Audiology Final
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
electroacoustic
__ tests are useful for populations that are otherwise difficult to test.
nonbehavioral
electroacoustic/electrophysiologic tests are __; that is, they don’t rely on patient responses.
otoacoustic emissions
__ __ is a type of testing that evokes a response from the cochlea.
transient evoked
this type of OAE involves a brief stimulation of the cochlea.
distortion product
this type of OAE involves a complex stimulation of the cochlea.
true
T/F: the presence of OAEs does not signal normal hearing sensitivity.
transient evoked
this type of OAE does not rule out mild HL.
distortion product
this type of OAE does not rule out mild to moderate HL.
auditory brainstem response
acronym: ABR
auditory steady state response
acronym: ASSR
distortion product otoacoustic emissions
acronym: DPOAE
transient evoked otoacoustic emissions
acronym: TEOAE
VIII
this CN is tested during brainstem response studies.
false
T/F: you can use ABR/ASSR alone to identify HL.
ASSR
this type of electrophysiologic measure can differentiate between severe and profound HL.
ABR
this type of electrophysiologic measure uses a click stimulus.
ABR
this type of electrophysiologic measure can be used for screening.
electronystagmography
acronym: ENG
videonystagmography
acronym: VNG
videonystagmography
this type of electrophysiologic measure is beyond the scope of the SLP
microtia
congenital malformation of the pinnaa
anotia
complete absence of the pinna
true
T/F: microtia is unilateral in 90% of cases.
impacted cerumen
wax buildup causing occlusion of outer ear canal
otitis externa
infection of skin in the external ear canal
otitis externa
the medical term for “swimmer’s ear”
exostosis
benign tumor of the external ear canal
osteoma
benign, slow-growing neoplasm of the bone
outer
microtia, impacted cerumen, otitis externa, exostosis, and osteoma are all disorders of the __ ear.
tympanic membrane perforation
hole in the eardrum
otitis media
negative pressure in the middle ear space
otosclerosis
buildup of spongy bone in the ear
cholesteatoma
overgrowth of skin cells in the middle ear
ossicular chain discontinuity
disarticulation of ossicles
middle
tympanic membrane perforation, otitis media, otosclerosis, cholesteatoma, and ossicular chain discontinuity are all disorders of the __ ear.
false
T/F: a sensorineural HL will show an ABG on the audiogram.
waardenburg syndrome
cochlear syndrome also causing pigmentary abnormalities of skin/hair/eyes
usher syndrome
hereditary syndrome affecting hearing, vision, and balance
acoustic trauma
technical term for noise-induced hearing loss
ototoxicity
“poisoning” of the ear
Meniere’s disease
disease of excess endolymphatic fluid
presbycusis
age-related hearing loss
auditory processing disorder
acronym: APD
auditory processing disorder
impairment of auditory information interpretation
sensorineural
syndromes, trauma, infections, ototoxicity, Meniere’s, and presbycusis cause __ hearing loss.
auditory processing disorder
poor listening, decreased attention, and poor phonological awareness are possible signs of __.
listening strategies, metalinguistics, self-advocacy
3 skills the SLP can target when treating APD
conductive
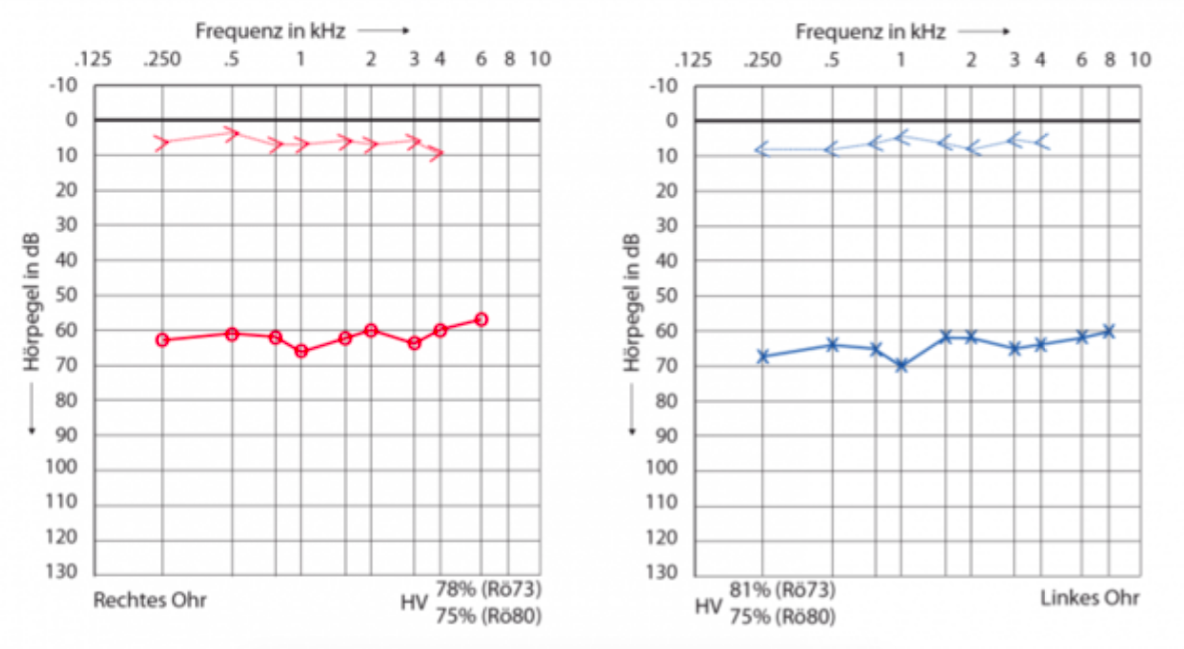
HL type
impacted cerumen
condition
osteoma
exostosis
tympanic membrane perforation
a type B tympanogram with ECV of 3.5 is likely caused by __.
excess fluid
a type B tympanogram with ECV of 1.3 is likely caused by __
bilateral otitis media
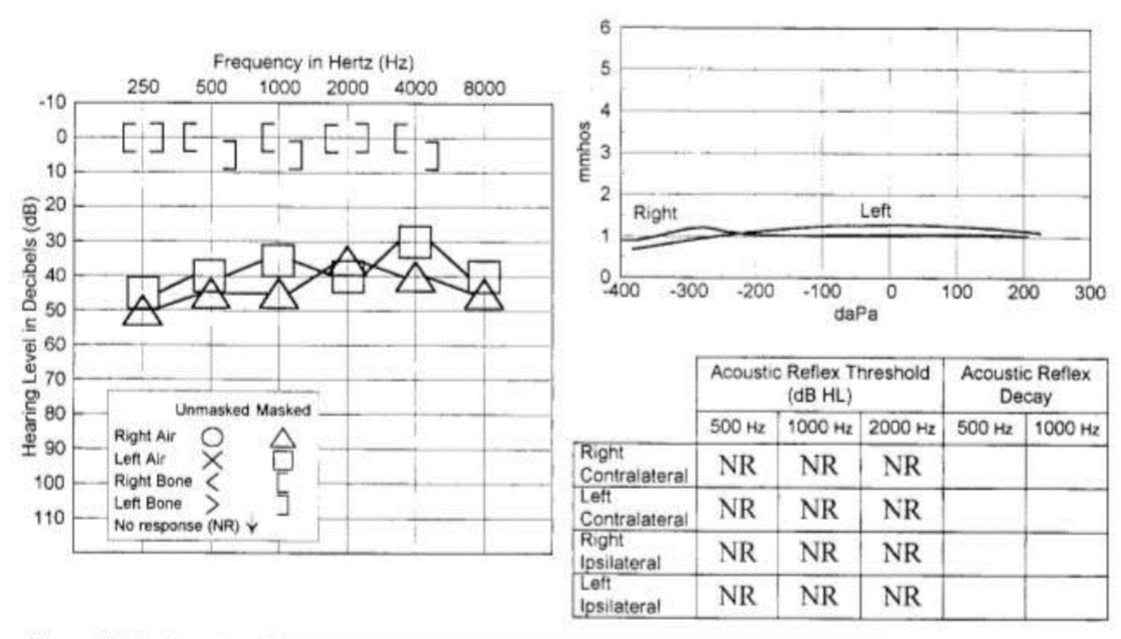
condition
otosclerosis
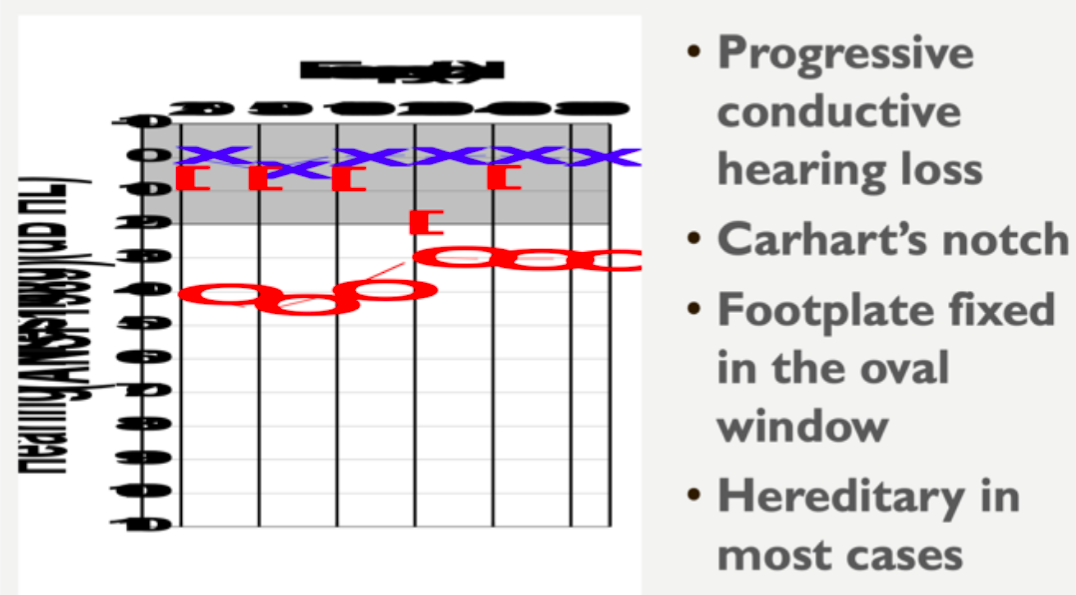
condition
ossicular chain discontinuity
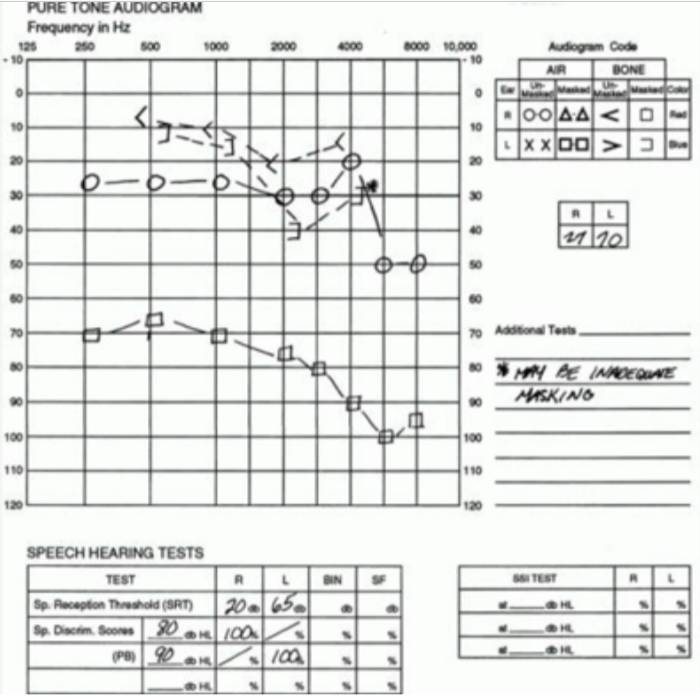
condition
conductive
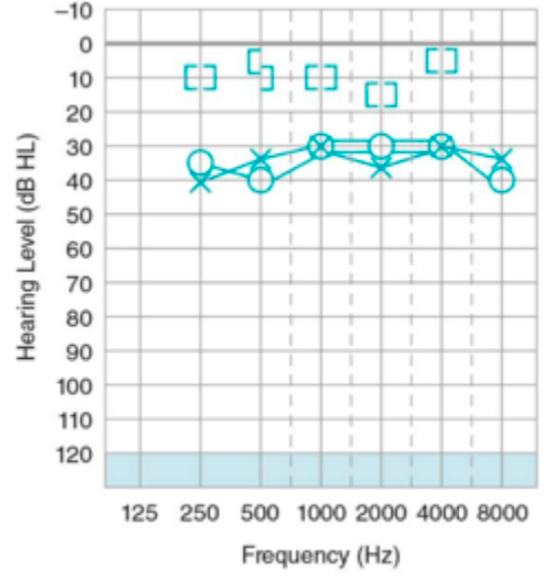
HL type
sensorineural
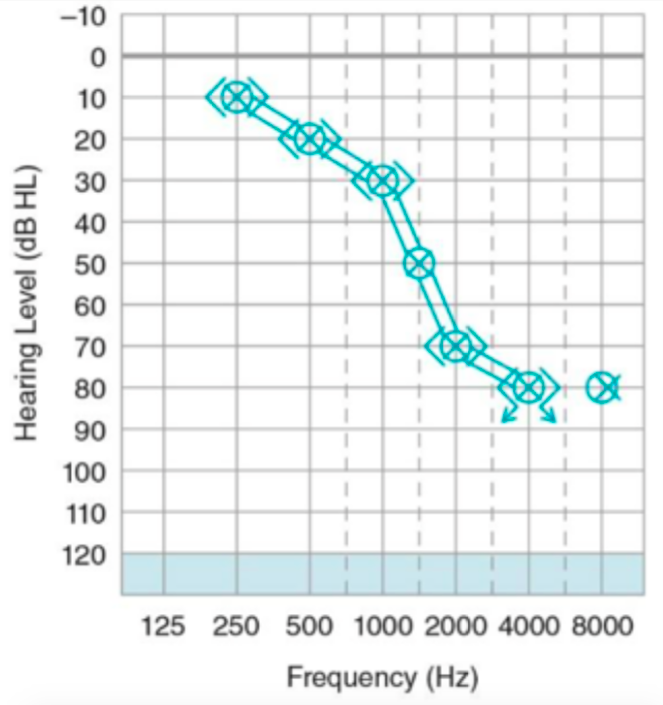
HL type
VIII nerve tumor
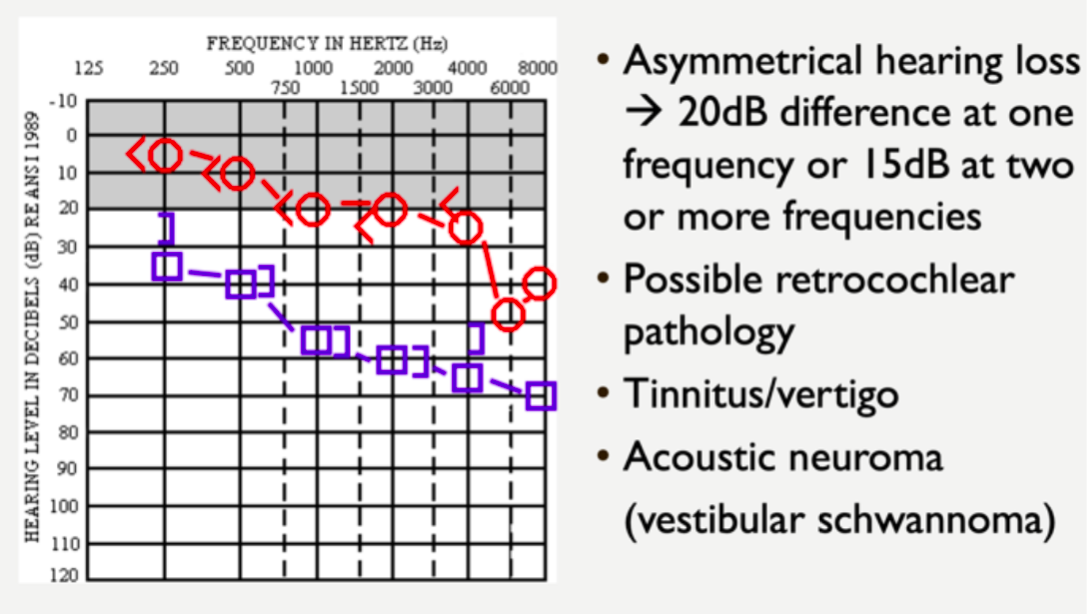
condition
Meniere’s disease
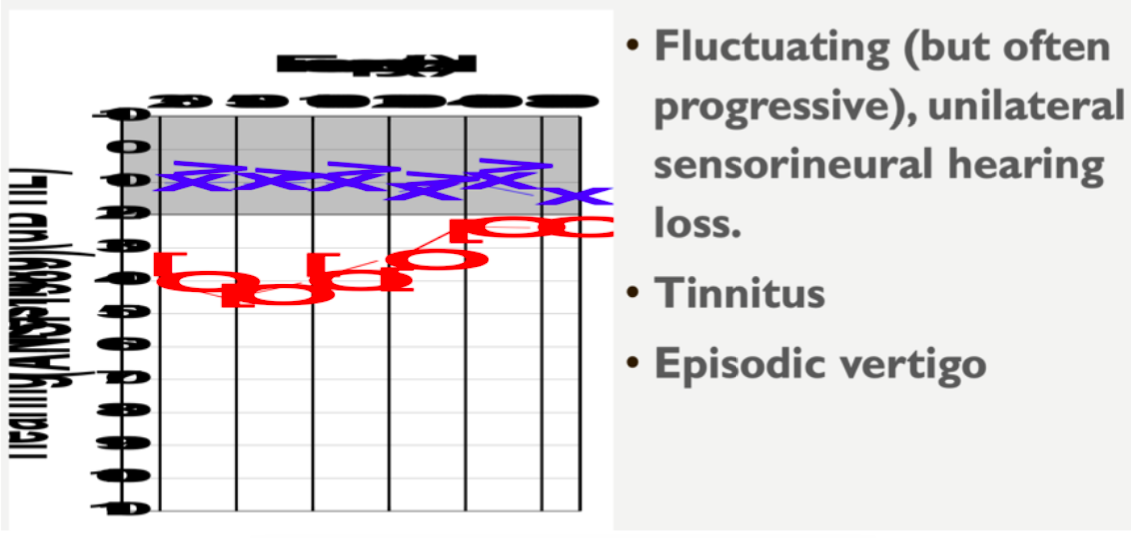
condition