CH4710 RM23
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Cells are covered with a dense coating of ______ called ______. (Fill in the blank).
glycans, glycocalyx
in glucose all OH are ____.
equatorial
alpha and beta anomers
alpha: OH on the anomeric carbon is trans to carbon 6
beta: OH on the anomeric carbon is cis to carbon 6
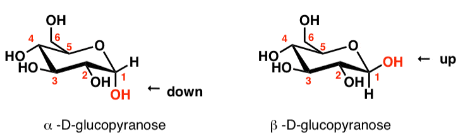
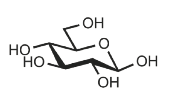
Identify
D-glucose
Glc
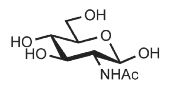
Identify
N-Acetyl-D-glucosamine
GlcNAc
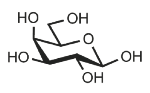
Identify
D-galactose
Gal
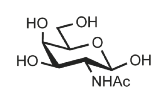
Identify
N-Acetyl-D-galactosamine
GalNAc
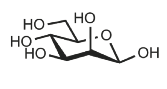
Identify
D-mannose
Man
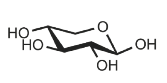
Identify
D-xylose
Xyl
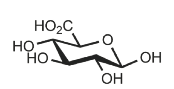
Identify
D-glucuronic acid
GlcA
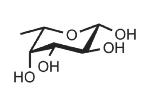
Identify
L-Fucose
Fuc
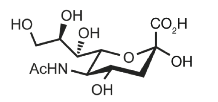
Identify
N-Acetylneuraminic acid
NeuAc
carbohydrates
aldehydes or ketones with at least two OH groups
4 classes of carbohydrates
monosaccharides- simple sugar, one polyhydroxy unit
oligosaccharides- short chains of monosaccharide units
disaccharides- 2 monosaccharide units
polysaccharides- 10+ monosaccharide units
What joins monosaccharide units together to form chains?
glycosidic bonds
2 examples of polysaccharides
cellulose
glycogen
2 families of monosaccharides
aldoses
ketoses
aldose
structure in which the carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon chain (in the aldehyde group)
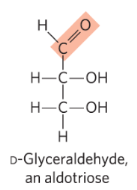
ketose
structure in which the carbonyl group is at any position besides the end of the carbon chain (in the ketone group)
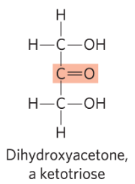
trioses
simplest monosaccharides, three carbon backbone
tetroses
four carbon backbone
pentoses
five carbon backbone
How to draw Fischer Projection Formulas to represent 3D sugar structures
bonds drawn horizontally indicate bonds that project out of the paper
bonds drawn vertically indicate bonds that project into the paper
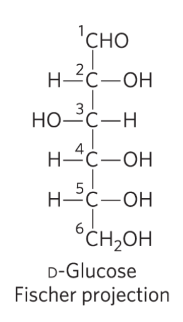
epimers
two sugars that differ only in the configuration around one carbon atom
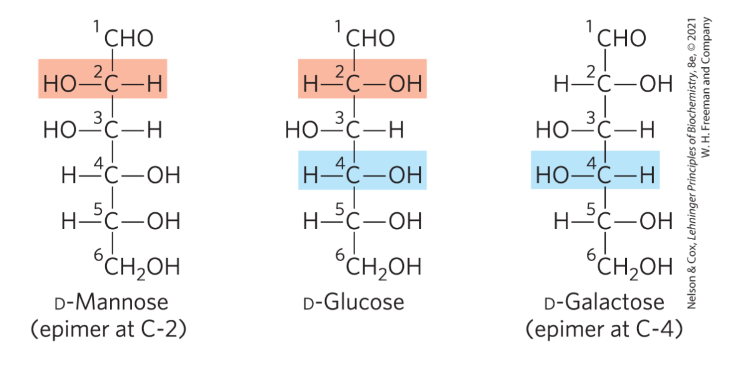
True or false: In aqueous solutions, all monosaccharides with 5+ carbon backbone occur as cyclic structures
True as hell
anomers
isomeric forms of monosaccharides
(there are alpha anomers and beta anomers)
anomeric carbon
the carbonyl carbon atom
mutarotation
the interconversion of alpha and beta anomers
How to draw Haworth perspective formulas to represent 3D sugar structure
six membered ring is tilted to make its plane almost perpendicular to paper
bonds closest to reader are drawn thick
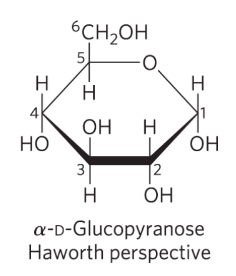
Are Fischer projections or Haworth perspectives more accurate?
Haworth perspectives
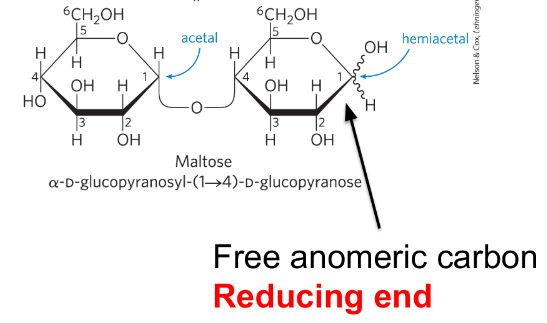
O-glycosidic bond
covalent linkage joining two monosaccharides
formed when an OH group of one sugar molecule reacts with the anomeric carbon of the other
reducing end
the end of a disaccharide/polysaccharide with a free anomeric carbon

Label the symbols
Fuc
Gal
Glc
Man
(Xyl is an orange star btw)
reducing end
the end of a disaccharide or polysaccharide chain with a free anomeric carbon
when sugar monomers are joined together, the anomeric carbon (carbon 1) is usually used to bond with other monomers, so the reducing end is going to have carbon 1 free with no bond