2a- Biological molecules: Carbohydrates and Water
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
What is water?
a major component of cells
1 oxygen atom, 1 hydrogen atom
What bond is formed between water molecules?
hydrogen bond
Explain how bonds form in water
Water is a polar molecule (unequal distribution of charge)
The slightly negatively charge O2- atoms attract slightly positively charged H+ atoms of other H2O molecules.
The hydrogen bonds formed are relatively weak but strong in large numbers
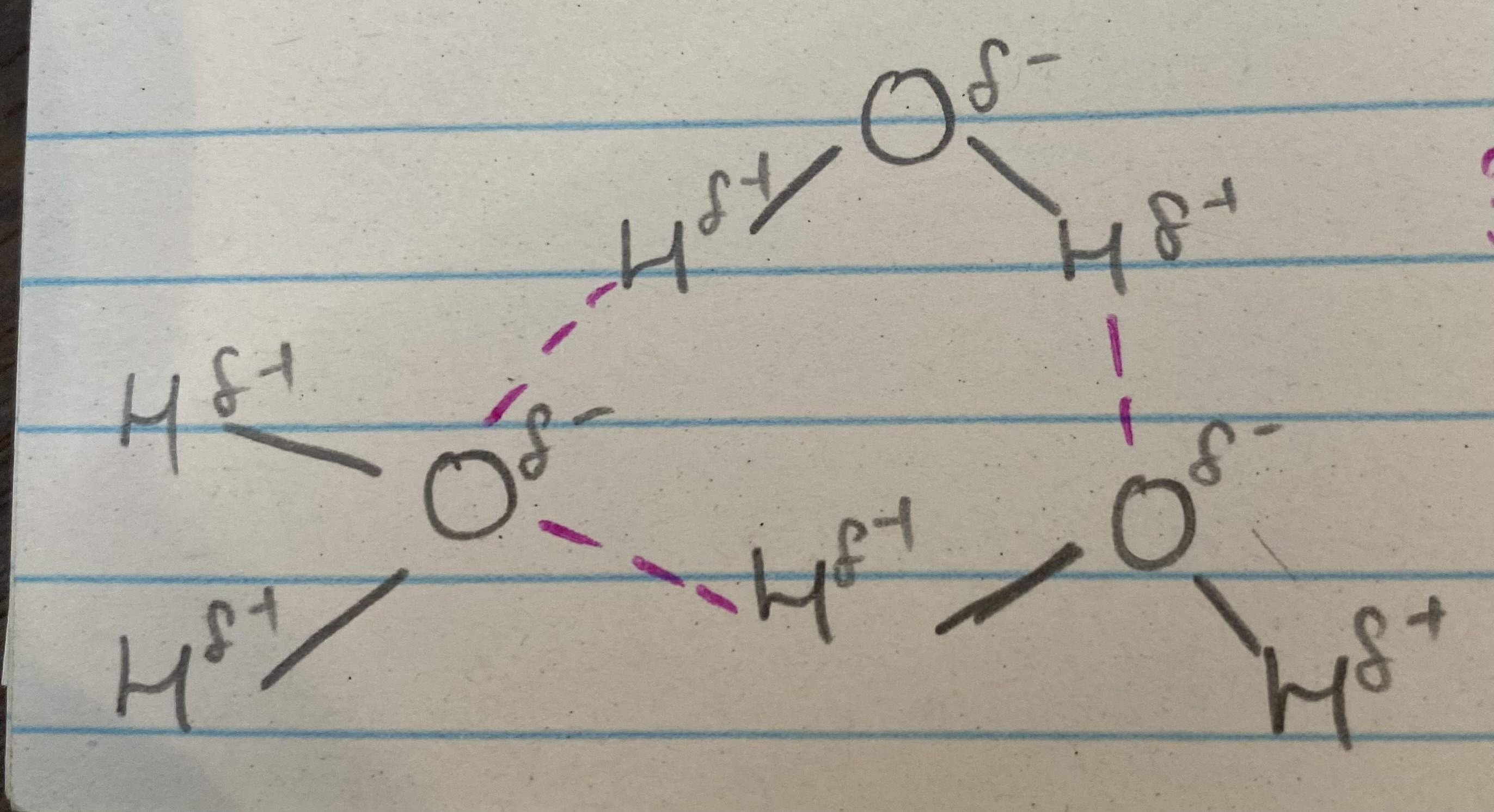
What does this image show?
3 water molecules bonding to each other
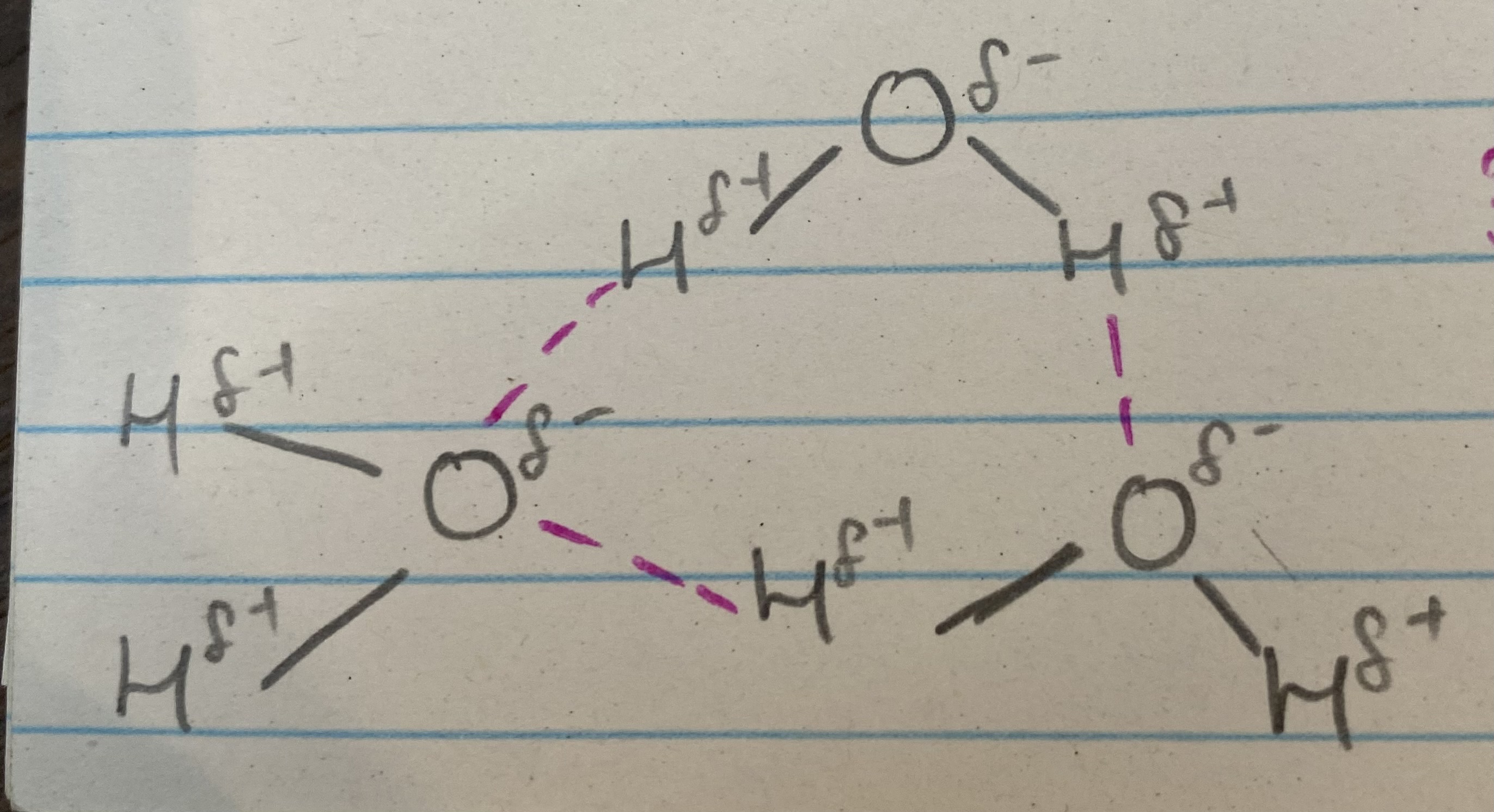
What do the pink and grey lines represent?
pink= hydrogen bond
grey= covalent bond
What are the 5 properties of water?
High specific heat capacity
Large latent heat of vaporization
Strong cohesion and surface tension
Solvent
Metabolite
What is the importance of water having a high specific heat capacity?
allows water to act as a buffer to sudden temp changes= can gain/ lose lots of heat without changing
What is the importance of water having a large latent heat of vaporization?
explains why sweating is an effective means of cooling= helps organisms maintain constant internal body temp
What is the importance of water having a strong cohesion and surface tension?
allows water to be pulled up xylem tissues in continuous columns in plants
What is the importance of water being a solvent?
allows metabolic reactions to occur faster in solution
allows transport of substances around an organism
What is the importance of water being a metabolite?
metabolite involves in many metabolic reaction. Used in hydrolysis and is formed in condensation. Used in photosynthesis
What is a monomer?
small repeating molecules from which polymers are made
What is a polymer?
a large chain of many similar monomers joined together
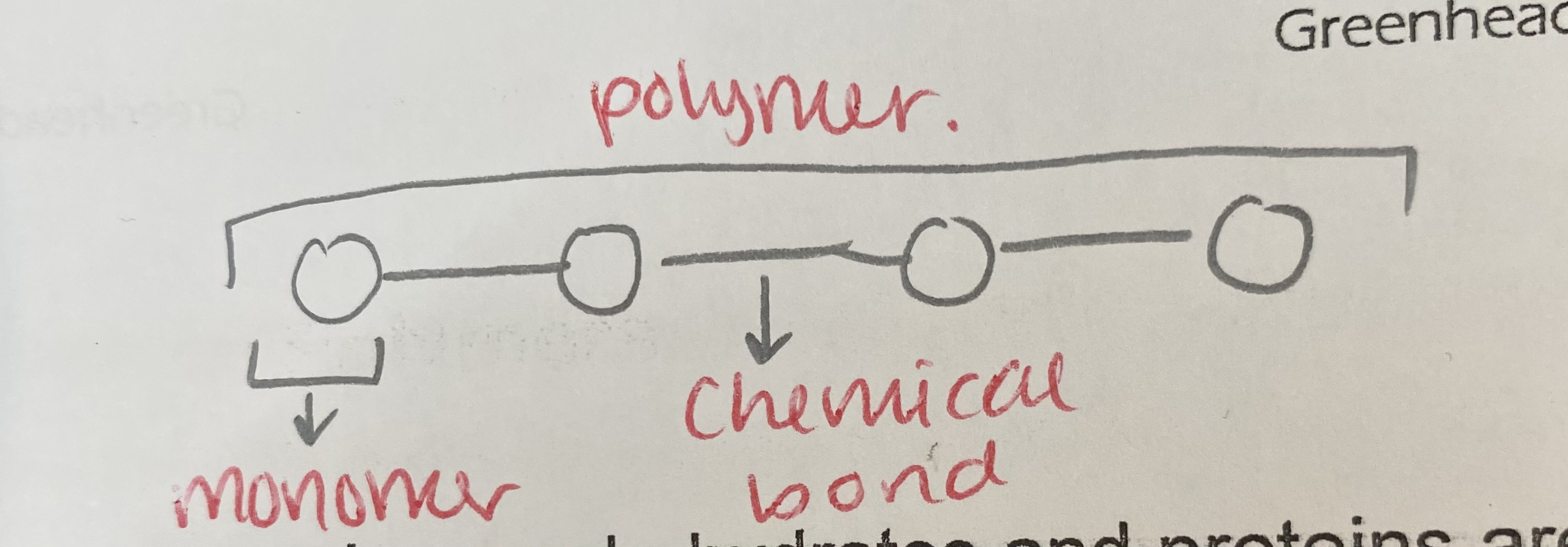
What reaction joins monomers?
condensation reactions to form polymers
What happens in condensation and hydrolysis reactions?
Condensation= 2 molecules join together forming a chemical bond, releasing water
Hydrolysis= 2 molecules separate, breaking a chemical bond using water
What is the reversible reaction for condensation and hydrolysis?

What elements are all carbohydrates composed of?
carbon
hydrogen
oxygen
What is a saccharide?
a simple sugar
What are monosaccharides?
basic molecules units/ monomers of which larger carbohydrates are made. Usually soluble and sweet
What are the 3 monosaccharides?
glucose
fructose
galactose
What is the chemical formula of glucose and pentose?
Glucose:
C6H12O6
Pentose:
C5H10O5
What is an isomer?
same molecular formula, differently arranged atoms
What are the 2 isomers of glucose?
a glucose
B glucose
What is the difference between the 2 isomers of glucose?
OH group is below carbon 1 in a glucose but above carbon 1 in B glucose
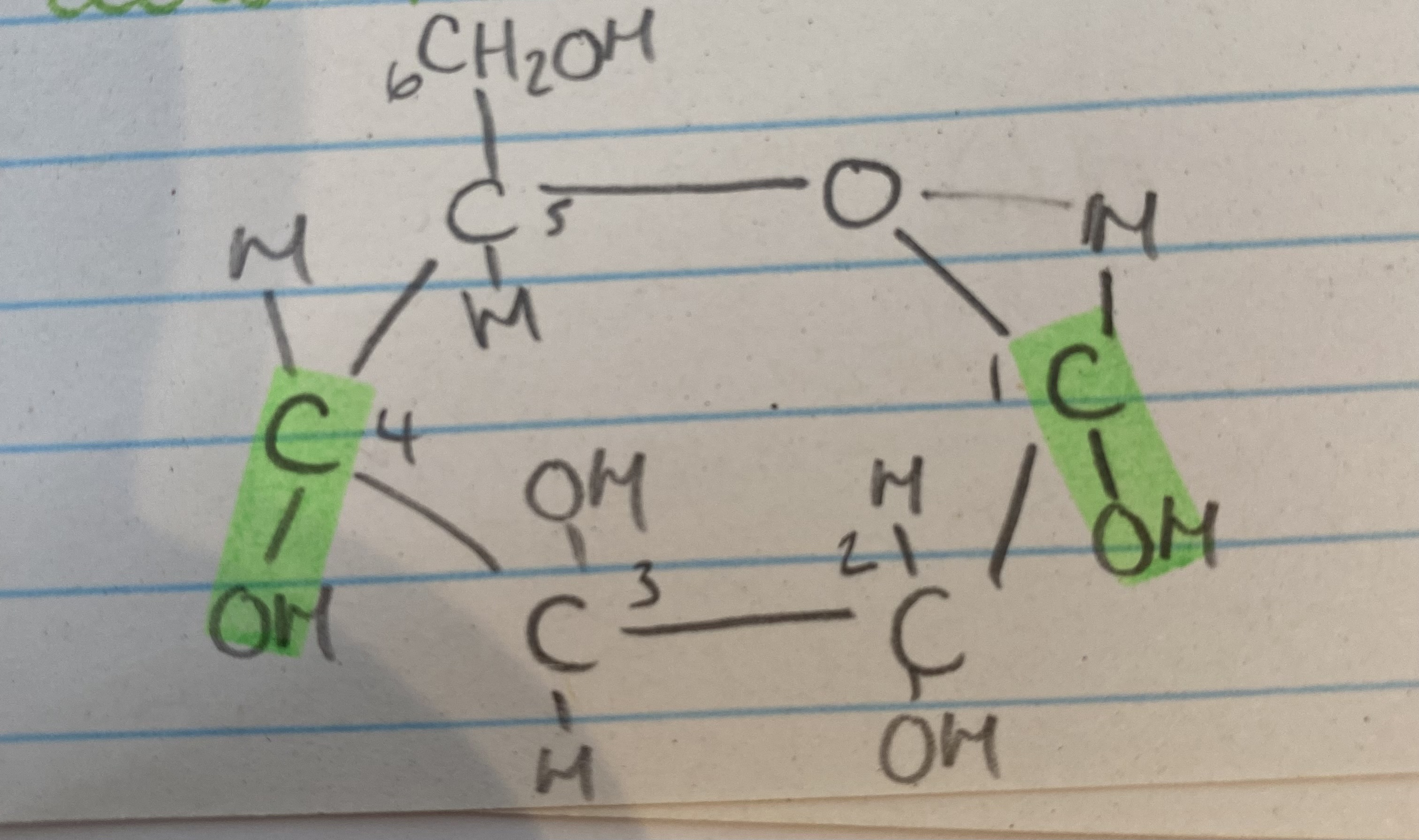
What isomer of glucose is this?
a glucose
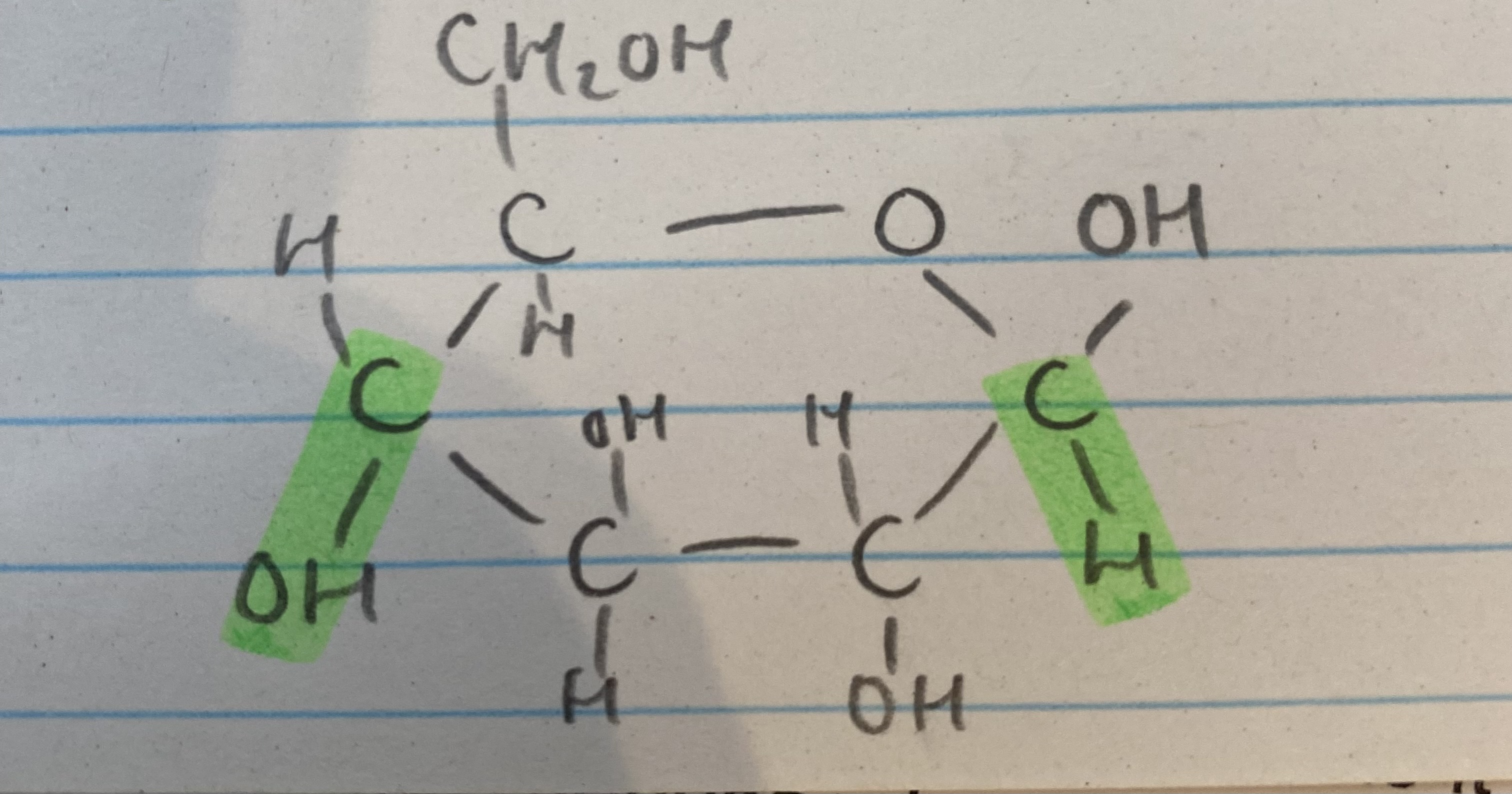
What isomer of glucose is this?
B glucose
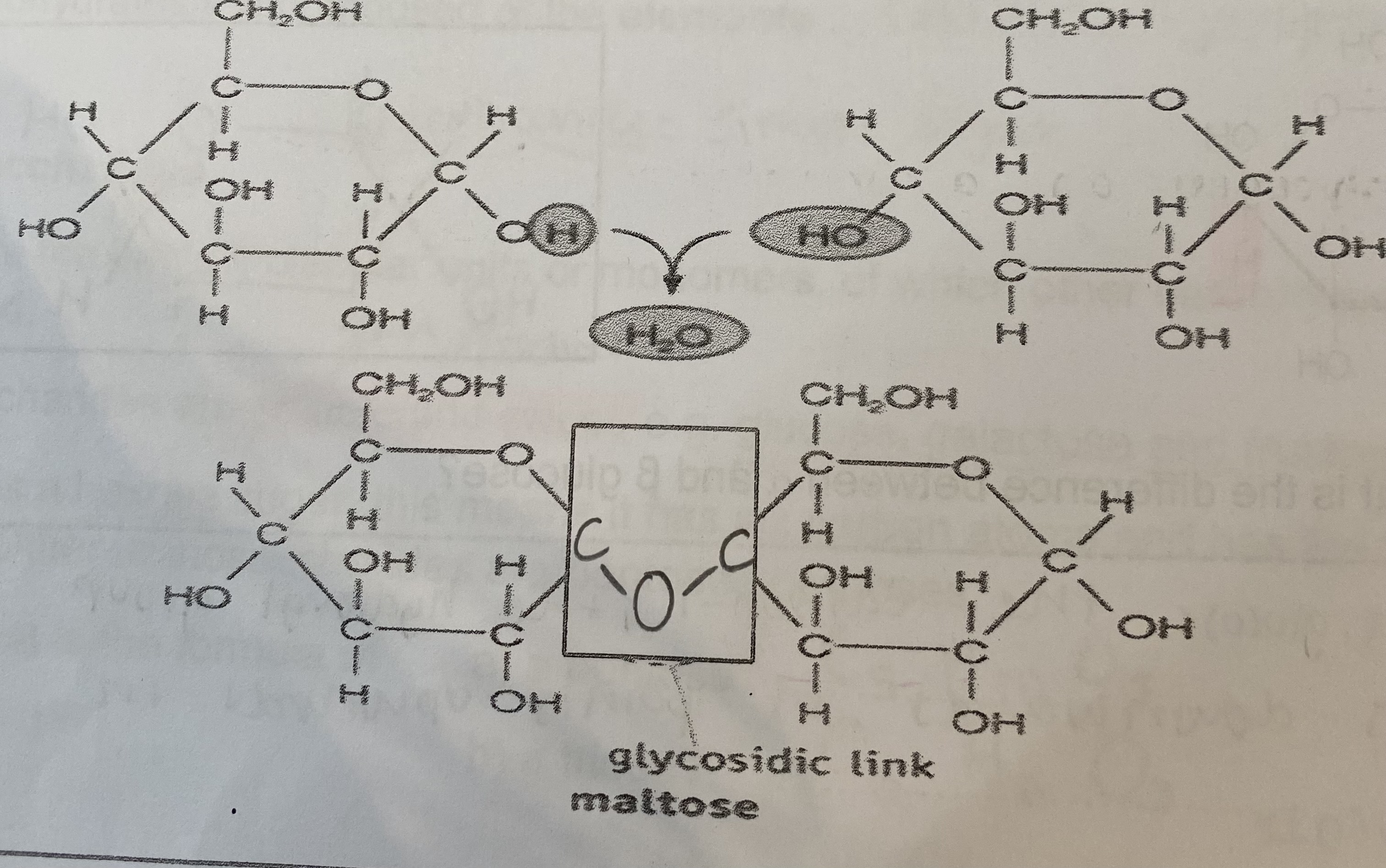
What are disaccharides and how are they formed?
2 monosaccharides joined together with a glycosidic bond formed by a condensation reaction, releasing water
What are the 3 common disaccharides?
maltose
sucrose
lactose
What monosaccharides is maltose made from?
glucose + glucose
What monosaccharides is sucrose made from?
glucose + fructose
What monosaccharides is lactose made from?
glucose + galactose
How is a glycosidic bond formed? (diagram)
What are polysaccharides and how are they formed?
many monosaccharides joined together with glycosidic bonds formed by many condensation reactions, releasing water
What are the 3 main polysaccharides?
starch
glycogen
cellulose
What is the function of starch?
energy storage (found in plants)
What is the function of glycogen?
energy storage in animals
What is the function of cellulose?
strength/ structural support to plant cell walls
What is starch?
polysaccharide of a glucose
What are the 2 polymers of starch?
Amylose:
1-4 glycosidic bonds, helical chain, unbranched
Amylopectin:
1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, branched
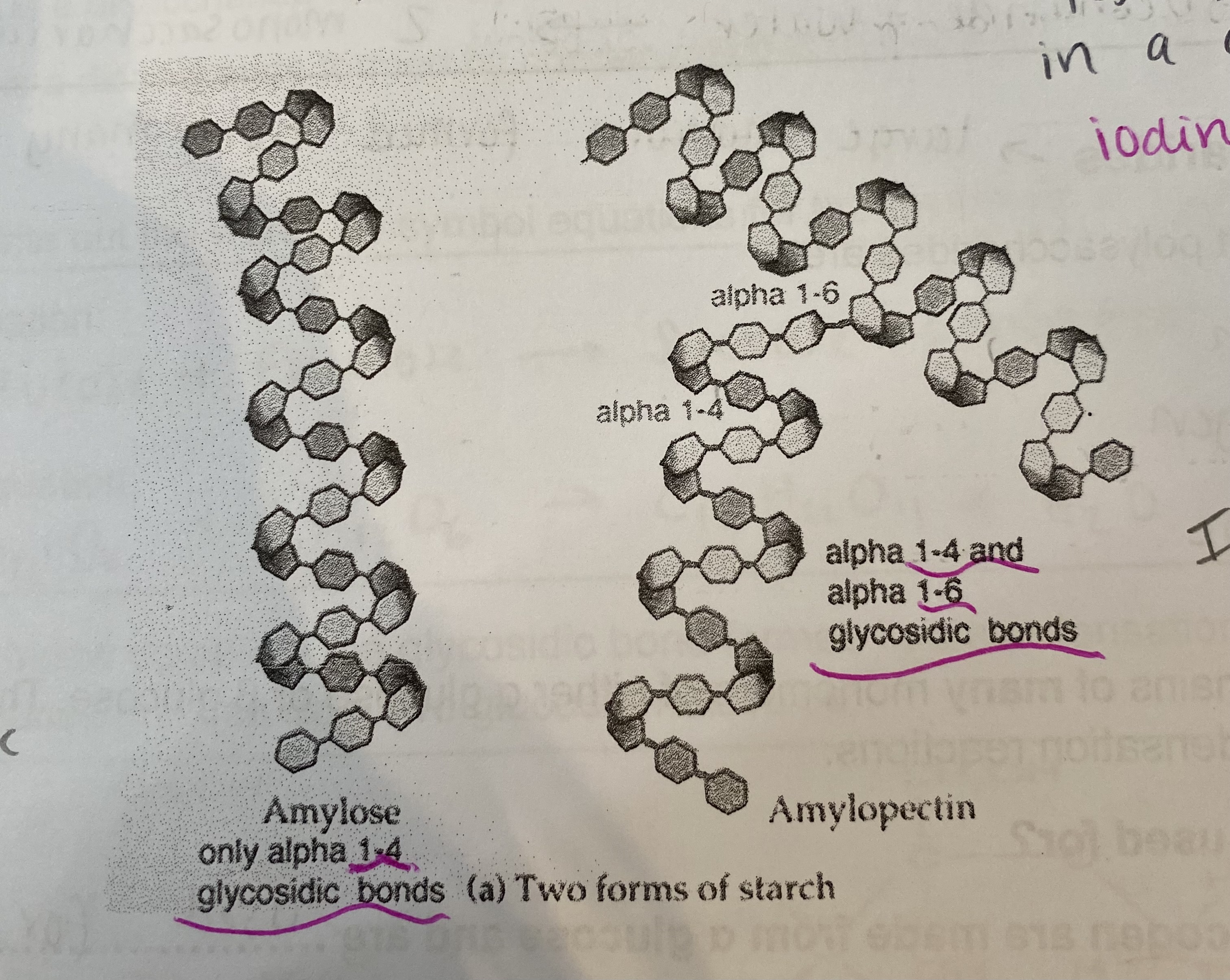
Explain how the structures of starch relate to its function
Helical= compact for storage in cell
Large and insoluble= can’t diffuse out of cell
Insoluble in water= water potential of cell not affected (no osmotic effect)
What is glycogen?
polysaccharided of a glucose.
1-4 and 1-6 glycosidic bonds, branched.
Where is glycogen found?
liver cells and muscle tissue in animals
Explain how the structures of glycogen relate to its function
Coiled/ compact= store lots of glucose in small space
Branched= quickly hydrolysed= release glucose for respiration to make ATP for energy release
Large + insoluble= can’t diffuse out of cell
Insoluble in water= water potential of cell not affected= no osmotic effect
What is cellulose?
polysaccharide of B glucose
1-4 glycosidic bonds, straight unbranched chains
What type of reaction is involved in joining cellulose (B glucose) molecules?
condensation
Name the additional molecule forming during the reaction of joining B molecules
water
Draw 2 B glucose molecules to form cellulose
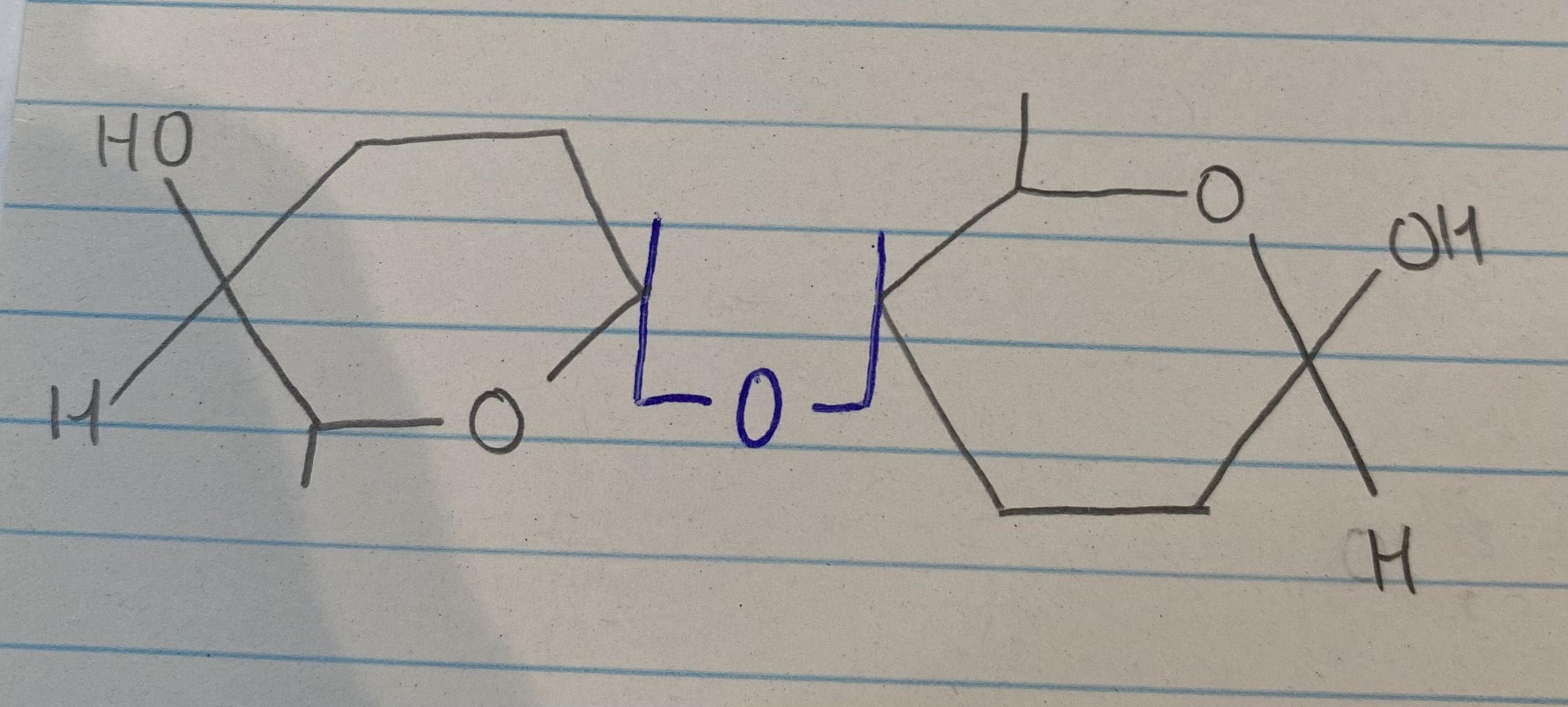
Explain how the structures of cellulose relate to its function
Every other B glucose molecule is inverted= long, straight, unbranched chain
Chains run parallel to each other and hydrogen bonds form cross linkages between chains to form microfibrils
Many hydrogen bonds are strong= provide high tensile strength= makes cell wall rigid and prevents osmotic lysis
Name the monomer, shape of polymer, types of bonds, and solubility in water for…
STARCH
a glucose
amylose= helical, amylopectin= branched
glycosidic
insoluble
Name the monomer, shape of polymer, types of bonds, and solubility in water for…
GLYCOGEN
a glucose
branched
glycosidic
insoluble
Name the monomer, shape of polymer, types of bonds, and solubility in water for…
CELLULOSE
B glucose
straight long chains forming microfibrils
glycosidic (hydrogen between chains)
insoluble
What is the food test for starch?
Add iodine solution and colour changes from brown/ orange to blue-black
What is a reducing sugar?
those with the ability to donate electrons/ hydrogen (has spare hydrogen)
What is the food test for reducing sugars?
Add benedicts solution to sample. Heat in water bath. If reducing sugar present, colour will change blue to red
What are the 5 reducing sugars?
glucose
fructose
galactose
maltose
lactose
What is the food test for non-reducing sugars?
Do benedicts test and result stays blue
Boil fresh sample with dilute HCl (acid)
Neutralise with alkali
Heat in water bath with benedicts solution
Positive result turns red
What is the only non-reducing sugar?
sucrose
Explain the quantitative benedicts reagent test
more concentration of glucose solution= more white precipitate
> remove precipitate= more transparent solution
What readings do you get from the quantitative benedicts reagent test?
Transmission %= increases as increase glucose
Absorbance= decreases as glucose increases
What are some issues related to the benedicts tests and how are they resolved?
Non-specific (doesn’t tell us the reducing sugar)= a biosensor can test for specific sugars
Qualitative (can’t obtain a value from the concentration)= spectrum of concentrations
Subjective= use a colourimeter and a calibration curve
How do you use a colourimeter and a calibration curve?
Make sugar solutions of known concs (series of dilutions).
Heat a set volume of each sample with benedicts solution.
Use colourimeter to measure absorbance of each conc.
Plot calibration curve quantitative benedicts reagent test (conc=x, absorbance=y)
Repeat on unknown sample.
Read off calibration curve to find conc associated with unknown sample’s absorbance
What is an inorganic ion?
an ion that has a charge
Where are inorganic ions found in the body?
in solution in cytoplasm and body fluid, same in high concs and low concs
What are the 4 main ions?
Iron (FE2+/ FE3+)
Sodium (Na+)
Phosphate (PO4 3+)
Hydrogen (H+)
Describe the role of hydrogen ions
Affects pH levels= high conc= low pH
> affects enzyme rate of reaction as can cause enzyme denaturation
Describe the role of sodium ions
Involved in absorbance of glucose and amino acids in small intestine (co-transport)
Describe the role of iron ions
Component of haem group of haemoglobin= allows oxygen to bind for transport
Describe the role of phosphate ions
Component of DNA, ATP (an energy-containing molecule used by cells) and phospholipids