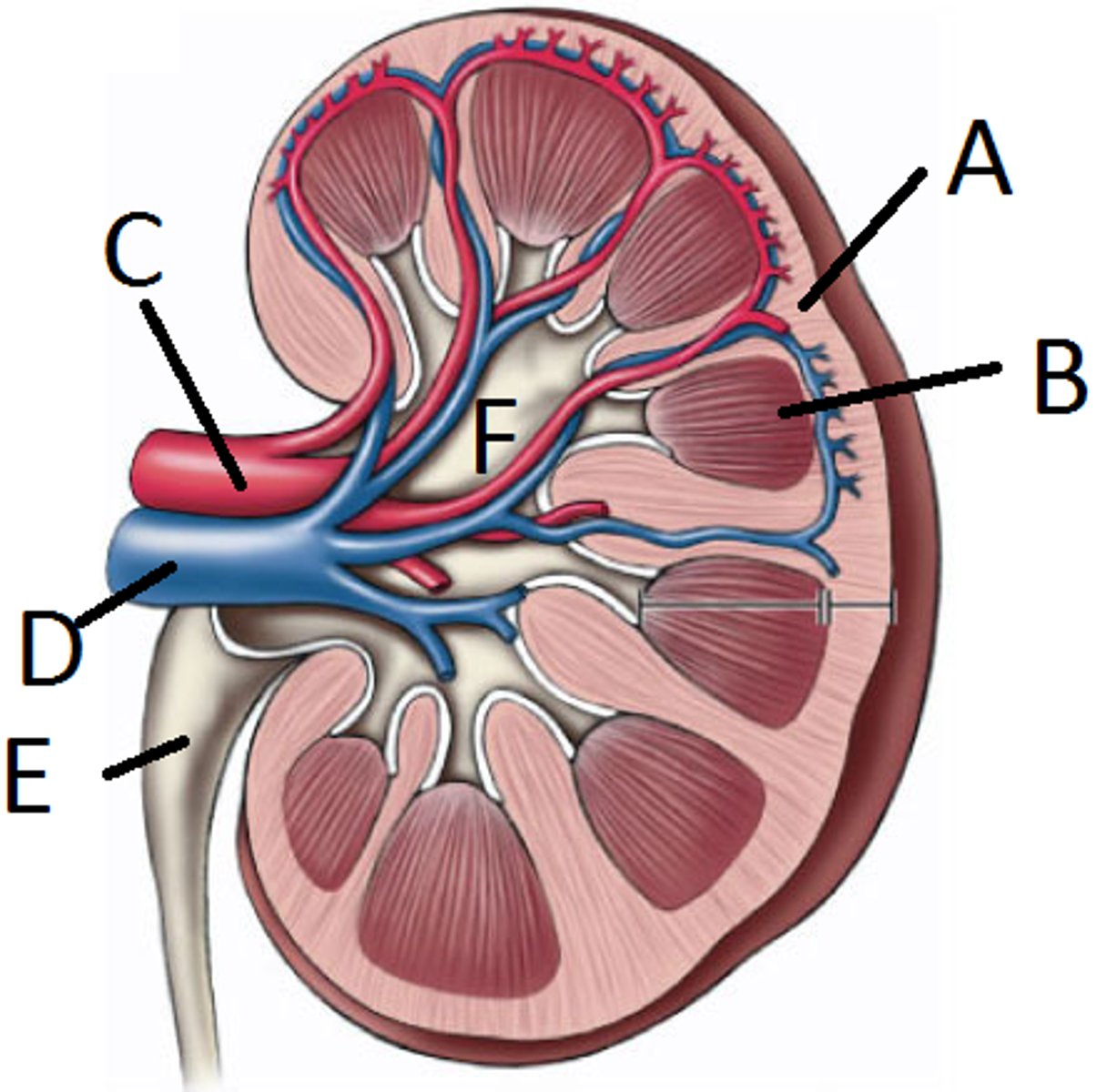
kidney blood flow:
1. oxygenated blood comes down from the descending aorta to what
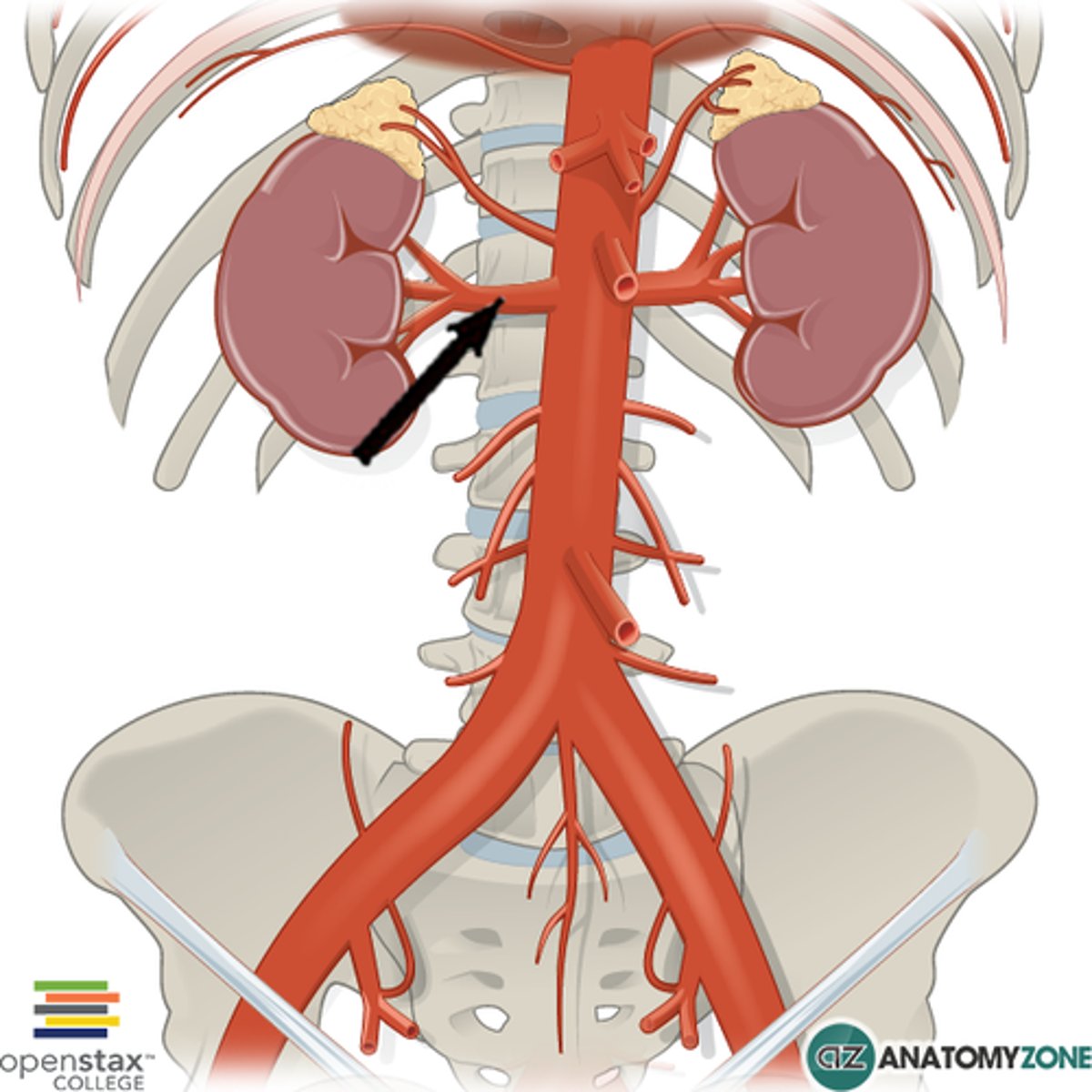
segmental arteries
kidney blood flow:
2. renal arteries split into two _____ and then break down smaller and smaller
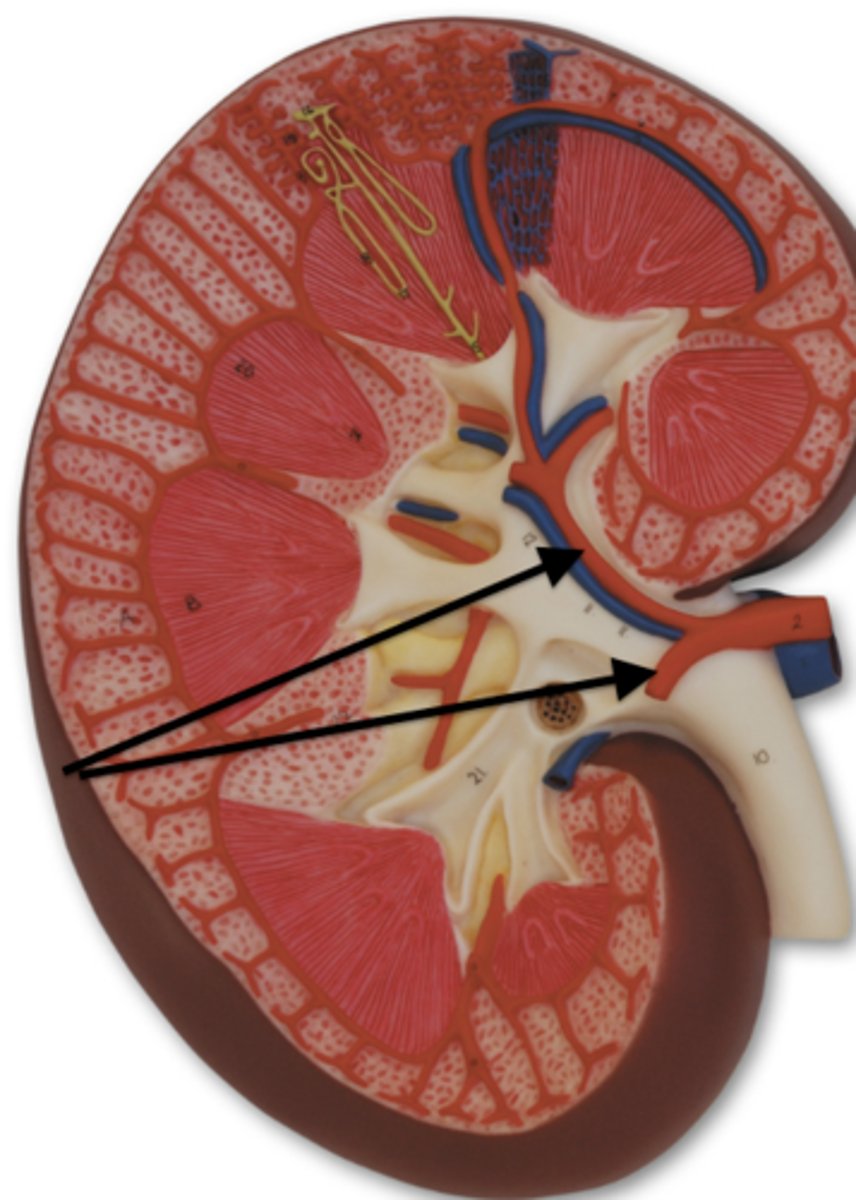
afferent arterioles
kidney blood flow:
3. the segmental arteries break down smaller until they become ______ ______
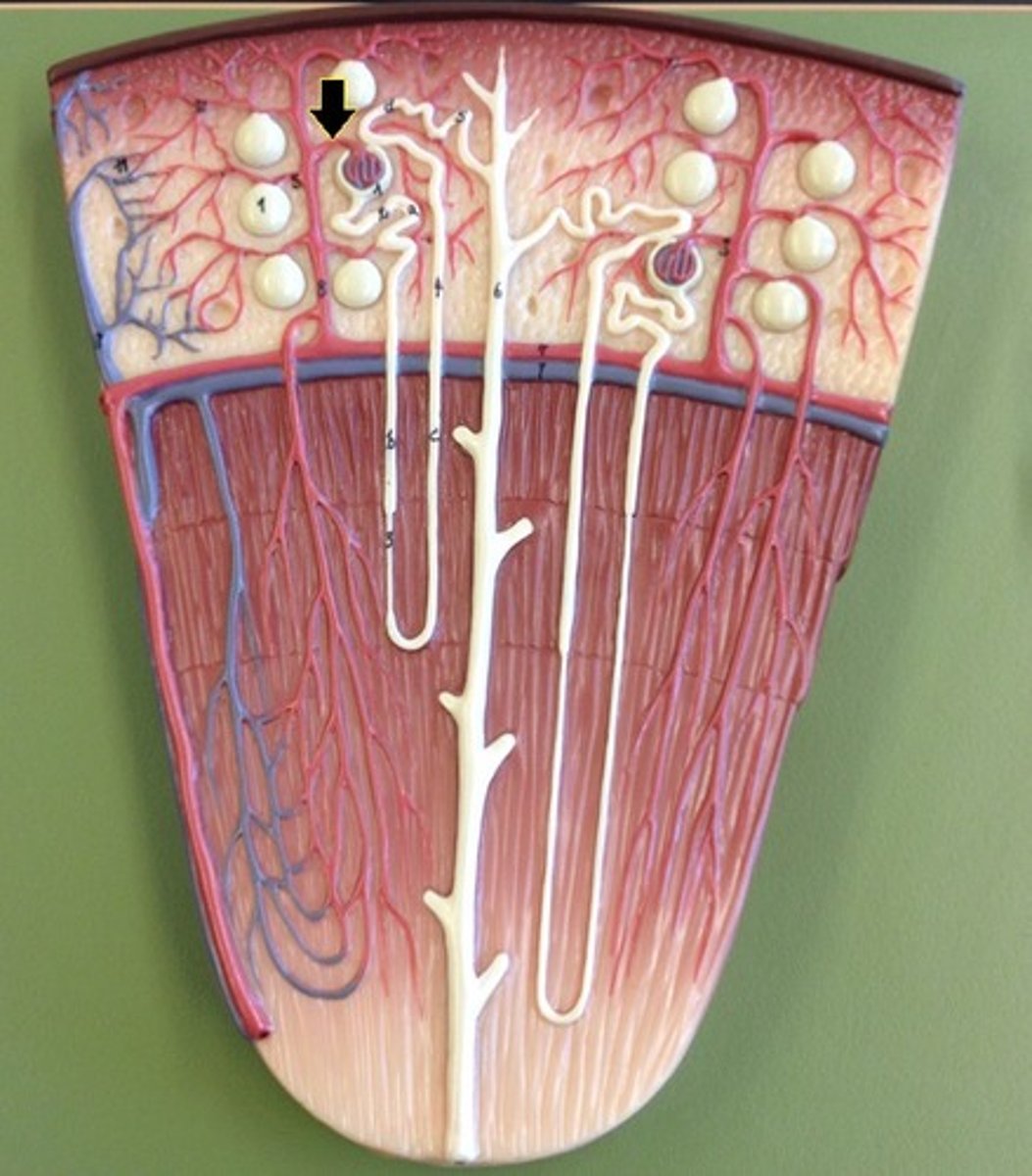
glomerulus
kidney blood flow:
4. the afferent arterioles are traveling towards the ______ (A), the structure where the beginning of blood filtration starts
nephrons
kidney blood flow:
5. what the glomerulus wants to excrete as urine will travel through the _______
efferent arterioles
kidney blood flow:
6. what the glomerulus wants to send back through circulation will then get sent to the ______ _____
peritubular capillaries
kidney blood flow:
7. the efferent arterioles will then become _______ _______
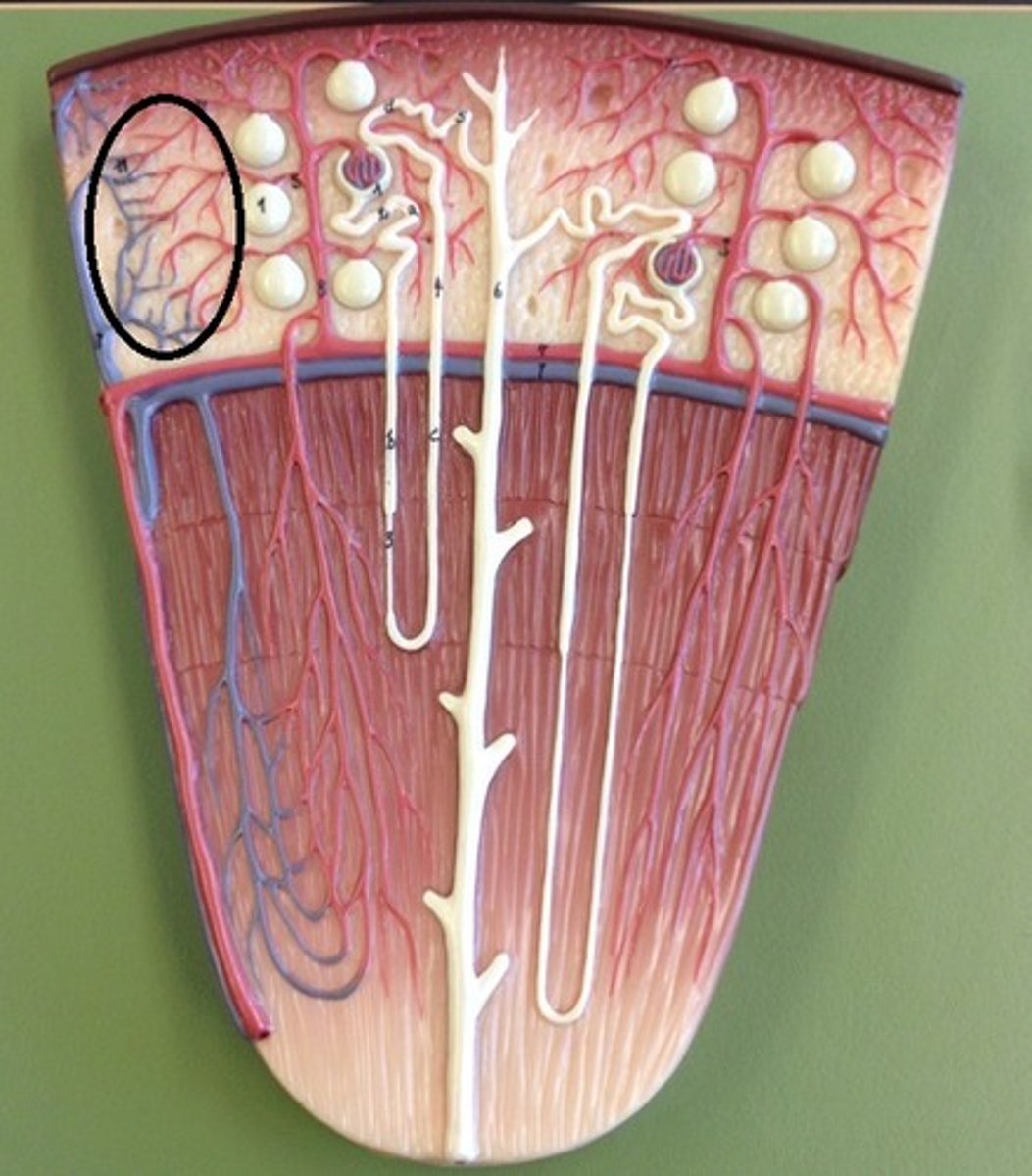
interlobular veins
kidney blood flow:
8. the peritubular capillaries will then connect with the ______ ______
segmental veins
kidney blood flow:
9. the interlobular veins will then become ______ veins
renal vein
kidney blood flow:
10. the segmental veins will then become the ____ vein (D)
inferior vena cava
kidney blood flow:
11. the renal vein will then flow to the _____ vena cava to go back into circulation/the heart
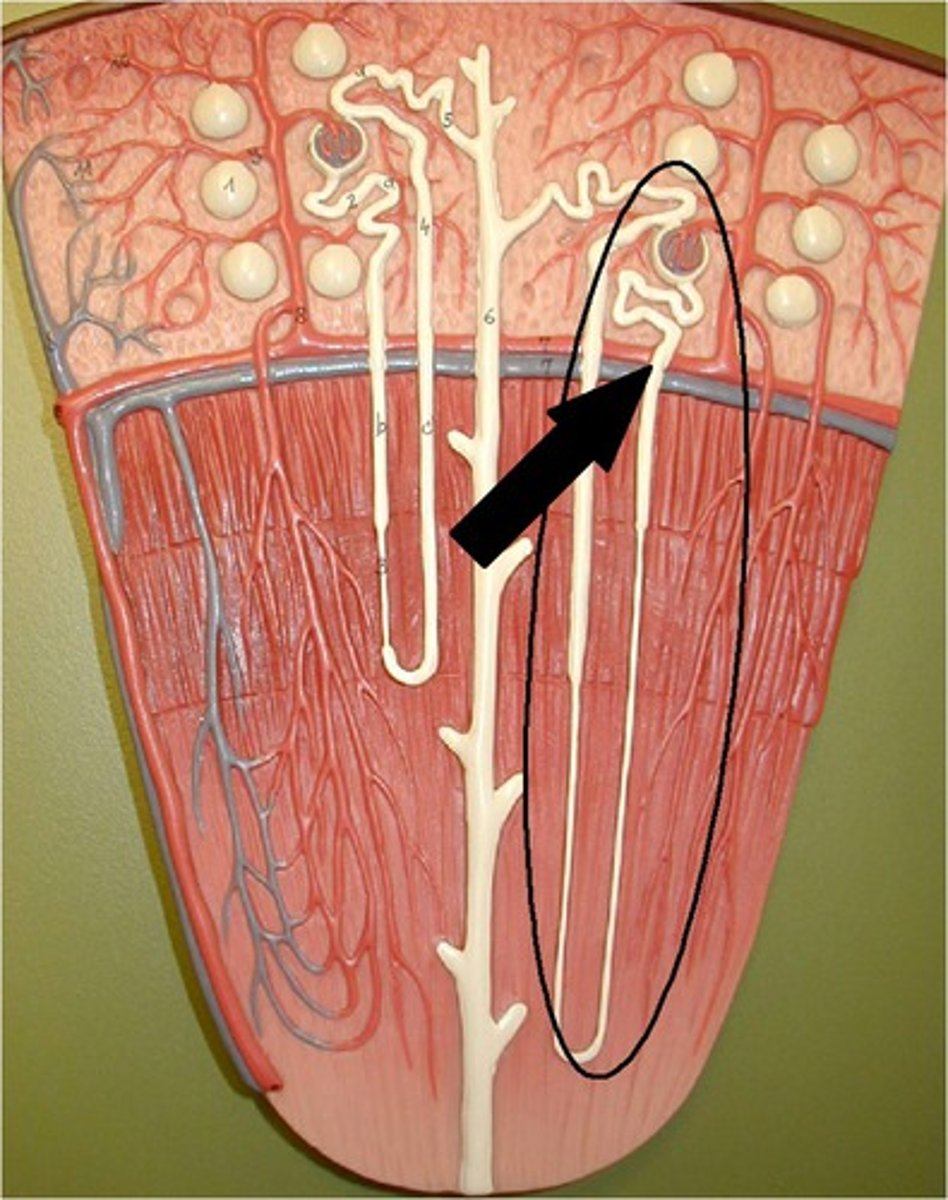
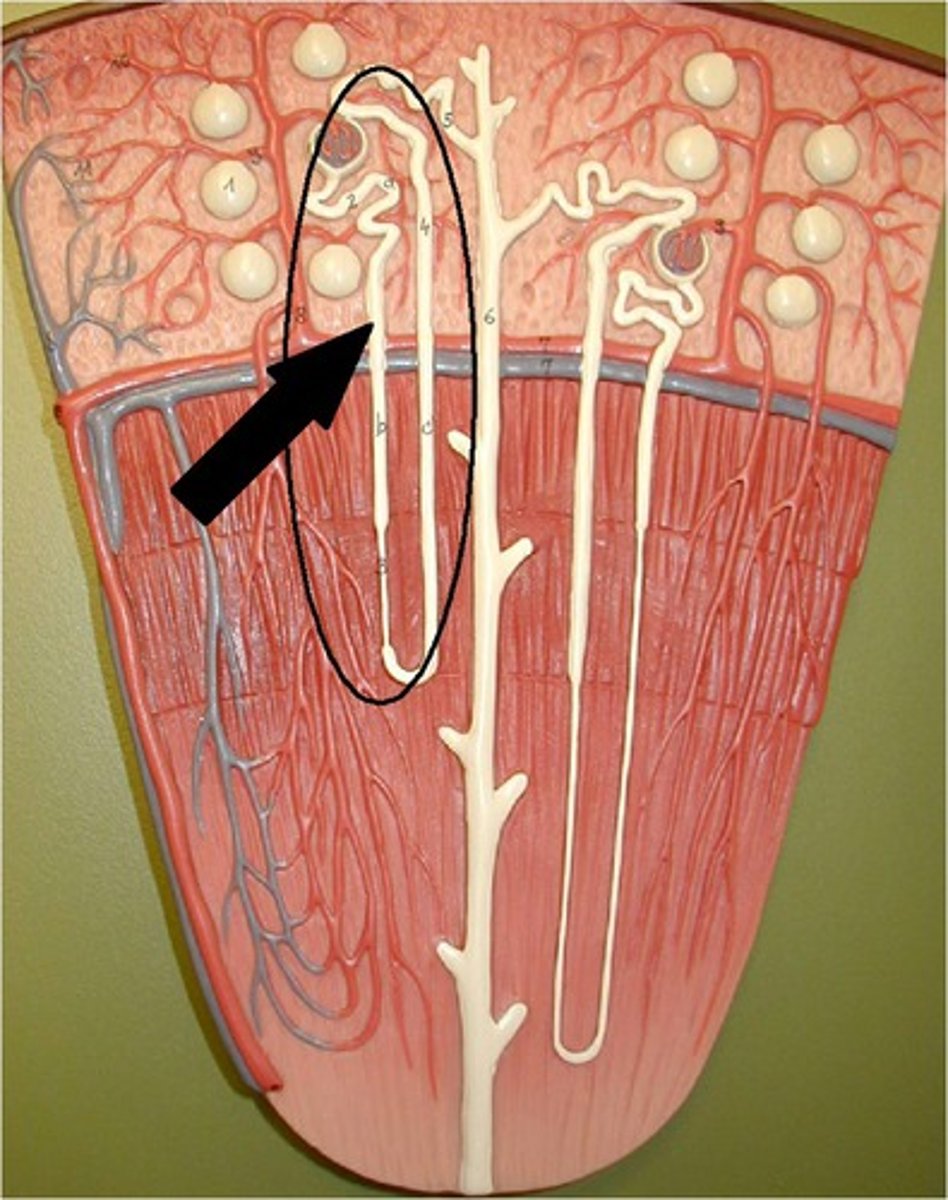
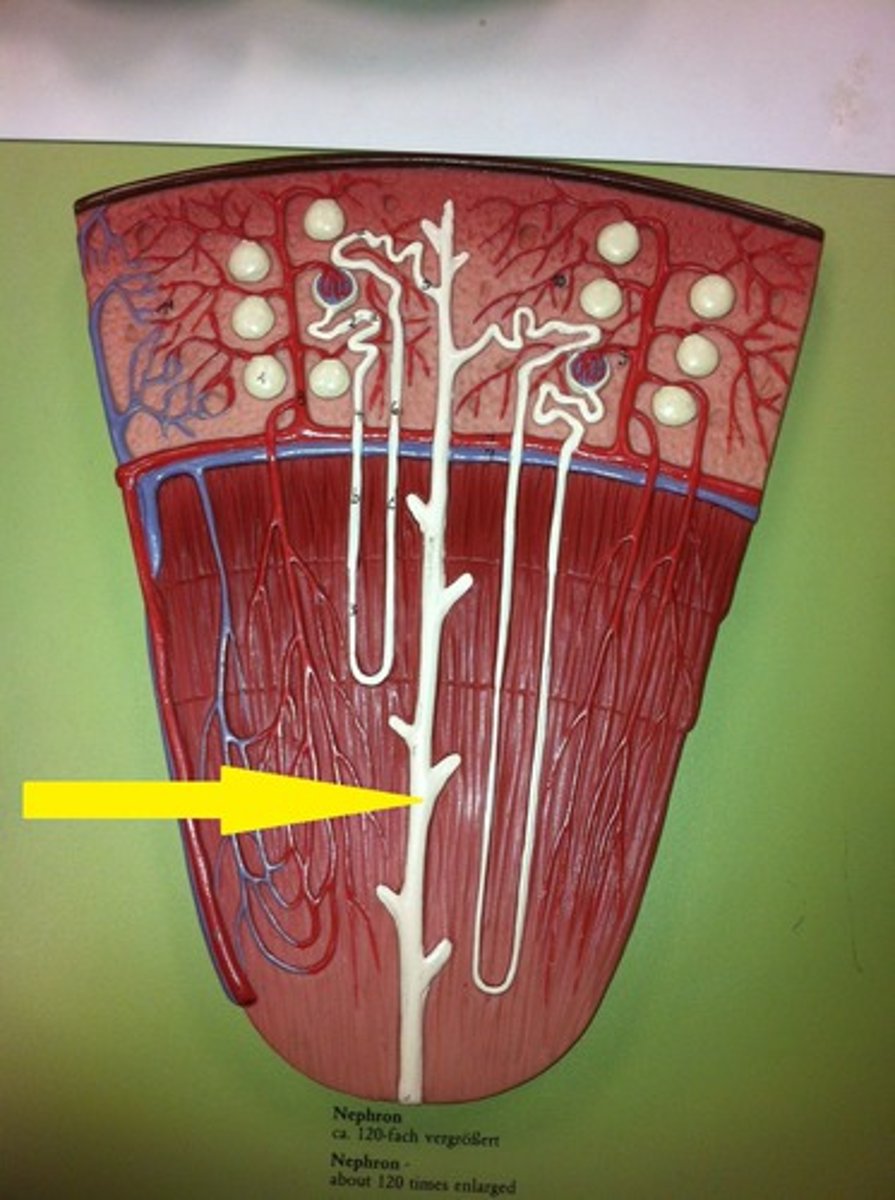
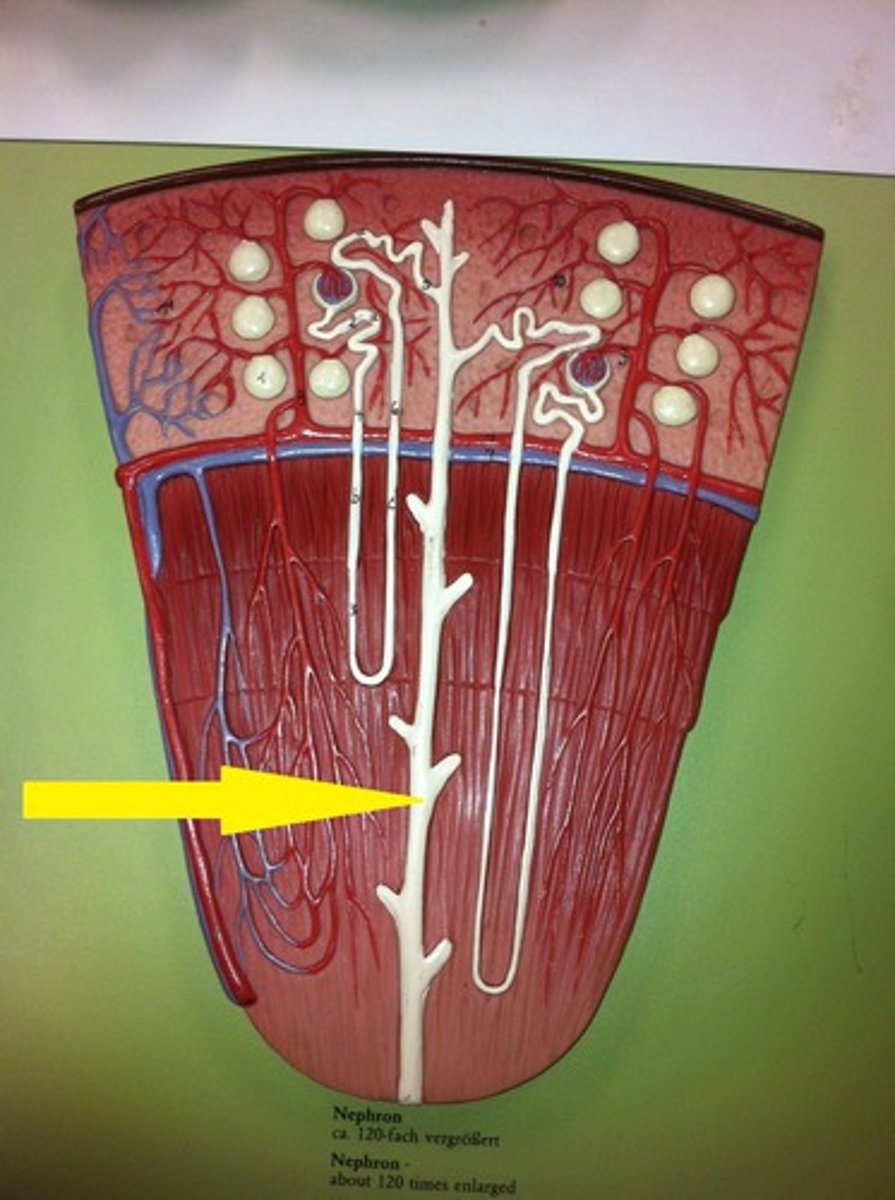
cortical nephrons
nephrons in the cortex are called
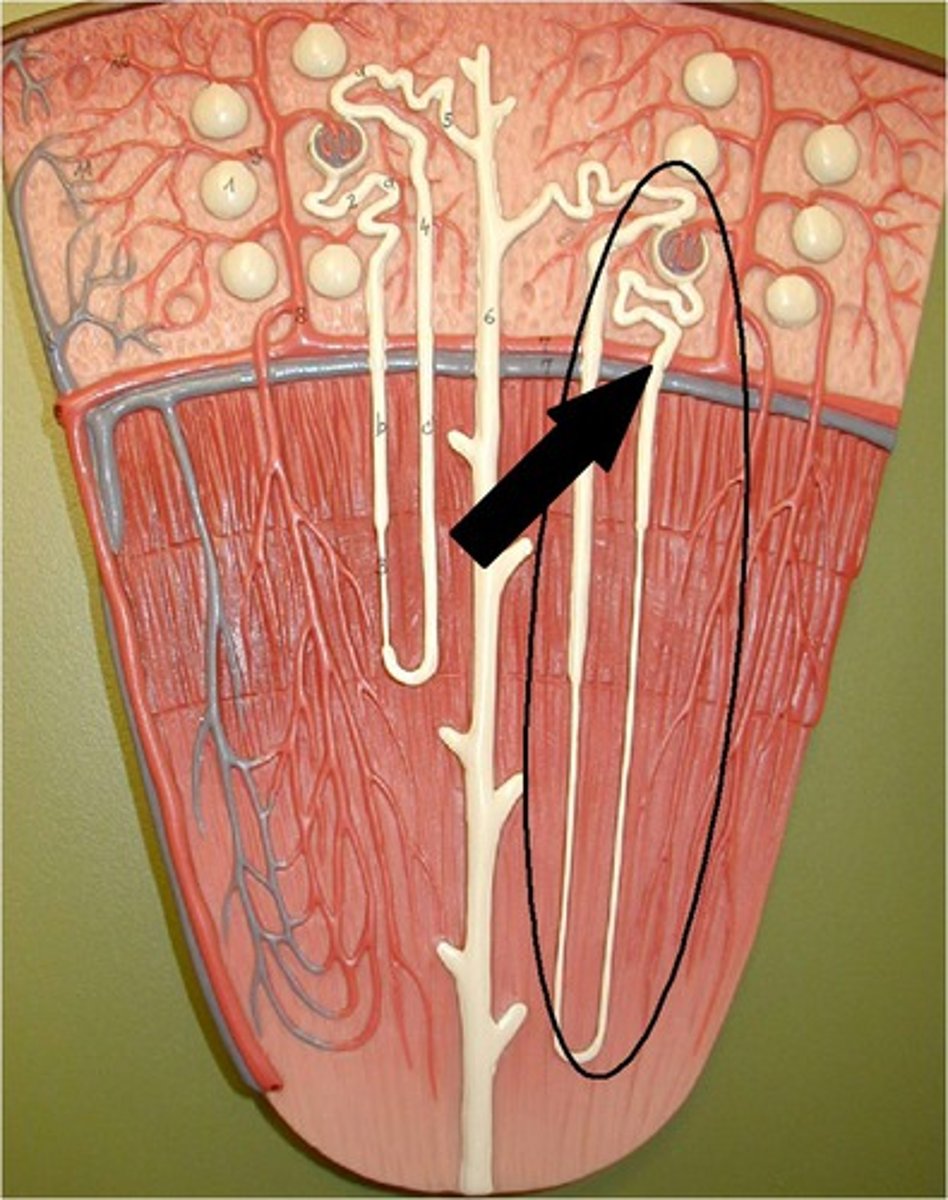
juxtamedullary nephrons
nephrons in the medulla are called
about 25%
the heart pumps 5 ml of blood per minute, and the kidneys can filter how much of that
smooth muscle
the ureters do not have valves but are lined with what for peristalsis so the urine doesn't just drop down
if there's too much urine in bladder, bladder will expand and ureters will close off preventing backflow
explain how urine doesn't back flow from the bladder into the ureters
UTI (if it travels all the way up to the kidneys, becomes a kidney infection)
sometimes urine can go back up from the bladder into the ureters. this could cause what
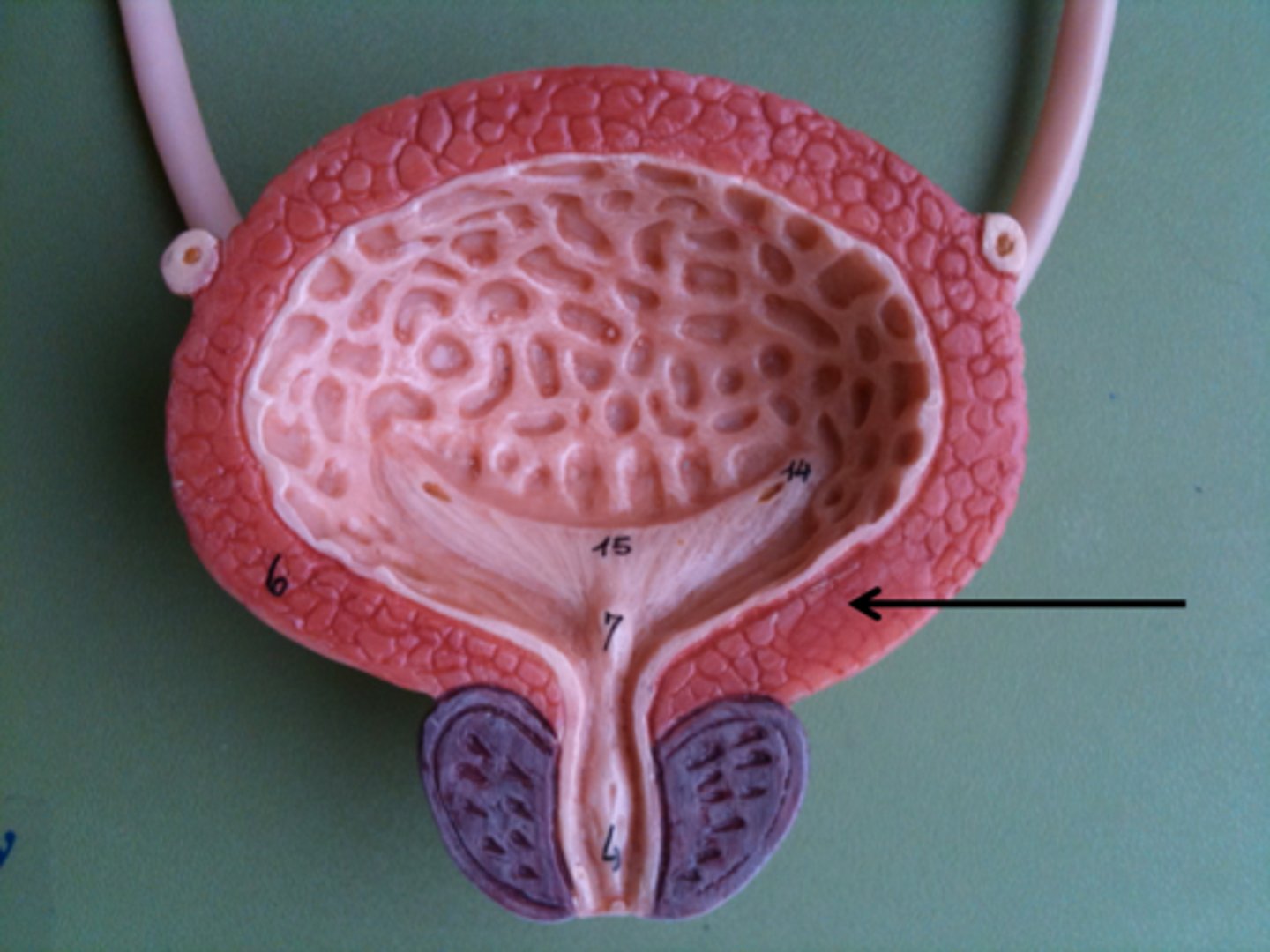
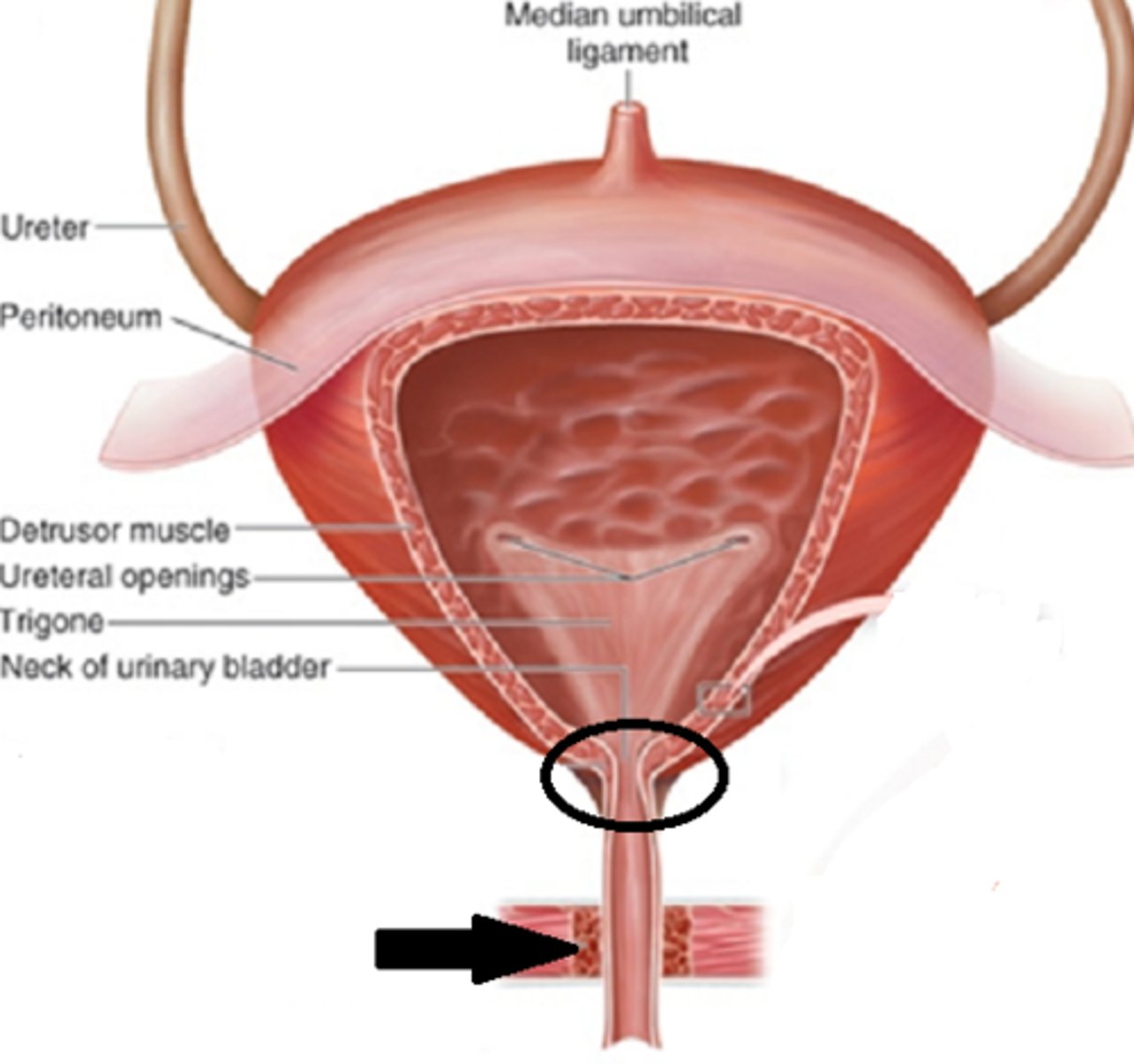
mucosa
innermost layer of bladder
detrusor muscle
second layer of bladder: smooth muscle called
no, it's an ANS function
do we have voluntary control over detrusor muscle
adventitia
outermost bladder layer (what anchors it onto back of peritoneum membrane)

symphysis
uterus
in females, the bladder is right behind the pubic _____ and right in front of the ____
trigone
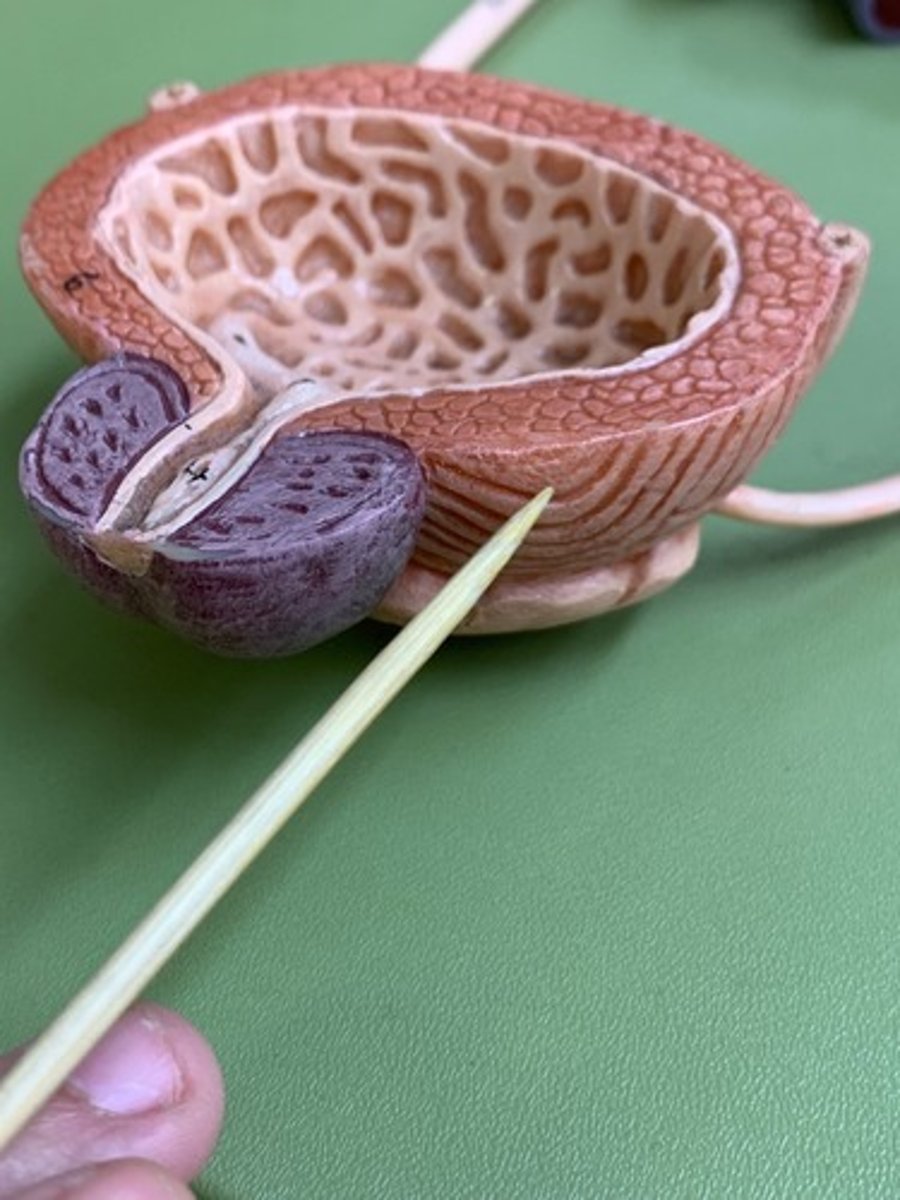
the triangle structure in the bladder that drops down into the urethra is called the
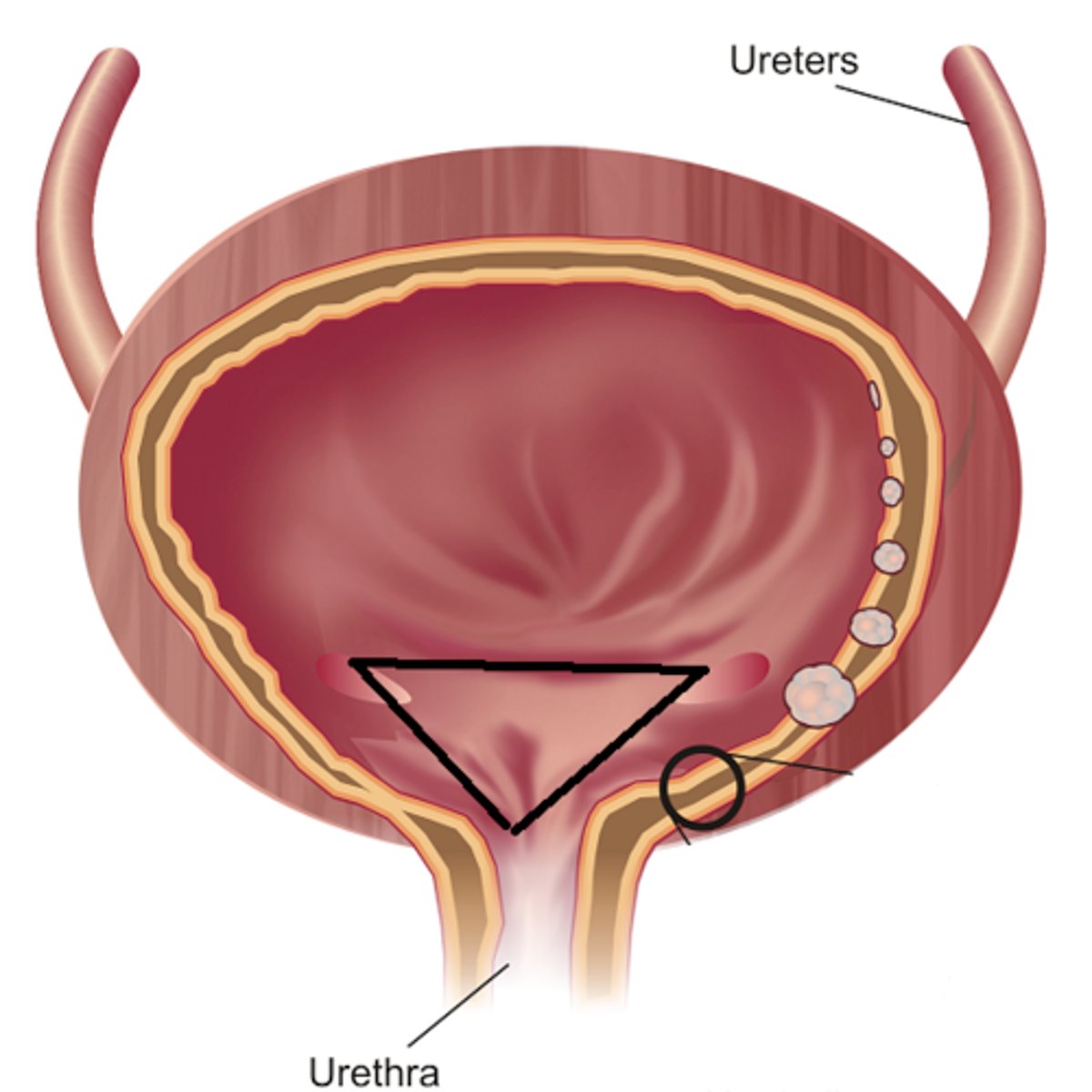
mucus
the trigone is heavily lined with what to help move bacteria so it is less likely to colonize and go back up through ureters into the kidneys
symphysis
rectum
in males, the bladder is right behind the pubic ____ and anterior to the _____
internal sphincter
what is this part of the urethra (involuntary control)
external spincter
what is this part of the urethra (voluntary control, where arrow is)
to help with urinary incontinence because of how short the urethra is
why do female external sphincters have a little more anterior muscle
males (extends all the way through the penis)
urethra longer in males or females
1. urethra is much closer to the rectum than males
2. females have much shorter urethra- in males, immune system has more chance to fight off bacteria in urethra since it's longer and takes longer to gets up to kidneys
see slide 22 for visual
2 reasons why women get bacterial infections easier
pudendal nerve
what nerve plays a critical role in controlling when we pee/poop
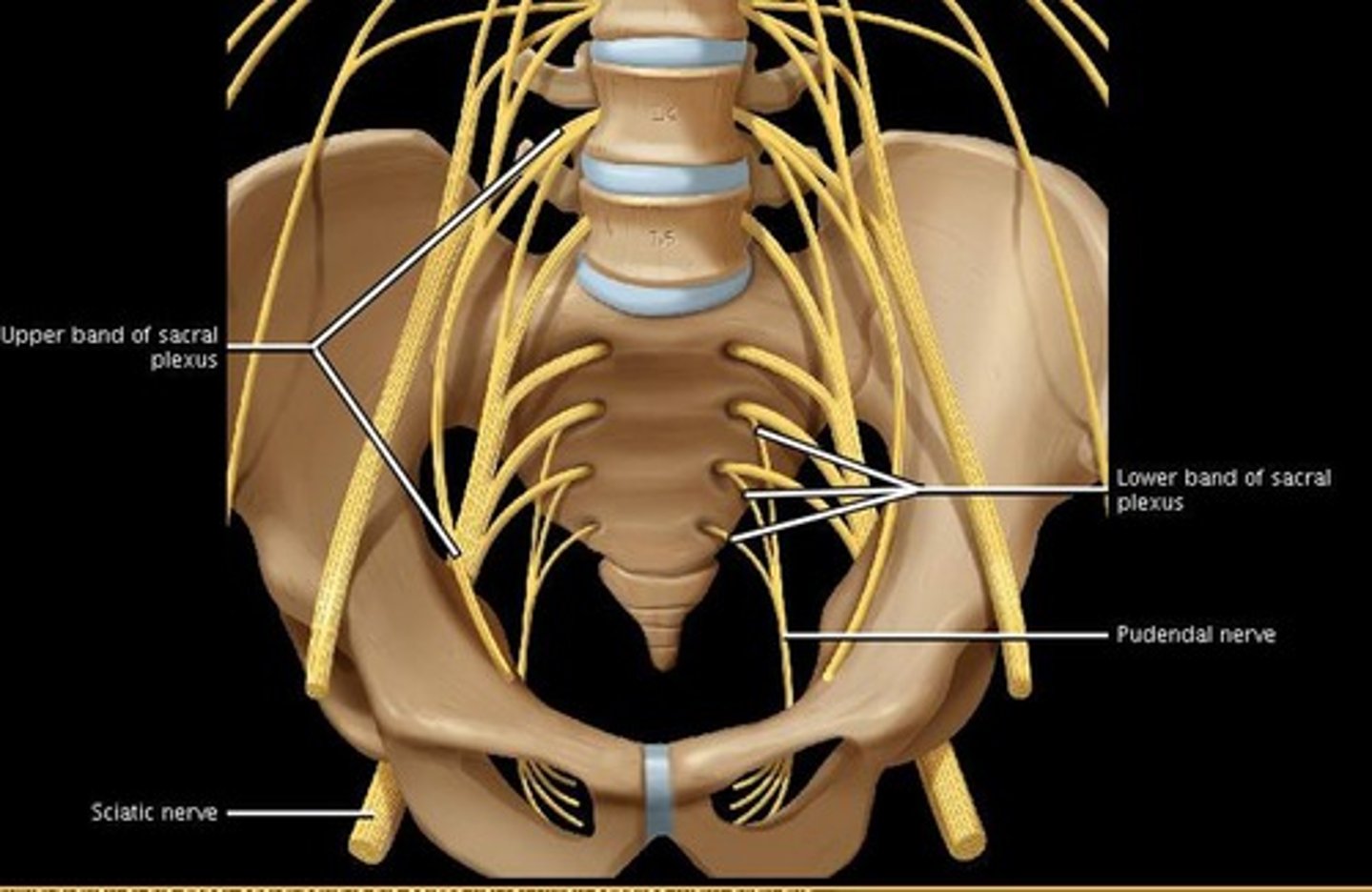
spinal cord
internal
1. as the bladder is filling up, detrusor muscle stretches -> stretch reflexes send message to brain via ___
2. the brain then sends message back down for ____ anal sphincter to open (now we feel like we have to go)
spinal cord
if the bladder gets too full, the voluntary control of external sphincter will be overridden. This reflex only happens at the level of the ____
nephron
the functional filtration unit of the kidney
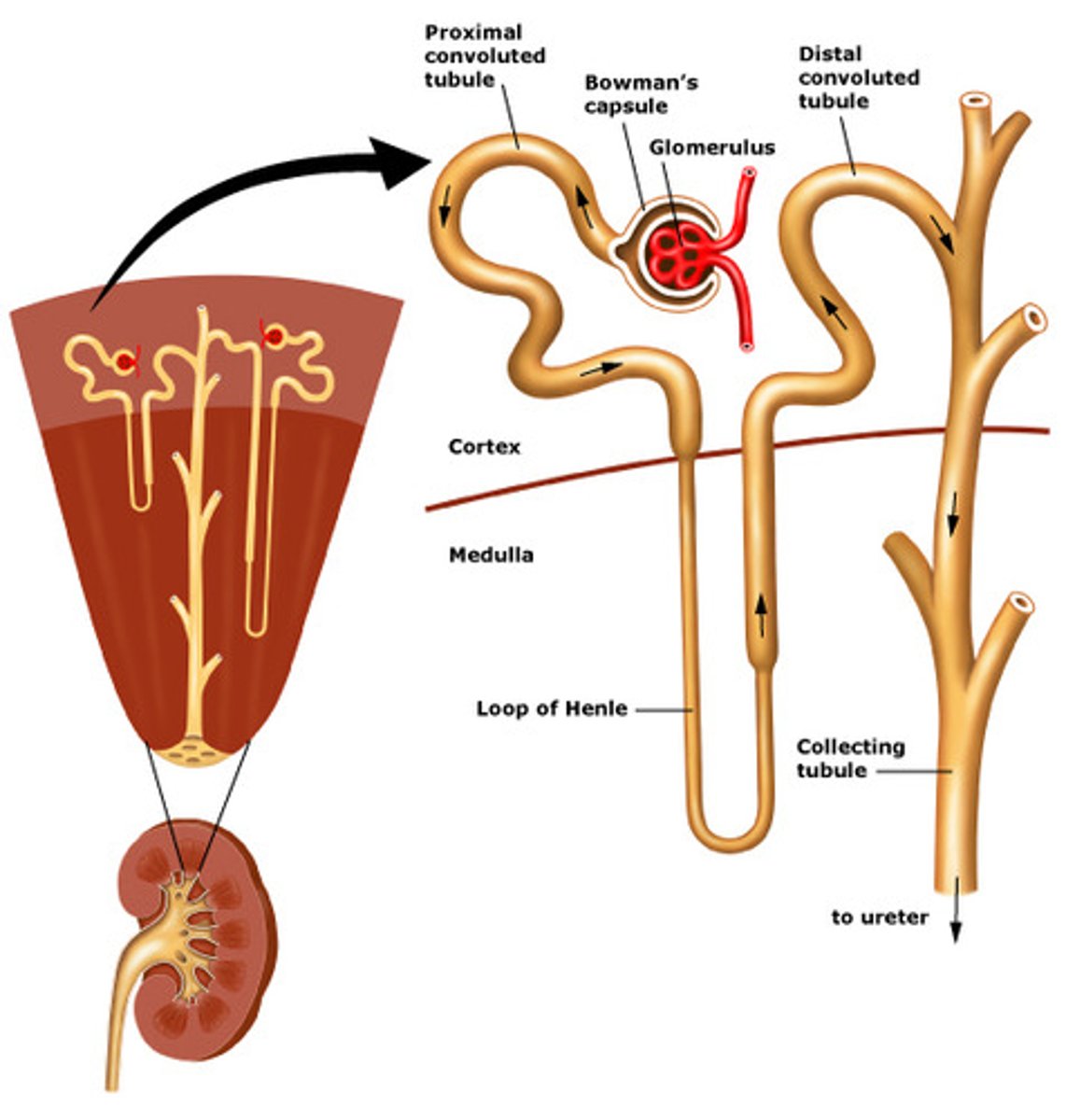
cortex
medulla
(the cortical nephrons create pressure for the blood to go down into the medullary nephrons)
20% of nephrons are in the ____
80% are in the ____
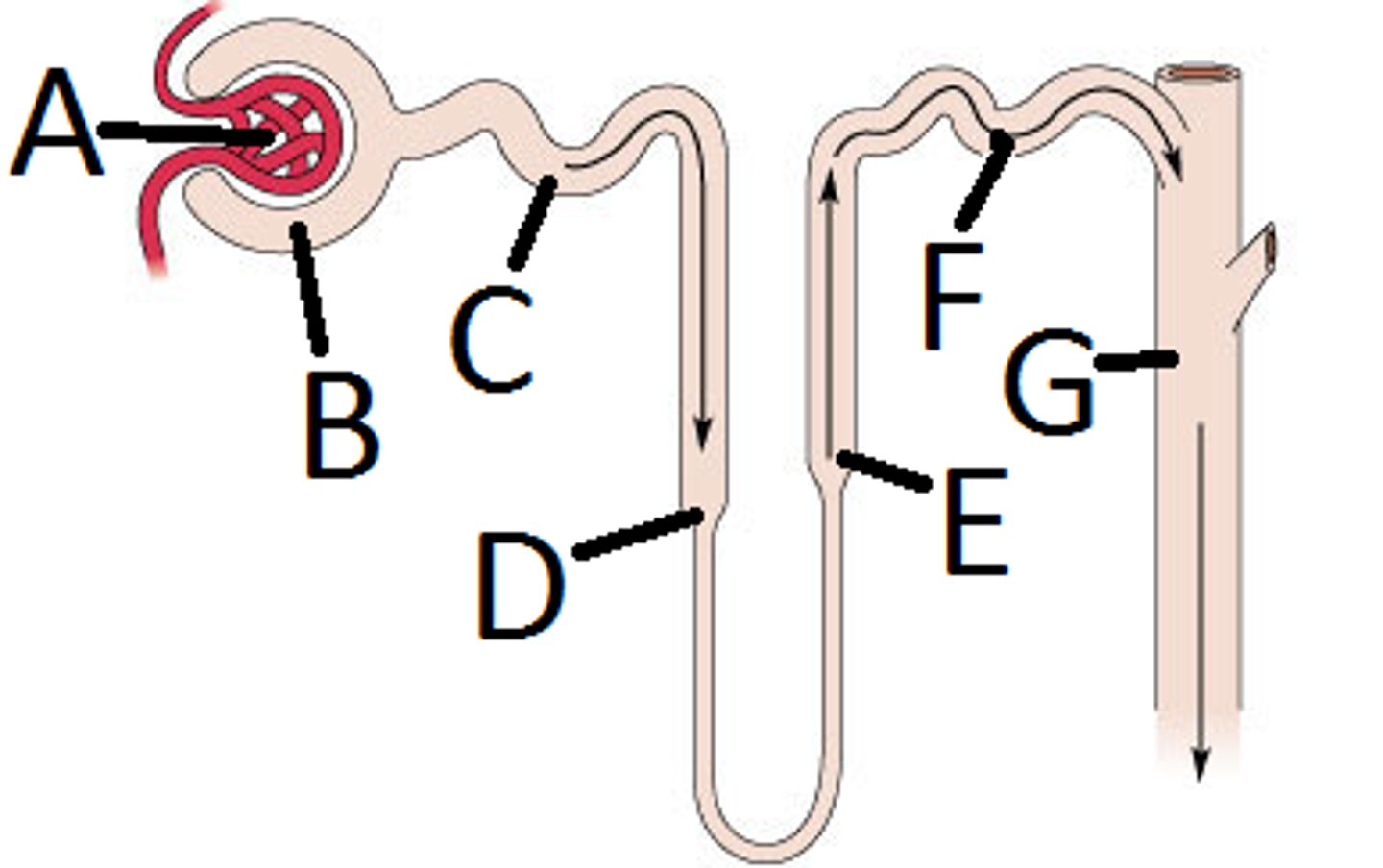
Bowman's capsule
what is the epithelial wrap around the glomerulus
Bowman's capsule
nephron
in the glomerulus, anything that needs to go back into circulation will pass through _____ _____. Anything that needs to go out as urine will keep travelling through the ______
millions
how many nephrons are in our kidneys
proximal tubule
also called proximal convoluted tubule or PCT
travel of urine:
1. after glomerulus, will travel to the
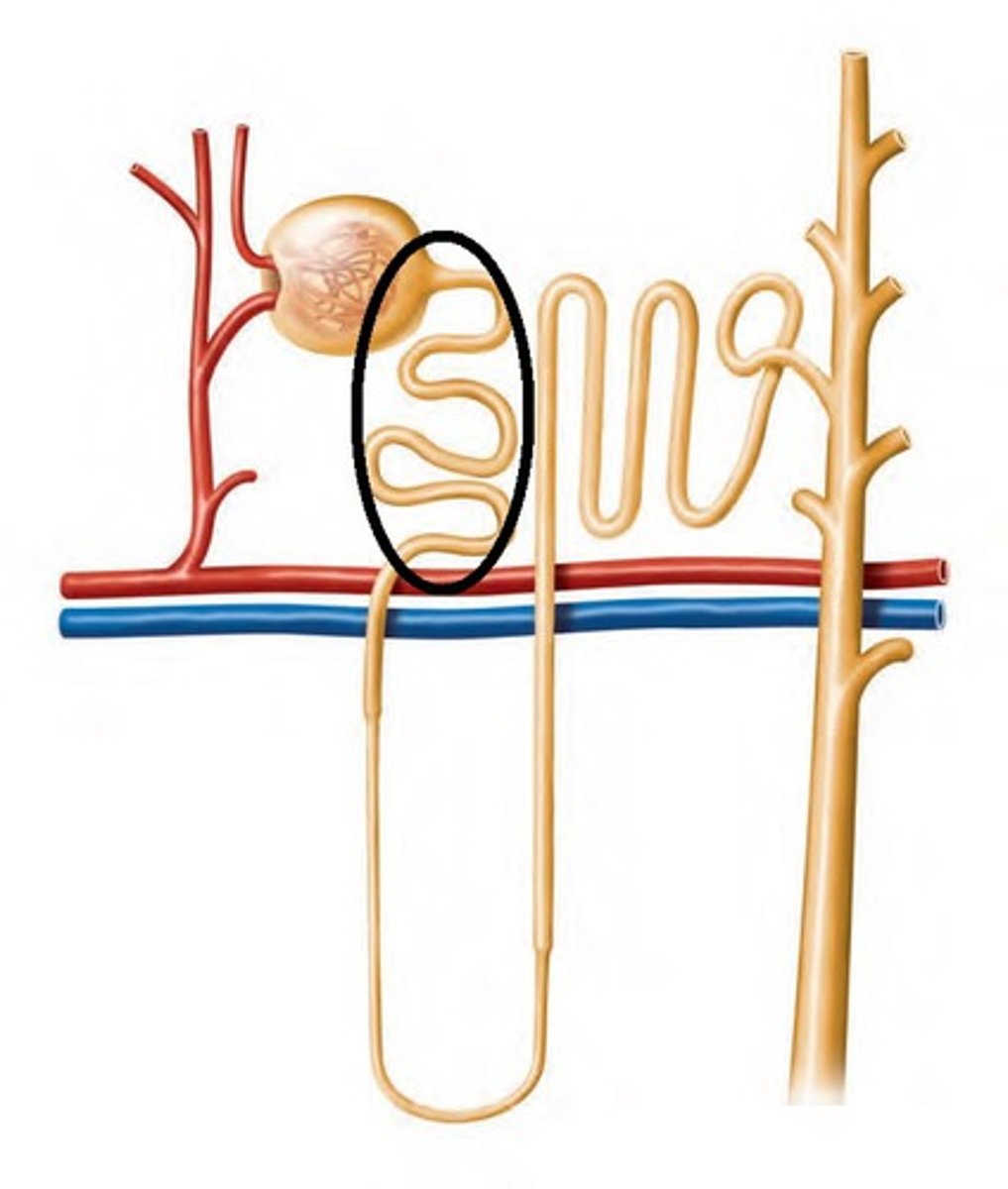
loop of Henle
travel of urine:
2. after the proximal tubule, urine will drop down into the
descending loop of Henle
loop of Henle
ascending loop of Henle
3 parts of loop of Henle
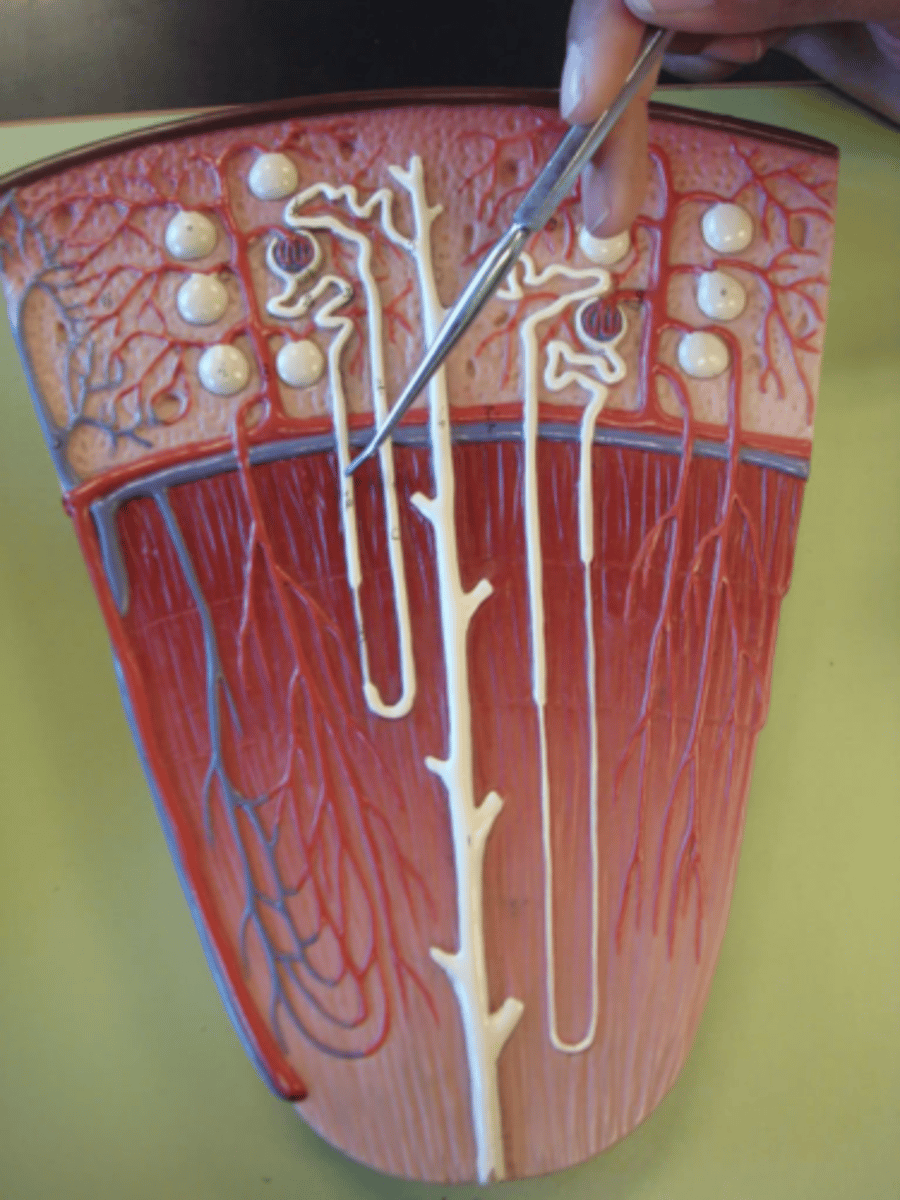

distal tubule
AKA distal convoluted tubule or DCT
travel of urine:
3. after the loop of Henle, goes to the
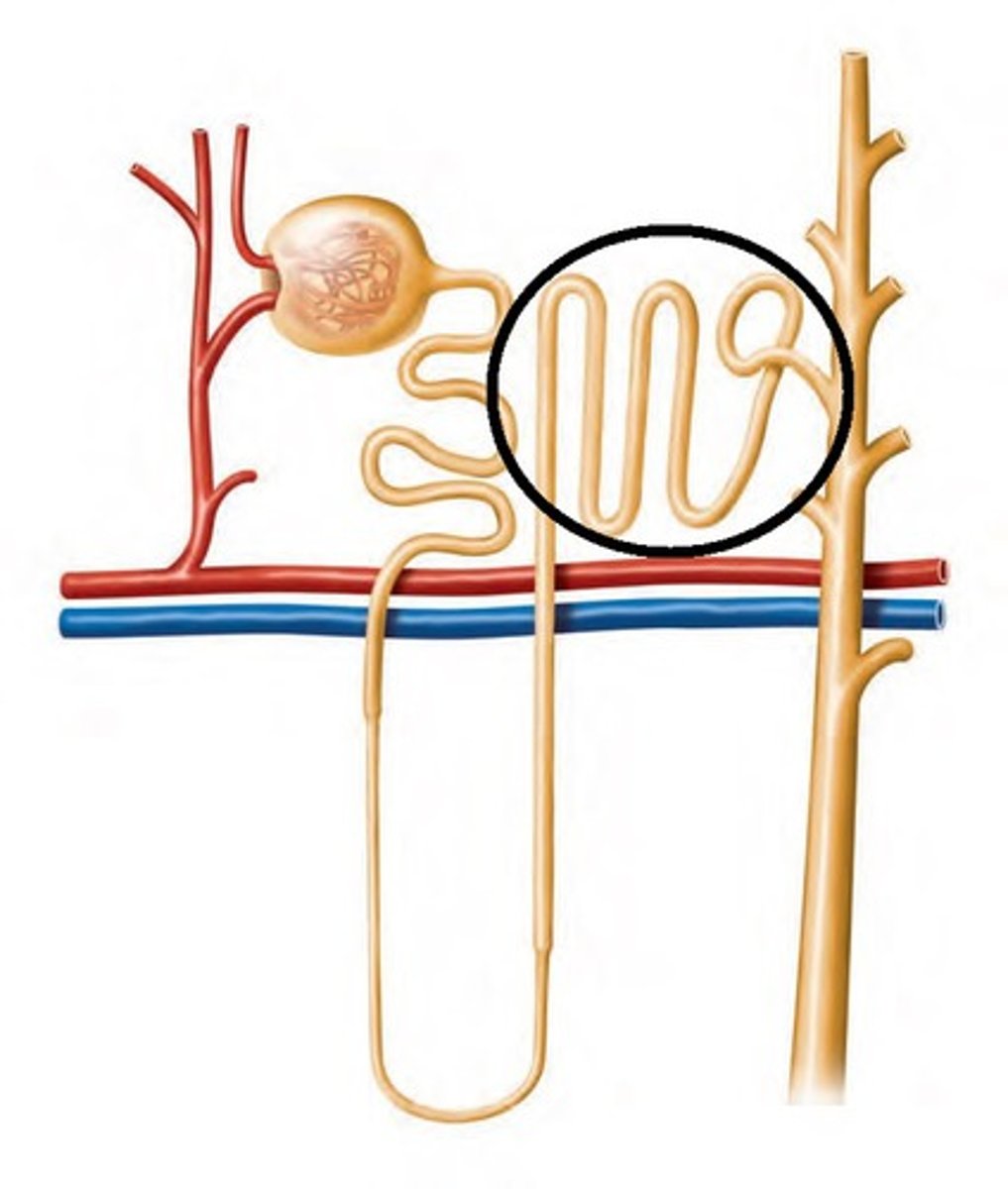
collecting duct
travel of urine:
4. after the distal tubule, goes to the
yes
do multiple nephrons attach onto one collecting duct
water
salt
glucose
what can filter out of Bowman's capsule and go back into circulation
protein
drugs
what can't filter out of Bowman's capsule
Bowman's capsule
in the nephron, filtration is happening at the level of where
PCT
loop of Henle
DCT
(things that get secreted out are reabsorbed via the peritubular capillaries that wrap around the nephron)
in the nephron, absorption and secretion are happening at the level of where
water
salt
glucose
at the PCT, more of what 3 things are going to come back out
descending loop of Henle
the primary secretion of water happens where in the nephron
ascending loop of Henle (will also loose some water in this area as well between ascending loop and collecting duct)
most of the salt is coming out where in the nephron
DCT
what area of the nephron fine tunes salt and water balance
collecting duct
formation of urine happening where in the nephron
urea
what substance is also traveling through the nephron that gives urine its smell and yellow color
ammonia
urea is a byproduct of
aldosterone
what hormone is regulating electrolyte/sodium balance at the area of the DCT
ADH (antidiuretic hormone)
what hormone is also starting to do its work at the DCT and a lot at the collecting duct (will determine if we need more water or need to pee out more water)
Lasix
what is a loop diuretic drug that acts on the loop of Henle
CHF or hypertension
loop diuretics will often be prescribed to patients with what conditions to get them to pee out more fluid
they stop sodium from getting secreted out of the nephron (water will also follow it and won't go out of the nephron) hence more urine being created in the nephron
how do loop diuretics (Lasix) work
kidney
principal urinary system organ
cystitis
an inflammation of the urinary bladder, often caused by a bacterial infection. It's a type of urinary tract infection (UTI). Symptoms include a frequent and urgent need to urinate, a burning sensation during urination, and pain in the lower abdomen.
urethritis
an inflammation of the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. It is commonly caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. Other causes include bacterial infections, irritation from chemicals or soaps, and certain medical conditions
hydronephrosis
a condition where one or both kidneys swell due to a buildup of urine, often caused by a blockage or obstruction in the urinary tract. This blockage prevents normal urine drainage from the kidney to the bladder, leading to urine backup and kidney swelling
the liver (they're both the same size though)
why is right kidney lower than the left
nephron
basic functional unit of kidney
180
how many liters filtrated in kidney each day
urea
most abundant nitrogenous waste product excreted in the urine
review GI slide 13 about dialysis (frequency/duration, access point, settings they occur in)
review GI slide 13 about dialysis (frequency/duration, access point, settings they occur in)
Blockage is a concern with lymphedema. Can the fluid even move to the kidneys to get processed out of the body? Blockage needs to be addressed first
Diuretic makes you pee more. With lymphedema, why don't they prescribe diuretics?