Lecture 14 - DNA & Chromosomes
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Watson and Crick
identified the double-helix model of DNA
DNA
Made up of nitrogenous base, deoxyribose, and a phosphate group
Nitrogenous bases
Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
Chargaff Rules:
%A=%T and %G=%C in DNA strand
A=T
2 hydrogen bonds
C=G
3 hydrogen bondsP
Purines
A and G, containing two carbon rings
Pyrimidines
T and C, contain one carbon ring
Sugar phosphate backbone
Made up of deoxyribose and phosphate molecules, run antiparallel to each other: One strand is 5’ - 3’ and the other runs 3’ - 5’
Semiconservative model of replication
Predicts that when DNA replicates, one strand is a parent strand and the other is the newly synthesized strand.
Origin Sites
Where DNA strands separate, forming a replication “bubble”, 100s-1000s per chromosome
DNA replication is remarkably accurate
1 error per 10 billion nucleotides
Replication Forks
Y shape structure that forms as helicase unwinds a DNA strand into to single parent strands.
Helicase
Untwists double helix, separating template DNA at the replication fork
Primase
Initial RNA primer (5-10 nucleotides long), short stretch. Necessary for initiating the synthesis of a new polynucleotide.
DNA polymerase
Synthesizes new DNA strand by adding nucleotides to preexisting chain (initial primer)
Can only place nucleotides on 3’ end… elongates from 5’—> 3’
Anitparallel
Two strands of DNA in a double helix are _____… meaning one strans runs 5’—> 3’ and other runs 3’—> 5’
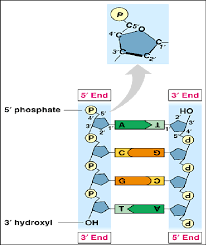
3’ end has a free hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to deoxyribose and a 5’ end with a free phosphate group attached to deoxyribose
What is attached to the 3’ end? What is attached to the 5’ end?
DNA Polymerase III
Synthesizes a complementary strand continuously by adding nucleotides to the new strand in the 5’ to 3’ direction
Leading Strand
Requires a single primer, DNA polymerase III moves towards junction of replication fork along the template strand in 5’ to 3’ direction, continuously adding nucleotides to the new complementary strand as the fork progresses
Lagging Strand
Synthesized through a series of short segments (okazaki fragments), copied away from the fork and requires multiple primers
Okazaki Fragments
How lagging strand is synthesized, each ____ must be primed separately on the lagging strand
DNA ligase
Joins sugar-phosphate backbones of Okazaki fragments to form a single DNA strand — joining 3’ end of fragment 1 to 5’ end of fragment 2
Initial Mistakes occur 1 per 100,000 base pairs
DNA polymerase proofreads each new nucleotides against template, if wrong, enzyme removes wrong base and resumes synthesis
Mismatch Repair
Enzymes fix incorrectly paired nucleotides that are missed by DNA polymerase or mutations that occur after DNA synthesis completed
DNA molecules subjected to harmful chemicals or physical agents (ex: X-rays, cigarette smoke)
DNA molecules incorrectly paired/altered nucleotides arise after replication by… OR spontaneous chemical changes under normal cellular conditions
Mutations
Mistakes in DNA replications. Can change phenotype of organism. If in germ cells, can be passed on from generation to generation.
Mutations
Source of variation in which natural selection operates during evolution… responsible for all traits and features for all species in our biosphere. Majority of changes are harmful… very small percentage beneficial.
Bacteria Chromosome
Single, circular, double-stranded DNA molecule w/ small amount of proteins
Eukaryote chromosome
Linear, double helix DNA molecule associated with large amount of protein
Histones
DNA packaged with ____ proteins form chromatin
Nucleosome
Basic structure of chromosome, made up of DNA would 2 ½ times around a bundle of 8 histone proteins. 10nm in diameter, looks like beads on a string
Euchromatin & Heterochromatin
Two forms of highly decondensed chromatin found during interphase
Euchromatin
10-nm fiber of chromatin found during interphase
Heterochromatin
30-nm fiber of chromatin found during interphase, can be further folded into more dense arrangements by a host of other proteins
Chromatin coils and condenses, formes short, thick metaphase chromosomes
Chromatin during Mitosis/Meiosis