End of Chapter 18 and Beginning of Chapter 19: Gene Expression and Control of Expression in Eukaryotes
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
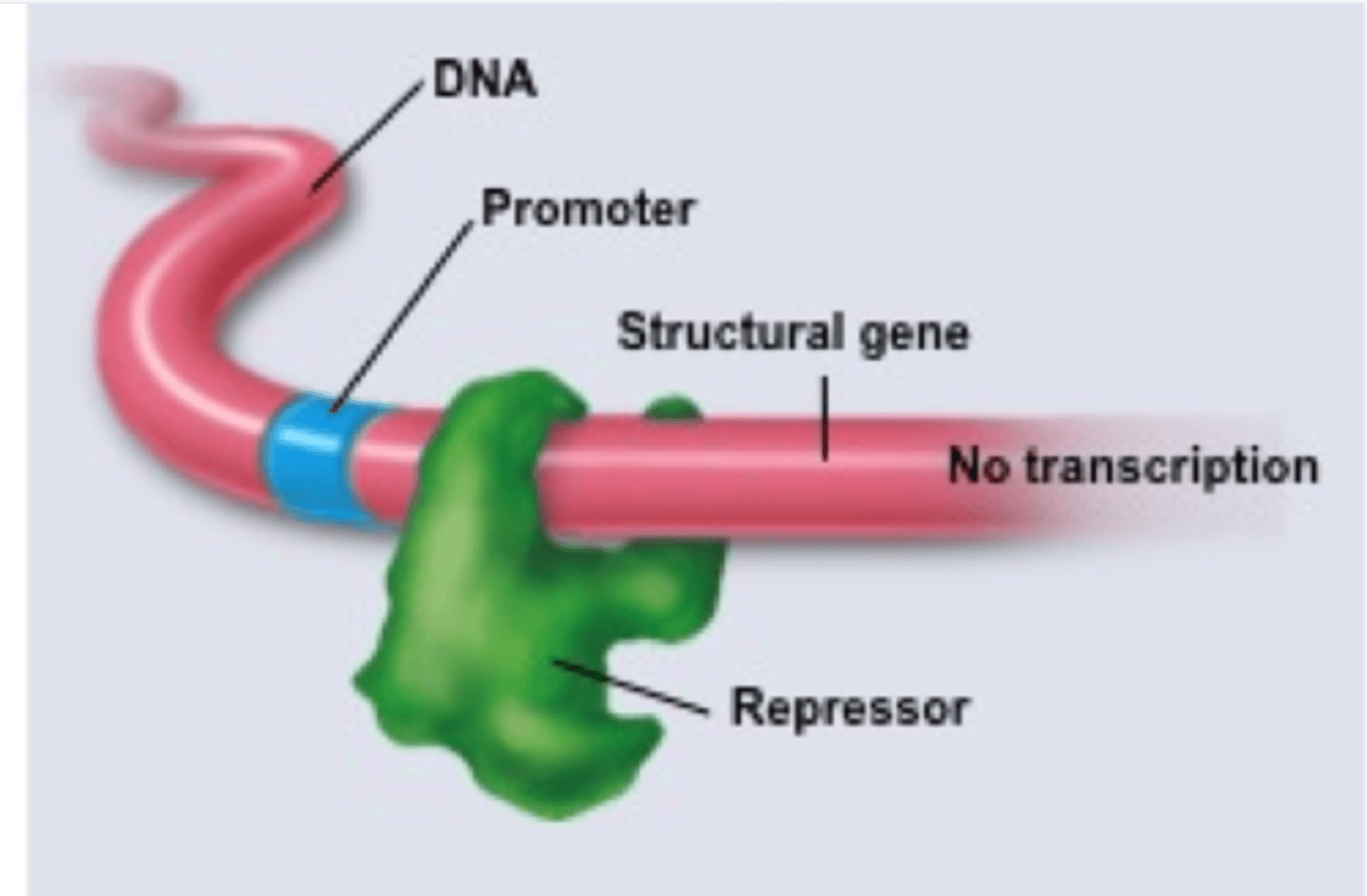
negative control
repressor shuts down transcription
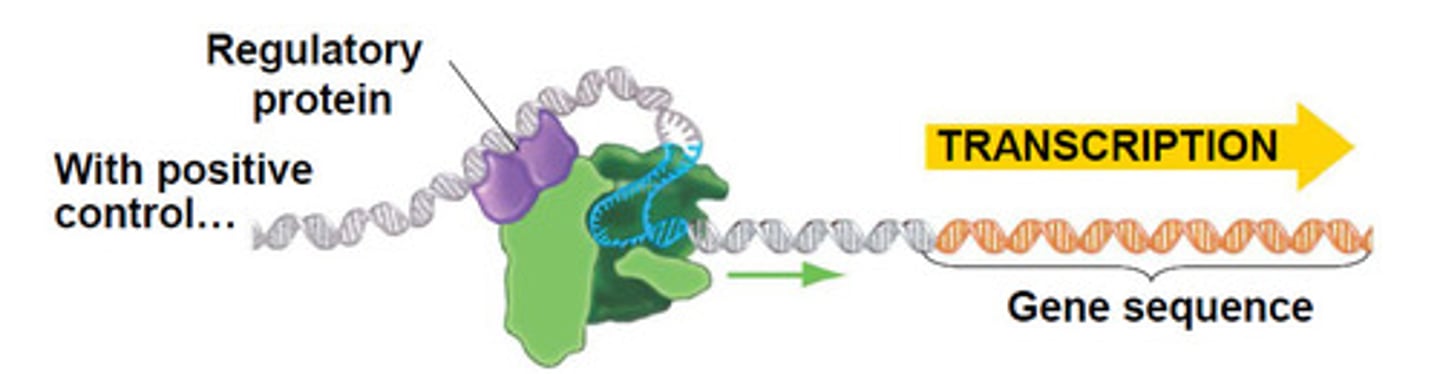
positive control
regulatory protein triggers transcription
Francois Jacob and Jacques Monod
used metabolism mutants to develop the lactose operon model
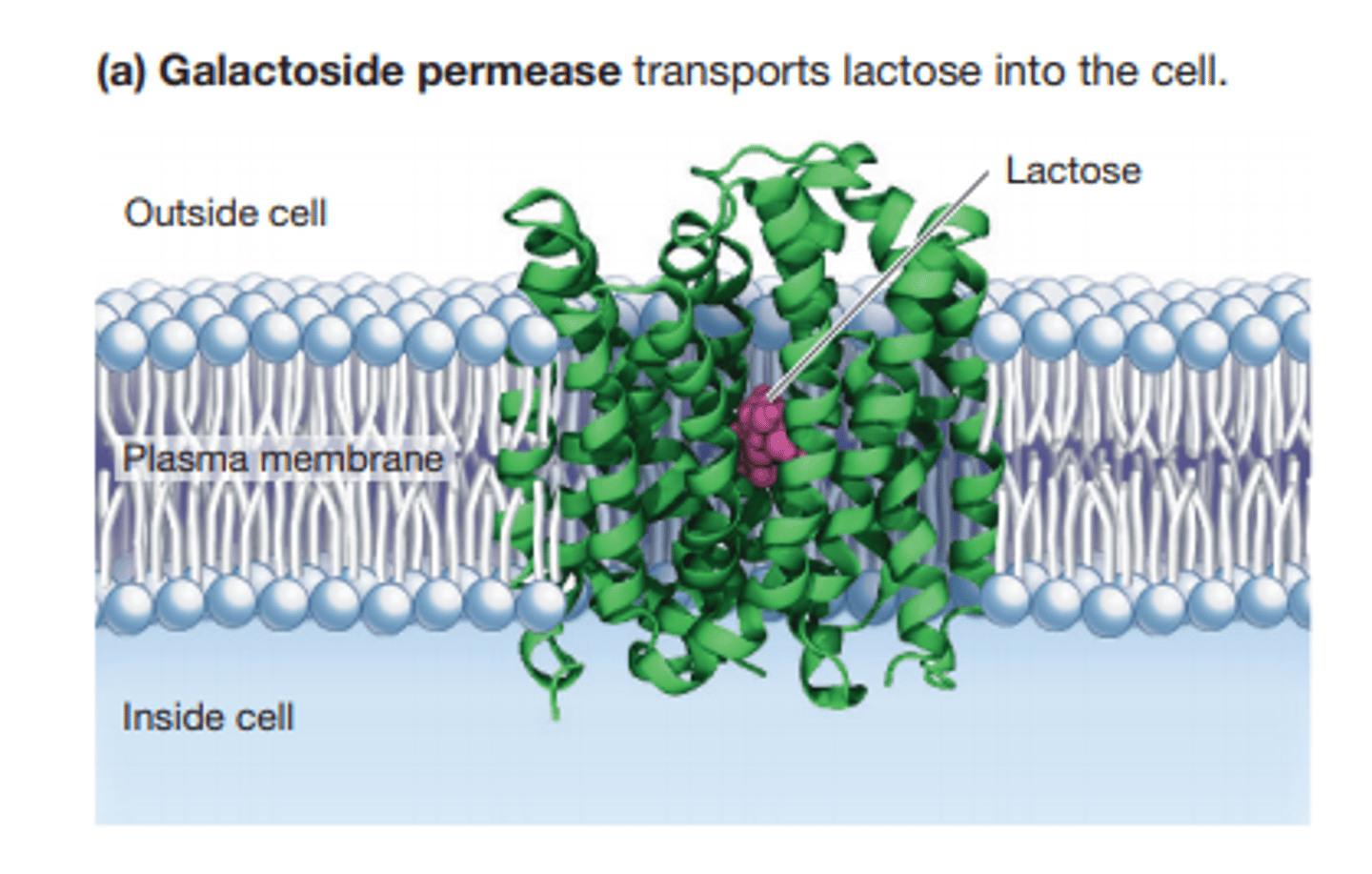
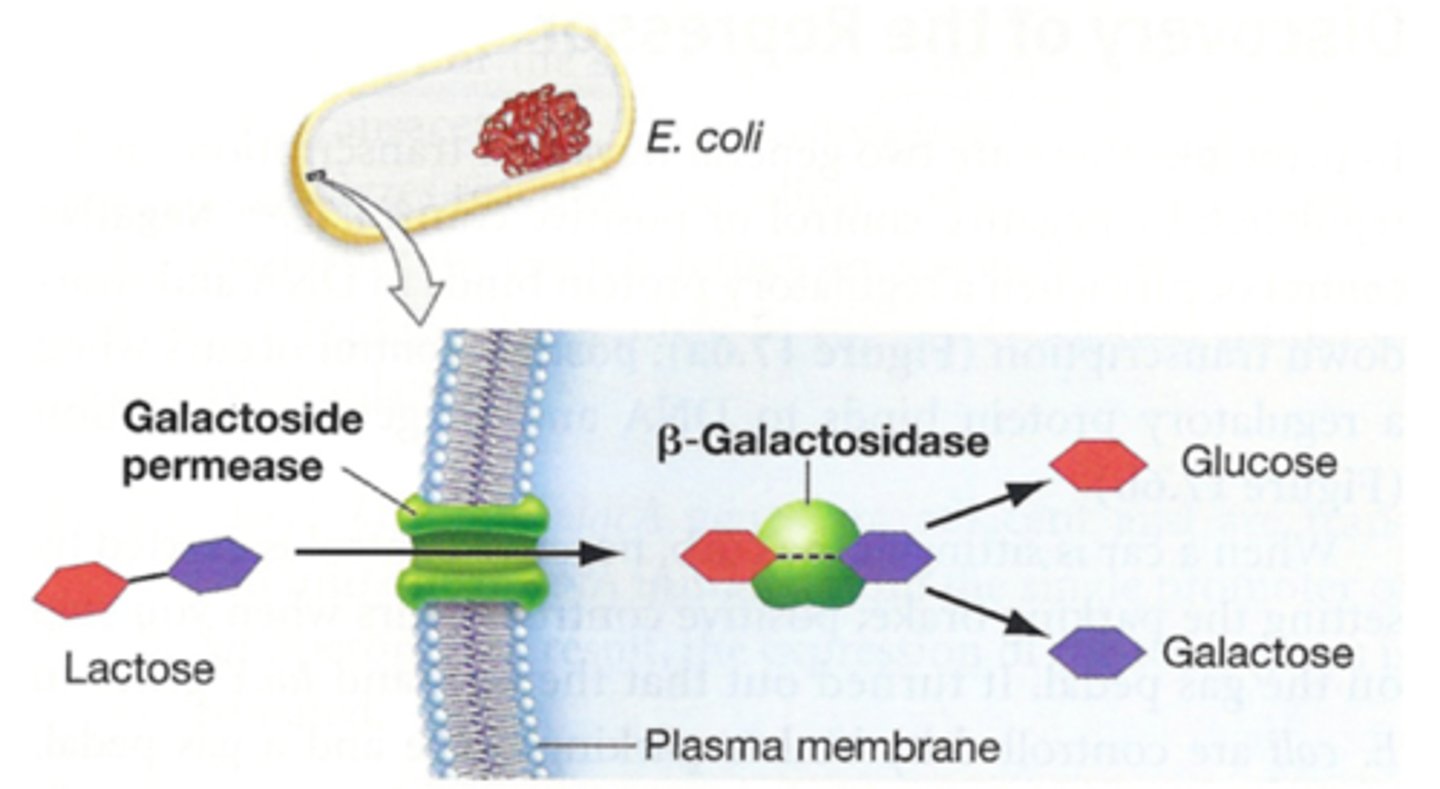
galactoside lactose permease
a symporter that imports lactose into the cell
B-galactosidase
breaks down lactose to produce glucose and and galactose
lacI
-encodes the lac repressor which prevents transcription of lacZ, lacY when lactose is absent
-has its own promoter and is regulatory gene
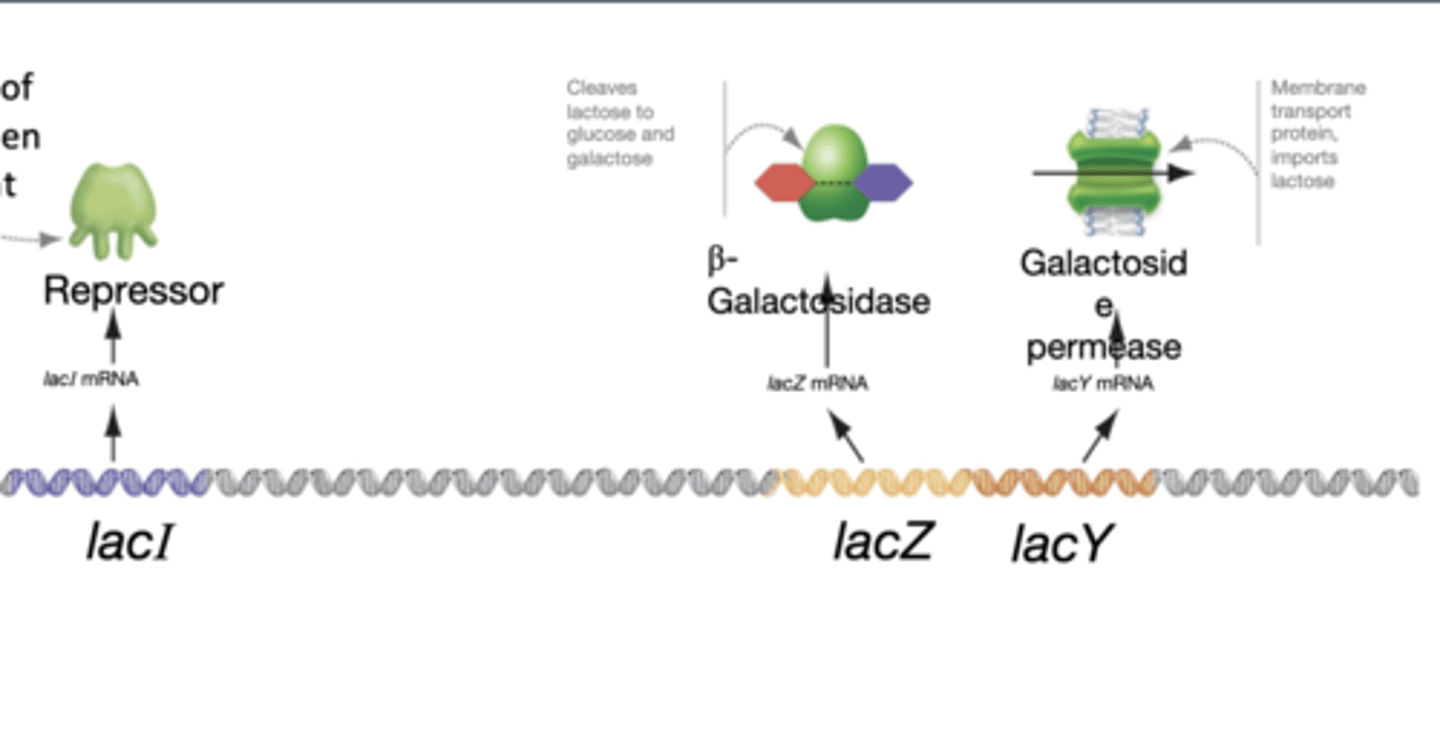
lacZ
encodes B-galactosidase and cleaves lactose to glucose and galactose
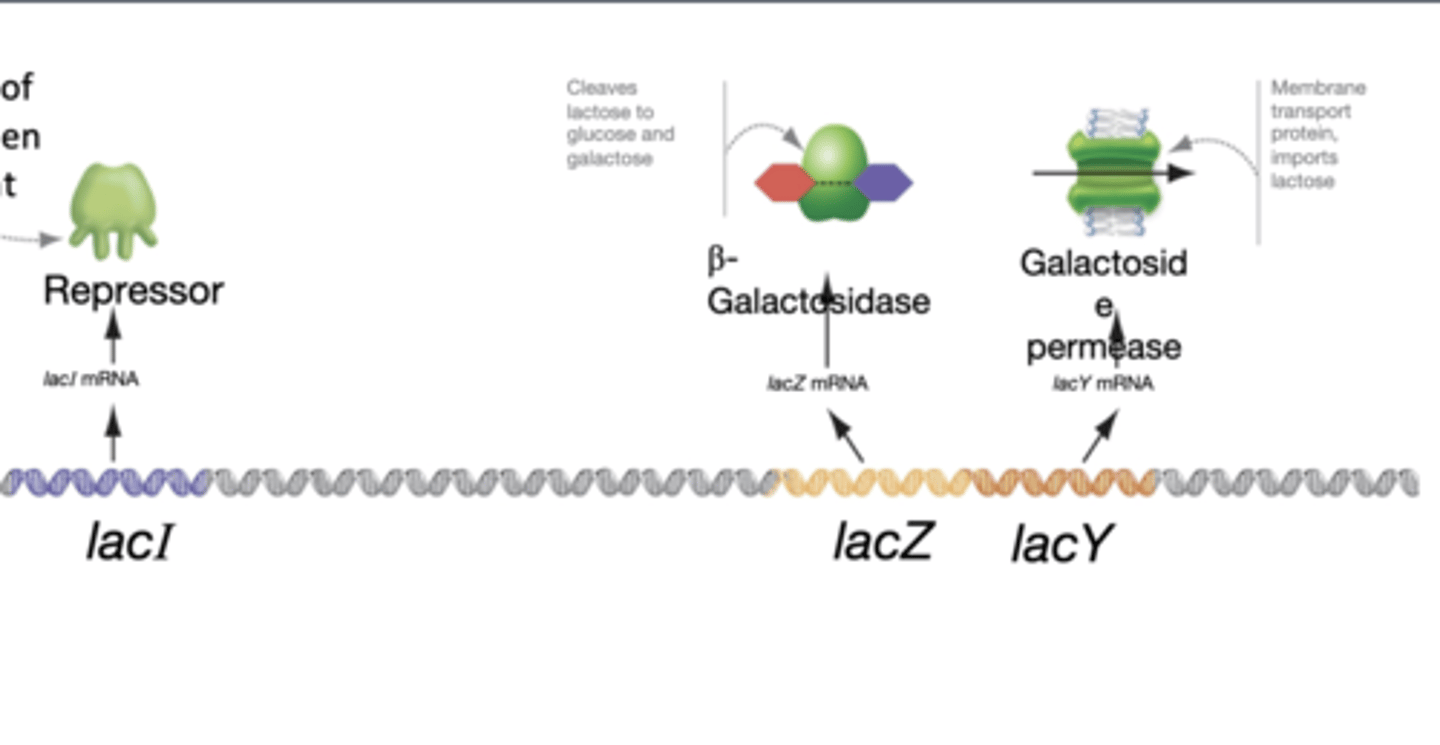
lacY
encodes lactose permease that imports lactose
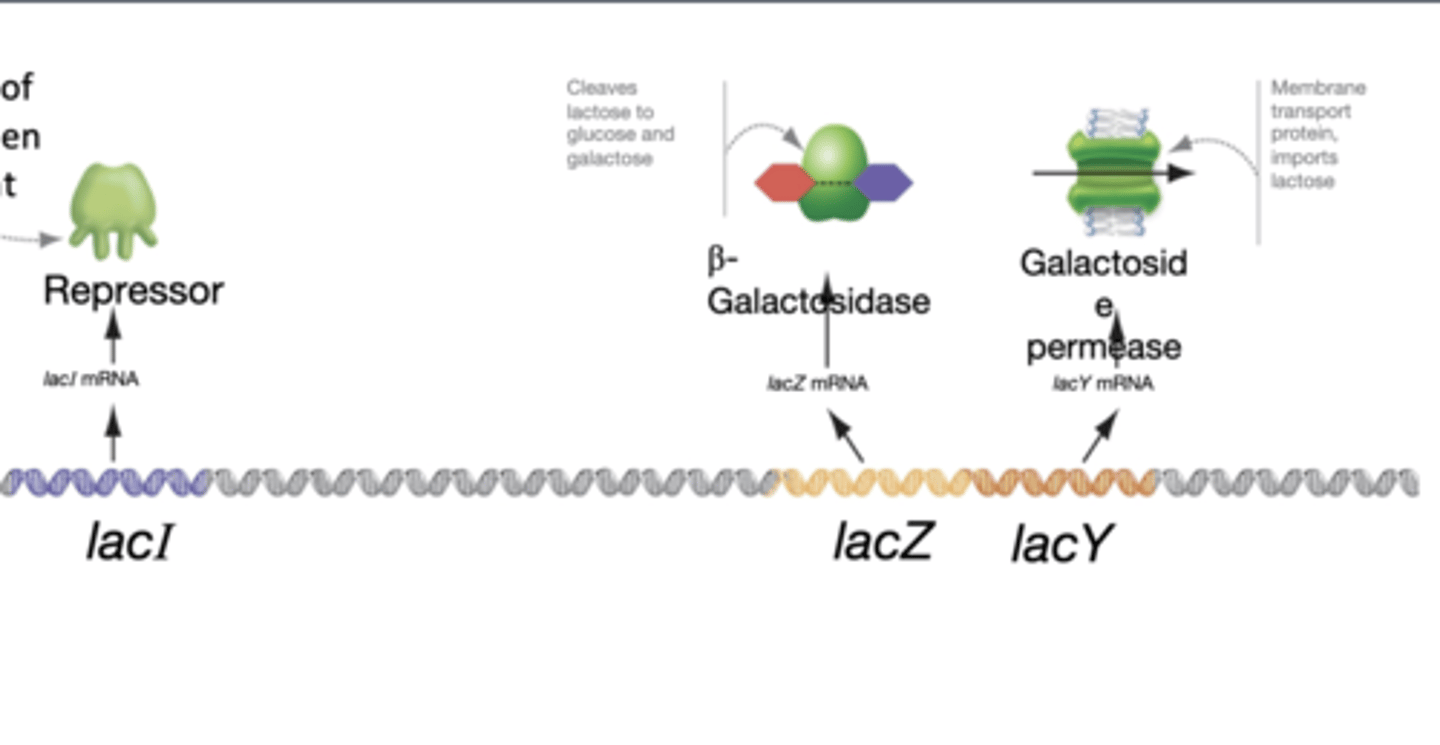
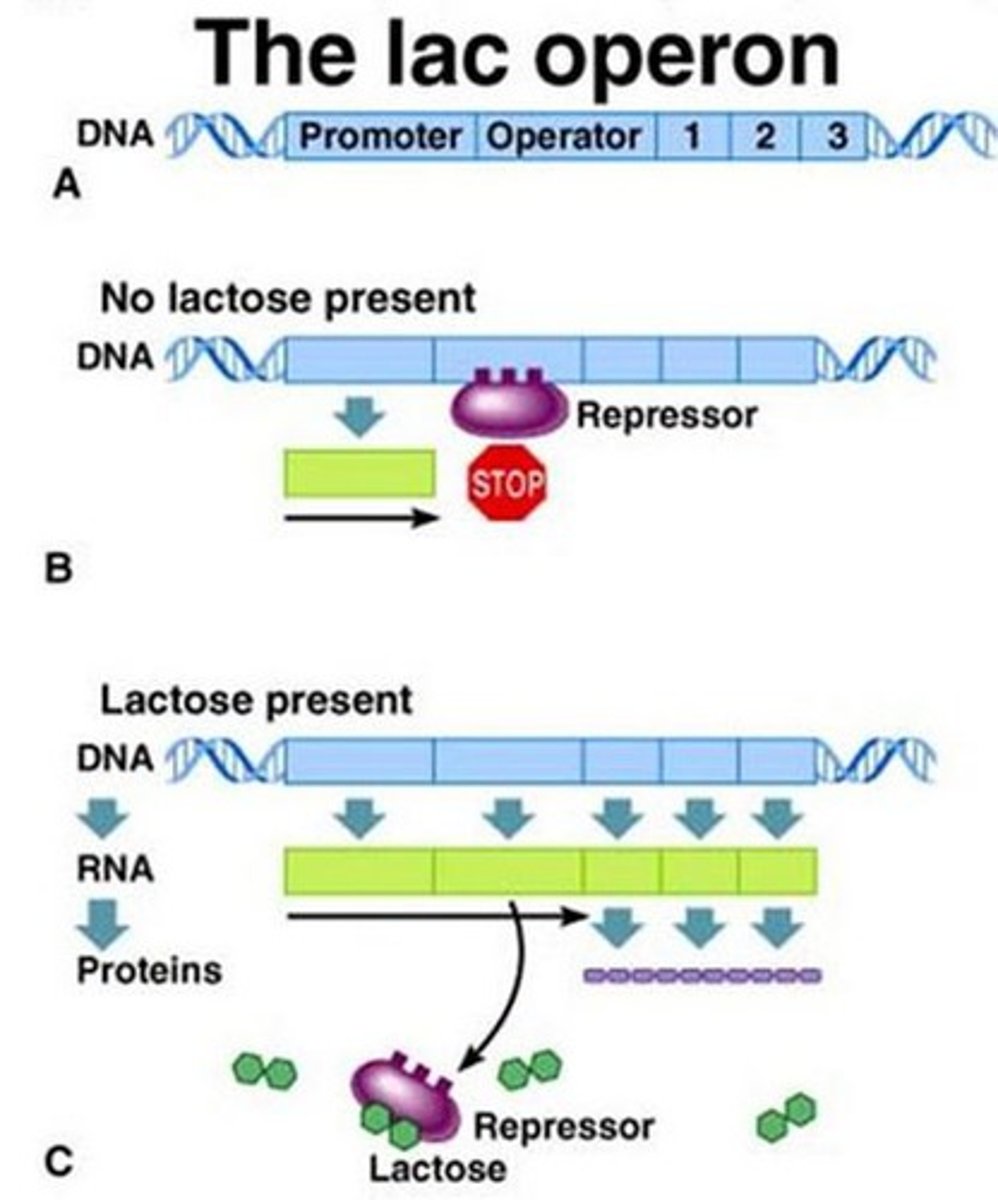
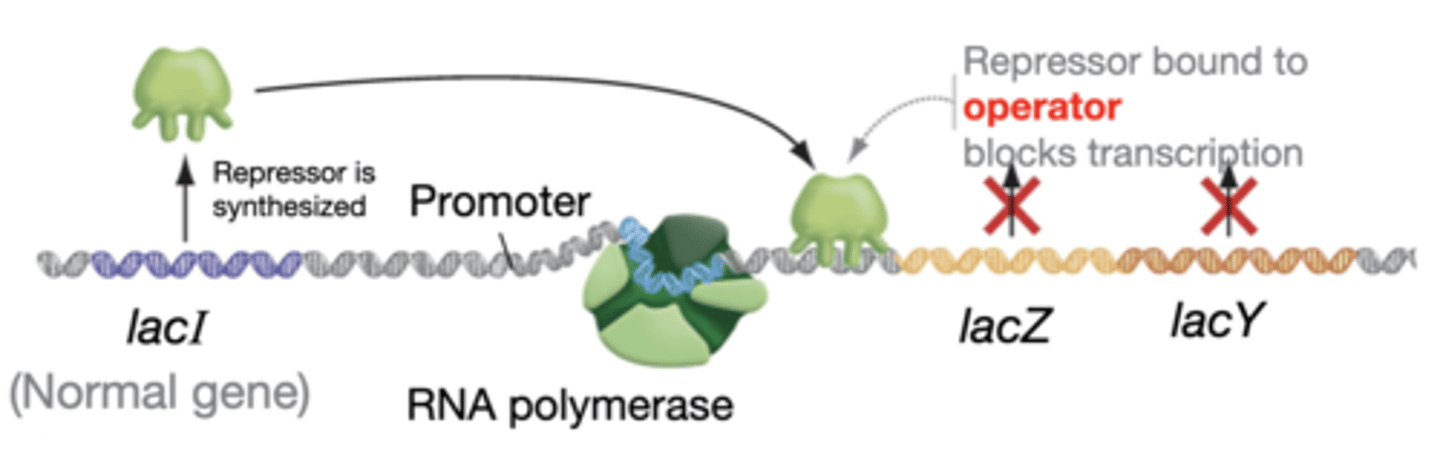
lactose absent
-repressor is active and binds to DNA
-transcription blocked
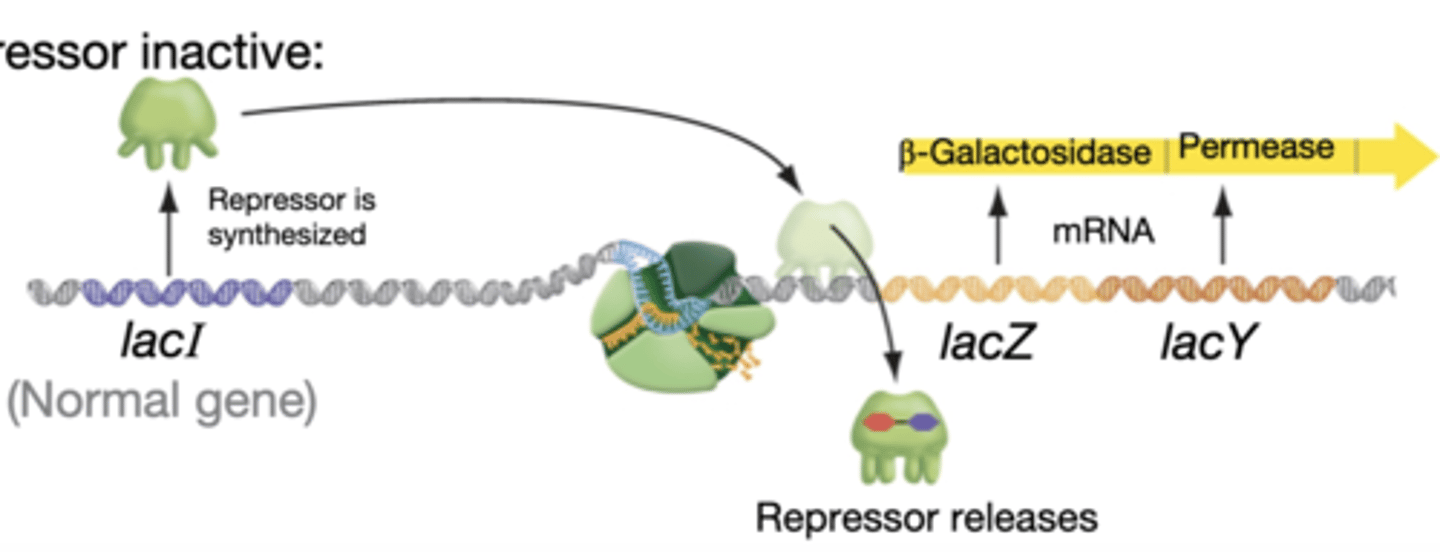
lactose present
-repressor inactive
-lactose (the inducer) binds to the repressor
-repressor releases from DNA and transcription occurs
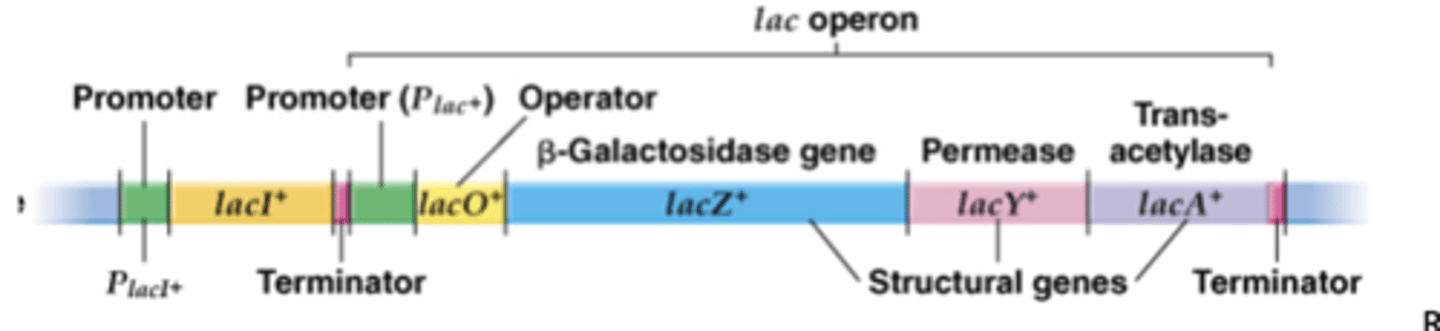
Lac operon
-one promoter, three genes in a row
-LacA: sugar export
-these three are structural genes and not involved in regulating genes
-negatively regulates and inducible
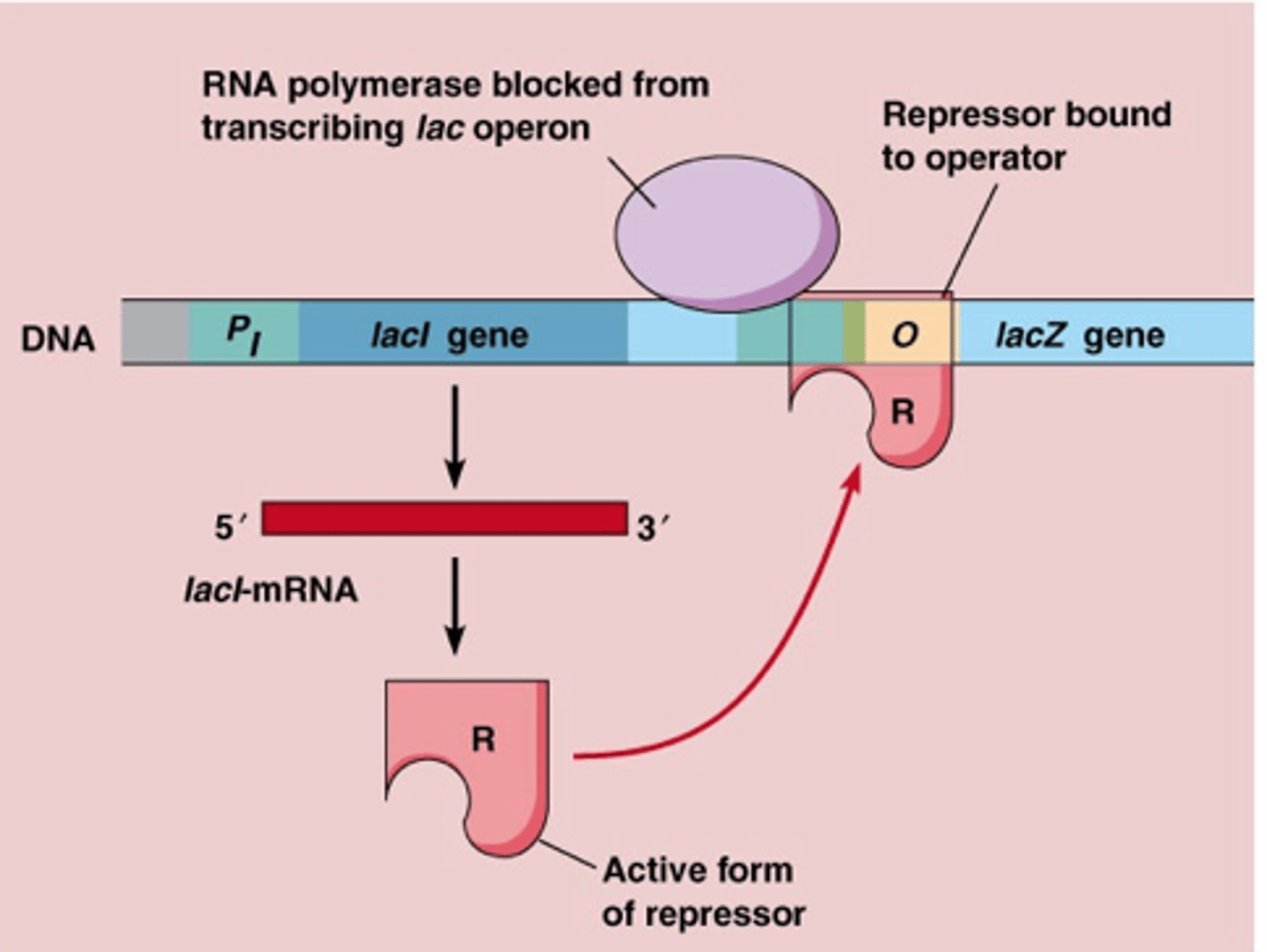
operator (lacO)
regulatory region where the repressor binds only regulates promotor its attached to in DNA (cis)
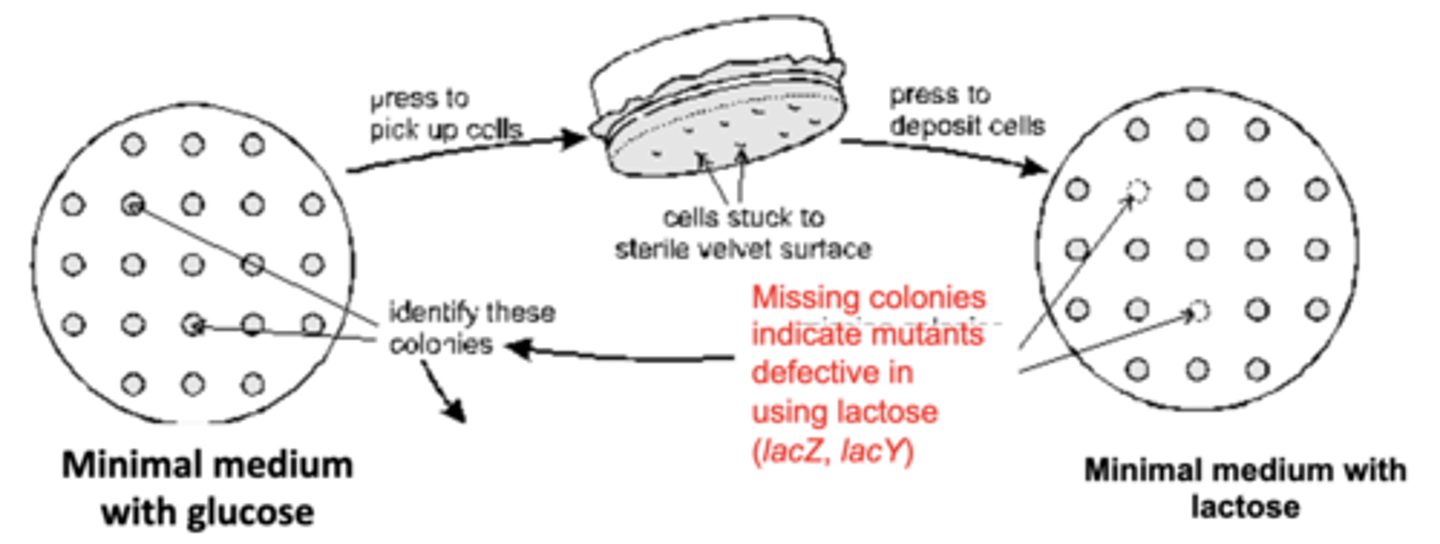
identification of mutants
-mutants grew colonies on minimal medium + glucose and replica plated on minimal medium + lactose
-those that didn't grow on minimal medium + lactose were defective is lactose usage (mutations in lacZ and lacY)
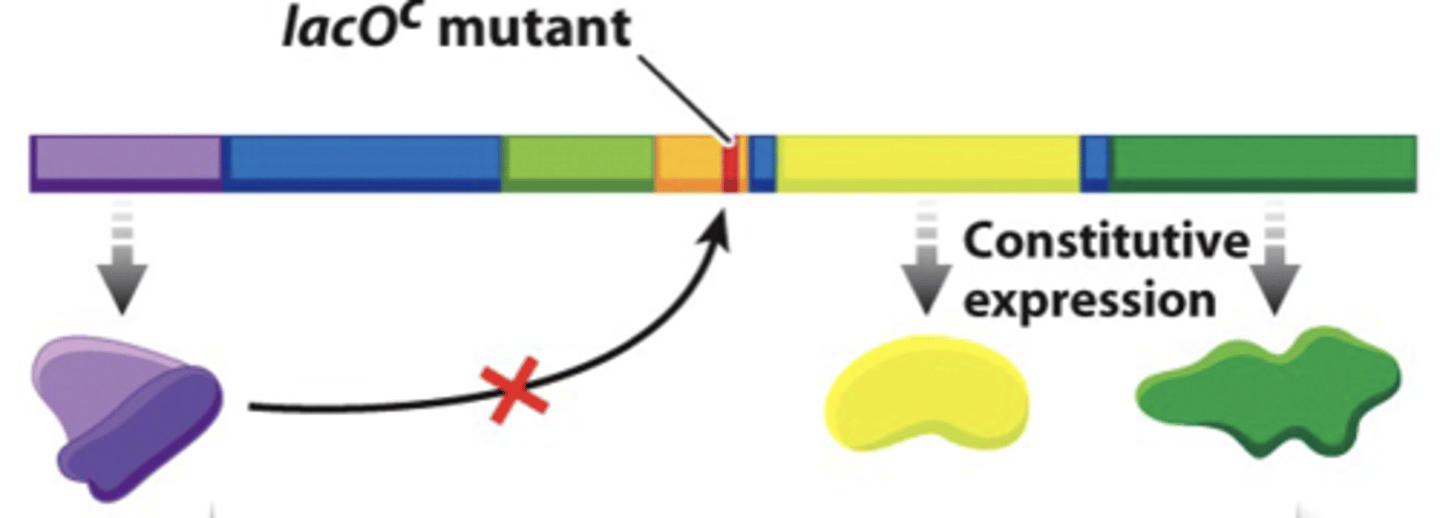
lacO^c mutation
results in constitutive expression of lac operon and repressor can't bind
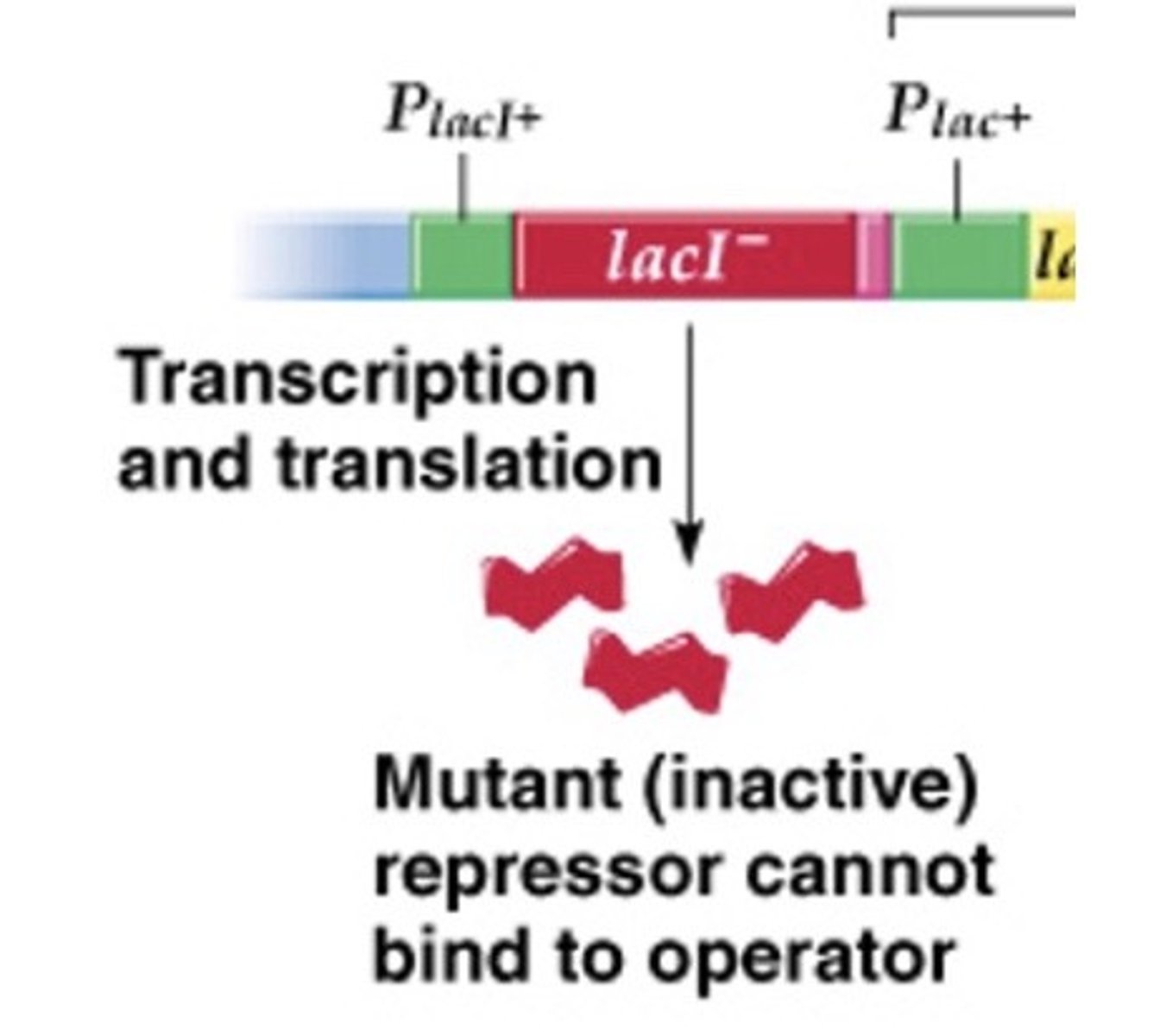
lacI- mutation
inactive repressor can't bind to operator
merodiploids
-partial diploids in which there are two copies of some genes, one gene is plasmid and F'(lac) factor
-made to test functions of operator and repressor
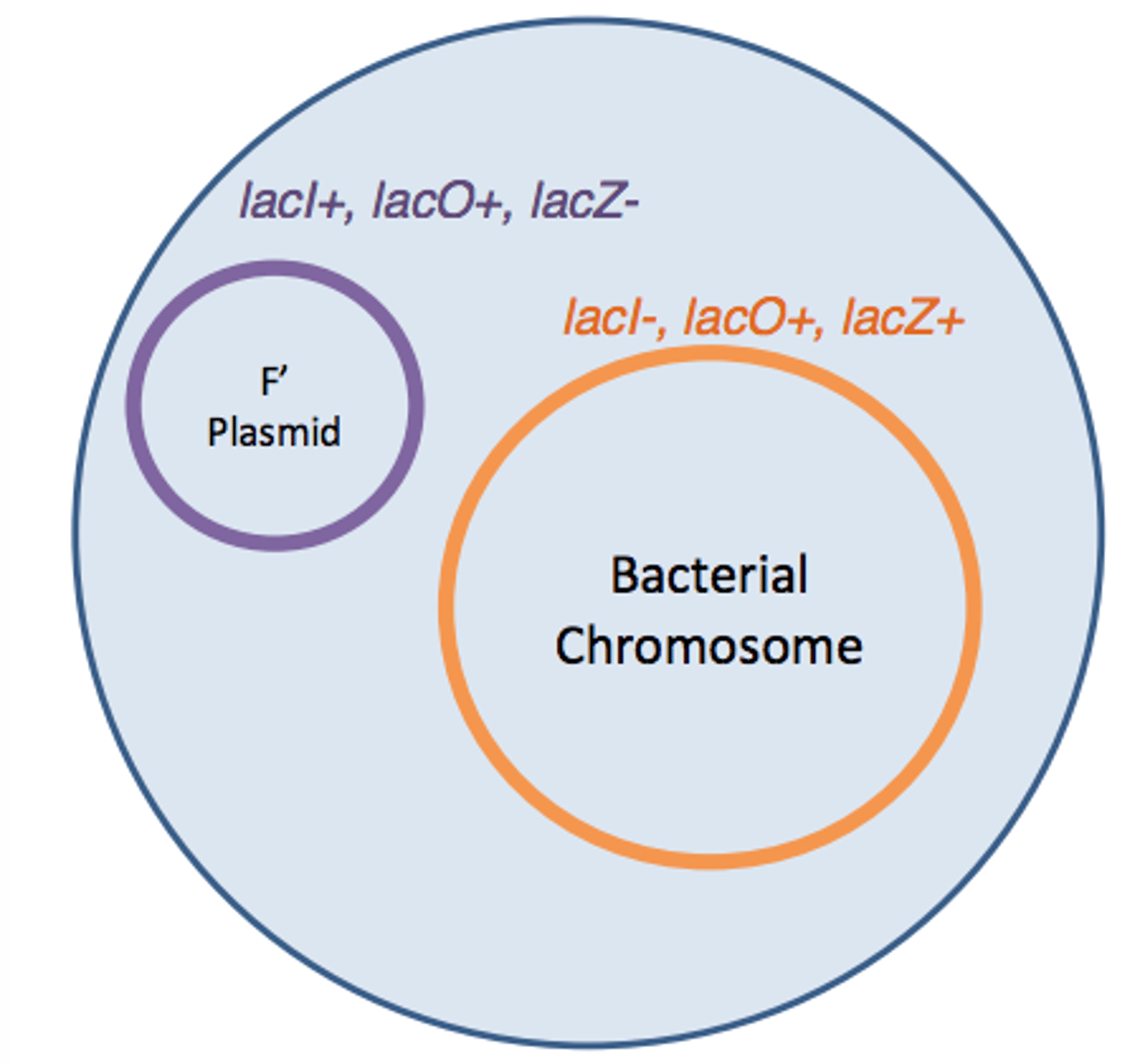
lacI+
is dominant because repressor can go anywhere is cell not just the strand of DNA the gene is associated with (trans)
global gene regulation
-coordinated regulation of many separate genes
-needed for responses that require the expression of dozens or even hundreds of genes
regulon
-set of separate genes or operons that are controlled by the same regulator
-target genes contains regulatory sequences recognized by same regulator
-can be pos. or neg. regulated
differential gene expression
-responsible for creating diff cell types
-arranges them into tissues
-coordinates their activity
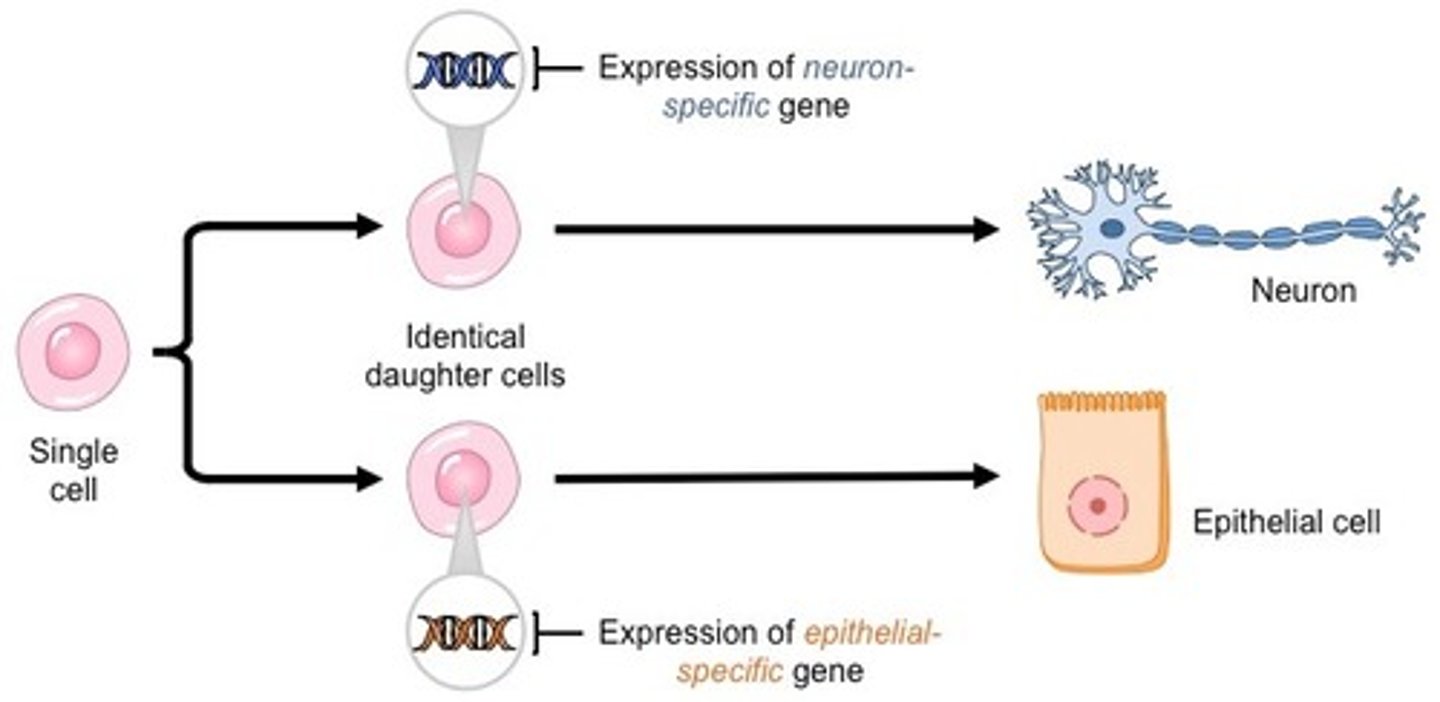
gene regulation in eukaryotes
-chromatin remodeling
-transcriptional control
-translational control
-post translational control
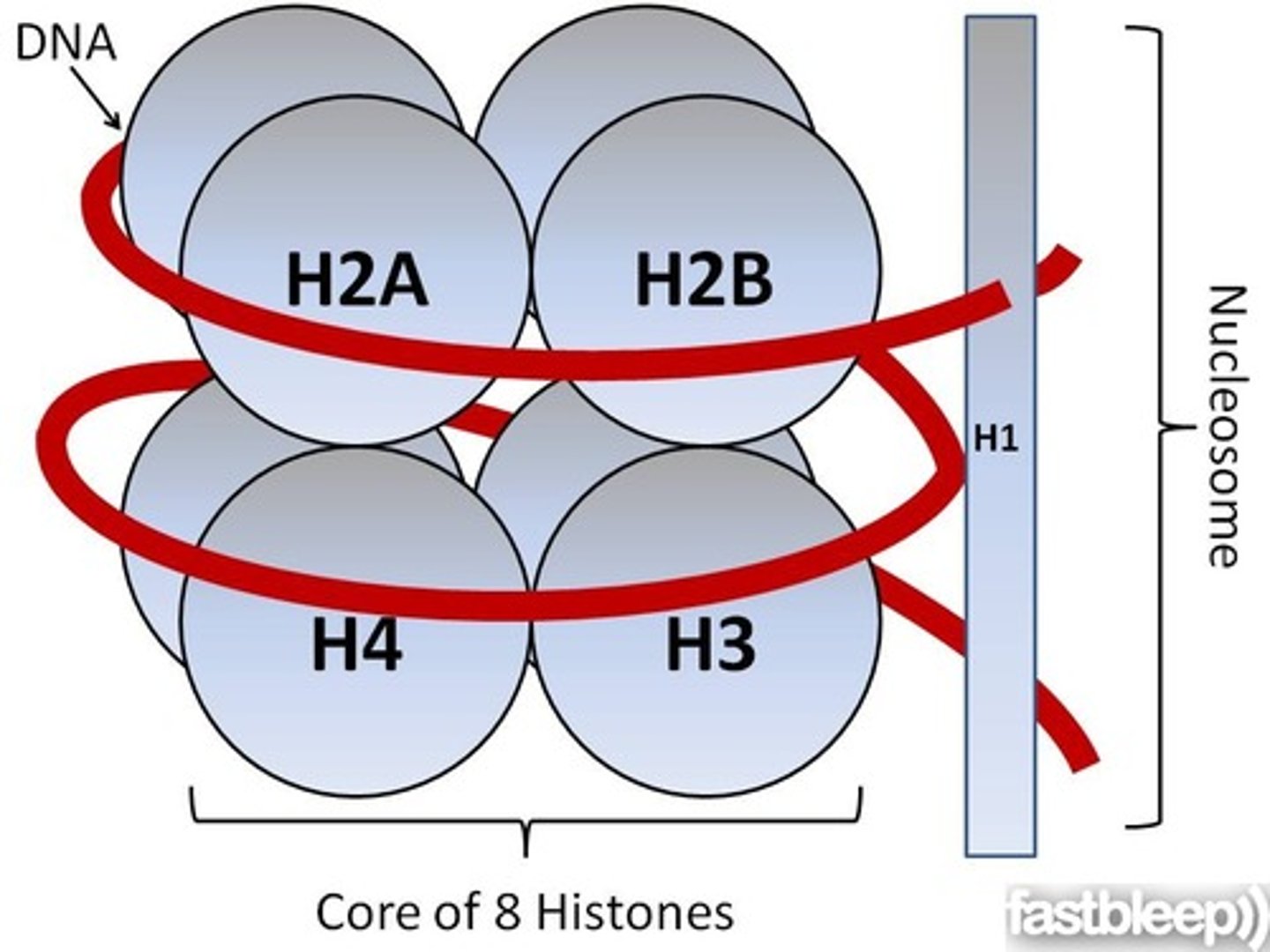
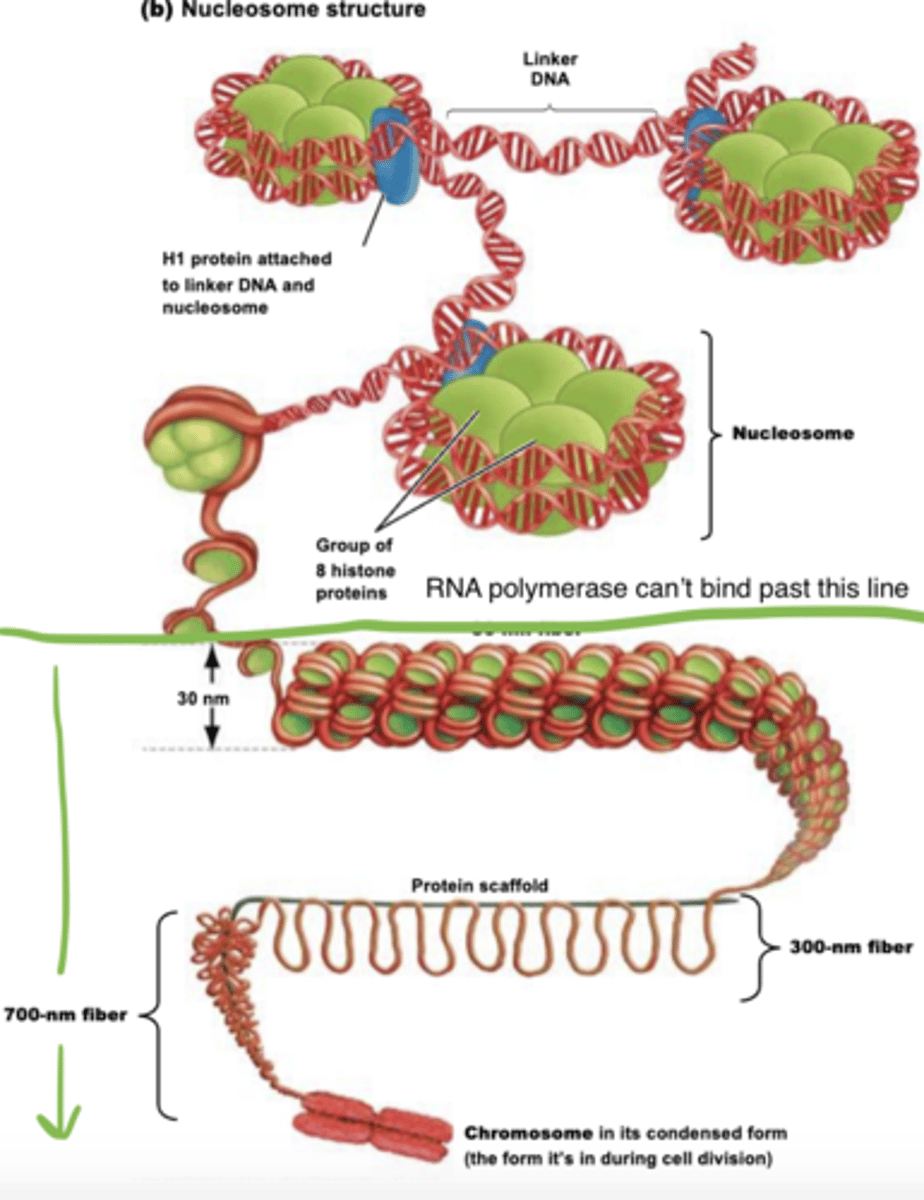
nucleosome
-simplest structural unit of eukaryotic chromatin
-made of histone core, 1.65 turns of DNA, condenses DNA 7x
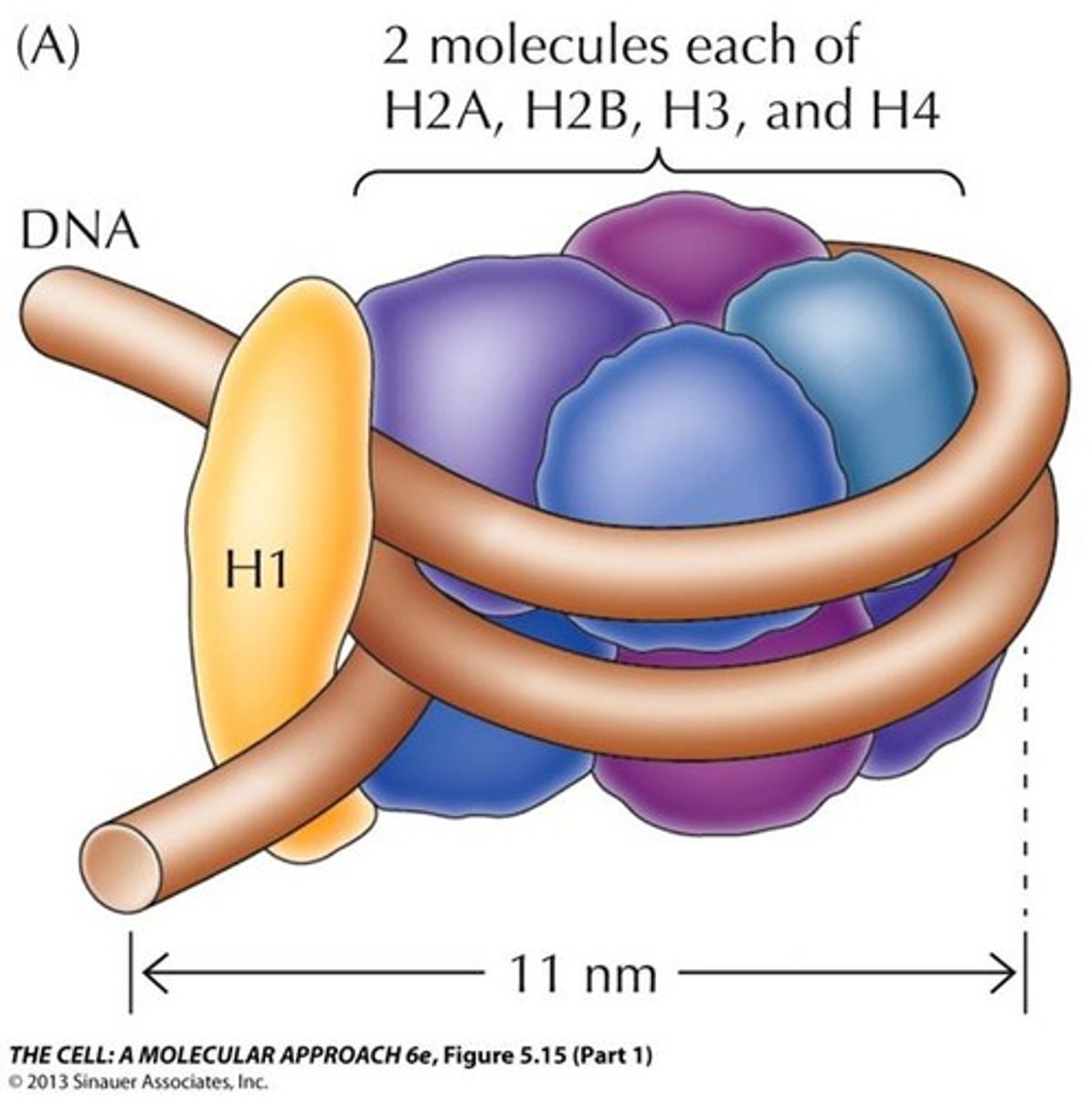
histones
-used for DNA packaging
-basic proteins with net positive charge (backbone of DNA is neg.)
-amino acid sequences are highly conserved cause mutations in a histone would be lethal
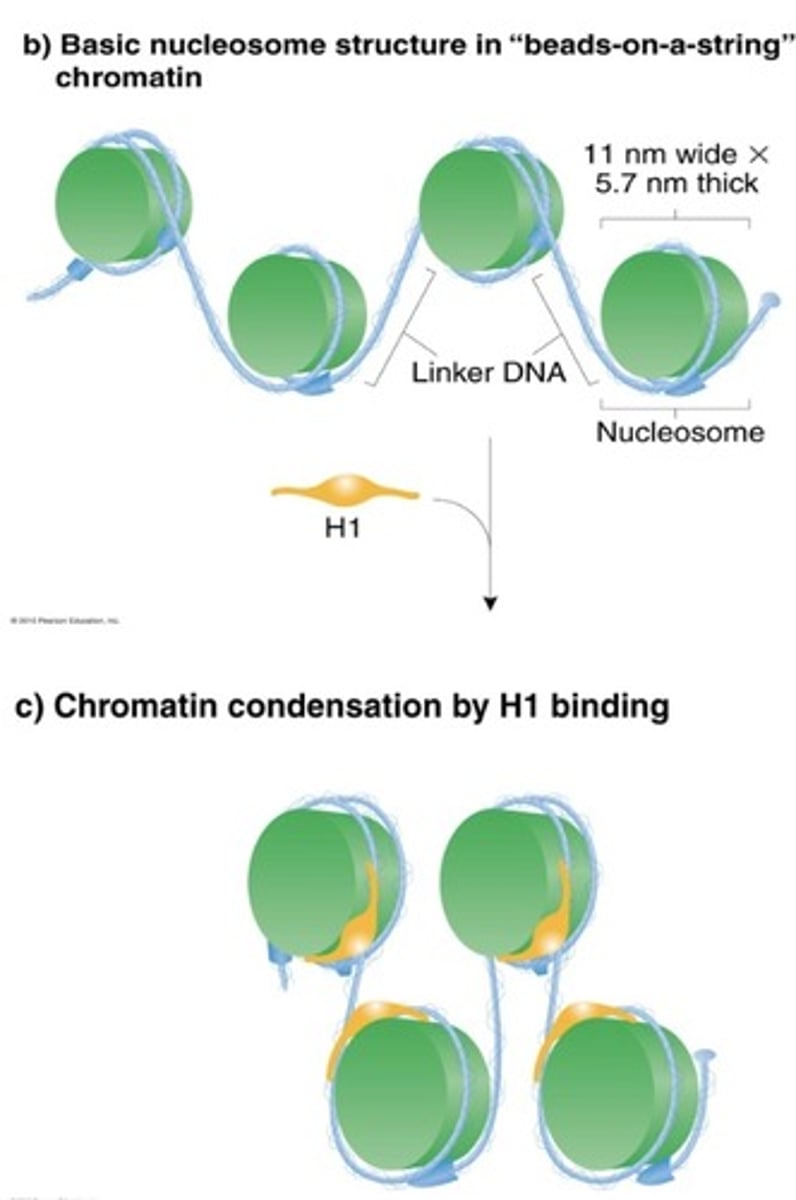
10 nm nucleofilaments
-11 nm wide and 5.7 nm thick
-H1 binds to one end and the middle of DNA segment is wrapped around nucleosomes closer together
-condenses DNA 7x
chromatin remodeling
-RNA polymerase cant access DNA when it is at the 30 nm level or higher
-this allows the DNA at particular genes to be unpacked so it can be transcribed
-remodeling uncoils it to 10 nm level
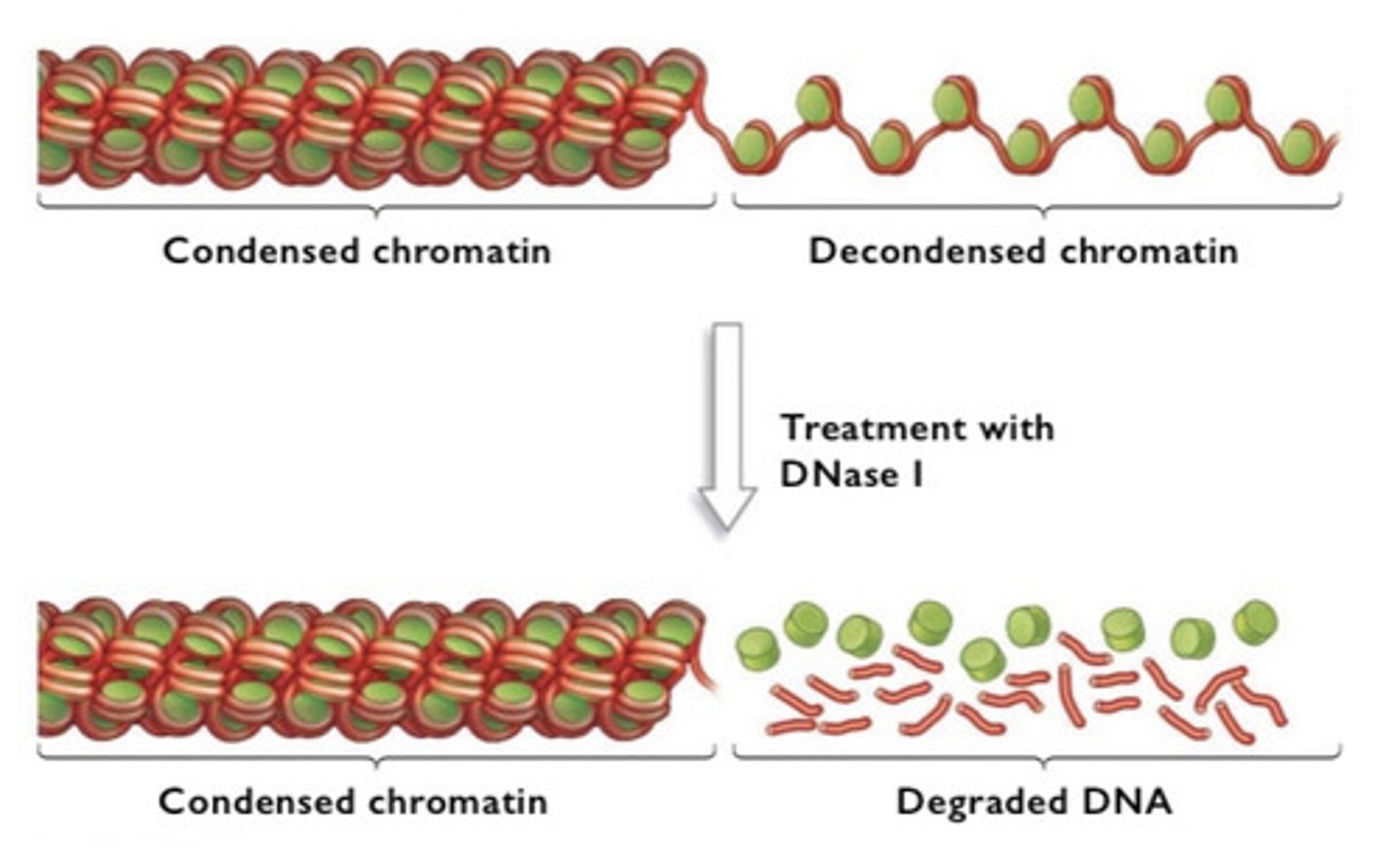
Weintraub and Groudine
-discovered remodeling using DNase to can cut decondensed DNA but not condensed DNA
-it cuts genes that are actively being transcribed, DNase degraded chromatin above 30 nm
DNA methylation
causes chromatin to condense and can block transcription of specific genes
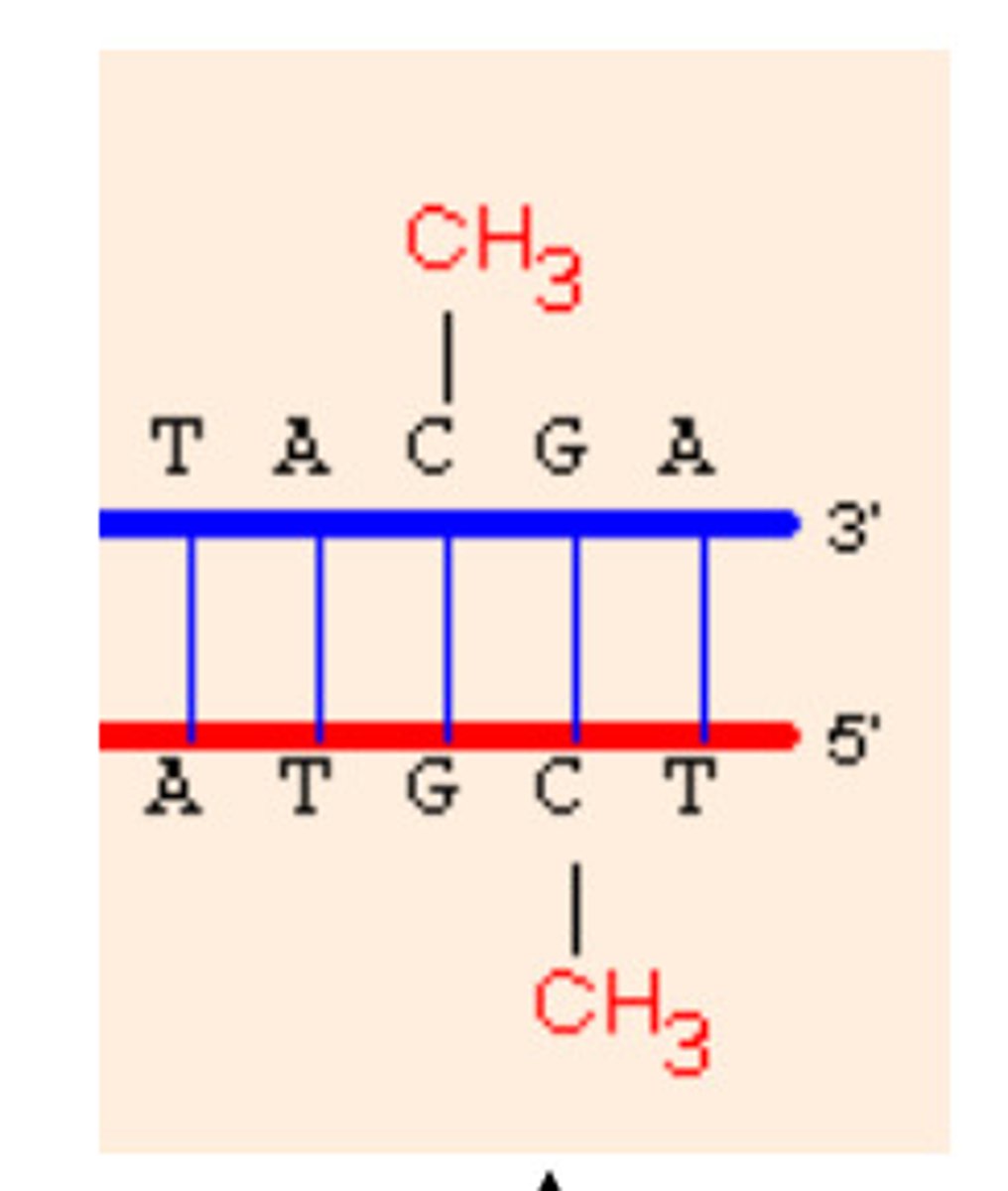
DNA methyl transferase
adds methyl groups (-CH3) to cytosines of DNA
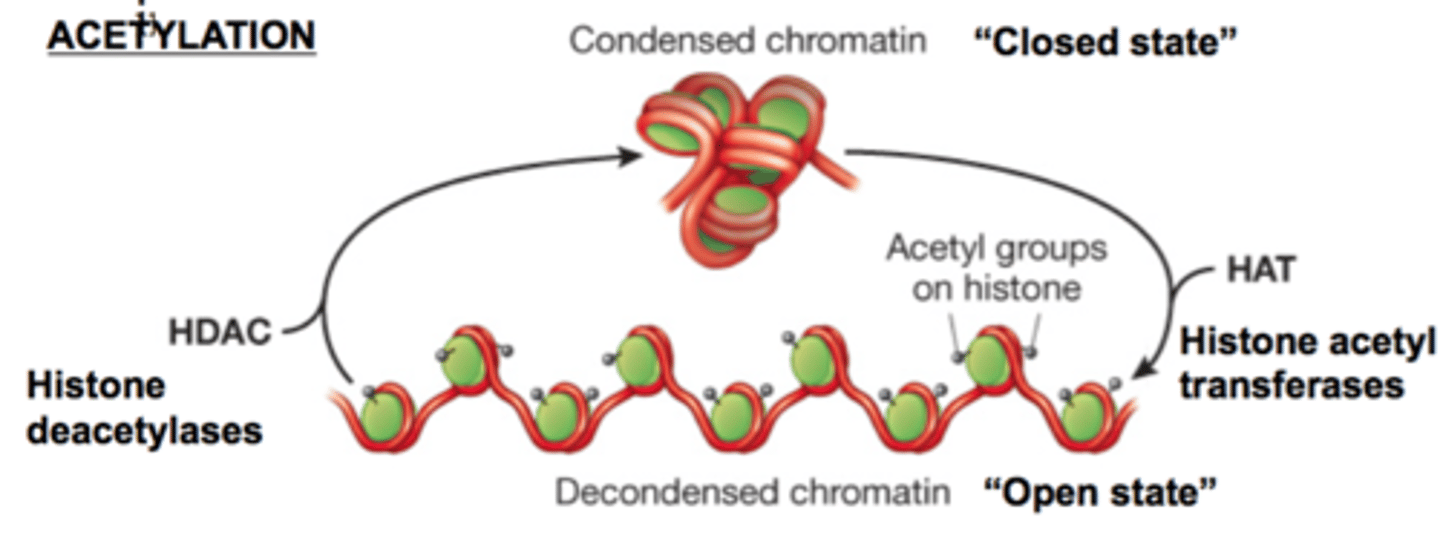
histone acetyltransferase
acetate groups added to histones make chromatin decondensed so chromatin can be transcribed
epigenetics
-the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
-these regulations are passed on through inheritance
-can record life events and affect phenotype of the child