Avian Biology Exam 4
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
How do birds meet temporary high demands for energy (molt, migration, egg production)?
Hyperphagia- rapid feeding
What are the stages of foraging and consumption?
• Search and recognition
• Capture and extraction
• Preparation and ingestion
• Pulveration and digestion
What is optimal foraging theory?
A model of foraging behavior with the goal of maximizing energy gain + minimizing energy acquisition
What is the ideal prey?
Gives maximum energy and requires the least amount of time and energy to obtain
Geophagy
The consumption of soil, clay or sand (to aquire sodium)
How do shorebirds reduce interspecific competition?
They have varying anatomy that allows them to use different niches
What are two types of interspecific competition?
Exploitation: One species is better at getting a resource
Interference: One species prevents another from getting a resource
What affects variation in beak size and shape?
Foraging
Body size
Food
Thermoregulation
Singing
How does foraging strategies influence wing shape?
Some wings are more pointed and better for fast gliding and quickly changing direction
Some wings are more rounded, allowing for fast takeoffs and tight maneuvering (e.g. through trees)
What is unique about crossbills?
They have crossed beaks that specialize in removing seeds from certain conifer (pinecone) plants
Some beaks are curved to the left and some to the right
Crossbills and conifers coevolved
What is special about hummingbird feeding?
Hummingbirds have hair-like lamella that allow them to soak up/trap nectar
What is special about flamingo foraging?
Flamingos feed upside down to filter out animals and plants through special lamellae beak structures
What does mate preference lead to?
The evolution of:
Ornamentation
Behavioral displays
Coercive mating (e.g. forced mating)
What mating systems are there?
Monogamy: One male and one female (may not be genetically monogamous)
Polygyny- One male with multiple females
Polyandry- One female with multiple males
What are the trade-offe of extra-pair mating?
Benefits of extra-pair:
More helpers
More parental care
Costs of extra-pair:
Main male feeds less with more extra-pair young
Helpers allow females to have time for more extra-pair breeding
Same-sex pair bonds
Occurs in albatrosses
There is less successful incubation, but more successful raising of young
What tupes of polygyny are there?
Female defense- Males defend females but not habitats
Resource defense- Males defend resources used by females
Lek
Classic- Many males at one location
Exploded- Males are more spread out
What is a lek?
a mating ground where multiple male animals of a species gather to display to attract and compete for females
What are the benefits of polyandry?
Fertility assurance- If a male is infertile, there is a chance of another that isn’t
More parental care
What is sequential polyandry?
a mating system where a female mates with multiple males, one after another, rather than simultaneously (Wilson’s phalarope, females have male-like plumage)
What is sound?
Waves if moving air molecules
Frequency- frequency of vibrations (kHz)
Amplitude- loudness, measured in decibels
How are bird vocalizations visualized?
Spectrogram (bw or color)
Oscillogram (pressure/ volume only)
Mnemonics
Memory strategies used to remember bird songs
What is a song?
Loud and complex
Used for mate attraction and territory defense
What is a call?
Shorter and simpler
Used for more than territory and mate attraction
What are common call types?
Contact call- for flock cohesion
Flight calls- for migratory flock cohesion
Food calls- to attract mates/offspring/conspecifics to a food source
Begging calls- Used to call a parent for feeding
Alarm calls- To alert others of a danger
Mobbing calls- To attract others to a danger
What is found in typical song structures?
Song bout- Song sung in rapid succession
Song- divided into phrases, separated by long gaps
Phrase- Combination of notes
Note- A continuous trace on a spectrogram
Trills- rapid repeats it short elements
What are some examples of non-vocal bird sounds?
Drumming- woodpecker
Feathers hitting
Tools
What are examples of species where females sing more than males?
Streak-backed Orioles
Stripe-headed sparrow
Oscines
Songbirds, show vocal learning
Suboscines
Do not learn song (innate)
When do birds mostly learn song?
The sensitive period
What are the developmental stages of song?
subsong
Plastic song
Crystallized song
What are species that learn songs throughout their whole lives?
Open-ended learners (e.g. mimicks)
Are dialects more common in oscines or suboscines?
Oscines- They can learn songs that may vary geographically (songs may be incomplete as they are learned/spread)
Why do dialects change over time?
Mistakes in learning
Immigration
Local noise selecting for best transmission
What is the primary sound producing organ in birds?
The strinx
Oscines/songbirds can control both sides
What other areas are invilved in song production (the song control system)?
Nerve cells
Neural pathways
The vocal tract
When do birds breed?
Right before the best nestling food is prevalent. To raise healthy chicks
Ehat do birds use to time their breeding?
The photoperiod (Daylight)
Plant/ insect abundance
Rainfall
What functions do nests serve?
Keep eggs contained
Protecting eggs from predation
Insulation of eggs
Attracting mates
Strengthening pair bond when buliding
Roosting site
Deter predators-termite nests
What types of nests are there?
Globe
Dombed
Cup
Statant
Pensile
Adherant
Scrape
Burrow
Cavity
Mound
Platform
Pendant
Did cup nests or domed nests evolve first?
Dombed nests (cup nests evolved from them)
What are possible consequences of laying eggs?
Nests and eggs can be easily identified
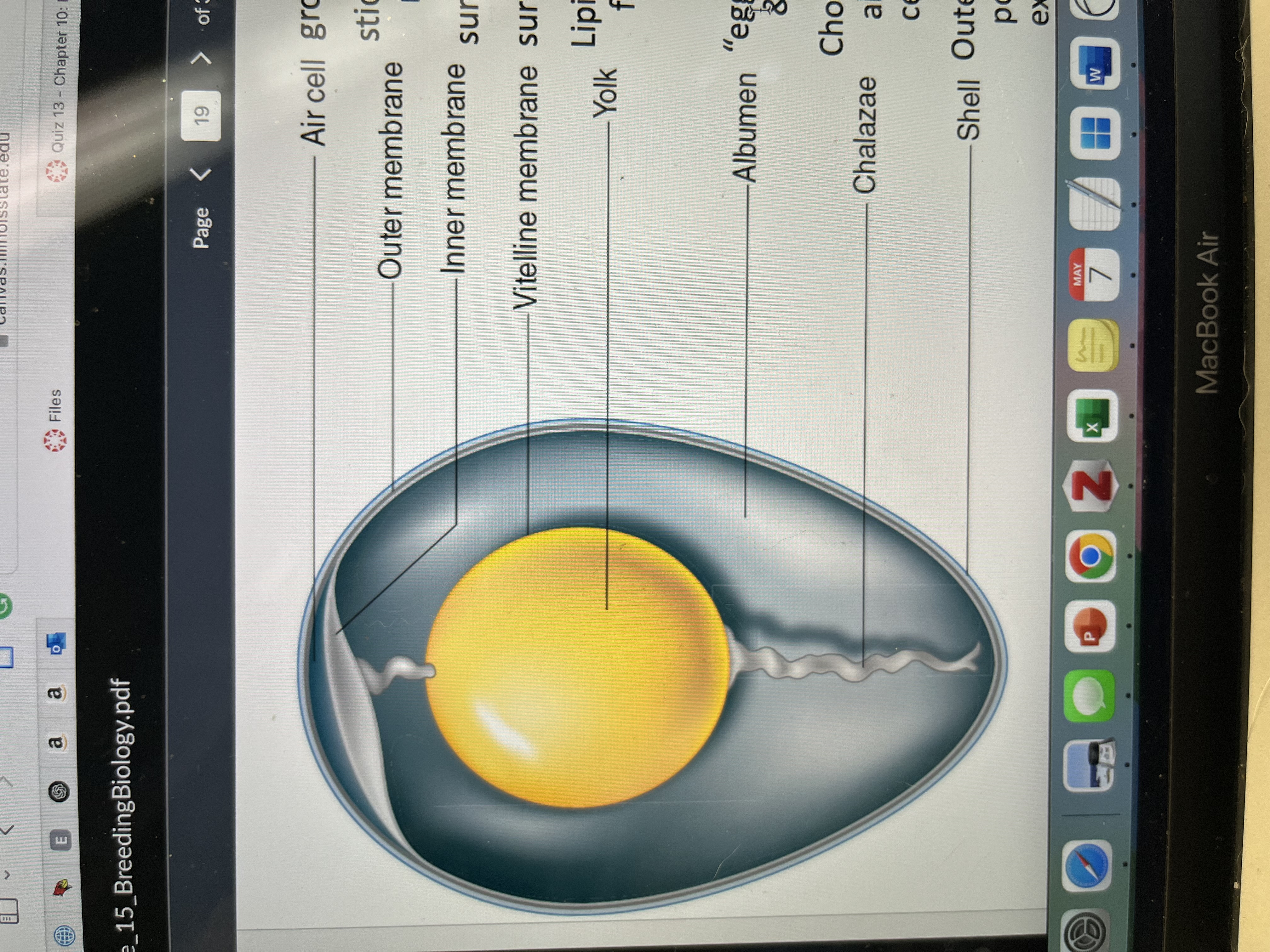
What are eggs made of?
Air cell
Outer/inner membrane
Vitelline membrane
Yolk
Albumen (whites)
Chalazae
Shell
What are the benefits/functions of eggs?
Promote flight
Promote bi-parental care
Possibility for abandonment
What are yolk rings?
The yolk is in rings, darker when feeding (day) lighter at night
How are eggs made?
Chorioalantonic membrane- The chorion and the allantosis fuse during embryo development
Allantois- collects waste
Chorion- similar to placenta, surrounds the yolk sac amnion and allantois
What is the function of the chorioallantoic membrane?
Similar to lungs, allowing gas exchange with shell pores
What affects the size of eggs?
Body mass
Lage clutches = smaller eggs
Precocial eggs are larger than altrucial
What is the difference between precocial and altricial?
Precocial- pre developed
Altricial- Underdeveloped
Clutch
A complete set of eggs laid in an uninterrupted series
What influences clutch size?
Food availability
Young independence
Larger clutches in cold environments
Less predation
Early nests are larger
Older females
Determinate layer
Lays a fixed number of eggs (no egg replacement)
Indeterminate layer
Lays eggs until clutch size is present (replaces eggs)
What is the goal of incubation
Maintaining a constant temperature
Favorite bird + 3 facts
European robin- The first wild bird I ever held (very cute)
Sing year round and are often residential (non migratory) in europe
Follow gardeners to get access to insects
European robins are not closely related to american robins, but rather flycatchers
What hormonal changes initiate incubation?
Prgesterone, LH are low
Prolactin is high