PRICE LEADERSHIP and COLLUSION/CARTELS
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
explain price leadership
firms set their own prices and move sequentially
the leader sets a price and the follower acts as a price taker
the leader may be dominant as it has lower costs and can win a price war
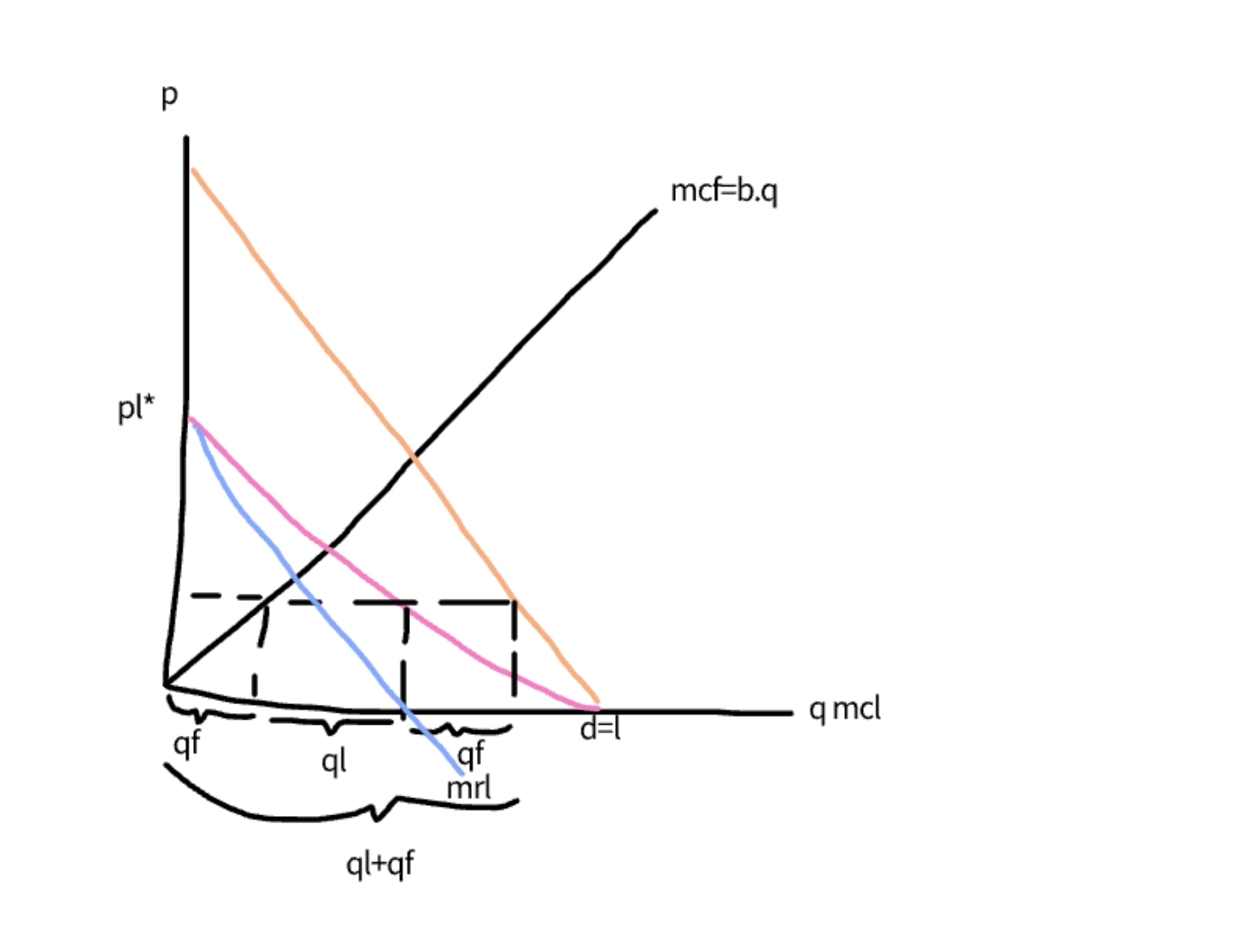
price leadership equilibirum
the leader is dominant as it has lower labour costs MCL=0 and MCF=1q>0
we solve via backwards induction
the follower takes the price set by the leader and sets P=MCf as MCf=P-MCf
to set a price L needs to work out the reaction of the follower for any price that it sets
the leader takes away this supply of the follower to find the leaders demand curve, this is the market demand-the reaction of the follower
the leader takes the leader demand curve and maximisises its profits where MC=MR this gives us the output of the leader and tells us the price itll set
once we have the price we work out how much the follower will supply
this adds on and gives us the market demand cirve
what is collusion in oligopolies
oligopolies jointly produce more then monopolies output there is an incentive to collude
this is a cartel
these are feasible and illegal and tacit
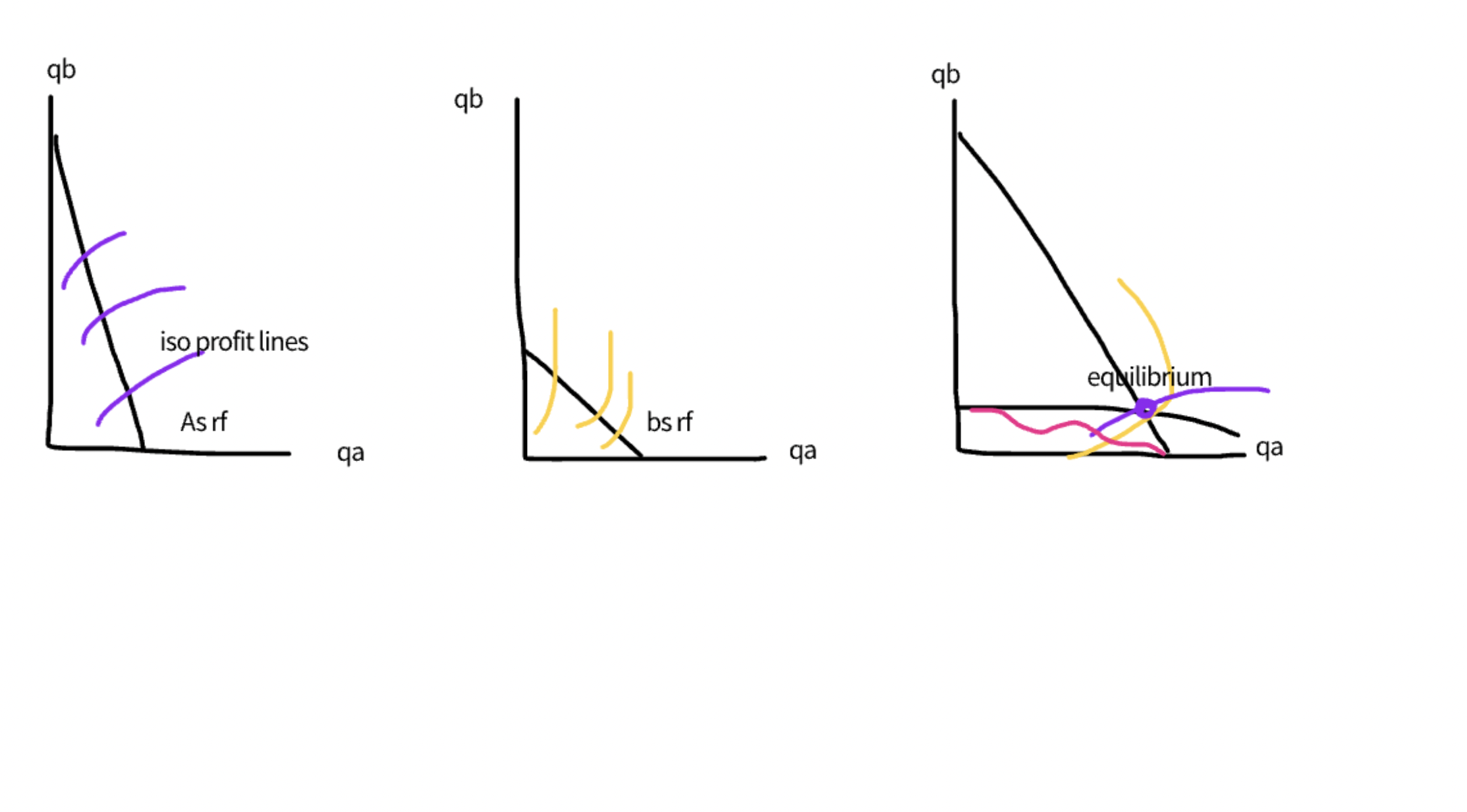
why is there incentive to collude in the cournot model
as theyll be on a higher iso profit line compared to their cournot equilibrium
to maximise the industry prift it is necessary that their iso profit lines are tangential
both firms must be better off under the agreement this may lead to side payments
what are the types of carteld
joint profit maximisation
market sharing agreement
price fixing in competitive tenders
these are investigated in the UK by the CMA
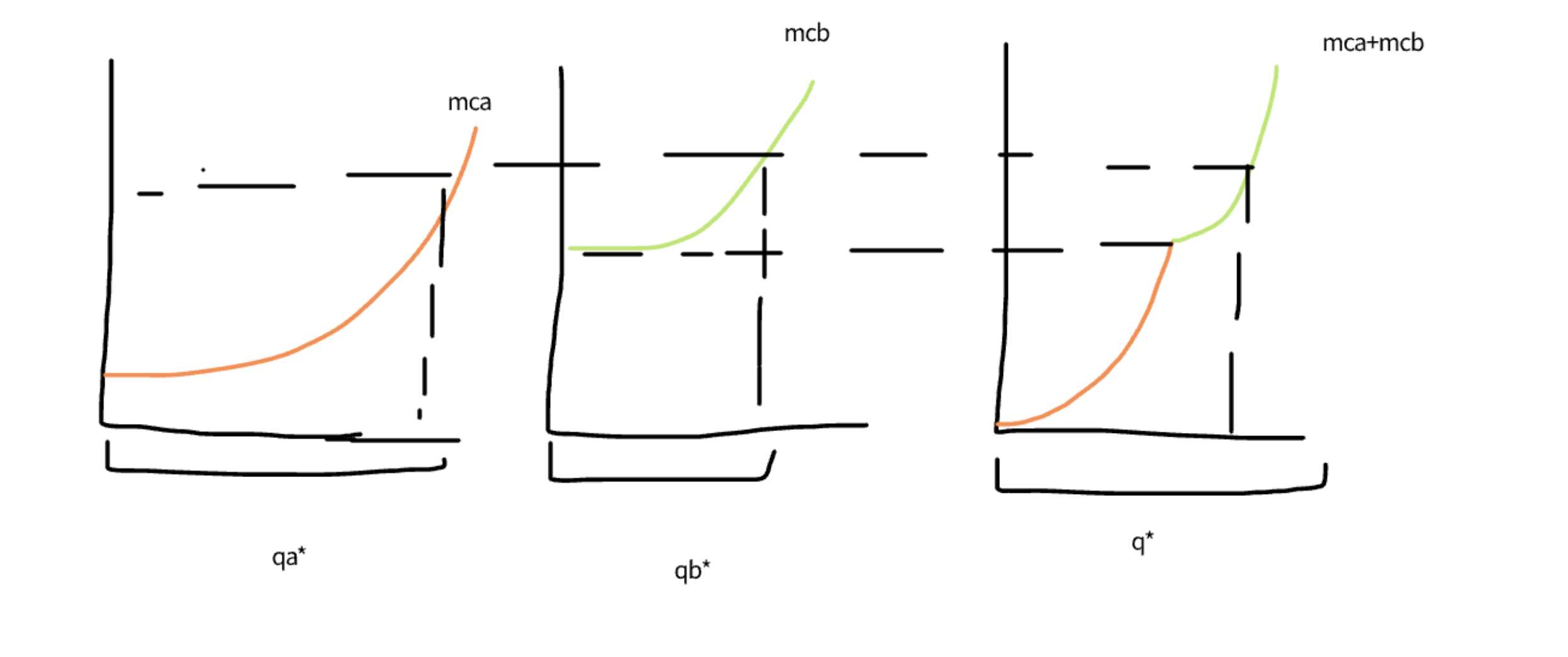
explain JPM
this is where firsm behave as a multiplant monopolist
they profit maximise where MR=MCA=MCB
there is formula for a share out side payment
this generates the same total otuput and price as a monopoly
this is formed by summing our MC curves horizontally
why is there an incentive to cheat in a cartel
cartels are unstable and at least one firm has an incentive to cheat on the agreement as collusion takes firms off their reaction functions
that is that the co-operative equilibrium isnt a nash equilibrium this relates to our prisioners dilemma
explain the market sharing agreemnet
there agreements operate geographically
the firms divide the market up and agree on a common price then produce according to their quotas
Da and Db represent the demand curves from dividing up the market
if they collude they agree on PC and produce Da and DB
costs in A are low and B are high
to maximise profits we produce at QA QB and PA PB when firms operate independantly and compete the price in B is greater then the price in A
if they collude they use PC this lies between pa and pb and depends on their bargining strength
they produce to support a and bs quotas
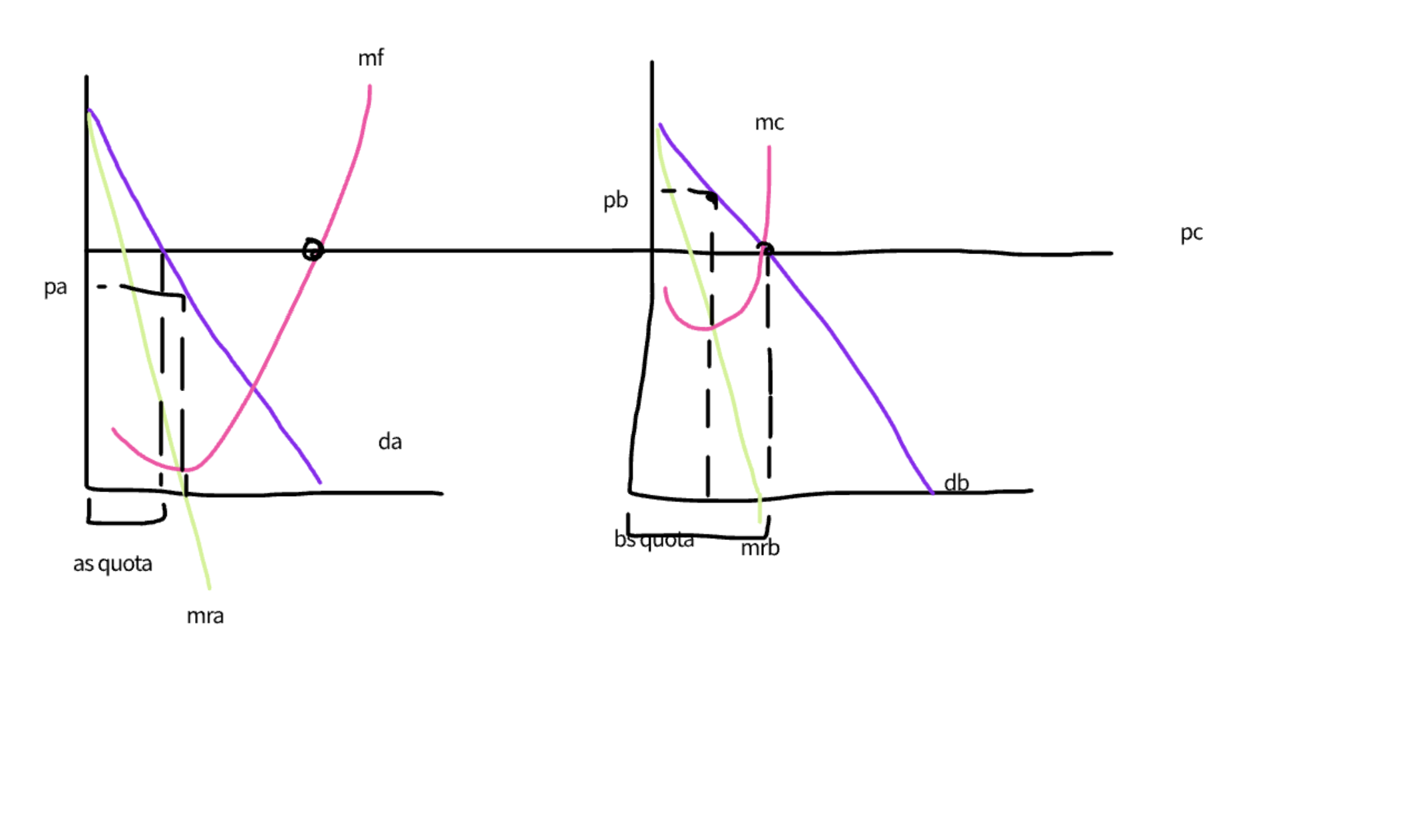
why is there incentive to cheat in the market sharing agreement
as we have perfectly elastic demand curves
both firms are thus price takers
pa has incentive to cheat as itll try sell units beyond the point as the P is above the MC
b will also have an incentive to cheat to rise their output above the quota
explain the stability of cartels
if a firm cheats it expands its output but the market price falls
this can be detectable and punishable
what are non price competition for cartels
sell at a higher quality
brand product to encourage loyalty
what is secret price competition
offer rebates that arent observes
set up a subsidary