Contract & Sales RULES
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Common Law vs. UCC
Common law applies to contracts for the sale of services/real estate.
Article 2 of the UCC applies to contracts for the sale of goods.
If transaction has both goods/services, then predominate purpose test asks if good or service played a larger role.
Contract Formation
Valid contract requires offer, acceptance, and consideration.
Under common law, offer must have essential terms (party, price, quantity, subject).
Under UCC, contract is formed if parties intend to contract and there is reasonably certain basis for remedy. Offer must have quantity and UCC “fills the gap” for missing terms.
Requirement/output contracts are specific enough and do not require quantity term.
If contract for sale of assorted goods does not specify who will choose goods, UCC imposes duty on buyer to make selection. If buyer fails to specify goods, then seller can treat that failure as a breach, but only if buyer's failure to specify materially impacts seller's performance.
Offer and Acceptance
Offer is a manifestation of willingness to enter into agreement by offeror that creates a power of acceptance in offeree. Offer must be directed to specific offeree (exception is contest/reward offer).
Offer/acceptance is governed by the objective test (offeror displays objectively serious intent to be bound).
Ads are invitation to deal, but can be offer if specific enough.
Offeror is “master of the offer” so offeree must accept according to terms of offer, but if offeror does not dictate manner and means of acceptance, then offeree can accept in any reasonable manner and means.
Generally, acceptance must be communicated to other party.
Acceptance by silence is effective if unilateral reward/contest offers, past history of silence as acceptance, or offer explicitly allows it.
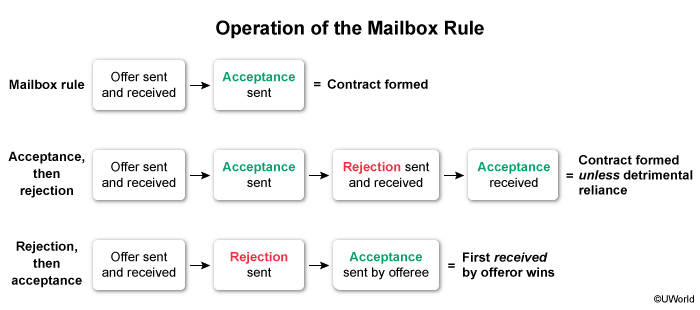
Mailbox Rule
Under mailbox rule, acceptance is effective when mail is sent.
Exceptions are irrevocable offers and if offeree sends rejection first.
Mirror Image Rule vs. UCC 2-207
Common law provides acceptance must be the mirror image of the offer (acceptance terms must exactly match offer terms).
UCC 2-207 provides acceptance terms do not have to exactly match offer terms.
New terms may control if both parties are merchants, term does not materially alter contract, initial offer does not expressly limit acceptance, and offeror does not object within reasonable time. If one party is nonmerchant, then new terms are proposed addition.
Under knock out rule, if acceptance has different terms (not additional terms), then majority “knocks out” different terms and UCC fills the gap. The minority keeps the initial offer.
Effect of new terms in reply to offer | ||
Common law (mirror-image) |
| |
UCC (battle of the forms) | ≥1 party is nonmerchant |
|
All parties are merchants |
| |
Offer Termination
Offeror revokes offer directly or indirectly.
Offeror dies or permanently mentally incapacitated.
Offeree rejects offer.
Offeree makes counteroffer.
Lapse of reasonable time.
Operation of law (ie. subject matter of offer is destroyed).
Offer Revocation
Generally, offer can be revoked by the offeror any time prior to acceptance.
Offer is revoked when offeror makes a manifestation of an intent not to enter into the contract before the offeree accepts.
Revocation can be made in any reasonable manner/means and must be communicated.
If offeree acquires reliable information that offeror has taken action inconsistent with offer, then offer is automatically revoked (constructive revocation).
Irrevocable Offers
Irrevocable offers are exception to revocations.
(1) Offeree buys option contract (independent promise to keep offer open for period of time).
(2) Firm offer by merchant (any business person when transaction is commercial) that is written, signed by offeror, and has explicit promise not to revoke.
If offer period is not explicitly stated, then 90 days.
(3) Offeree started performance for unilateral contract (promise in exchange for performance).
(4) Offeree reasonably/detrimentally relied on offer in foreseeable manner (promissory estoppel)
Consideration
Consideration is bargained-for exchange between parties.
$1 is still valid consideration.
Illusory promises are not consideration.
Modern rule allows illusory promise to be valid if there is some interpretation that promise can be valid.
Gift promises and conditional gifts are not consideration.
However, gift actually given is consideration.
Past or moral consideration is not consideration.
Promise not to sue is enforceable.
Promise to pay debt after SOL has run is enforceable.
Most jurisdiction requires new promise to be in writing and signed by debtor.
Promise to pay debt discharged by bankruptcy is enforceable.
Consideration Substitutes
Promissory estoppel is when a promise would be reasonably expected to induce reliance, party detrimentally relied on promise, and injustice can only be avoided by enforcement of promise.
Quasi-contract (implied in law) is when P confers measurable benefit to D, P reasonably expected to be paid, and it would be unfair to allow D to keep benefit without paying.
Applies when there is absence of valid contract.
Implied contracts | |
Implied-in-fact |
|
Implied-in-law* ("quasi") |
|
*Implied-in-law contracts are not true contracts since they lack mutual assent. | |
Modification
Under common law, preexisting duty rule provides a promise to something that a party is legally obligated to do is not consideration.
Modifications require additional consideration.
Exceptions include change in performance, third party promising to pay, unforeseen difficulties.
Under UCC, if modification was made in good faith, then it’s binding without new consideration.
Modification can be oral or written.
Under UCC, clause prohibiting oral modifications is valid.
Mutual modification is allowed if fair and reasonable under the circumstances.
Defenses (MMIIFDU)
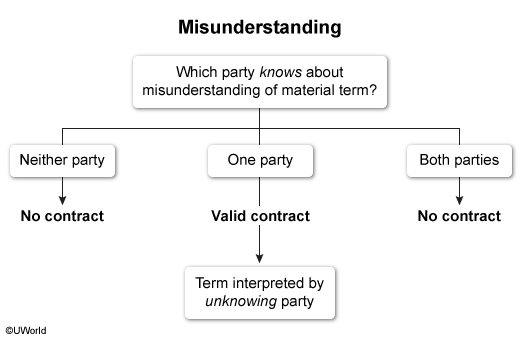
Misunderstanding
Parties attach different meaning to the same words.
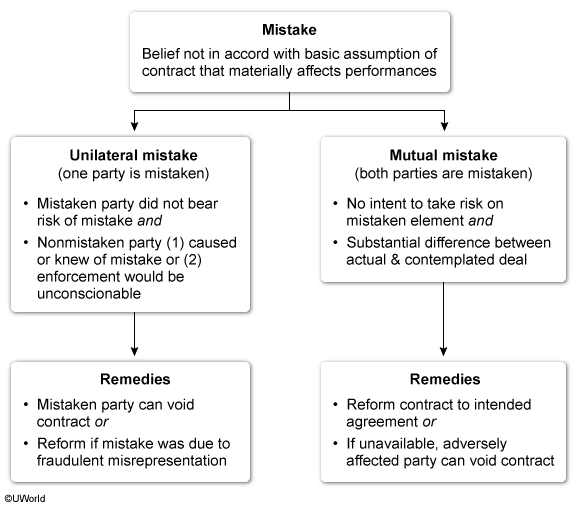
Mistake
Incapacity
Minors, mentally ill, intoxication (other party knows or has reason to know)
Contract entered by minor is voidable by minor.
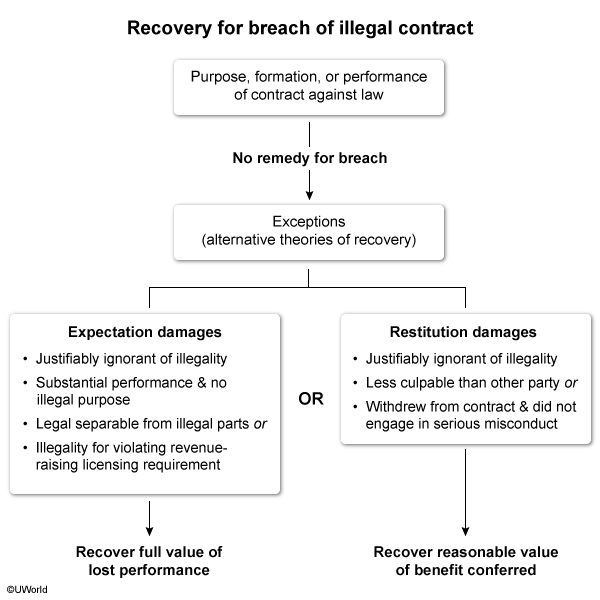
Illegality
Illegal contracts are void and unenforceable, but contract entered in furtherance of illegal act (that is not itself illegal) is enforceable.
Misrepresentation
Untrue assertion of fact made by words or conduct.
Contract is voidable by adversely affected party if misrepresentation was fraudulent OR material, misrepresentation induced assent to contract, and adversely affected party justifiably relied on misrepresentation.
Misrepresentation can be cured if misrepresentation becomes true before adversely affected party avoids the contract.
Duress
Improper threat that deprives party from making meaningful choice to contract.
Unconscionability
Contract shocks the conscious.
Statute of Frauds
SOF provides that certain contracts must be in writing.
Marriage
Surety
Must be in writing and signed by party against enforcement.
If purpose of guaranteeing debt is to own benefit, then contract does not need to be in writing.
Not performed within one year
If contract is fully performed, then contract does not need to be in writing.
UCC sale of goods of $500 or more
If party sends part of goods or partial payment, then contract does not need to be in writing.
If merchant sends written confirmation of order that is signed by party against enforcement, states quantity and parties, and other party does not object within 10 days, then confirmation will act like writing for contract. UCC relaxes signature requirement between merchants and allows only one merchant to sign.
Modifications does not need to be in writing unless they affect subject matter or quantity.
Real property transfer
If party pays value and possesses land or makes improvements (at least two), then contract does not need to be in writing.
Executor/administrator estate contract
Warranties
Warranty is a promise about a term in the contract that shifts risk to the party making the promise.
Seller can disclaim all warranties.
Express warranty affirms/describes the goods and is part of the contract unless it’s the seller’s opinion.
Use of sample or model creates express warranty that goods sold will be the same.
Implied warranty of merchantability affirms that goods are fit for ordinary commercial purposes.
Only triggers when seller is a merchant dealing with the goods at issue.
Warrant is waived for defect that examination would have revealed if buyer had examined goods as fully before entering the contract or refused to examine goods before entering the contract.
Implied warranty of fitness for a particular purpose affirms that goods will satisfy special purpose.
Only triggers when buyer relies on seller’s expertise for good that will be used for special purpose.
Seller can disclaim warranty if disclaimer is in writing and conspicuous so a reasonable person would notice it.
Performance (Common Law)
Under common law, doctrine of substantial performance provides that party who substantially performs can recover on the contract.
However, doctrine does not apply if there is material breach of contract.
For material breach, nonbreaching party can withhold promise performance and pursue remedies.
Substantial performance is less likely to be found if party intentionally furnishes materially different services.
Performance (UCC)
Under UCC, perfect tender rule provides that seller must strictly perform contract (perfect goods and delivery).
If seller fails to tender perfect goods, then buyer can either accept or reject goods.
If rejecting, then must be done in reasonable time.
If accepting, then buyer must pay amount of goods in original contract.
If nonconforming goods tendered prior to delivery date, then seller can deliver with reasonable notice to cure.
If seller has reasonable grounds to believe buyer would accept nonconforming goods, then seller can deliver with reasonable notice to cure.
Impossibility, Impracticability, Frustration of Purpose
Impossibility provides contract can no longer be performed (ie. goods destroyed, contract became illegal).
If temporary impossibility or parties prepared for event, then defense cannot be used.
Impracticability provides contract can be performed, but with great difficulty or expense due to unforeseen event.
Impracticability can arise if there’s unanticipated event, parties did not know event would occur, and offeror was not at fault for event.
If party assumed the risk of event happening that made performance impracticable, then defense cannot be used.
Frustration of purpose provides contract can be performed, but some event undermines the core reason for the contract.
Anticipatory Repudiation
Anticipatory repudiation occurs when party clearly and unequivocally repudiates the contract OR party creates reasonable grounds for insecurity and fails to give adequate assurance within 30 days of demand.
Under UCC, demand for assurance must be in writing.
Upon repudiation, nonrepudiating party may treat repudiation as a breach or ignore it and demand performance.
Repudiating party may retract repudiation unless other party accepted repudiation, relied on repudiation, or brought action for breach.
Accord and Satisfaction
Parties agree to new performance that will satisfy the contract.
If new performance is not satisfied, party can sue on either original or new performance.
Accord and satisfaction is valid if amount is in dispute, debtor gives check stating that it’s paid in full, and creditor cashes in check.
3 scenarios:
I have $100 debt that is undisputed and write check for $50 marked “paid in full”; You deposit check, but can pursue other $50.
I have $100 debt that is undisputed, but I cannot pay so we negotiate I pay $70 (negotiation/settlement/compromise) and you cannot pursue other $30.
I doubt I have $100 debt, but decide to pay $50 anyways, then you cannot pursue other $50.
Non-Compete Clauses
Non-compete clauses are enforceable, but must be reasonable under the circumstances.
Parol Evidence Rule
Parol evidence rule applies when parties ask court to admit evidence that was discussed prior to or at the time of the contract.
Evidence after contract is admissible and PER does not apply.
UCC presumes that written contract is partially integrated.
For complete final integration, parol evidence is not admissible.
Exception is when parol evidence is used to clear ambiguity.
Merger clause (declares written contract is complete and final agreement) is strong but not definitive evidence that a contract is completely integrated.
For partial integration, parol evidence is admissible for evidence that explains/supplements terms, but not evidence that contradicts/materially alters terms.
Express terms, course of performance, course of dealing, trade usage (in order)
Exceptions |
Evidence of prior or contemporaneous oral or written agreement is admissible to establish:
|
Risk of Loss
If there is no carrier:
If seller is merchant, then risk of loss is on seller until buyer takes possession.
If seller is not merchant, then risk of loss is on seller until seller tenders goods to buyer (drops off goods for pick up).
If there is carrier:
For shipment contract (FOB seller - does not require delivery to specific location), then risk of loss is on seller until seller gives good to carrier; once goods are given to carrier then risk of loss is on buyer.
For destination contract (FOB anything else - require delivery to specific location), then risk of loss is on seller until goods get to actual destination.
Conditions
If condition is not met, then other party does not have to perform and discharged from performance.
Exceptions are when there is waiver of condition, bad faith, or party would suffer a great loss or forfeiture.
If condition is within control of promisor, then it’s illusory promise which is not enforceable.
Generally, time is not of the essence in contract unless stated.
If there is express condition, then party still breaches contract even if there was substantial performance.
Express condition includes “on the condition that” or “provided that”.
If condition is based on subjective standard and party is dissatisfied (even unreasonable), then condition has not been met and dissatisfied party is discharged from obligation without breach.
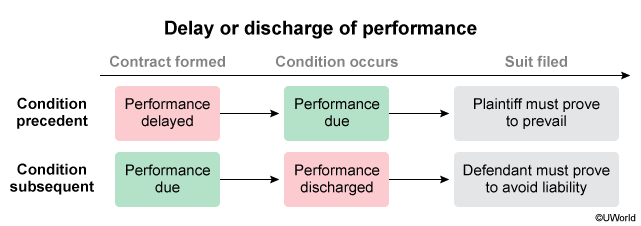
Condition precedent is when party's duty to perform arises on occurrence or nonoccurrence of uncertain future event (event creates the duty).
Condition subsequent is when party's duty to perform is released upon occurrence or nonoccurrence of uncertain future event (event extinguishes the duty).
Installment Contract
Installment contract involves delivering goods in several different shipments.
Payment by buyer is due upon each delivery unless price cannot be apportioned.
Buyer's rights under installment contract | |
Each installment |
|
Whole contract |
|
Third Party Beneficiary
Third party beneficiary benefits from the contract between the original parties.
Incidental beneficiary has no rights in the contract.
Intended beneficiary may have right in contract
Intended beneficiary does not need to be specifically named.
If intended beneficiary’s right has not vested, beneficiary cannot sue.
If intended beneficiary’s right has vested, beneficiary can sue and has same rights/defenses as the original parties.
Intended beneficiary’s right vests when third party is informed of rights and accepts it OR third party learns of rights and relies on it
Intended beneficiary of a gift (donee beneficiary) may sue promisor and not promisee.
Exception is when promisee reasonably foreseen reliance and donee beneficiary justifiably and detrimentally relied on contract.
Assignment and Delegation
Assignment transfers contractual rights to another.
Delegation transfers contractual duties to another.
Assignments and delegations are valid as long as transfer is present intent (not future intent).
Unique or personal services cannot be assigned or delegated.
Third party only gets rights/duties original parties agreed and cannot change terms.
Third party is liable if third party received consideration or consideration substitute and original party is still liable unless there was novation.
Mere consent to delegation does not create novation.
Gratuitous assignment is assignment with no consideration and generally revocable.
Revocable assignment is automatically revoked upon death, incapacity, or bankruptcy of assignor.
If contract explicitly prevents assignment, then assignment is still valid but original party is liable for damages for breach.
If assignment materially alters risk/obligation of other party, then assignment is invalid.
If contract explicitly prevents delegation, then delegation is invalid.
Contract provisions prohibiting assignments/delegations | |||
Type of provision | Explicit prohibitions | Assignment of rights | Delegation of duties |
None | N/A | Allowed | |
Specific | Assignment of rights & delegation of duties | Barred | |
Assignment of rights only | Barred | Allowed | |
Delegation of duties only | Allowed | Barred | |
General | Assignment of "the contract" | ||
Compensatory Damages (Money Damages)
Compensatory damages compensate nonbreaching party for actual economic losses.
Non-breaching party’s failure to mitigate does not give breaching party a right to sue the non-breaching party for such failure; it only reduces non-breaching party's damages recovery.
(1) Expectation damages is default and puts non-breaching party in the same position had the contract been performed.
Damages awarded if foreseeable with reasonable certainty.
Calculation = contract price (what was promised) - what was received + costs
(2) Reliance damages put party in position prior to contract and awards amount paid due to reliance on contract (unreimbursed costs).
Party cannot recover both reliance damages and expectation damages for same breach (must choose one).
(3) Restitution damages allow recovery of value of benefits that have been actually given.
Calculation is market value of service.
Quantum meruit allows recovery of reasonable value of service; similar to restitution, but allows breaching party to recover.
(4) Consequential damages allow foreseeable losses due to breach (ie. lost profits).
Breaching party must have reasonably foreseen the consequential damages for them to be recoverable.
P must prove consequential damages with reasonable certainty not speculatively.
(5) Incidental damages allow for commercially reasonable expenses that nonbreaching party incurred as a result of the breach.
(6) Liquidated damages are damages determined at time of contract.
Liquidated damage clauses are enforceable if reasonable and not like a penalty.
Generally, 10% or less of value of contract is reasonable (beyond 10% looks like penalty).
Purpose of compensatory damages | |
Primary (expectation measure) |
|
Fallback (reliance measure) |
|
Money Damages UCC
Seller remedies
If goods have been delivered and accepted (something happens afterwards), then seller recovers contract price.
If some or none of goods have been delivered and not resold, then seller recovers contract price – market price.
If some or none of goods have been delivered and are resold, then seller recovers contract price – resale price.
Seller can also recover incidental damages for any additional costs related to reselling the goods.
If seller is lost volume seller (sell as many widgets as possible), then lost profits amount is the answer (expected profit + costs - any payment for reselling).
Buyer remedies
If buyer purchased replacement goods after breach, then formula is contract price – cost of replacement goods.
If buyer did not purchase replacement goods after breach, then formula is contract price – market price of goods at time you learn of breach.
Equitable Remedy
Equitable remedy provides remedy when money damages are inadequate.
Specific performance occurs when court make party perform in a certain way when item is unique.
Land is always unique.
Not available to enforce duty to perform personal services (ie. entertainer, designer, lawyer, architect).
Injunction occurs when court stops party from doing something to prevent irreparable harm.
Trade secrets, employment contracts, proprietary information.
Recission occurs when there is no meeting of the minds so parties can act as if contract didn’t occur.
Mistake, misrepresentation, duress, lack of capacity.
Auction Sale
UCC governs two types of auction sales.
For both, bidder has right to withdraw bid until the auctioneer announces the completion of the sale.
Reserve auction where auctioneer may withdraw the goods any time before announcing the completion of the sale (auction is with reserve unless it is specifically announced as no-reserve auction).
No-reserve auction where goods cannot be withdrawn after auctioneer calls for bids unless no bid is received within a reasonable time.
Reformation
Reformation is a modification by a court of a written contract that fails to reflect the contracting parties' intent.
Party can seek reformation as equitable remedy on several grounds including mutual mistake.