epithelial tissues quiz (anatomy)
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
tissues
groups of cells with similar structure and function
4 primary tissue types
- epithelial tissue
- connective tissue
- muscle tissue
- nervous tissue
where can you find epithelial tissue?
- body coverings
- body linings
- glandular tissue
what are the functions of epithelial tissue?
- protection
- absorption
- filtration
- secretion
hallmark of epithelial tissues
- cover and line body surfaces
- form sheets with one free surface, the apical surface, and an anchored surface, the basement membrane
- avascular (no blood supply)
- regenerate easily if well nourished
2 ways to classify epithelial tissue
- number of cell layers
- shape of cells
number of cell layers
- simple
- stratified
simple
one layer
stratified
more than one layer
shapes of cells
- squamous
- cuboidal
- columnar
squamous
flattened like fish scales
cuboidal
cube shaped, like dice
columnar
shaped like columns
simple epithelia
- function: absorption, secretion, and filtration
- very thin (not suited for protection)
simple squamous epithelium
single layer of flat cells
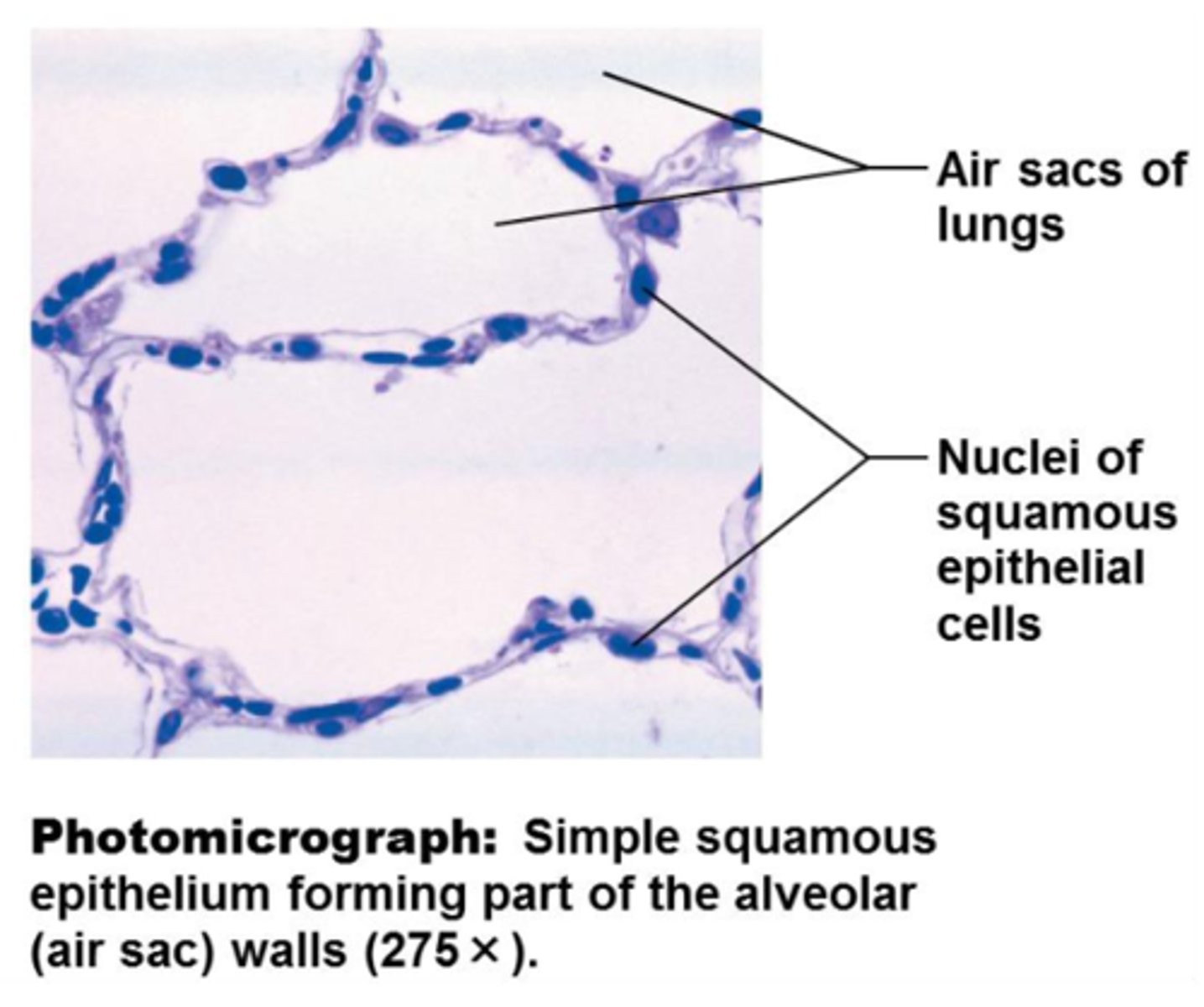
simple squamous epithelium location
- lines air sacs of the lungs
- forms walls of capillaries
- forms serous membranes (serosae) that line and cover organs in ventral cavity
simple squamous epithelium functions
- diffusion
- filtration
- secretion
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cub like cells
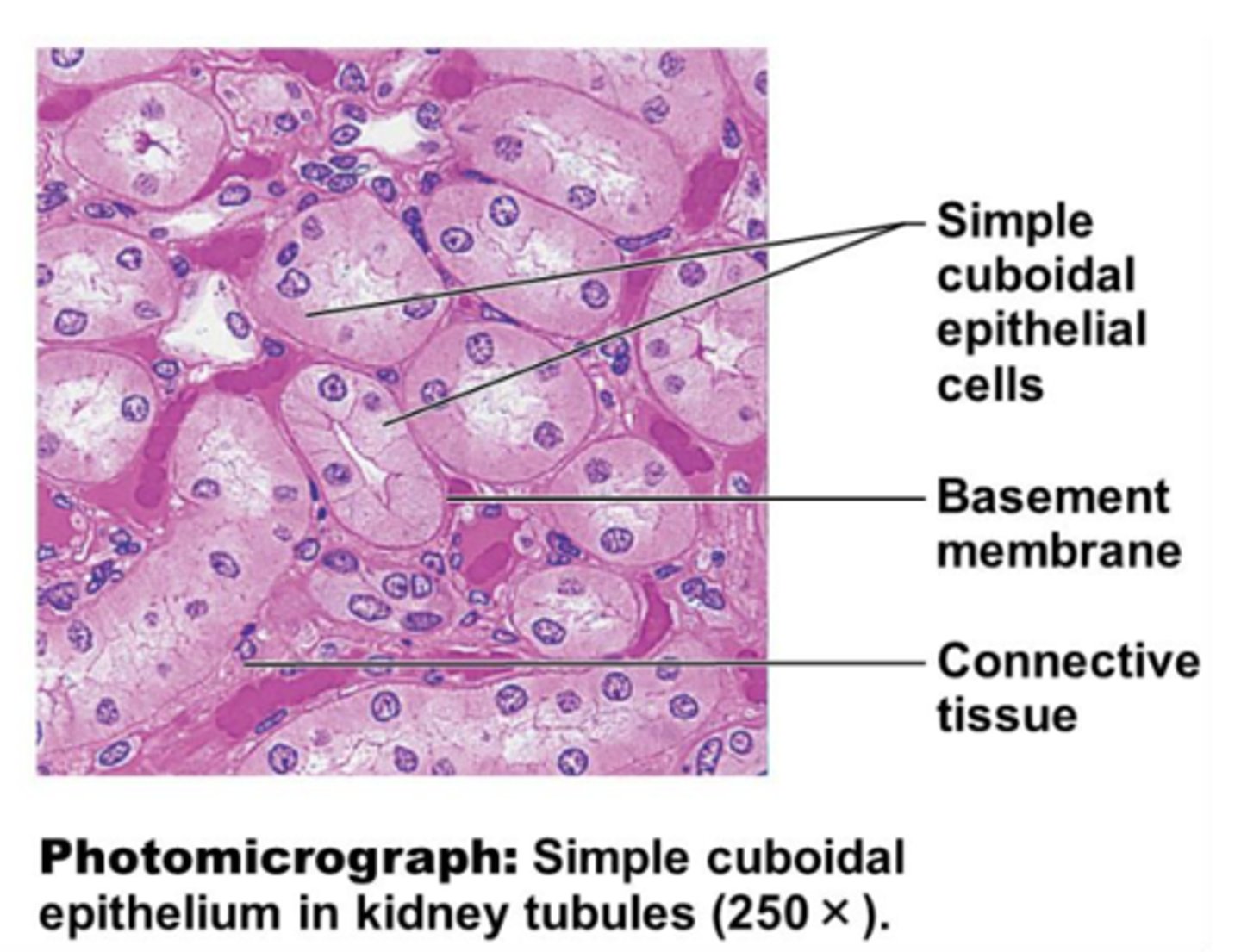
simple cuboidal epithelium location
- common in glands and their ducts
- forms walls of kidney tubules
- covers the surface of ovaries
simple cuboidal epithelium functions
- secretion
- absorption
- ciliated types propel mucus or reproductive cells
simple columnar epithelium
single layer of tall cells
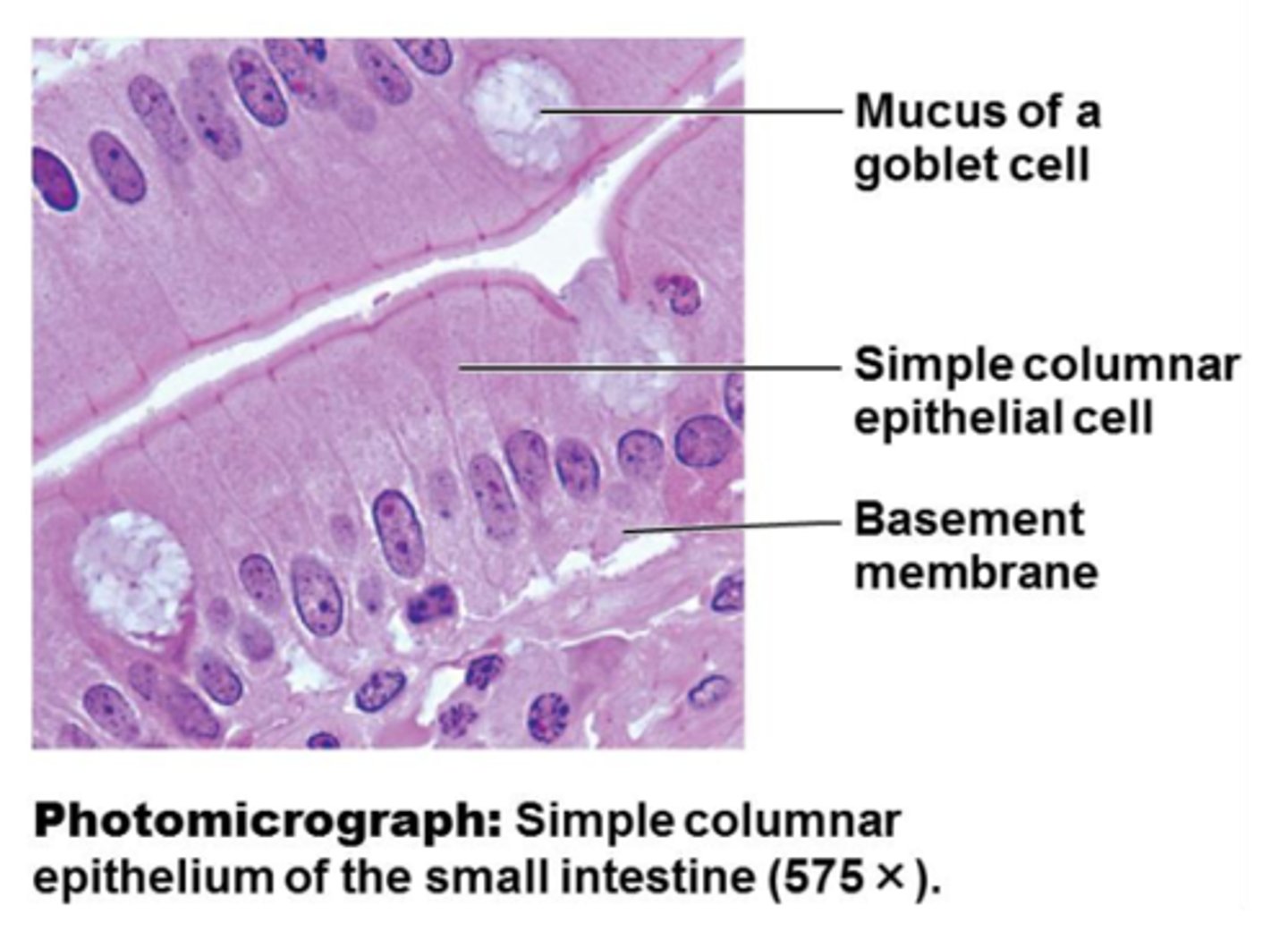
simple columnar epithelium location
- lining of the digestive tract from stomach to anus
- mucous membranes (mucosae) line body cavities opening to the exterior
simple columnar epithelium function
- secretion
- absorption
- ciliated types propel mucus or reproductive cells
pseudostratified columnar epithelium
- all cells rest on a basement membrane
- single layer, but some cells are shorter than others giving a false (pseudo) impression of stratification
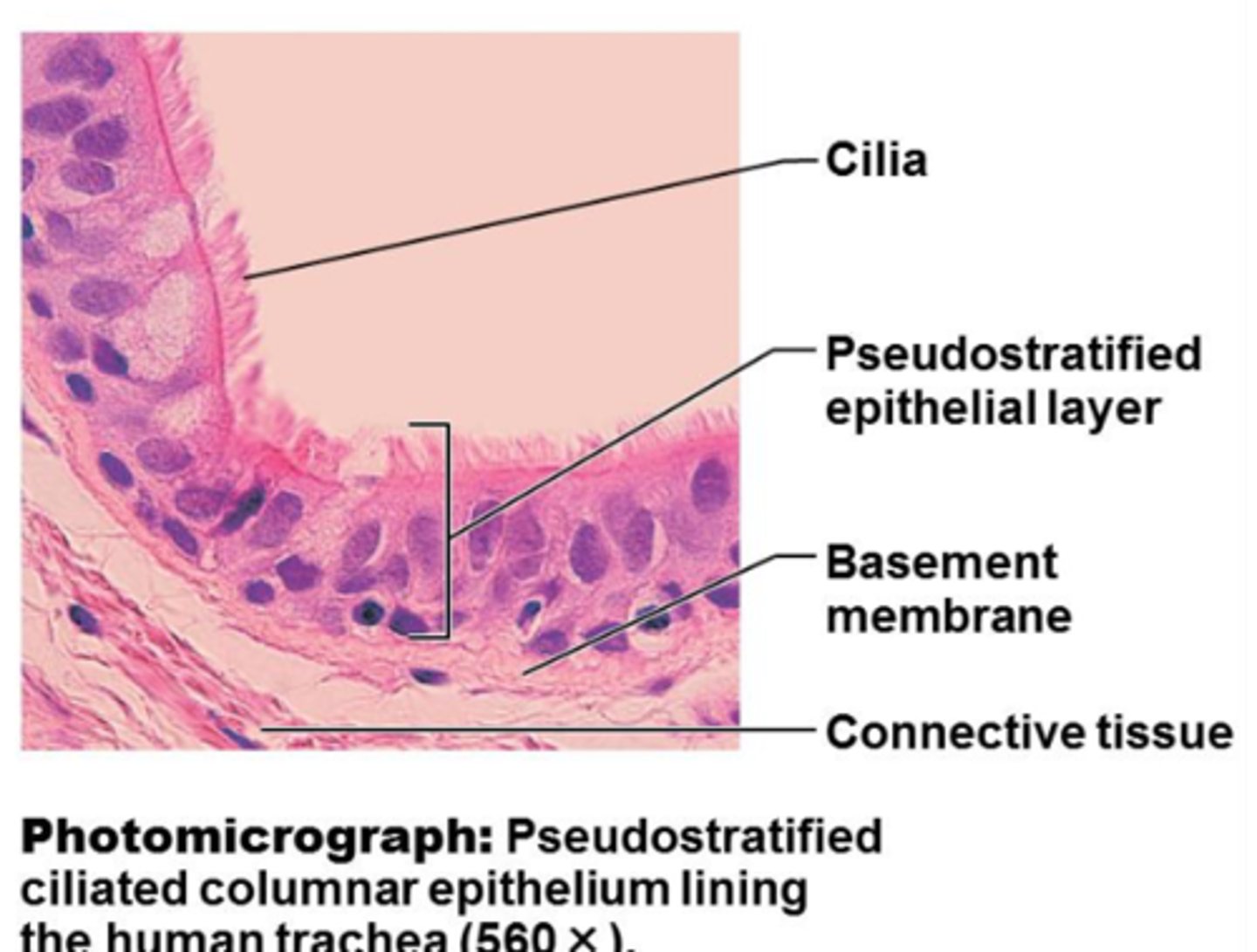
pseudostratified columnar epithelium location
- respiratory tract, where it is ciliated and known as pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
pseudostratified columnar epithelium function
- absorption
- secretion
stratified epithelia
- consists of two or more layers of cells
- function: protection
stratified squamous epithelium
- named for cells present at the free (apical) surface, which are squamous
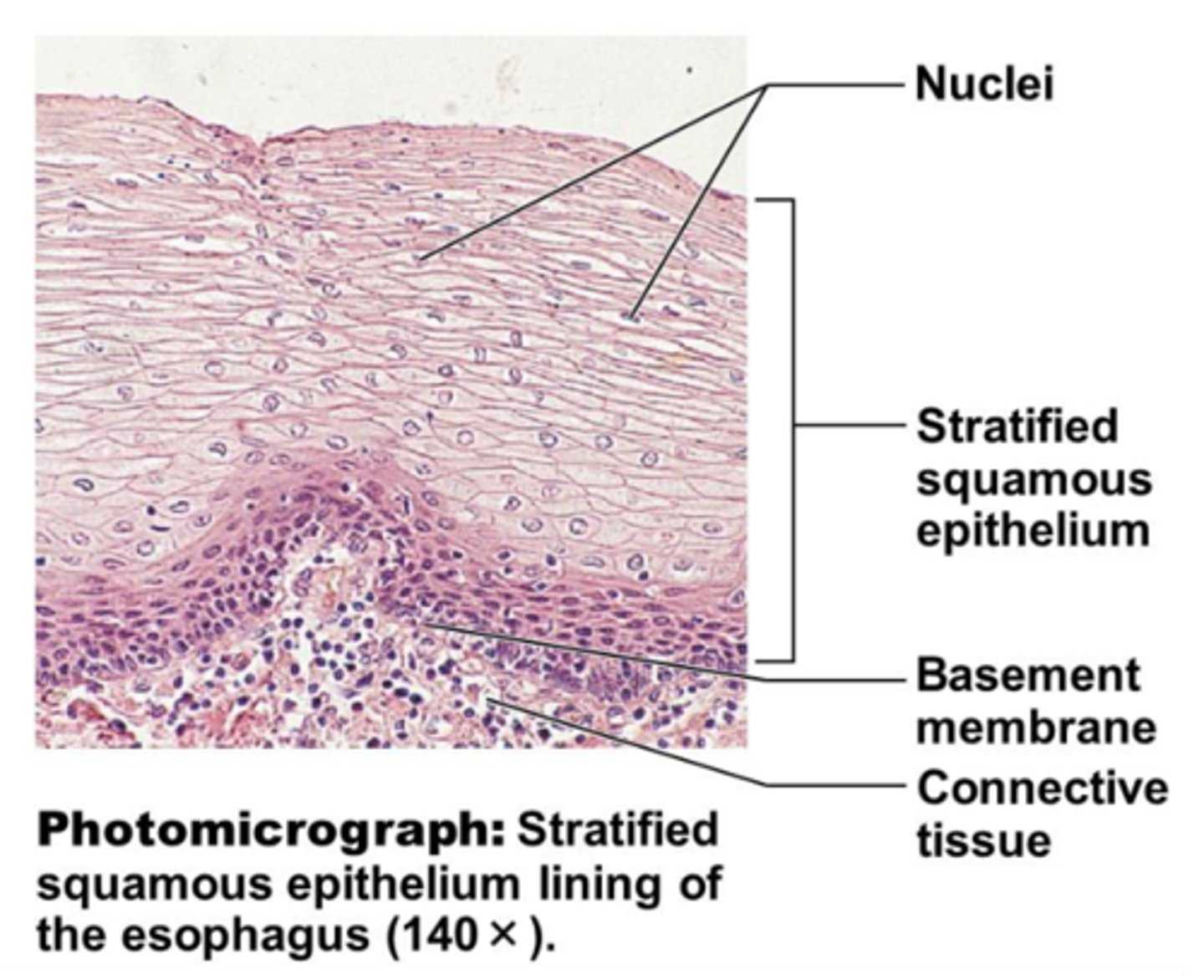
stratified squamous epithelium location
- skin (outer portion)
- mouth
- esophagus
stratified squamous epithelium function
- protective covering where friction is common
stratified cuboidal epithelium
two players of cuboidal cells
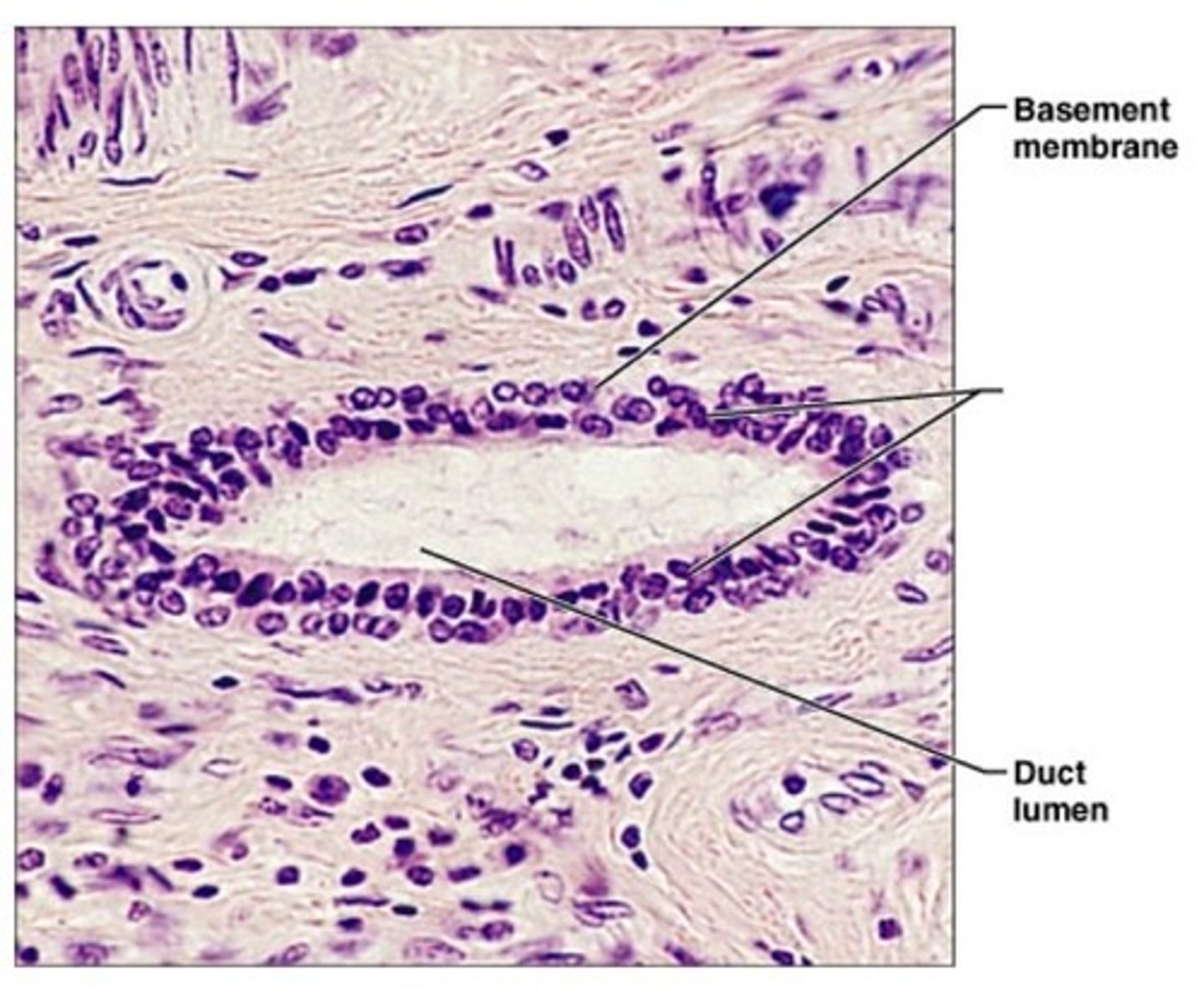
stratified cuboidal epithelium location
- rare in human body
- found mainly in ducts of large glands
stratified cuboidal epithelium function
protection
stratified columnar epithelium
surface cells are columnar and cells underneath vary in size and shape
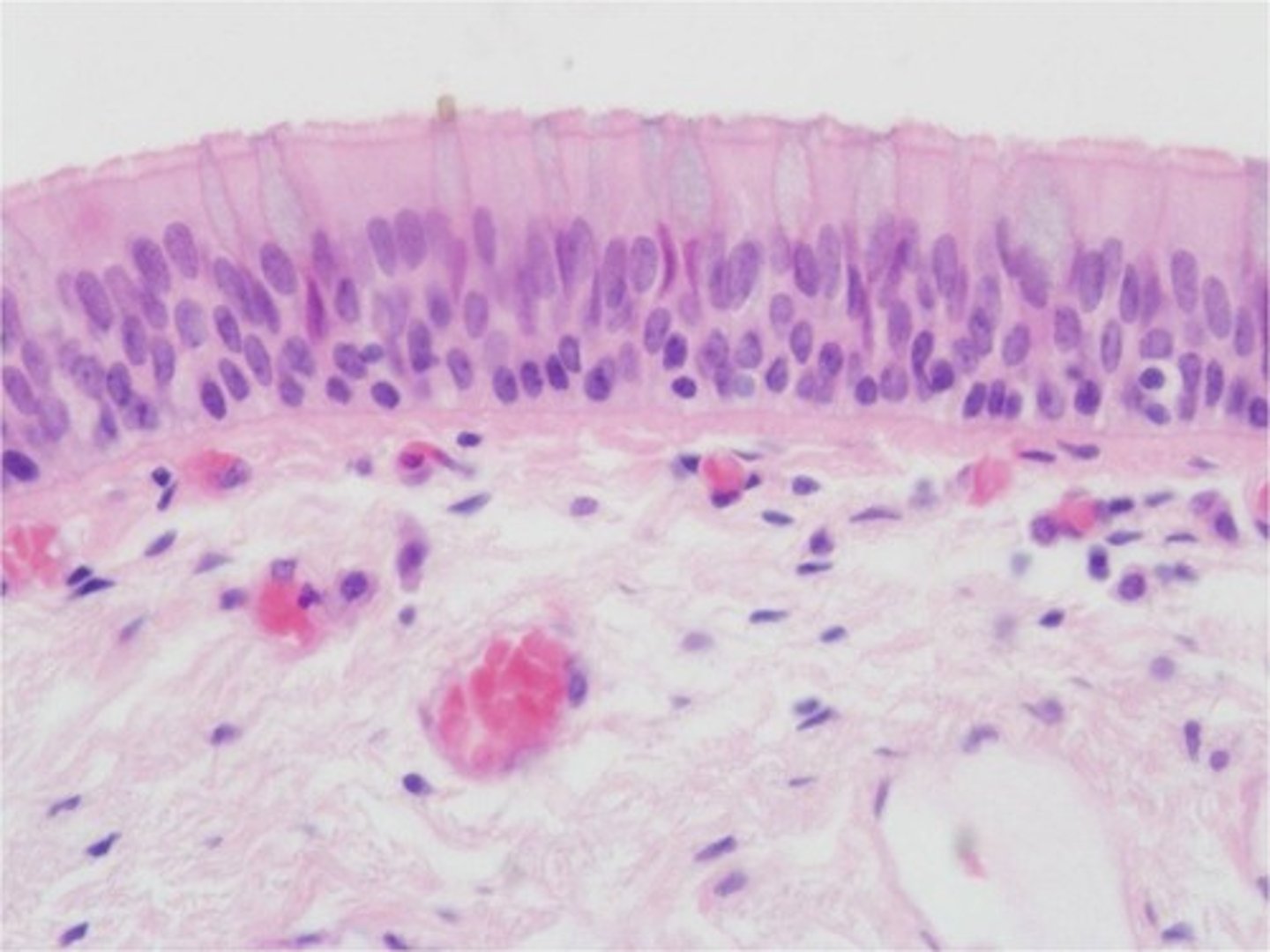
stratified columnar epithelium location
- rare in human body
- found mainly in ducts of large glands
stratified columnar epithelium function
protection
transitional epithelium
- composed of modified stratified squamous epithelium
- shape of cells depends upon the amount of stretching
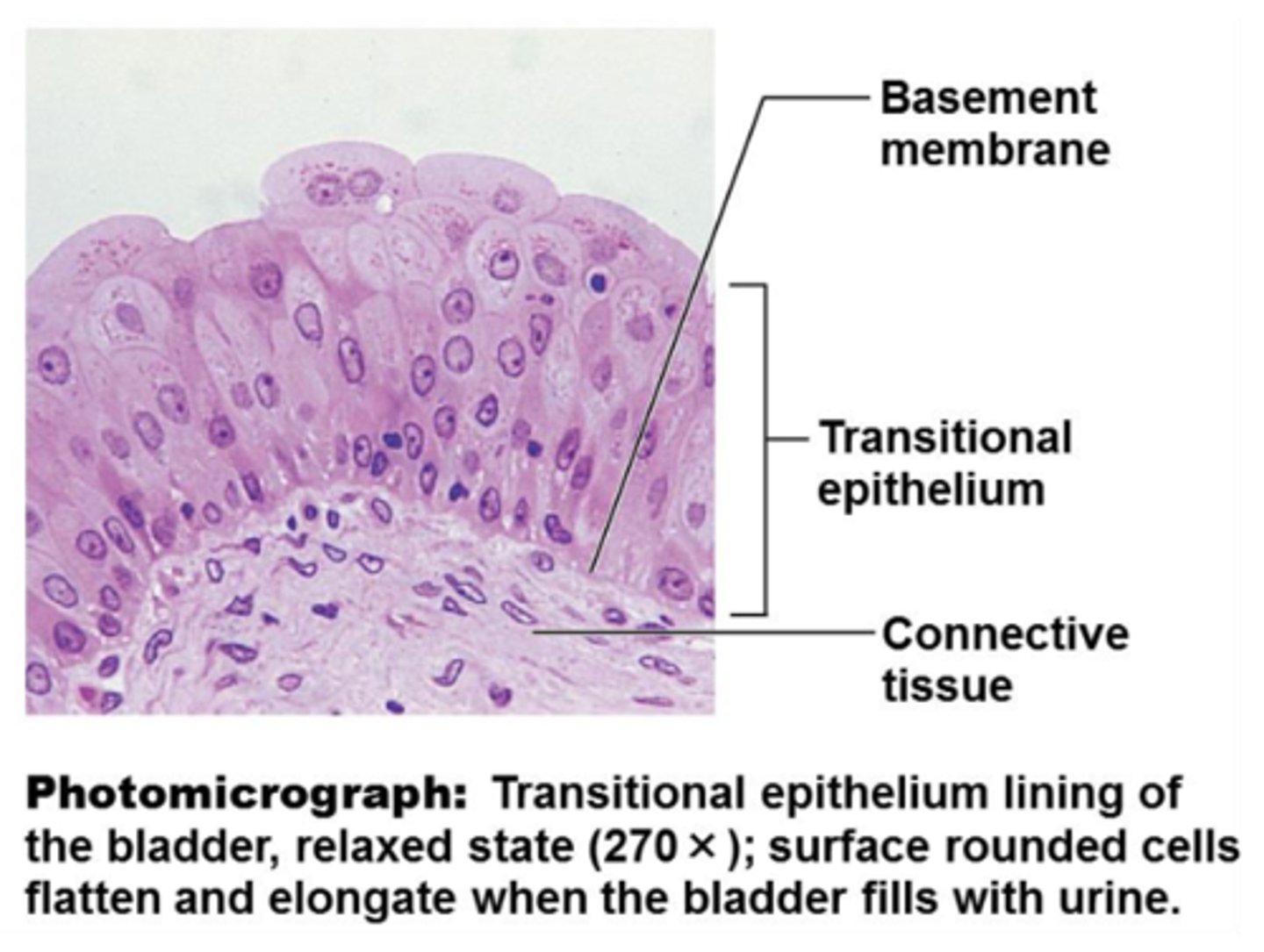
transitional epithelium location
- lining of urinary system organs
transitional epithelium function
- stretching
- the ability to return to normal shape
glandular epithelium
one or more cells responsible for secreting a particular product
2 major gland types that develop from epithelial sheets
- endocrine glands
- exocrine glands
endocrine glands
- ductless
- secretions diffuse into blood vessels
- includes: thyroid, adrenals, and pituitary
exocrine glands
- secretions empty through ducts to the epithelial surface
- includes: sweat and oil glands, liver, and pancreas