Cartilage (Histology)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What is the most common type of cartilage _______
What is the color of it? (fresh) _______
What type of collagen is prevalent in this type of cartilage _______?
Hyaline ; bluish-white & translucent ;
collagen type II
How many types of cartilage are there?
3 types
hyaline, elastic and fibrocartilage
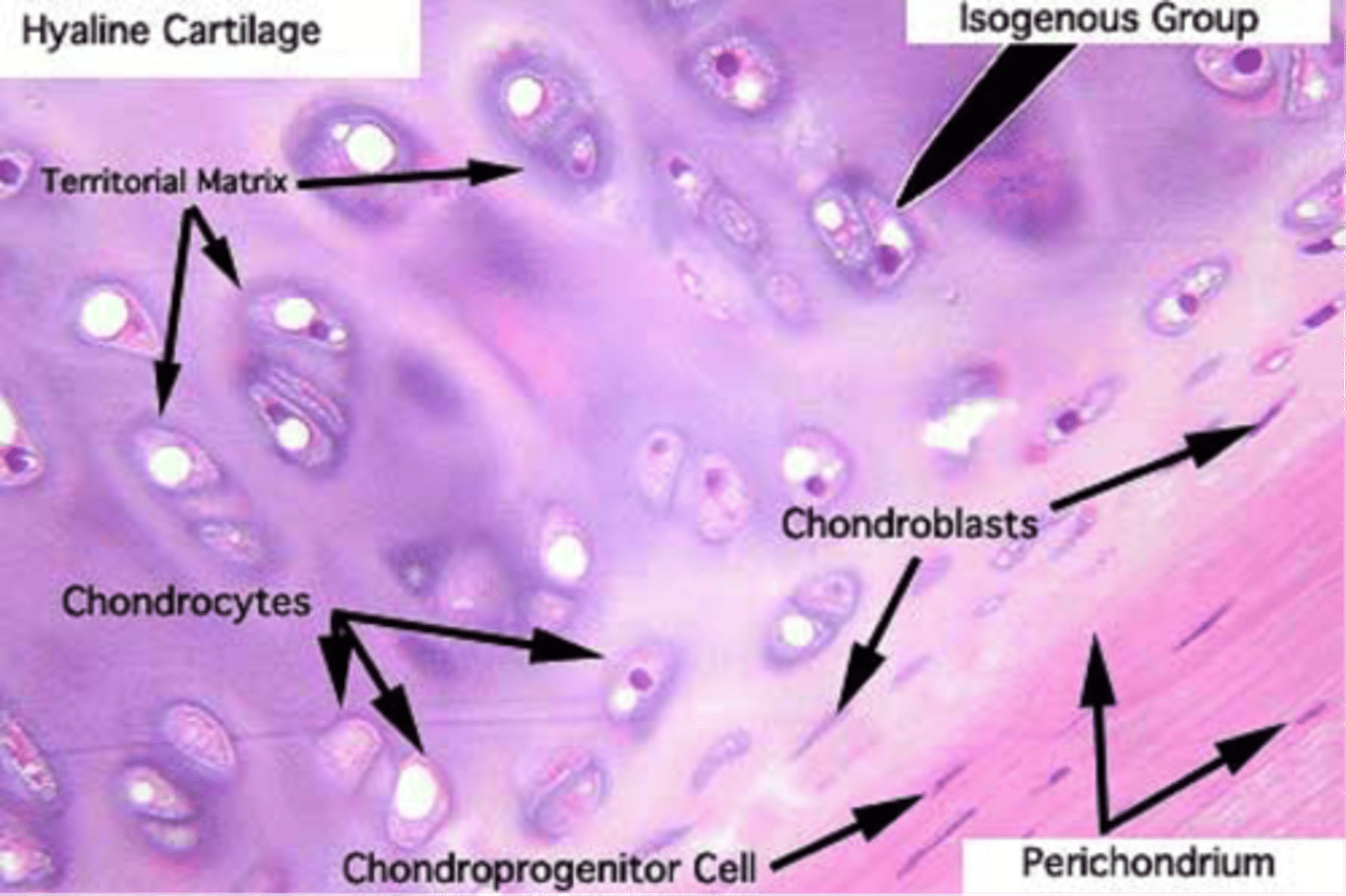
Where is hyaline cartilage located?
1) In the articular surfaces of movable joints
2) In the walls of larger respiratory passages (down to the bronchi)
3) In the ventral ends of the ribs where they articulate with the sternum
4) In the epiphyseal plate, where long bone growth occurs
_______% of the dry weight of hyaline cartilage consists of _______ collagen embedded in what _______?
40% ; type II ; a firm, hydrated gel of proteoglycans and structural glycoproteins
What do you call the space where a chondrocyte sits in?
Lacuna
A typical hyaline matrix has up to _______ linked to a molecule of _______
200 proteoglycans ; hyaluronic acid
Cartilage proteoglycans contain _______ and _______ linked to _______
chondroitin sulfate ; keratin sulfate ; core proteins
type II collagen fibril <=> Proteoglycans <=> Hyaluronic acid
What type of chemical bonds links the proteoglycans to the collagen fibrils in cartilage matrix?
electrostatic bonds (form cross-linked matrix)
[give the cartilage matrix its strength]
What cells produce proteoglycans/collagen/GAGs? (Question #10)
chondroblasts
Note: chondrocytes are mature cells
Name the three components/types of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
Chondroitin sulfate, keratin sulfate, hyaluronic acid
What do glycosaminoglycans do and how do they influence the function of articular cartilage?
they have a negative charge, so they
attract water ;
This large amount of solvation water acts as a shock absorber or biomechanical spring
What is the protein, which binds to the type II collagen and proteoglycans aggregates and mediates the adherence of the chondrocytes to the extracellular matrix?
Chondronectin
(similar function to fibronectin in CT)
What is the dense connective tissue that lines the outside of cartilage
Perichondrium (rich in type I)
the cells in the inner layer of the perichondium act as chondroblasts, which can differentiate into chondrocytes
What synthesizes collagens and the other matrix molecules?
Chondrocytes
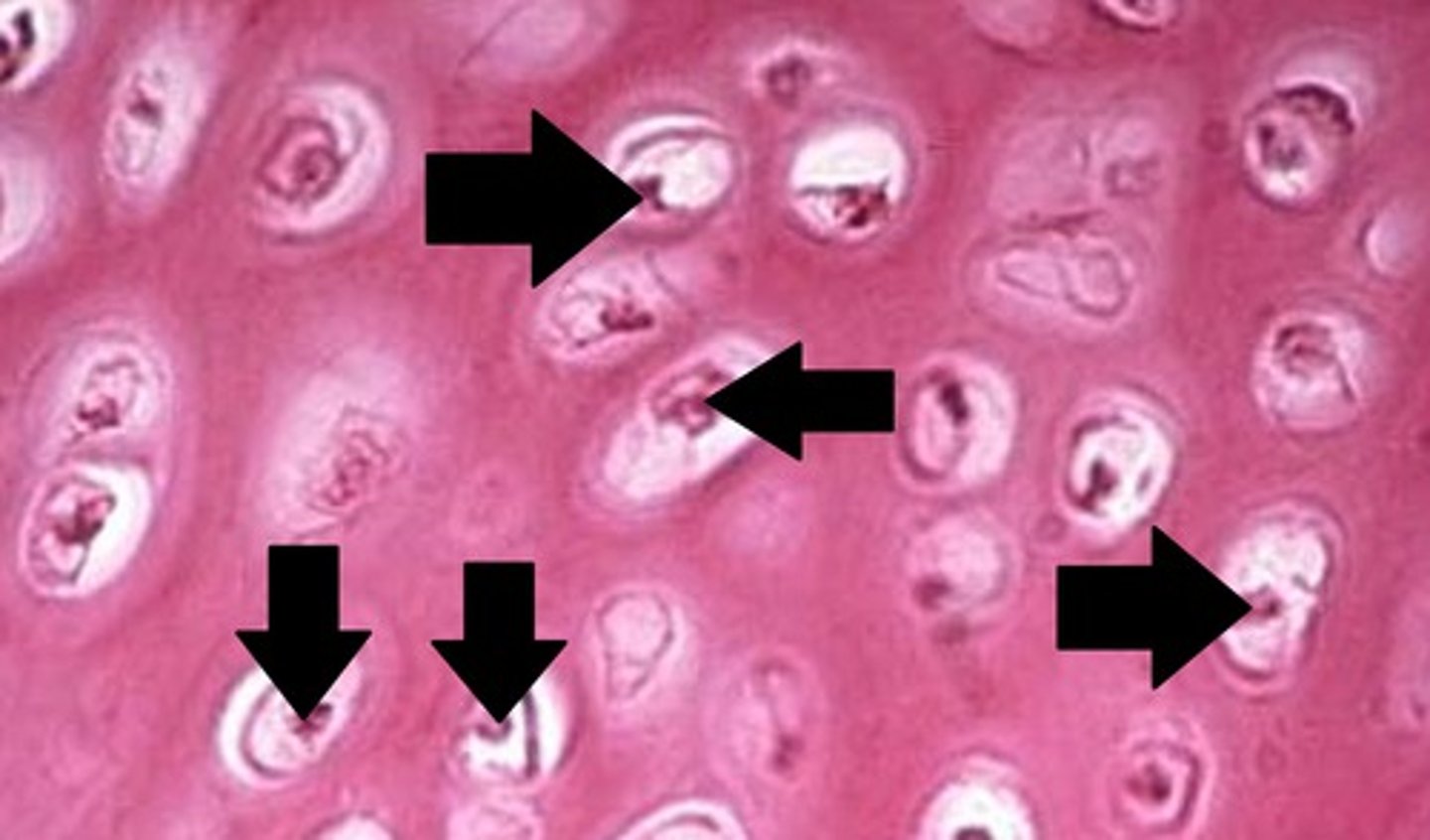
Where are chondrocytes located?
in the periphery of hyaline cartilage: immature/eliptical
further in: rounder and in groups
What do you call a group of chondrocytes which lie close to one another in the matrix?
Isogenous group (originated from a single progenitor by mitotic division)
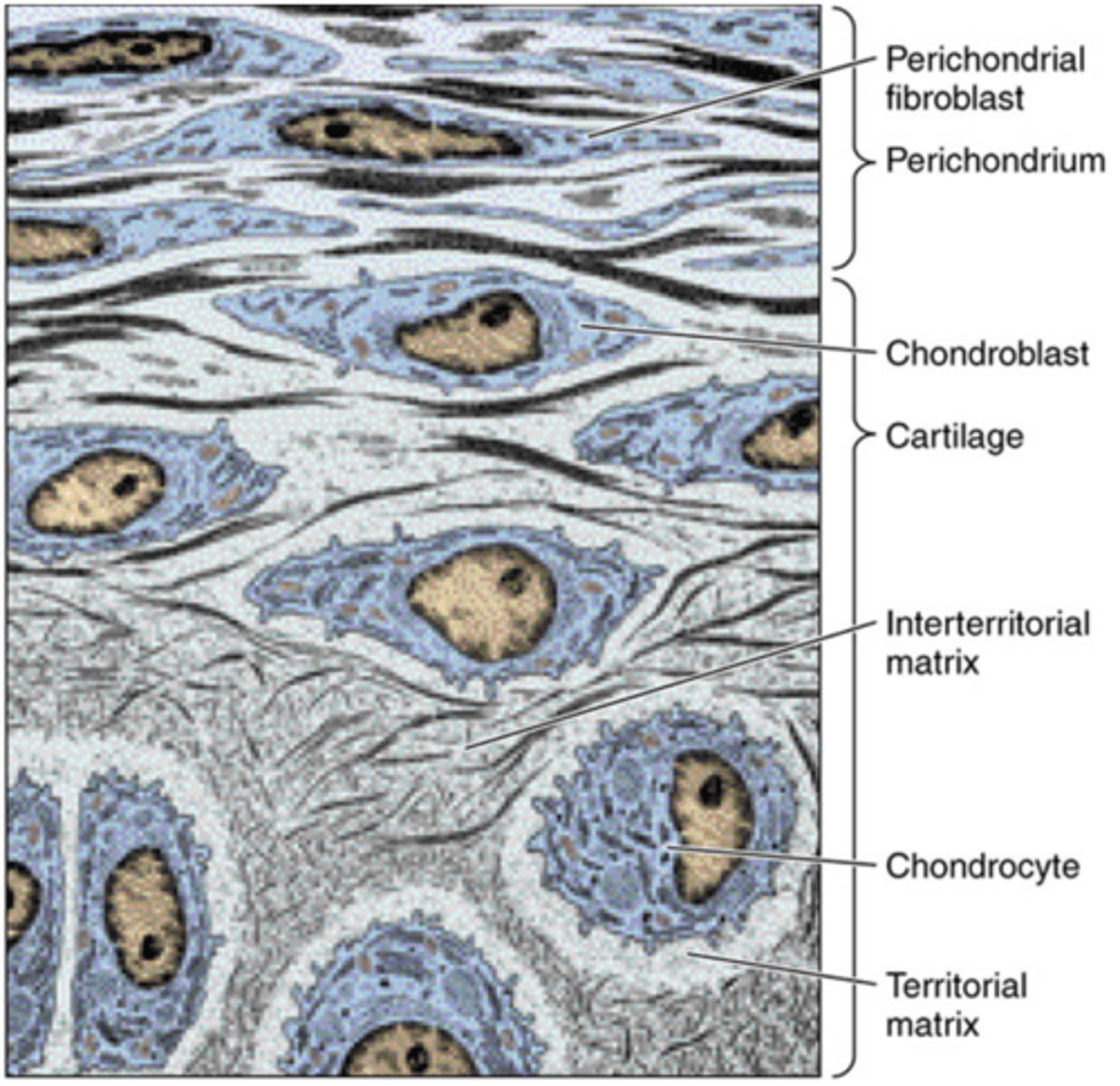
Does cartilage have a blood supply? How do nutrients get in to cartilage?
NO ;
The diffusion of nutrients from outside the perichondrium is aided by pumping action which occurs when the cartilage is compressed and decompressed during normal movement.
Chondrocyte activity depends on _______
Proper hormonal balance
growth hormone, thyroxin, testosterone.
cortisone, hydrocortisone, estradiol
Chondrocyte activity is accelerated (promotes synthesis) by what hormones?
Growth hormone, Thyroxin, Testosterone [GTT]
Chondrocyte activity is slowed (reduces synthesis) by what hormones?
hydrocortisone, estradiol, cortisone [HEC]
[Histogenesis] describe this stage A
The mesenchyme is the precursor tissue of all types of cartilage

[Histogenesis] describe this stage B
Mitotic proliferation of mesenchymal cells gives rise to a highly cellular tissue
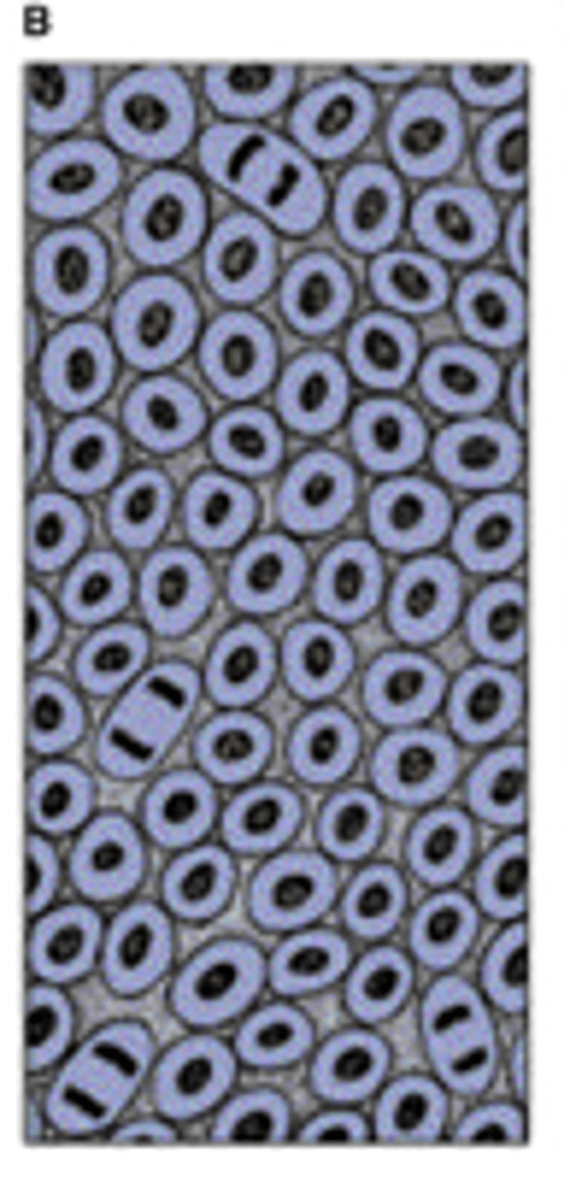
[Histogenesis] describe this stage C
Chondroblasts are separated from one another by the formation of a great amount of matrix
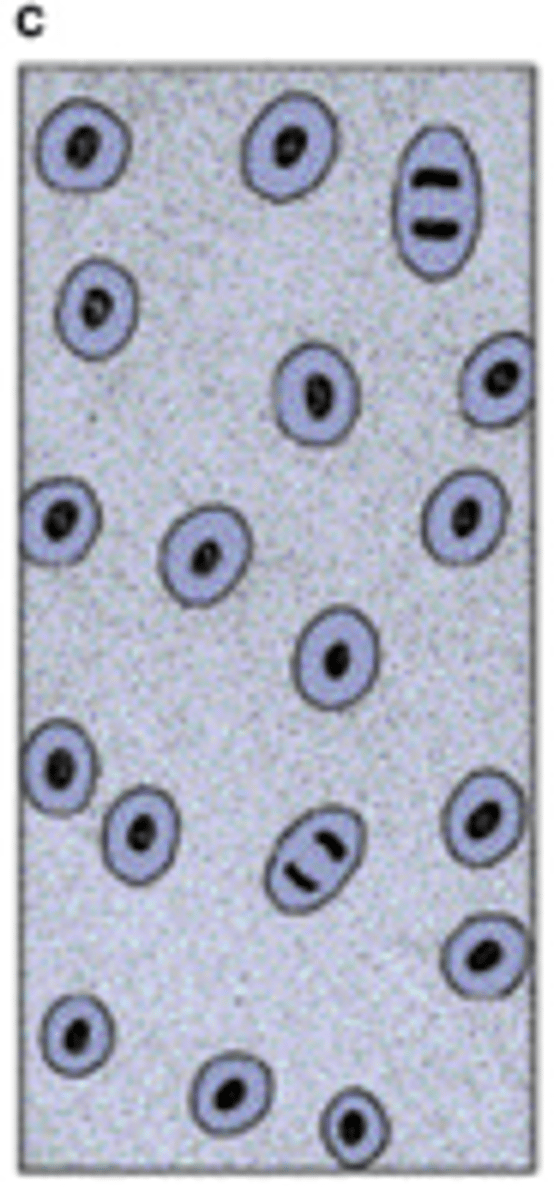
[Histogenesis] describe this stage D
Multiplication of cartilage cells gives rise to isogenous groups, each surrounded by a condensation of territorial (capsular) matrix
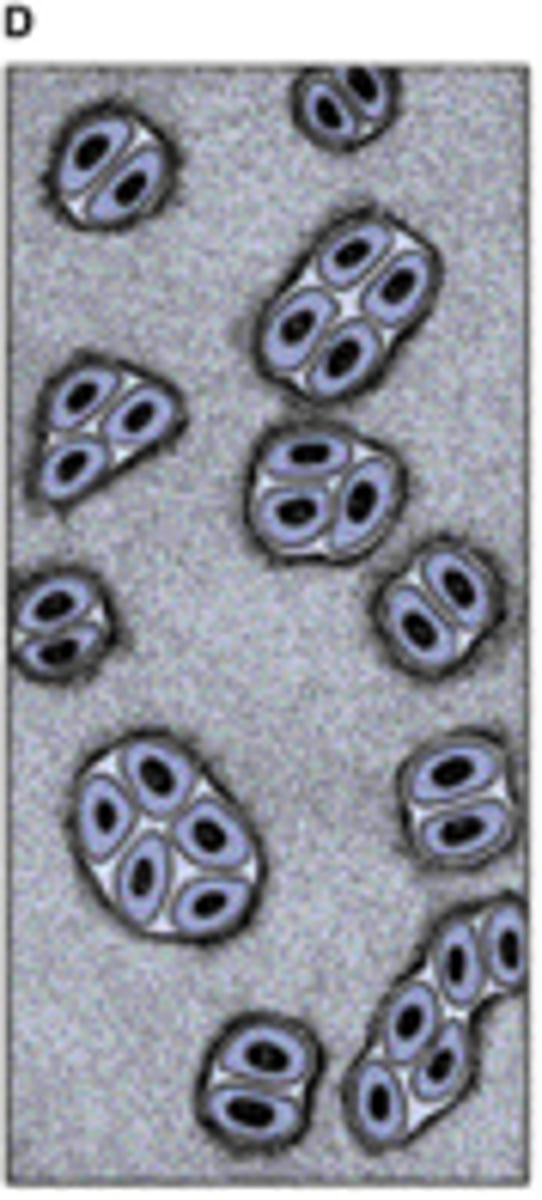
Name da two ways cartilage grows
Growth of cartilage occurs in two ways: interstitial growth, and appositional growth.
_______ results from the differentiation of perichondrial cells.
Appositional growth
_______ results from the mitotic division of preexisting chondrocytes
Interstitial Growth
"In both cases, synthesis of matrix contributes to the growth of the cartilage"
_______ growth occurs mostly during the early phases of cartilage formation
Interstitial Growth
Where does appositional growth occur?
a. at the surface of articular cartilage
b. at the epiphyseal plates of long bones
c. at the center of chondrication
d. only in development
a. at the surface of articular cartilage
b, c, d are all interstitial growth
Hyaline cartilage is susceptible to ________
Name the two ways
degenerative aging processes ;
1) Calcification of the matrix (which occurs when chondrocytes die)
2) Asbestiform degeneration
Does damaged cartilage regenerate?
damaged cartilage regenerates only with difficulty, except in very young children. hen regeneration does occur, it is by activity of the perichondrium...
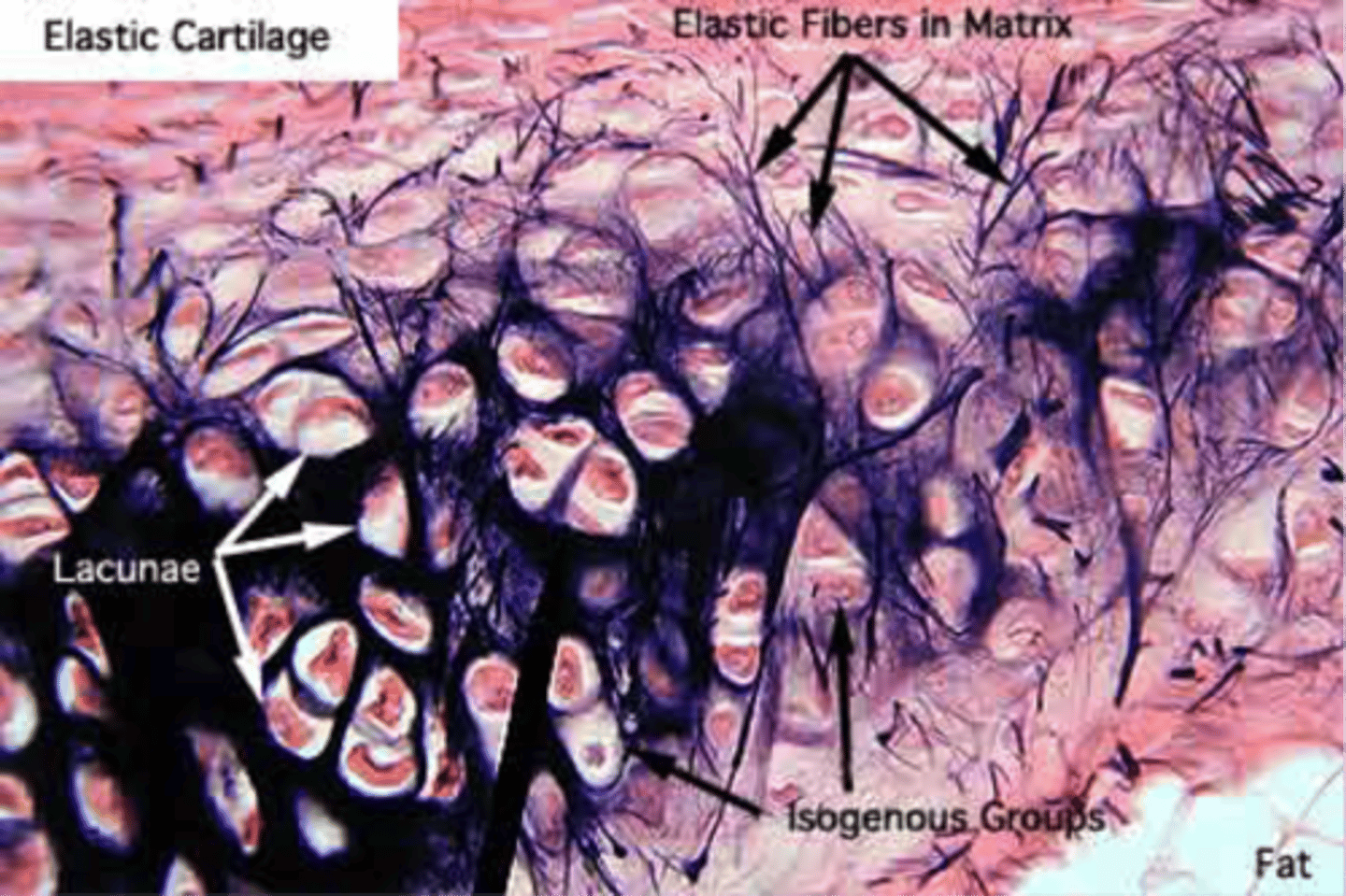
Elastic Cartilage is essentially identical to hyaline except that it ...
...contains an abundant network of fine elastic fibers in addition to the collage type II fibrils
Where is elastic cartilage NOTfound?
a. auricle of ear
b. epiglottis
c. articular surface of ribs
d. walls of the external auditory canal
e. the cuneiform cartilage of the larynx
c. articular surface of ribs (hyaline)
Does elastic cartilage contain chondrocytes?
NO
(fibrocartilage does thougth)
What is the most distinguishing features of elastic cartilage (i.e. not found in other cartilage?
abundant network of elastic fibers
What type of cartilage?
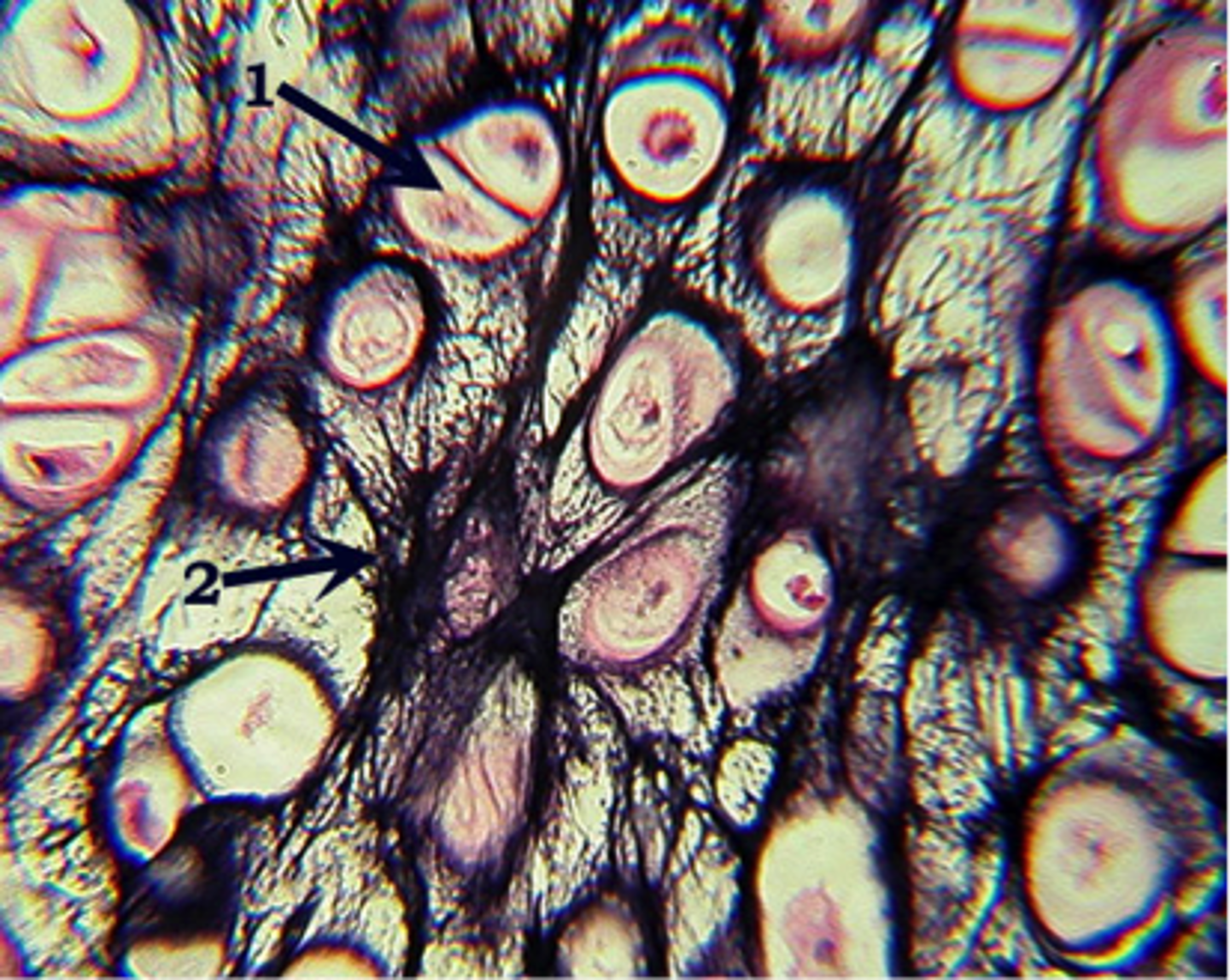
What type of cartilage?
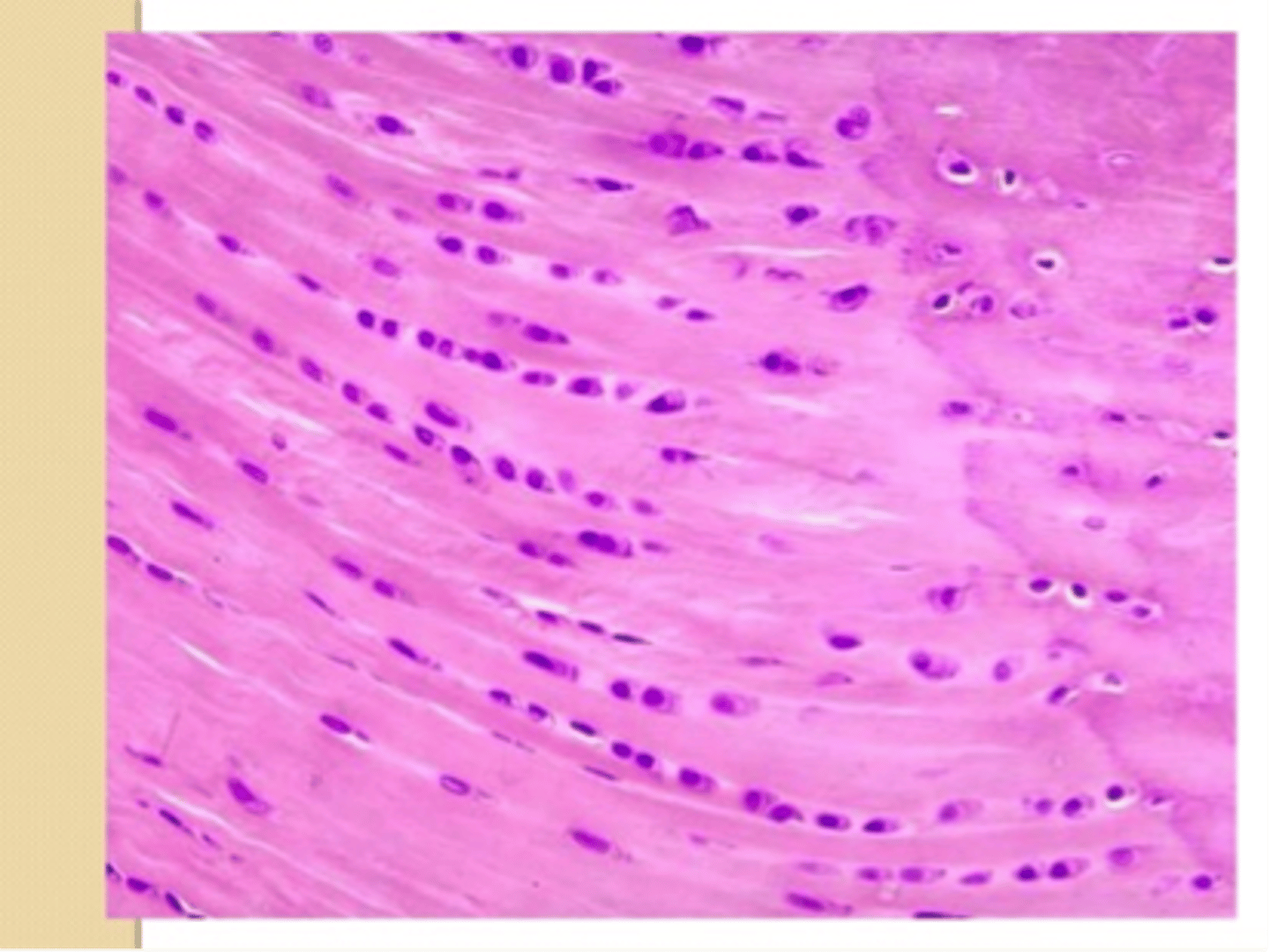
What type of cartilage?
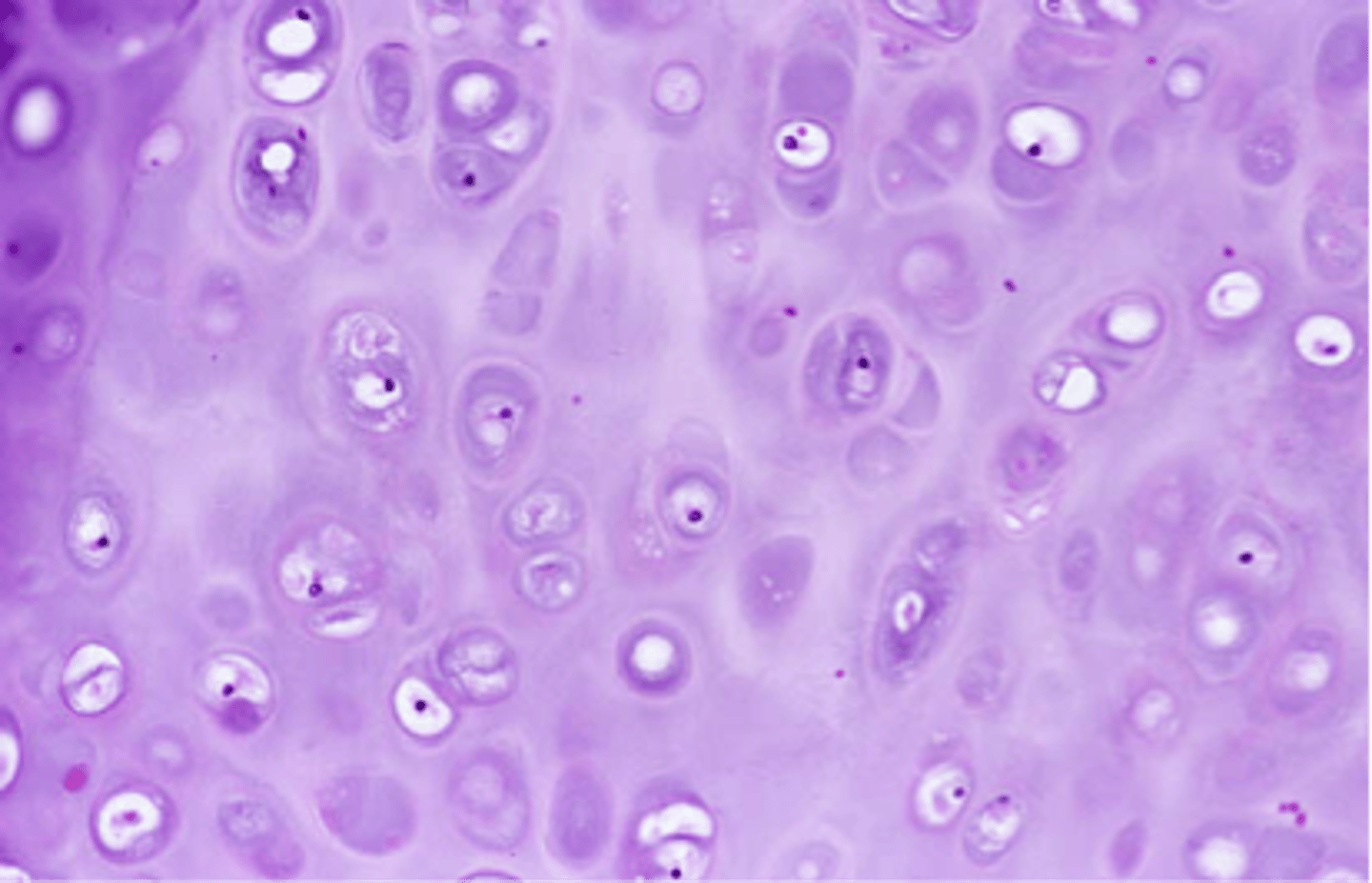
What type of cartilage is found in intervertebral discs?
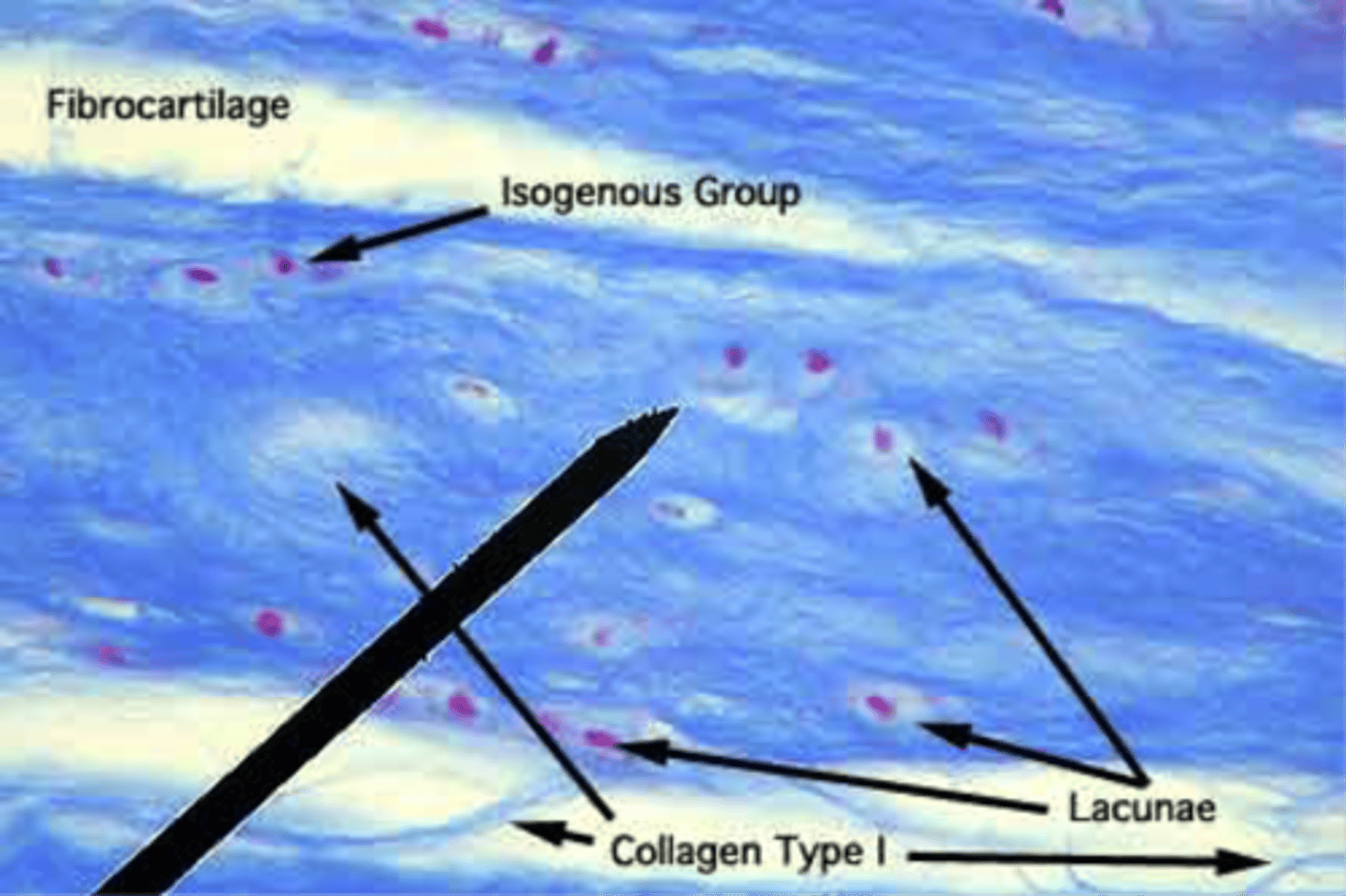
Fibrocartilage
What is intermediate tissue between hyaline cartilage and dense connective tissue?
Fibrocartilage
Fibrocartilage is usually arranged _______ separated by coarse collagen type I fibers
...in long rows
Intervertebral dics have two components _______ and _______
annulus fibrosus (perimeter) ;
nucleus pulposus (inner - with age, most of the nucleus pulposus is replaced with fibrocartilage)
What is annulus fibrosus composed of?
It has an external layer of dense connective tissue, but it is mainly composed of overlapping laminae of fibrocartilage
type I collagen fibers provides the disk with unusual resilience that enables it to withstand the pressures generated by impinging vertebrae
What part of the intervertebral disc is derived embryologically from notochord and consists of a few rounded cells embedded in a viscous matrix rich in hyaluronic acid and type II collagen fibrils.
nucleus pulposus
Does fibrocartilage contain a perichondrium?
NO
Fibrocartilage labeled
Hyaline cartilage labeled
Elastic cartilage labeled
_______ is sometimes referred to as yellow cartilage
_______ is sometimes referred to as white cartilage
Elastic cartilage ; Fibrocartilage
Which type of cartilage forms the skeleton of the fetus?
Hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue makes up the "Adam's apple"?
Hyaline cartilage
only the HYALINE part of the larynx!
Which type of cartilage forms the intervertebral disc?
Fibrocartilage
Which type of cartilage is found in the larynx?
Hyaline cartilage and Elastic cartilage
Which type of cartilage is characterized by a glassy matrix?
Hyaline cartilage
Which type of cartilage forms the articular surface on bones?
Hyaline cartilage
Costal cartilage is composed of what type of cartilage?
Hyaline cartilage
Which type of cartilage forms the symphysis pubis?
Fibrocartilage
Which type of cartilage forms the epiphyseal growth plate?
Hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue makes up the rings of the trachea?
Hyaline cartilage
What type of tissue makes up the epiglottis?
Elastic cartilage
Which type of cartilage is present in the temporomandibular joint?
Fibrocartilage