Oncology 6 (canine hemangiosarcoma)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
what is hemangiosarcoma?
malignant tumor arising from endothelial cells (blood vessels)
what is the biologic behavior of hemangiosarcoma?
depends on primary location
what is the metastatic rate of hemangiosarcoma?
visceral forms have high metastatic rates
how does hemangiosarcoma metastasize?
via hematogenous spread or direct intracavitary seeding
what are the common sites of hemangiosarcoma metastasis?
lungs (65%)
liver (50%)
omentum
peritoneum
most common tumor to metastasize to brain in dogs
what is the common signalment of dogs that get hemangiosarcoma?
-middle aged to older animals
-any breed (GSDs, goldens, labs, and other large breed dogs)
-maybe a slight male predilection
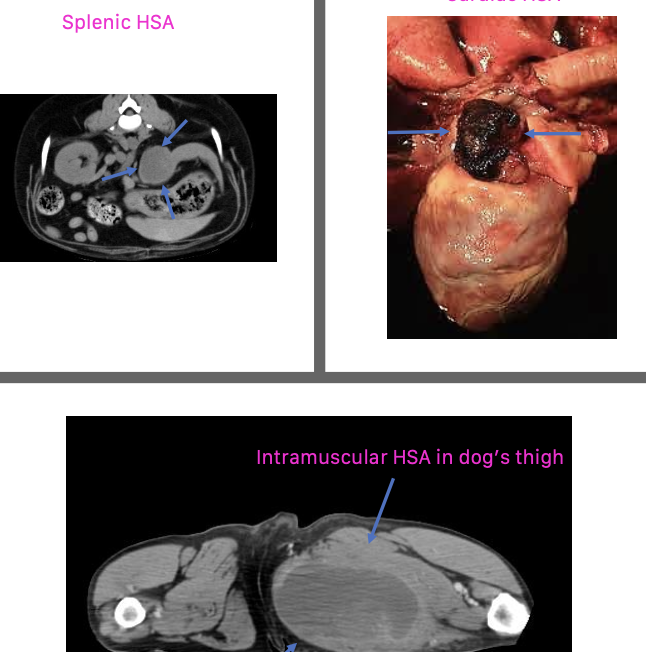
what are common locations of primary hemangiosarcoma?
can occur anywhere:
1. visceral
2. cardiac
3. dermal/SQ/intramuscular
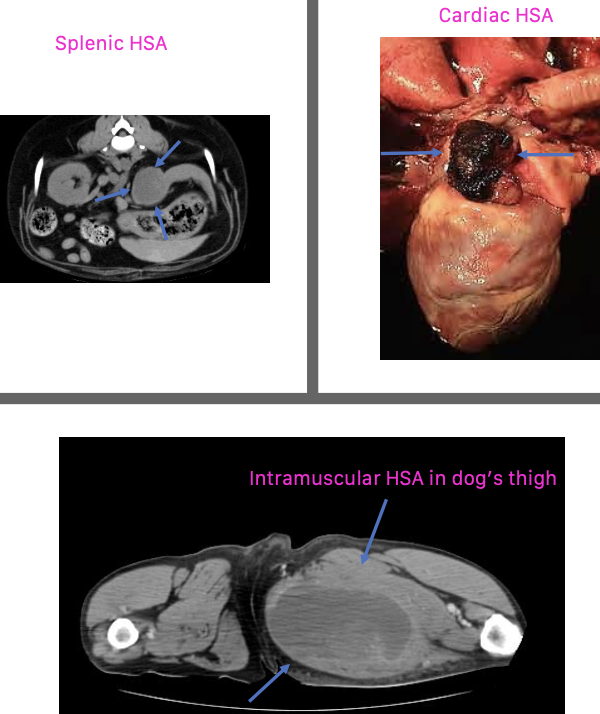
what are the common primary visceral sites of hemangiosarcoma?
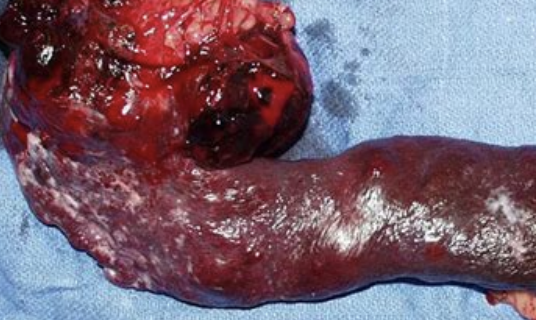
-spleen is the most common location
-liver
-other: kidney, retroperitoneal space, nasal cavity, oral cavity, bone
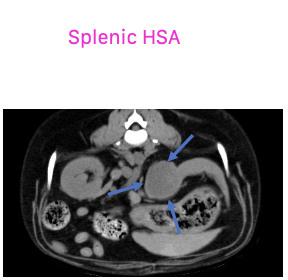
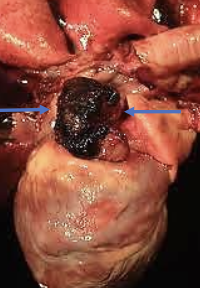
what are the common primary cardiac sites of hemangiosarcoma?
second most common primary site:
-right atrium
-right auricle
what do the presenting clinical signs of hemangiosarcoma depend on?
depends on the amount of blood loss and location of primary tumor
what are the acute presenting clinical signs of hemangiosarcoma?
-splenic rupture (hemoabdomen)
-collapse or sudden death
-cardiac tamponade
-abdominal distension (fluid wave)
-hypovolemic shock signs (pale mm, prolonged CRT, dyspnea)
-DIC
what are the chronic presenting clinical signs of hemangiosarcoma?
-anorexia
-lethargy
-exercise intolerance
-non-specific signs
-signs can be transient and resolve as blood is reabsorbed and new RBCs are formed

what does the patient work-up with suspected hemangiosarcoma consist of?
1. blood panels (CBC/chem)
2. blood pressure and ECG
3. stabilize patient (hypovolemic shock-fluids; +/- blood transfusions)* DO FIRST
4. imaging
5. +/- sampling

what clinical lab work findings are seen with hemangiosarcoma?
-anemia is common
-imbalances in coagulation parameters (50%)
-neutrophilia
-thrombocytopenia (75-97%)
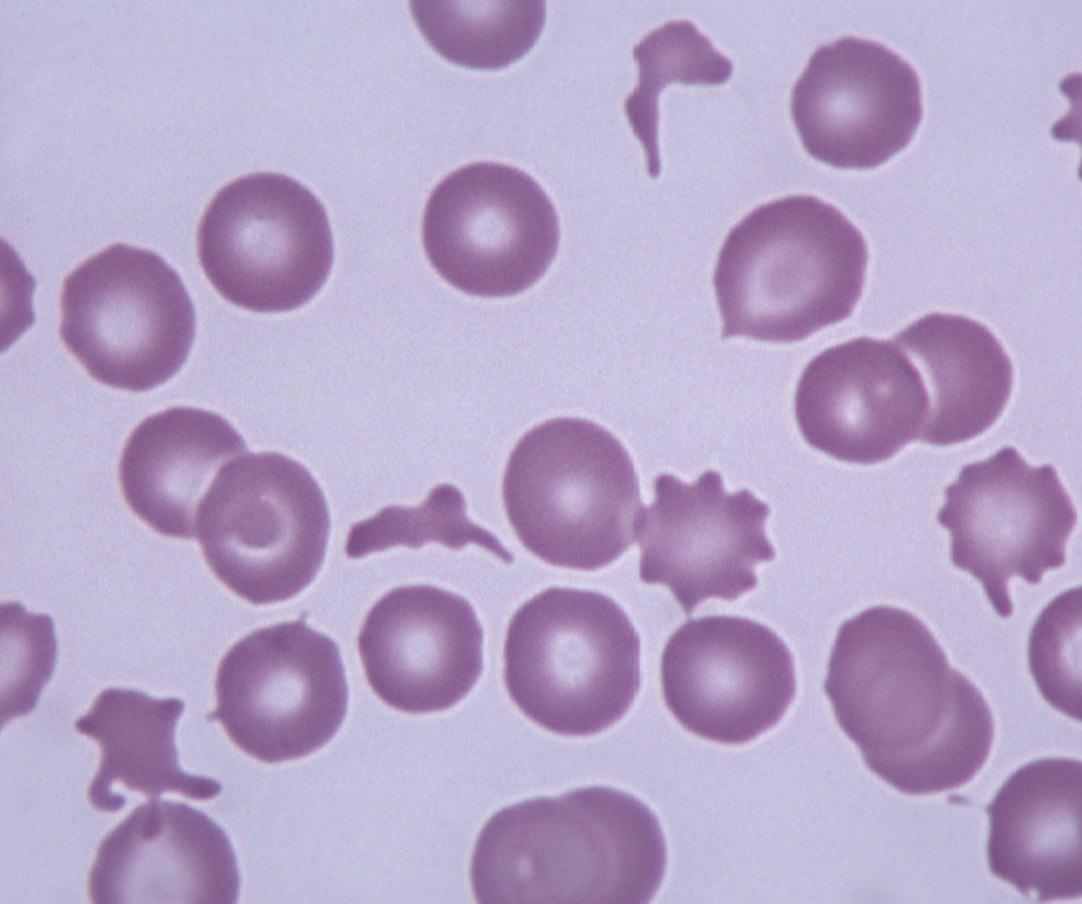
what RBC morphology changes are seen with hemangiosarcoma?
polychromasia
schistocytes
acanthocytes
microangiopathic related damaged
what chemistry panel abnormalities are seen with hemangiosarcoma?
nonspecific:
-hypoalbuminemia
-liver enzyme elevations
-azotemia
what other diagnostic abnormalities are seen with hemangiosarcoma?
blood pressure abnormalities
ECG abnormalities (arrhythmias)
what diagnostic imaging modalities are used to diagnose hemangiosarcoma?
-thoracic imaging (radiographs or CT)
-abdominal imaging (radiographs, ultrasound, or CT)
-echocardiogram
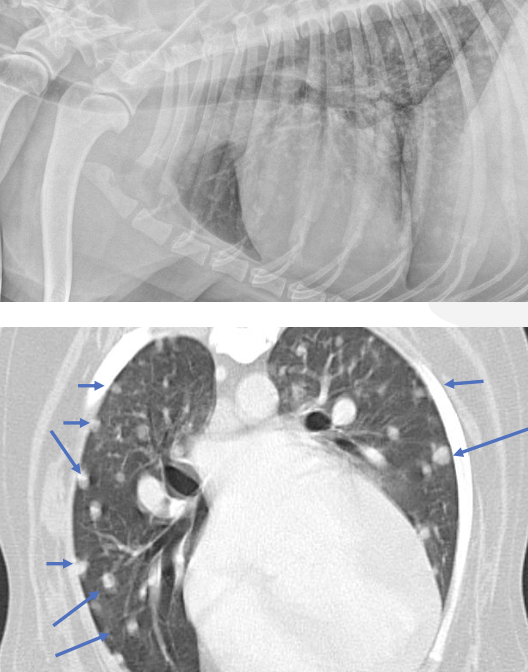
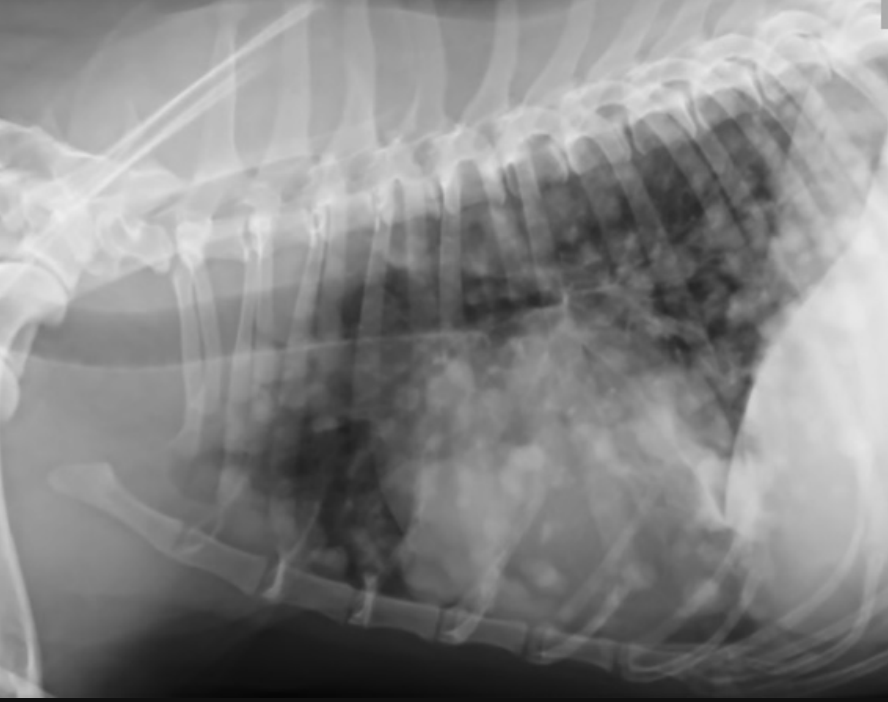
what is the purpose of thoracic imaging when diagnosing hemangiosarcoma?
search for mets:
-described as nodular to interstitial coalescing miliary pattern (ill-defined, fuzzy appearance)
radiographs: 78% sensitivity for detecting mets (false negative rate decreases w/ 3 views)
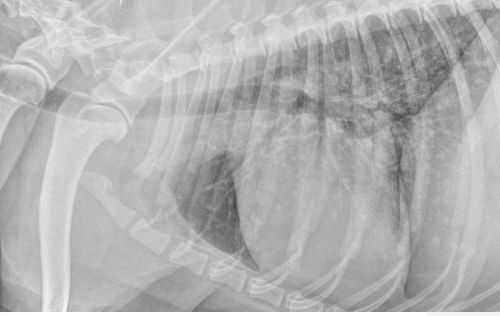
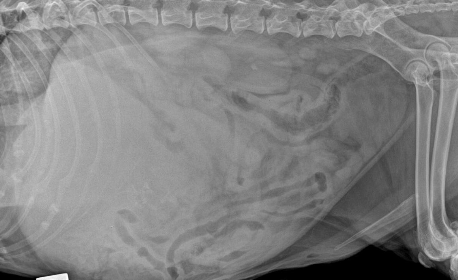
what will be seen on abdominal radiographs in patients with hemangiosarcoma?
nonspecific: mass
loss of serosal detail
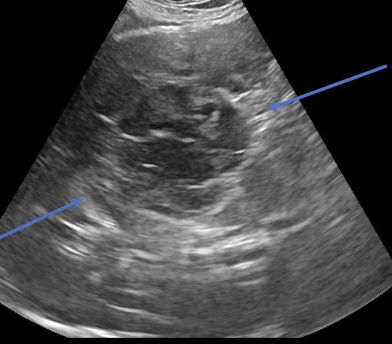
what is the appearance of hemangiosarcoma lesions in the abdomen using abdominal ultrasound?
-heterogenous (hypoechoic to targetoid to mixed)
-cavitation
- +/- peritoneal effusion
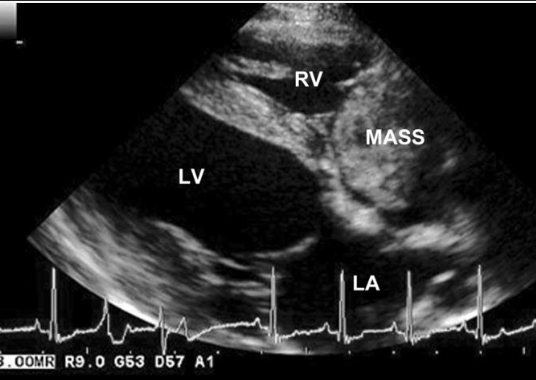
how can echocardiogram be used to diagnose hemangiosarcoma?
-to identify mass in right atrium or appendage
-pericardial effusion improves detection of mass (SP=100%, SN=82%)
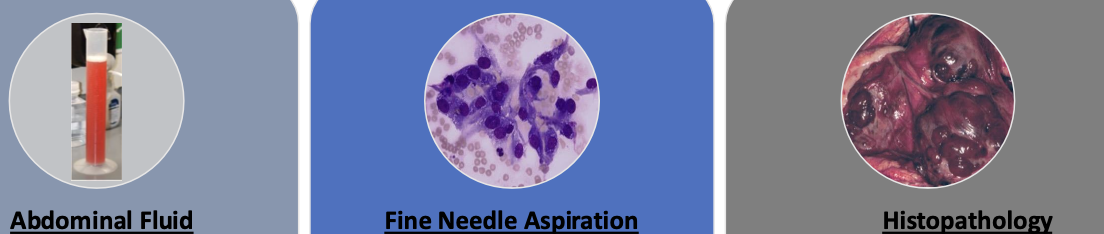
what sampling methods are used to diagnose hemangiosarcoma?
1. abdominal fluid
2. fine needle aspiration
3. histopathology
how can sampling abdominal fluid help diagnose hemangiosarcoma?
-if sample contains frank blood or is serosanguineous
-does not clot
-neoplastic effusion (lower glucose + higher lactate than non-neoplastic)
-often no evidence of malignant cells in effusion

is FNA sampling beneficial in diagnosing hemangiosarcoma?
not really, has low diagnostic yield
-can also hemodilute sample
-may also increase bleeding risk
is histopathology beneficial in diagnosing hemangiosarcoma?
yes, it is often required for definitive diagnosis
difficult to do with widespread necrosis and hemorrhage (will need multiple sections/cuts)
how are hemangiosarcomas clinically staged?
stage 1
stage 2
stage 3
substages defined by primary tumor (T0, regional LNs (N), and distant metastasis (M)
how are the substages for the primary tumor (T) classifed?
-T0: no evidence of tumor
-T1: <5cm in diameter and confined to primary tumor
-T2: greater or equal to 5cm or ruptured, invading SQ tissue
-T3: invading adjacent structures including muscle
how are the substages for regional lymph nodes (N) classifed?
-N0: no regional LN involvement
-N1: regional LN involvement
-N2: distant LN involvement
how are the substages for distant metastasis (M) classifed?
M0: no distant metastasis
M1: distant metastasis
what are the substages of stage 1 hemangiosarcoma?
T0 or T1
N0
M0
what are the substages of stage 2 hemangiosarcoma?
T1 or T2
N0 or N1
M0
what are the substages of stage 3 hemangiosarcoma?
T2 or T3
N0, N1, or N2
M1
what is the general treatment overview for hemangiosarcoma?
1. stabilize patient
2. surgery
3. chemotherapy
4. alternative therapy
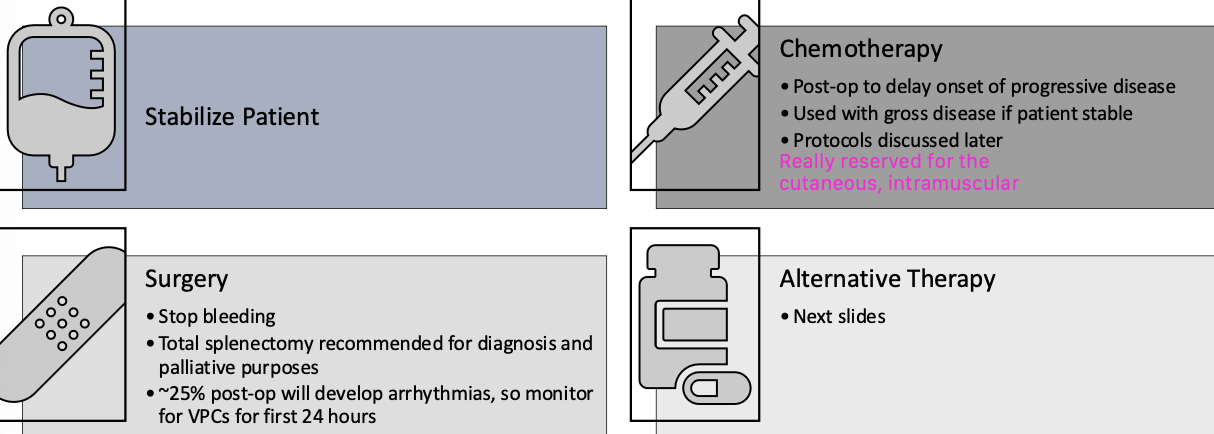
how is surgery used to treat hemangiosarcoma?
-stop bleeding
-total splenectomy recommended for diagnosis and palliative care
what is the importance of monitoring patients post surgery for hemangiosarcoma?
25% of post-op patients will develop arrhythmias, so monitor for VPCs for first 24 hours
what is the goal of chemotherapy for treating hemangiosarcoma?
-post-op: to delay onset of progressive disease
-used with gross disease if patient is stable
what alternative therapies may be used for treatment of hemangiosarcoma?
-yunnan baiyao
-coriolus versicolor
-beta adrenergic receptor inhibition
-immunotherapy
what is yunnan baiyao? how can it be beneficial for hemangiosarcoma?
chinese herbal medicine
in canines, used to control bleeding in non-malignant and malignant conditions
what is coriolus versicolor? how can it be beneficial for hemangiosarcoma?
turkey tail mushroom, contains the bioactive agent polysaccharopeptide (PSP)
small study in dogs with splenic hemangio, showed modest improvement in MST
follow up study showed PSP alone had no benefit (so not really beneficial)
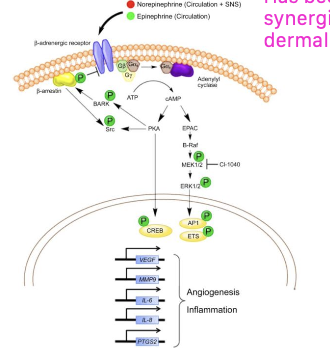
how can beta-adrenergic receptor inhibition be used for treatment of hemangiosarcoma?
beta-blockade is selective for vascular tumor cells and synergistically effective when combined with chemo
what immunotherapies have been used to treat hemangiosarcoma in dogs?
-novel tumor vaccines (vx prepared with lysates of allogenic canine HSA cells mixed with adjuvant composed liposome-DNA complexes)
-autologous vaccine Torigen
how common are splenic hemangiosarcomas in dogs?
make up 45-51% of canine splenic malignancies
8.7% chance of concurrent right atrial masses
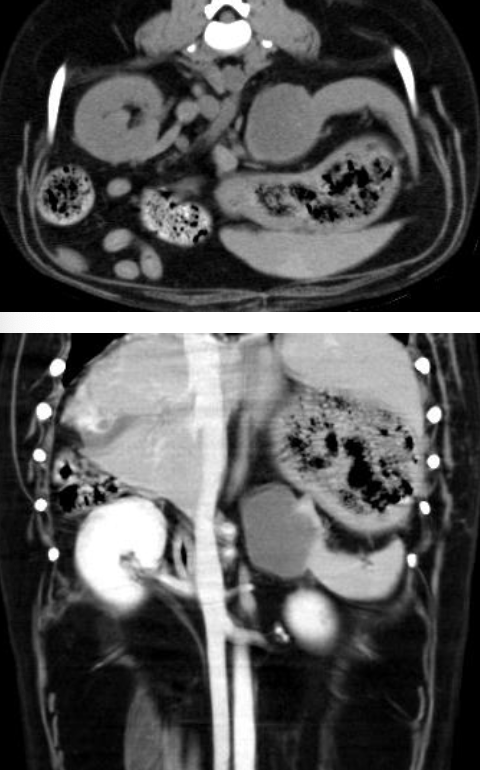
what is the double 2/3s rule for splenic hemangiosarcoma?
2/3 of splenic masses are malignant
2/3 of those are hemangiosarcoma
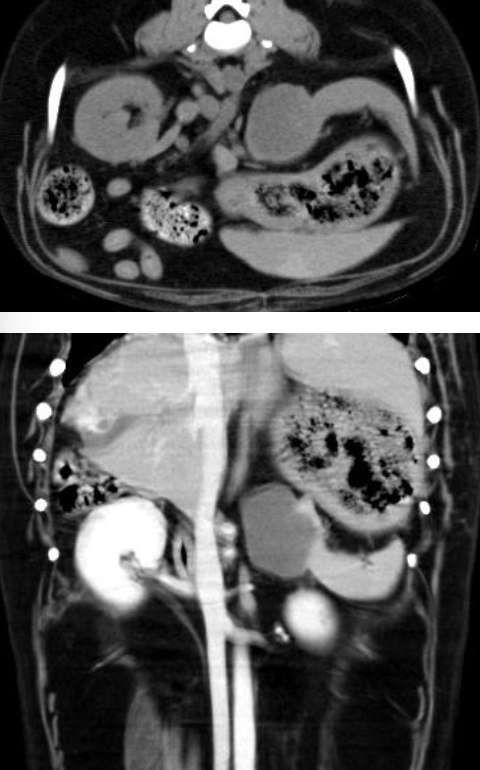
can imaging alone determine if a splenic mass is benign or malignant?
no, not all splenic masses are obvious if malignant or benign with imaging alone
-->hemoabdomen can be seen with both
what criteria can be used to help increase confidence that a pet has hemangiosarcoma pre-op?
1. lesion size
2. breed
3. incidentally found
are incidentally found splenic masses more likely malignant or benign?
non-ruptured masses or nodules found with diagnostic imaging are more commonly benign
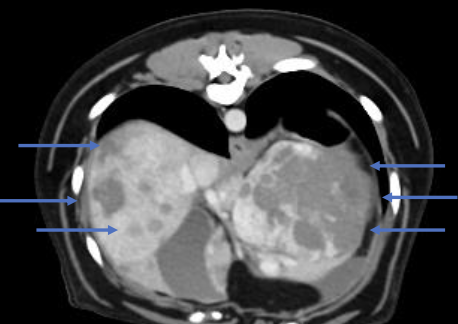
how can lesion size on imaging predict if a splenic mass is benign or malignant?
large lesions are more likely to be benign
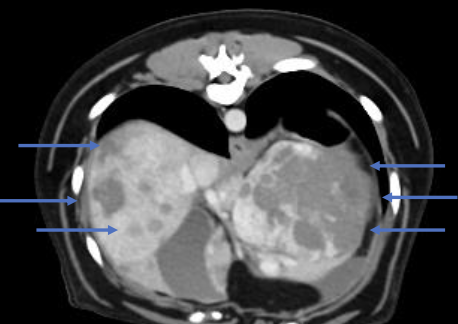
how can dog breed/size predict if a splenic lesion found on imaging is benign or malignant?
dogs <27kgs are less likely to have hemangiosarcoma compared to other malignant splenic tumors
what are the clinical signs/PE findings of visceral hemangiosarcoma?
-acute lethargy
-weakness
-collapse secondary to blood loss
non-specific signs: weight loss, hyporexia, abd. distension, vomiting, dyspnea, exercise intolerance
what is the treatment for visceral hemangiosarcoma?
1. splenectomy or complete surgical removal (primary tx for localized, nonmetastatic hemangiosarcoma)
2. perform thorough ab-explore for other suspicious lesions (remove if possible)
3. follow up with chemotherapy
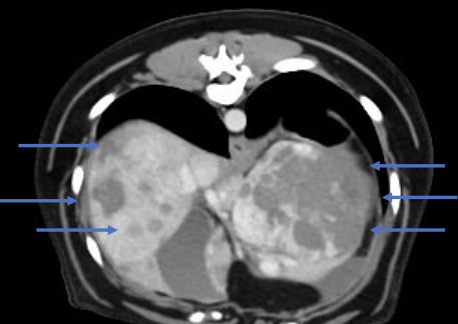
what chemotherapy is used post-op for hemangiosarcoma?
doxorubicin- or carboplatin-based chemotherapy, or metronomic chemotherapy
what chemotherapy drugs are used for treatment of hemangiosarcoma?
doxorubicin
metronomic chemotherapy
carboplatin
what is the MST of treating hemangiosarcoma with doxorubicin?
MST= 172 days (5.7 months)
stage 1: 196 days (6.5 months)
stage 2: 117 days (3.9 months)
stage 3: 23-60 days (0.8-2 months)
what is the overall response rate (ORR) of hemangiosarcoma with doxorubicin?
38% with bulky disease
what is the MST of treating hemangiosarcoma with metronomic chemotherapy?
MST= 178 days (5.9 months)
use following doxorubicin or in addition to doxorubicin did not improve survival in most studies
what is the MST of treating hemangiosarcoma with carboplatin?
MST= 160 days (5.3 months)
what is the median survival time (MST) of hemangiosarcoma treated with splenectomy alone?
MST= 19-86 days (0-3 months)
what is the median survival time (MST) of hemangiosarcoma treated with splenectomy and doxorubicin?
stage 1: 239-355 days (7-12 months)
stage 2: 120-148 days (4-5 months)
stage 3: 140 days (5 months)
what is the median survival time (MST) of hemangiosarcoma treated with splenectomy and metronomic therapy?
MST= 178-225 days (5-7 months)
what is the median survival time (MST) of hemangiosarcoma treated with splenectomy and carboplatin?
MST= 160 days (5 months)
how common are cardiac tumors in dogs?
infrequent in dogs, overall incidence of 0.19%
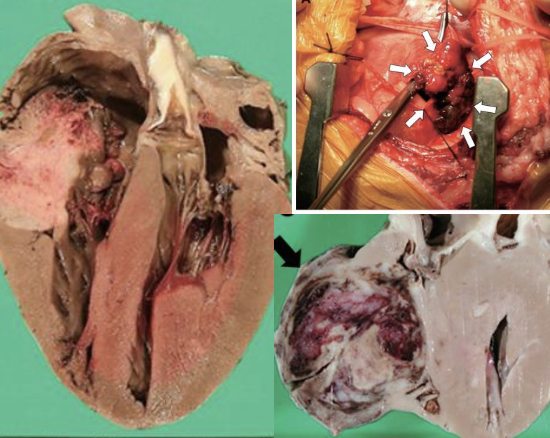
what are the most common cardiac tumor types in dogs?
hemangiosarcoma (69%)
10x higher than second most common tumor
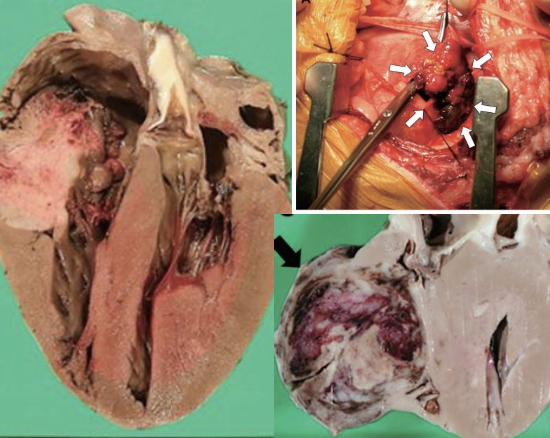
which breeds have a higher incidence of cardiac hemangiosarcomas?
GSDs and goldens
what are the locations of cardiac hemangiosarcomas?
right atrium or auricle most common
can also occur in the left-sided chambers
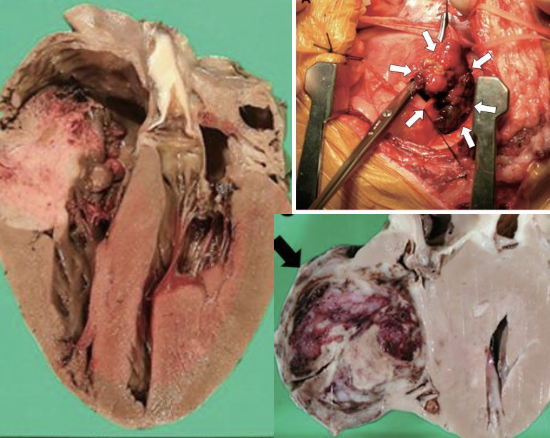
what are the clinical signs/PE findings of cardiac hemangiosarcoma?
-cardiac tamponade (most common clinical presentation)
-muffled heart sounds
-pulsus paradoxus
-ascites
-collapse
what is the treatment for cardiac hemangiosarcoma?
1. pericardiocentesis (for immediate resolution of tamponade)
2. pericardectomy
3. right atrial appendafe resection (often not feasible)
4. chemotherapy
5. radiation
what is the MST of treating cardiac hemangiosarcoma surgically with pericardectomy?
palliative MST= 2.7-4 months
what is the MST of treating cardiac hemangiosarcoma with resection of the right atrial appendage?
sx alone MST= 1-3 months
surgery + chemo MST= 175 days (5.8 months)
what is the MST of treating cardiac hemangiosarcoma with doxorubicin?
MST= 139.5 days (4.5 months)
what is the MST of treating cardiac hemangiosarcoma with radiation therapy?
MST=79 days (2.6 months)
is cutaneous hemangioma or cutaneous hemangiosarcoma more common?
cutaneous hemangioma more common than hemangiosarcoma
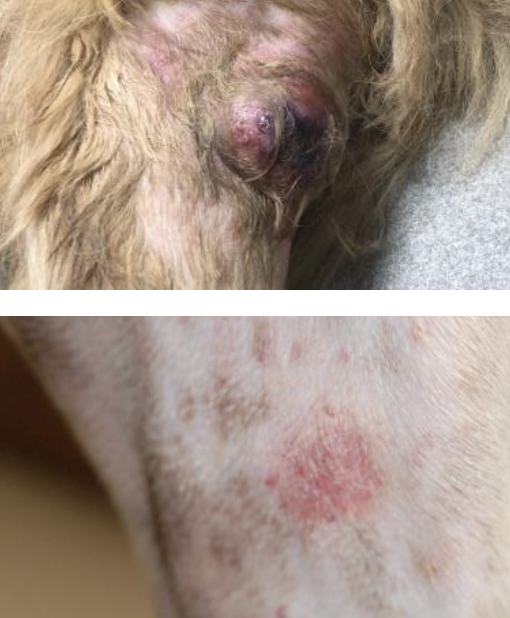
what is the common signalment of dogs with cutaneous hemangiosarcoma?
common in lightly pigmented breeds that like to sunbathe (UV is a physical factor associated with HSA)
breeds: beagles, white bulldogs, white boxers, whippets, pitbulls
what are the clinical signs and PE findings of cutaneous hemangiosarcoma?
small, discrete, blood-blister-like lesions to much larger deeply seated, painful, bruised and/or bleeding masses
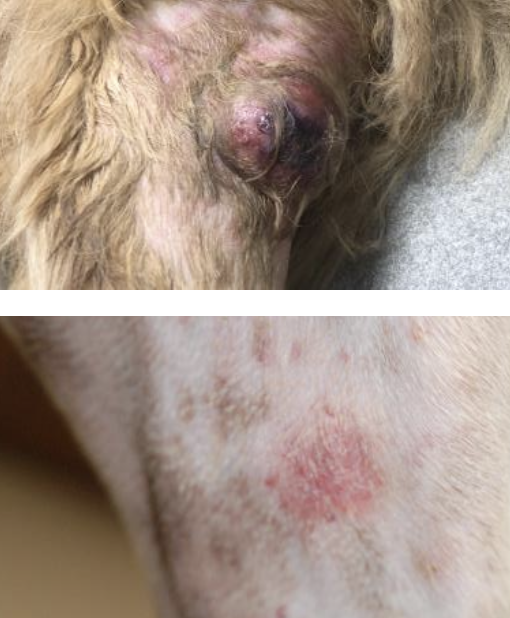
what should be done prior to resection of cutaneous hemangiosarcoma?
full staging of mass
what is survival of dermal hemangiosarcoma based on?
based on location within the dermis
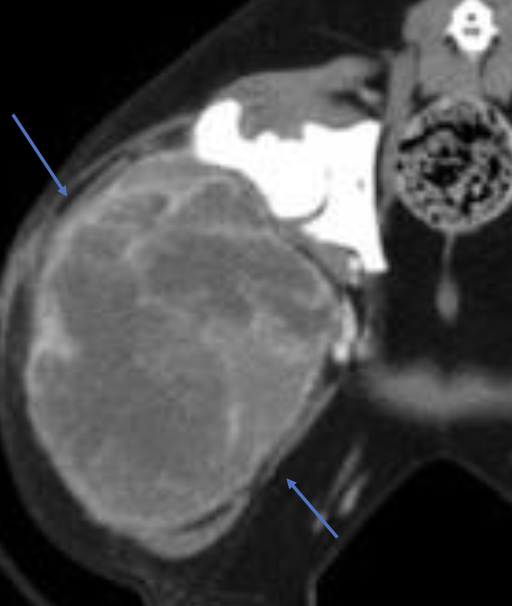
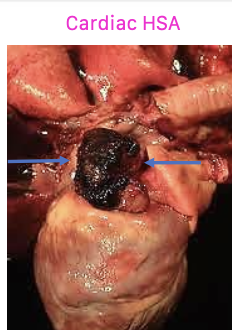
what are the stages of dermal hemangiosarcoma?
stage 1: strictly dermal
stage 2: hypodermal/SQ
stage 3: intramuscular
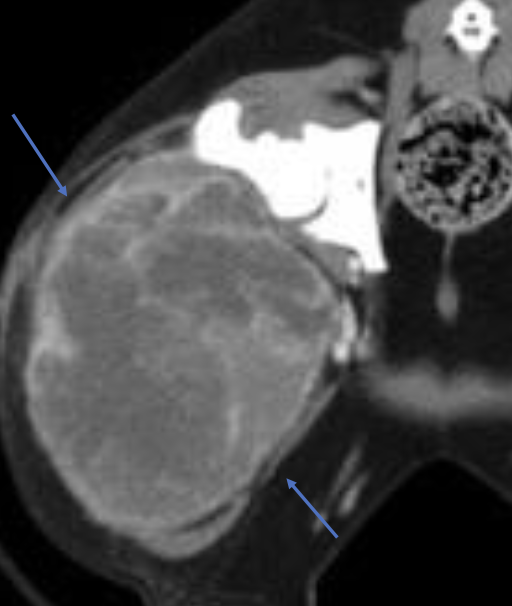
what is the treatment for stage 1 cutaneous hemangiosarcoma?
treat with wide surgical resection (surgical considerations similar to other malignant skin tumors)
what is the MST of stage 1 cutaneous HSA treated with surgical resection?
MST= 780-1570 days, 26-52 months (average= 987 days, 33 months)
what is the treatment for stage 2-3 cutaneous hemangiosarcoma?
stages 2-3 often behave more like visceral forms, so recommend surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy
what is the MST of stage 2 cutaneous hemangiosarcoma with chemo/surgery?
chemo alone: response duration is 53 days (1.7 months)
surgery alone: 172 days (5.7 months)
surgery + chemo: 242-1189 days (8-39 months)
what is the MST of stage 3 cutaneous hemangiosarcoma with chemo/surgery?
chemo alone: response duration is 53 days (1.7 months)
surgery + chemo: 272.5 days (9 months)