Module 5 (final): Variation Through Meiosis and Changes in Ploidy
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what are pseudoautosomal regions?
regions that mediate XY pairing in meiosis, and contain a few genes that “act” like autosomal genes
how is sex determined in drosophila?
the ratio of X chromosomes to autosomes, a female is when the X:autosome ratio is 1
XXY → female XO→ male
how is sex determined in mammals?
whether or not you have a Y chromosome
how do drosophila deal with gene dosage for genes on the X chromosome?
they alter gene expression levels, genes on the single X chromosome for males are hyperactivated
how do mammals deal with gene dosage for genes on the X chromosome?
one of the X chromosomes is randomly inactivated in somatic cells (barr bodies), and can create mosaic phenotypes.
how is sex determined in birds?
ZW = female ZZ = male (females are heterogametic), unclear how it is determined but some hypotheses include dosage (one Z is insufficient to make testis) or W determines femaleness
what can a karyotype show you?
different lengths of chromosomes, centromere location, banding patterns (heterochromatic vs. euchromatic regions)
what is aberrant euploidy?
when there is a change in number of the complete set of chromosomes (diploid to triploid)
what is aneuploidy?
plus or minus specific chromosomes in a set (2n+1, trisomy, etc. )
what are the different types of polyploids?
autopolyploids and allopolyploids
what are autopolyploids?
when there is an extra set from the same species
what are allopolyploids?
when there is an extra set from a different species
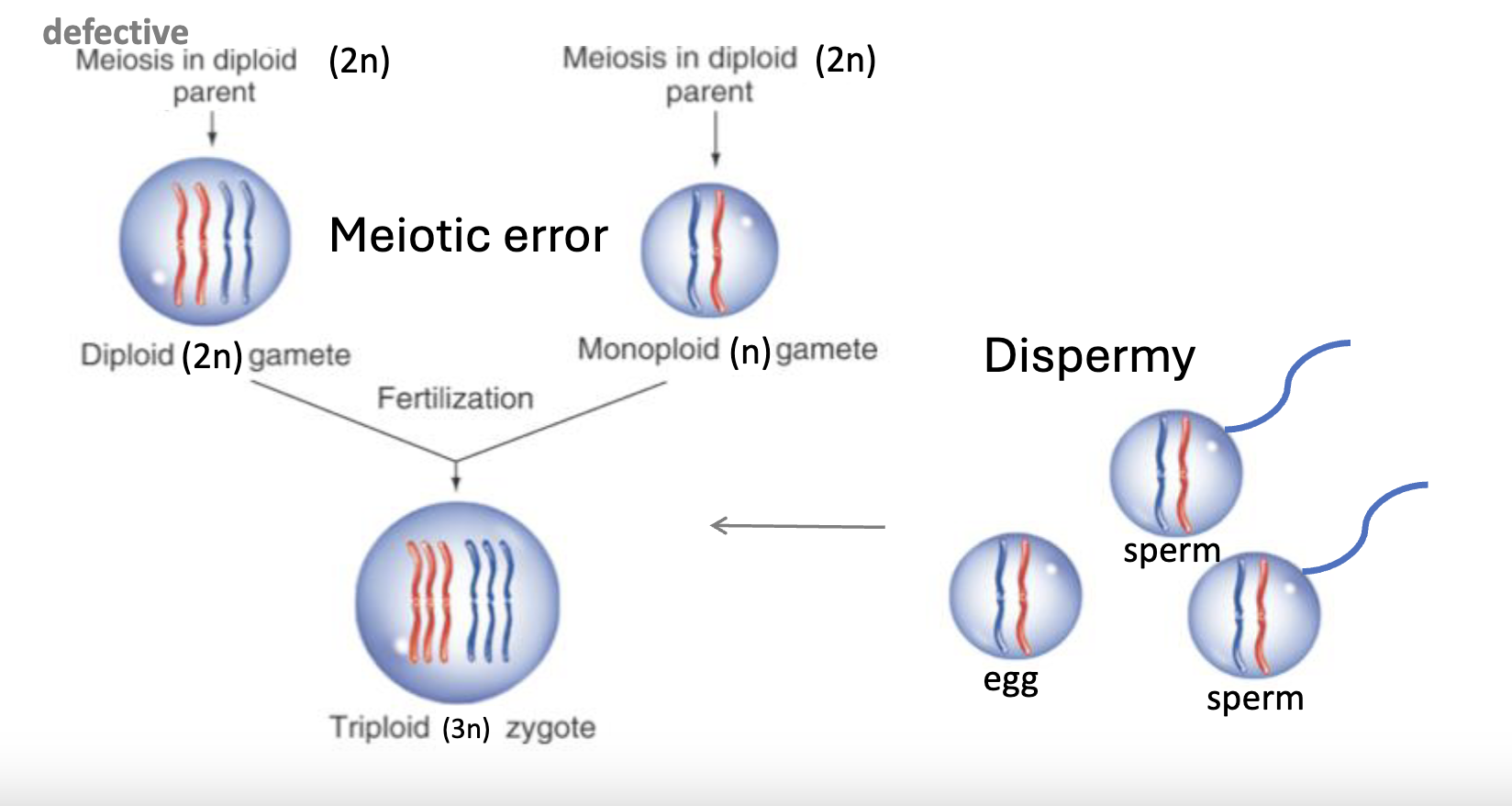
what are the causes of autopolyploidy?
Spontaneous:
a meiotic error that leads to a 2n gamete
dispermy (2 sperm fertilizing one egg)
Induced:
disruption in chromosome segregation (plants), disruption of microtubule polymerization, loss of segregation
what happens to an organism with autopolyploidy?
in somatic cells, organisms become larger.
in the gemline, it can lead to infertility
meiotic pairing in triploids
segregation in meiosis I leads to aneuploid gametes, often resulting in infertility

meiotic pairing in tetrapods
can segregate whole sets due to the even number of chromosome

what is another word for an individual that is an allopolyploid?
a hybrid
what are the characteristics of a hybrid?
they are infertile due to nonhomology of chromosomes (the number of chromosomes does not add up to an even number), and it can no longer breed with either of the parental species
how can a hybrid become fertile?
via spontaneous chromosome doubling, there are now two copies of each chromosome that can pair.
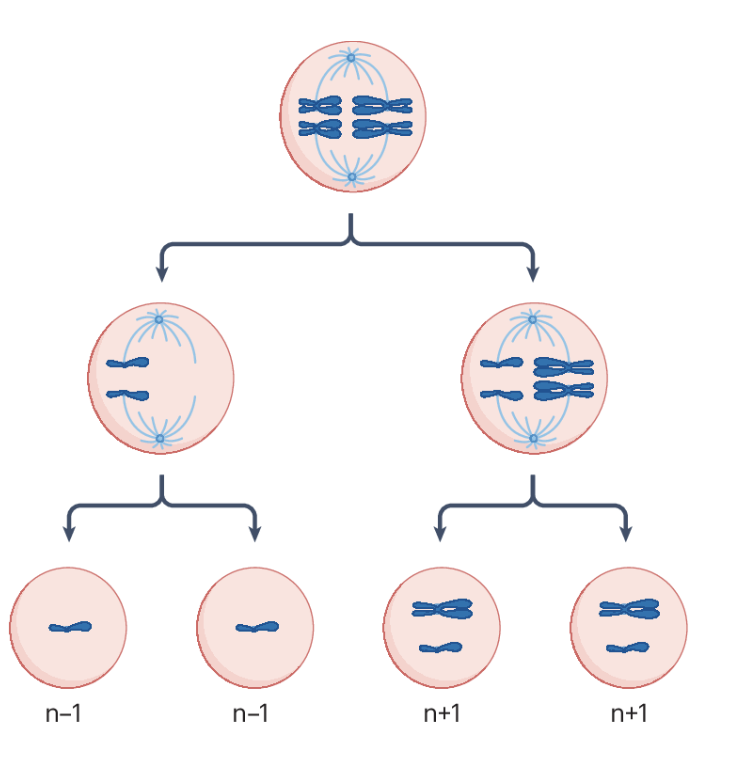
what are the gamete chromosome possibilities if non-disjunction happens in meiosis I?
n-1, n-1, n+1, n+1 (lack of separation of homologous chromosomes)
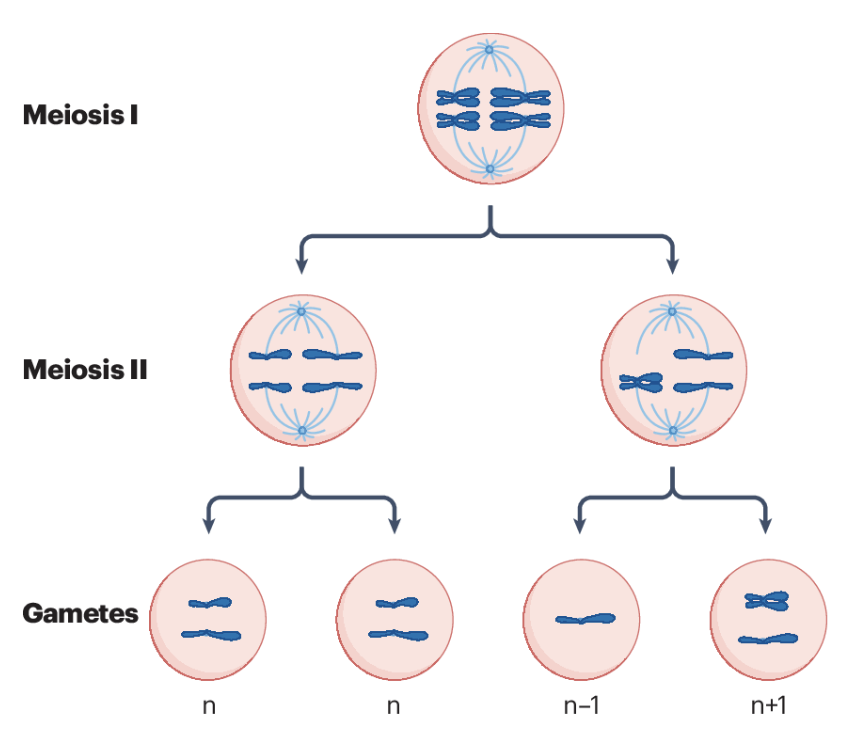
what are the gamete chromosome possibilities if non-disjunction happens in meiosis II?
n, n, n-1, n+1 (lack of separation of sister chromatids)
what are the viable trisomies in humans?
triple X (XXX), Jacob’s syndrome (XYY), Klinefelter syndrome (XXY), Down Syndrome (T21)
what are the less viable trisomies in humans?
Patau syndrome (T13), Edwards syndrome (T18)
what is the viable monosomy in humans?
Turner syndrome (X0)
why is trisomy 21 the only autosomal trisomy to survive past infancy?
it has the fewest protein-coding genes of the autosomes, suggesting that none are essential for embryonic development
why are sex chromosome aneuploids viable?
X-inactivation (X-ist), and other dosage compensation mechanisms can tolerate extra sex chromosomes
Y chromosome is small and mainly carries genes for sex-determination (not critical for survival)
Why is there only one viable monosomy (X0)?
being monosomic is equivalent to being homozygous. If there are deleterious alleles on the chromosome there is no second functional copy to rescue
Do extra X chromosomes get inactivated to become barr bodies?
Yes, but some genes escape inactivation, leading to a triple X phenotype
how does the number of chromosomes affect phenotype?
there are changes in gene dosage ratios (no longer 1:1), and can change the phenotype