liver physiology
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
week 3 ctb
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
functions of the liver
energy metabolism and substrate interconversion
cholesterol processing
production of bile
excretion of bilirubin
drug metabolism and detoxification
synthesis of plasma proteins
storage of vitamins and minerals
immune functions
histological organisation of the liver
2 major fluid inputs:
oxygenated blood from the arterial system via the hepatic artery
deoxygenated blood from the intestine via the hepatic portal vein
2 major fluid outputs:
deoxygenated blood to the venous system via hepatic veins
bile to the small intestine via bile ducts
these are linked by central veins running through liver lobules containing hepatocytes
histological organisation of the liver
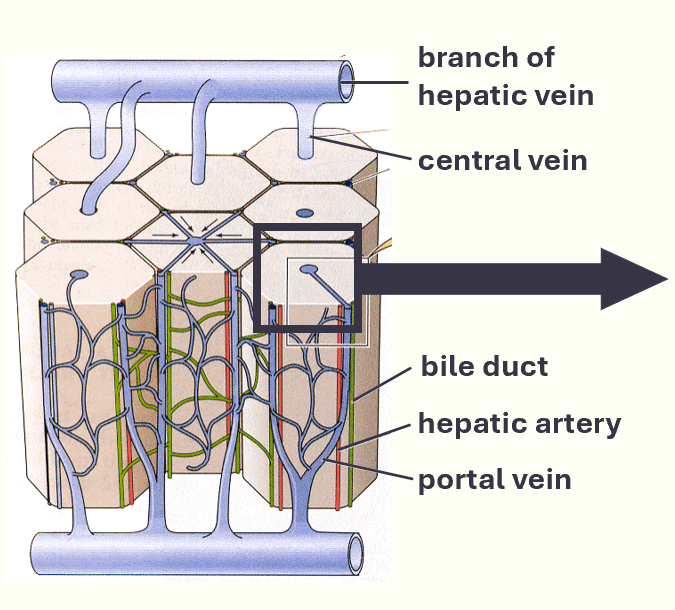
organisation of liver
zone I periportal hepatocytes:
most oxygenated
cells specialise in oxidative metabolism, gluconeogenesis. urea synthesis
zone II pericentral hepatocutes:
least oxygenated
cells specialise in drug metabolism, glycolysis, lipogenesis
differential of oxygen content from HIGH on the outside to LOW in the centre
histological organisation of liver cont.
liver lobules contain plates of hepatocytes, lying in a cage of reticuloendothelial cells
plates separated by vascular spaces called sinusoids
blood from sinusoids converges on the central vein
in turn, central veins coverge on the hepatic vein
liver cell type diagram
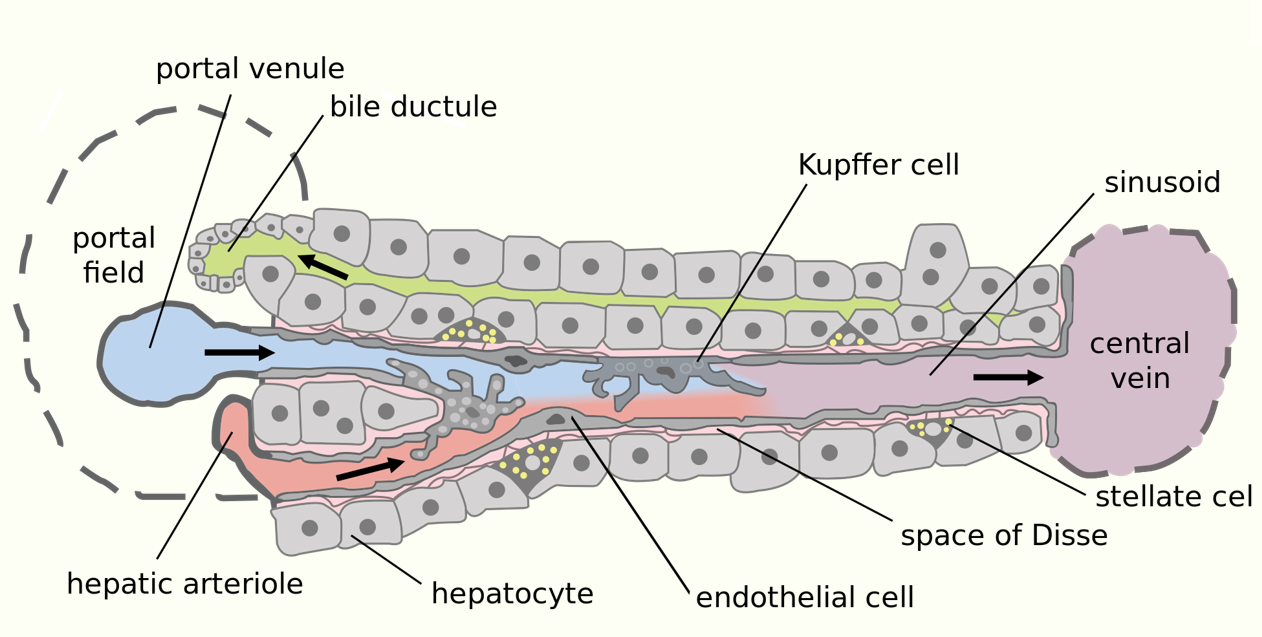
liver cell types
hepatocytes
endothelial cells
Kupffer cells
stellate cells
cholangiocytes
hepatocytes
major parenchymal (functional) cells of liver
responsible for metabolic and secretary roles
cuboidal in shape and contain abundant mitochondria, ribosomes and ER
endothelial cells
flattened and specialised
structural role lining the sinusoids
small in volume, form a large surface area
fenestrations for filtering fluid
Kupffer cells
tissue macrophages (capable of phagocytosis)
located in hepatic sinusoids
attached to the endothelial cell lining
stellate cells (lipocytes)
located in perisinusoidal space (space of Disse)
long protusions that wrap around the sinusoids and may act as APCs
contain lipid droplets and store lipid soluble vitamins
cholangiocytes
epithelial cells lining bile ducts of liver and hepatobiliary system
vary in shape from cuboidal in small interlobular bile ducts to columnar in the larger bile ducts
contribute to bile production through secretion of bicarb
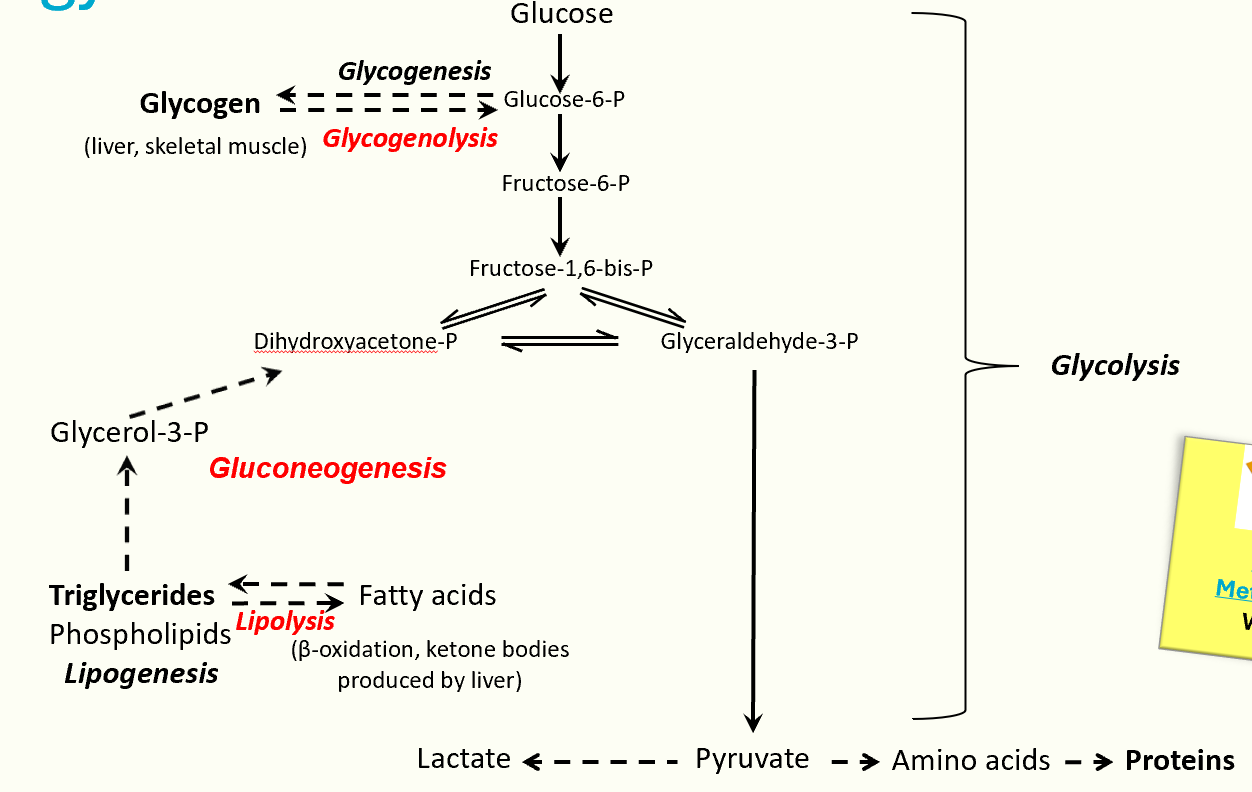
energy metabolism
carb metabolism
liver stores energy in the form of glycogen, performing glycogenesis in fed state and glycogenolysis in fasting state
all gluconeogenesis takes place in liver → produces new glucose from glyceral, lactate from anaerobic glycosis and AAs
lipid metabolism
liver carries out beta oxidation of fatty acids and triglyceride synthesis
in fasting state, liver performs ketogenesis, producing ketone bodies from acetyl-CoA and releasing them into the circulation
protein metabolism
liver carries out transamination and deamination of AAs, producing urea for excretion via urea cycle
energy storage diagram
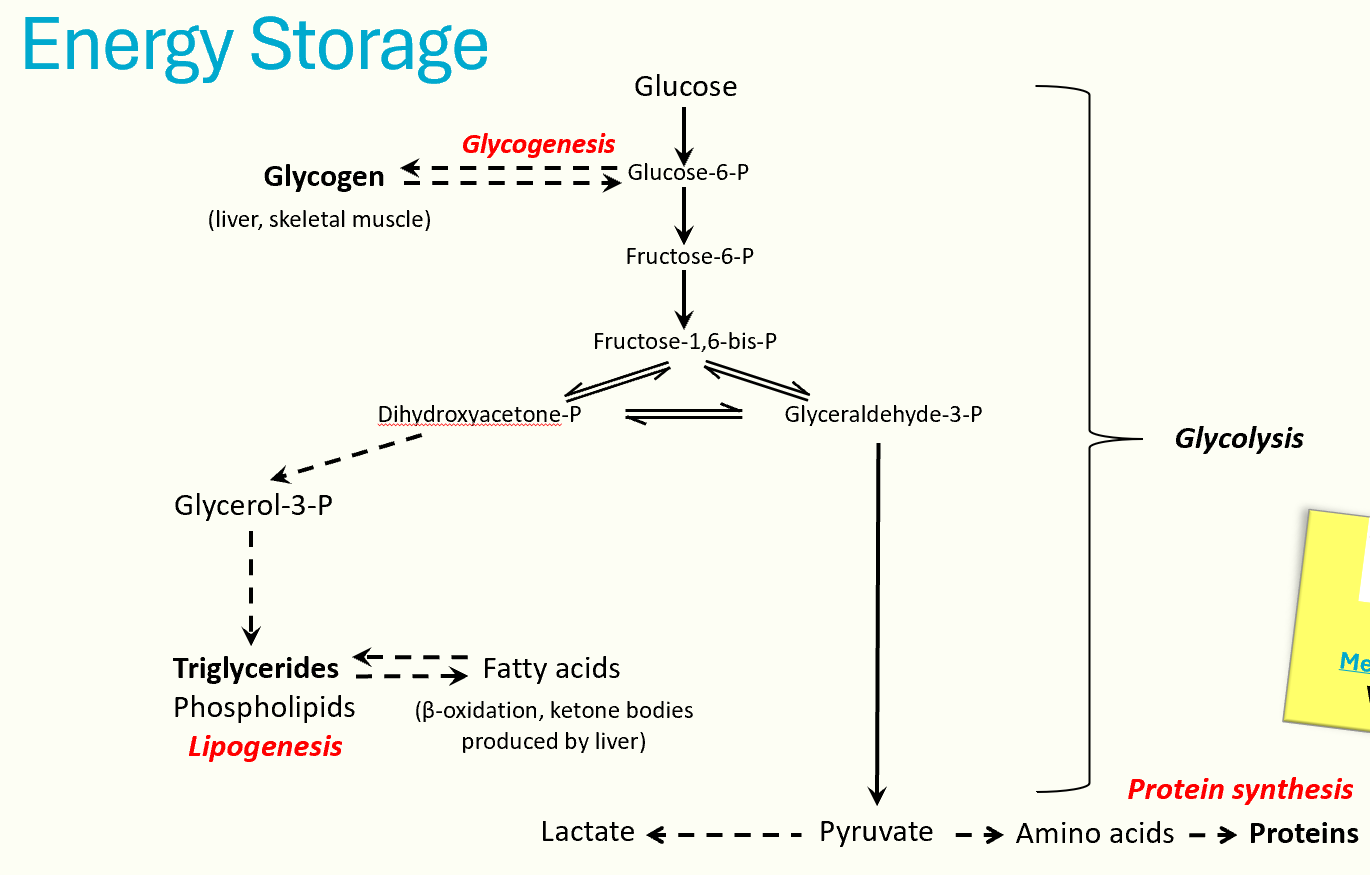
energy utilsation diagram
cholesterol
lipid molecule that has many important functions
plasma membranes
components of bile salts
precursor for steroid hormones
myelin
15% of cholesterol comes from diet
85% cholesterol is synthesised within body (mostly in liver)
transported in blood plasma in complexes called lipoproteins (synthesised mainly by liver)
cholesterol processing diagram
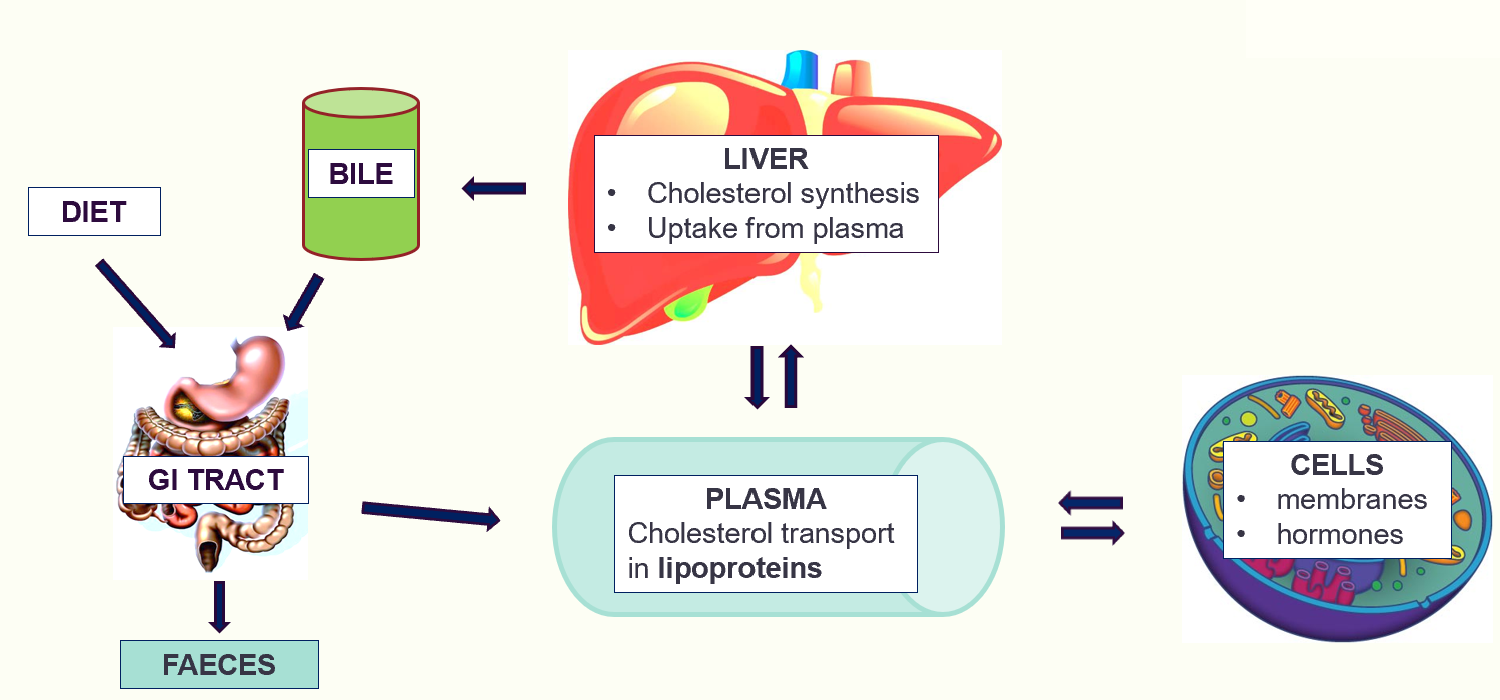
cholesterol processing
multiple key roles in cholesterol processing:
synthesises cholesterol from acetyl-CoA
synthesises lipoproteins, which transport cholesterol in blood plasma
distributes cholesterol via circulation to body cells, for synthesis of key products (steroid hormones)
utilises cholesterol for synthesis of bile salts
extracts excess cholesterol from blood plasma
exports excess cholesterol in bile for excretion in faeces
bile
complex aqueous solution produced by liver
released into SI to aid digestion of lipids
intially made by hepatocytes and then modified in bile duct system (involves both absorption and further secretion by epithelial cells)
its production and release into duodenum after a meal are stimulated by intestinal hormones secretin and CCK
bile salts act as a surfactant, emulsifying dietary lipid droplets in intestine by reducing surface tension at the lipid/water interface
bile composition
bile salts (steroid bile acids conjugated with taurine or glycine)
lecithin (amphiphilic phospholipids)
cholesterol
bile pigments (bilirubin)
HCO3- and other salts
trace metals
bile production
hepatocytes secrete
bile salts
lecithin
cholesterol
bile pigments
cholangiocytes secrete:
bicarb
water
components of bile are secreted into bile canaliculus and drain into bile duct
bile secretion
liver produces and secretes 1L of bile a day, stimulated by hormone secretin
bile is stored and concentrated in the gall bladder, which contracts when stimulated by CCK
then enters duodenum via common bile duct
excretion of bilirubin
bile pigments are excretory products being disposed of by the liver via the intestine
main bile pigments is bilirubin, formed from the breakdown of haem in the spleen and bone marrow
hepatocytes conjugate bilirubin with glucuronic acid to form a polar, water-soluble molecule
secreted in bile
biosynthetic functions of the liver
liver synthesises many proteins that are released into blood plasma:
carriage proteins (binding proteins)
albumin
transferrin (iron transport)
sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG)
thyroid binding globulin (TBG)
factors involved in haemostasis/fibrinolysis
coagulation (fibrinogen)
fibrinolysis (plasminogen)
pro hormones, apolipoproteins, immunoglobulins
liver function tests
allows clinical assessment of liver in a cheap, safe and non-invasive manner
decrease in blood component produced by liver (albumin) can indicate impaired liver function
increase in a substance normally cleared from blood by liver (bilirubin) can also indicate impaired liver function
increase in blood plasma conc of enzymes normally found in liver (transaminases) could indicate a loss of structural integrity of liver cells