Microbial Metabolism: ATP Generation, Pathways, and Photosynthesis
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
160 Terms
What is the primary purpose of ATP in organisms?
To regenerate ATP for continued metabolic activities.
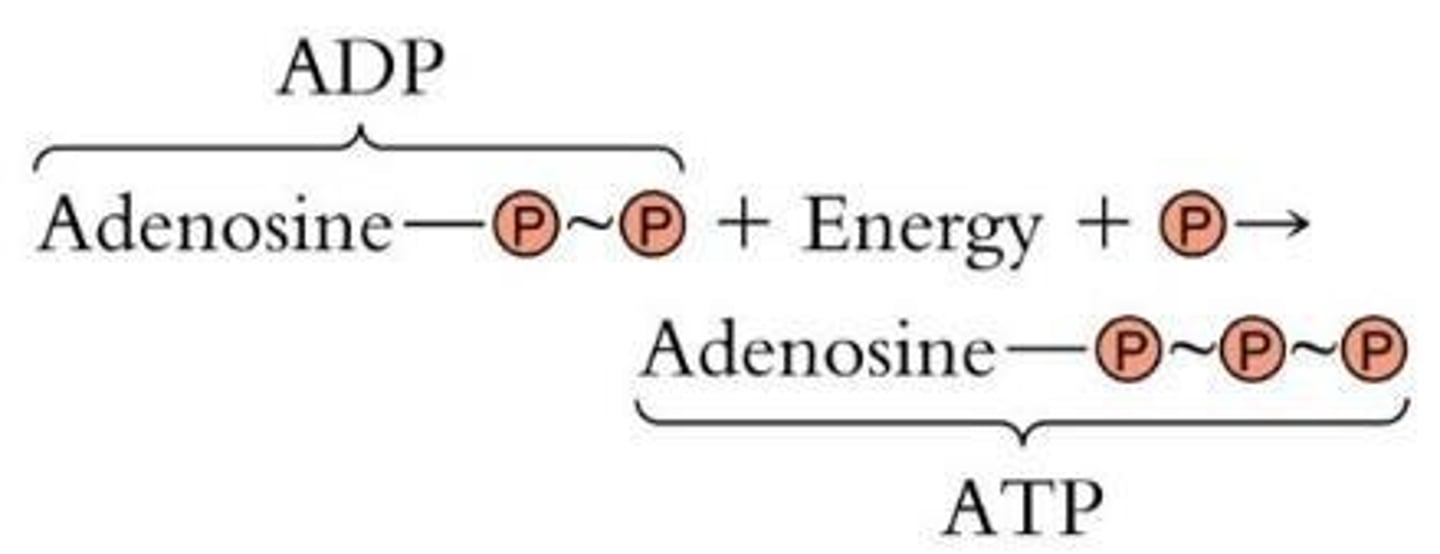
How is ATP generated from ADP?
By phosphorylation of ADP.
What are the end-products of glucose oxidation?
Pyruvic acid, ATP, and NADH.
How many ATP and NADH molecules are produced from one glucose molecule?
Two ATP and two NADH molecules.
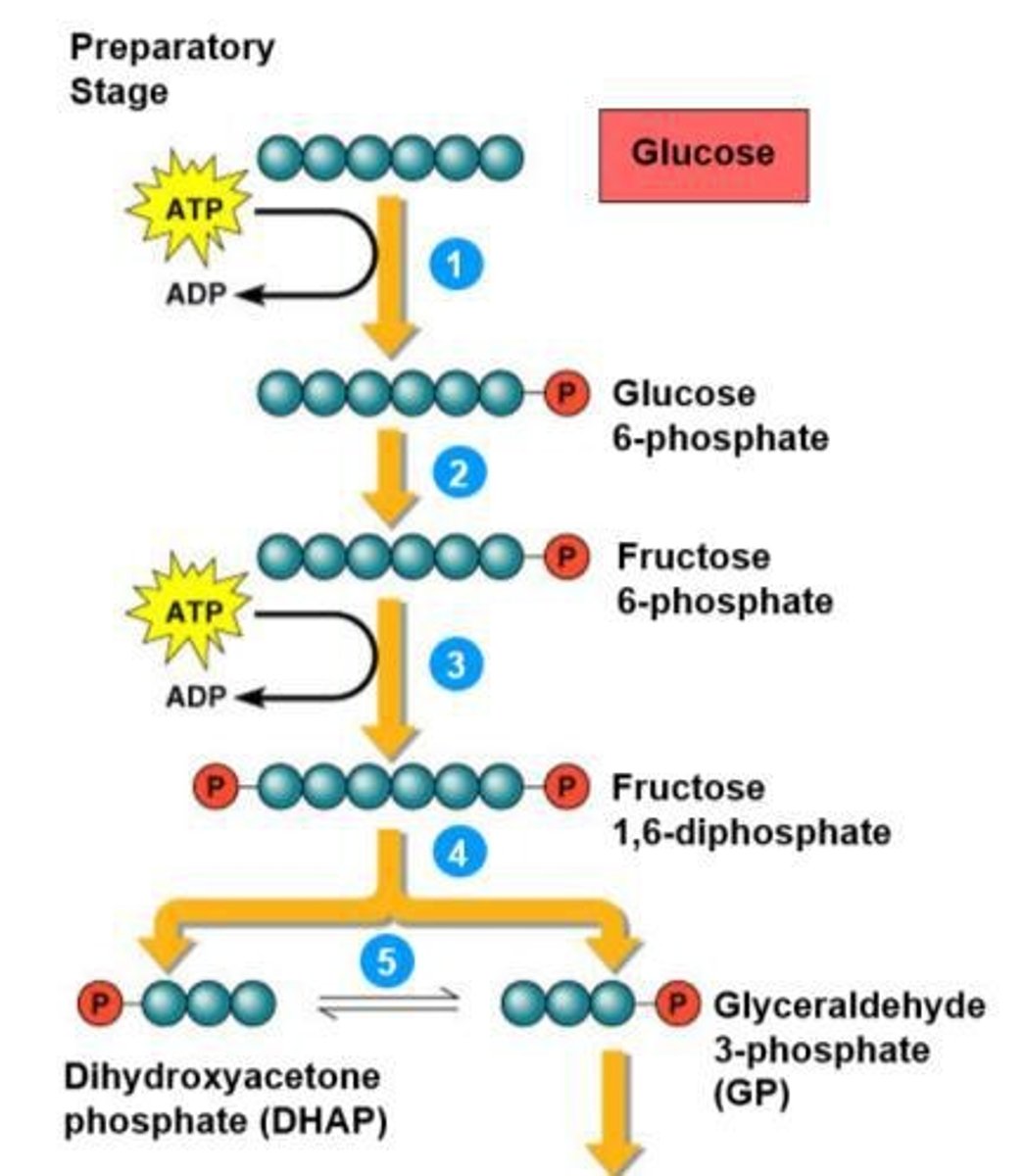
What is the preparatory stage of glycolysis?
2 ATPs are used, and glucose is split to form 2 glucose-3-phosphate.
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
The transfer of a high-energy phosphate group from a donor molecule to ADP to form ATP.
What mechanism uses energy from electron transfer to generate ATP?
Chemiosmosis.
What occurs during the energy-conserving stage of glycolysis?
2 glucose-3-phosphate are oxidized to 2 pyruvic acid, producing 4 ATP and 2 NADH.
How does ATP synthase generate ATP during chemiosmosis?
It is energized by protons moving through a channel, driving the phosphorylation of ADP.
What is photophosphorylation?
The generation of ATP through light energy causing chlorophyll to give up electrons.
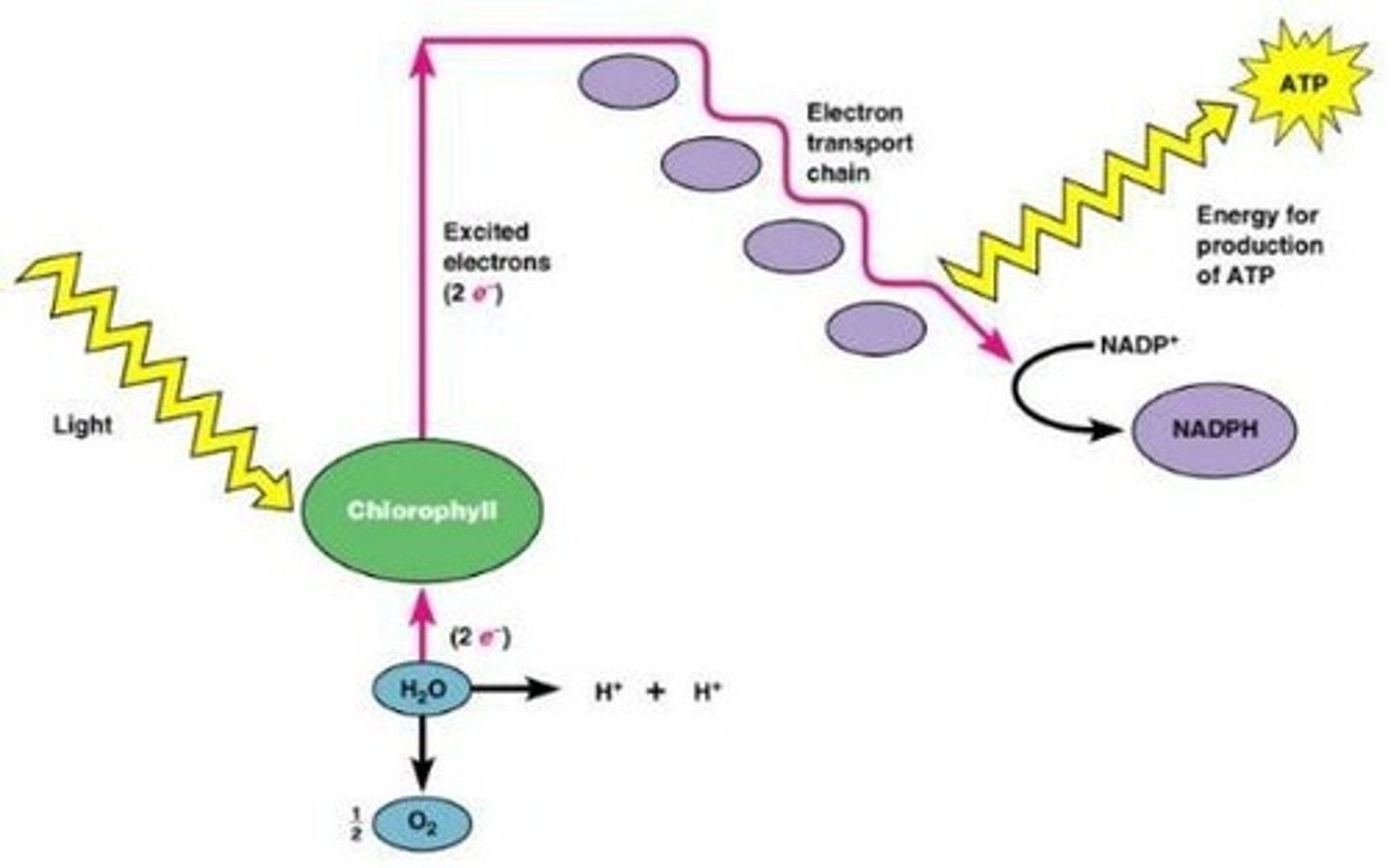
What are cyclic reactions in photosynthesis?
Reactions that produce ATP where electrons return to chlorophyll after passing through an electron transport chain.
What are non-cyclic reactions in photosynthesis?
Reactions that produce ATP and NADPH, where electrons are passed to NADP to form NADPH.
What is carbohydrate catabolism?
The breakdown of carbohydrates to release energy.
What are the two major types of glucose catabolism?
Respiration (complete breakdown) and fermentation (partial breakdown).
What is glycolysis also known as?
The Embden-Meyerhof pathway.
What is the primary function of glycolysis?
To oxidize glucose and produce energy.
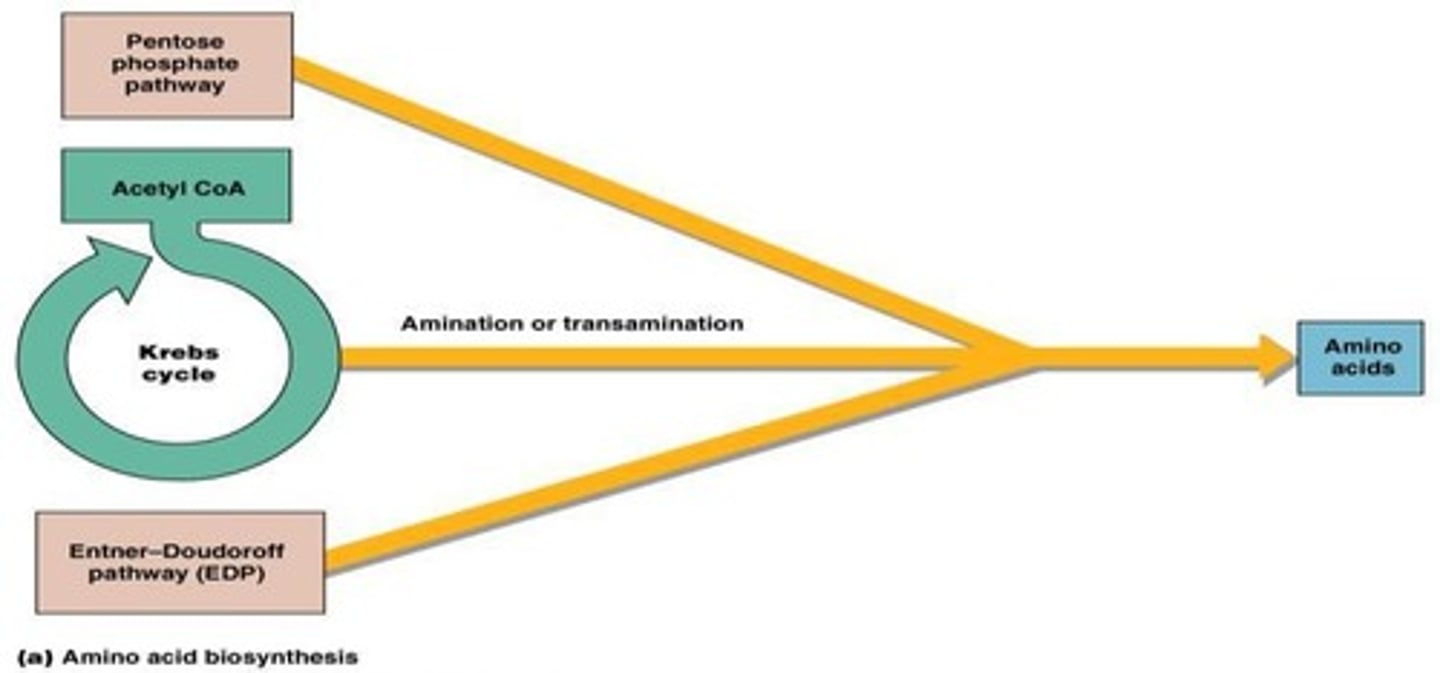
What is the pentose phosphate pathway?
An alternative to glycolysis that produces five-carbon sugars and high energy electrons.
What does the Entner-Doudoroff pathway yield from one glucose molecule?
One ATP, one NADPH, and one NADH.
Which bacteria typically use the Entner-Doudoroff pathway?
Gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas, Rhizobium, and Agrobacterium.
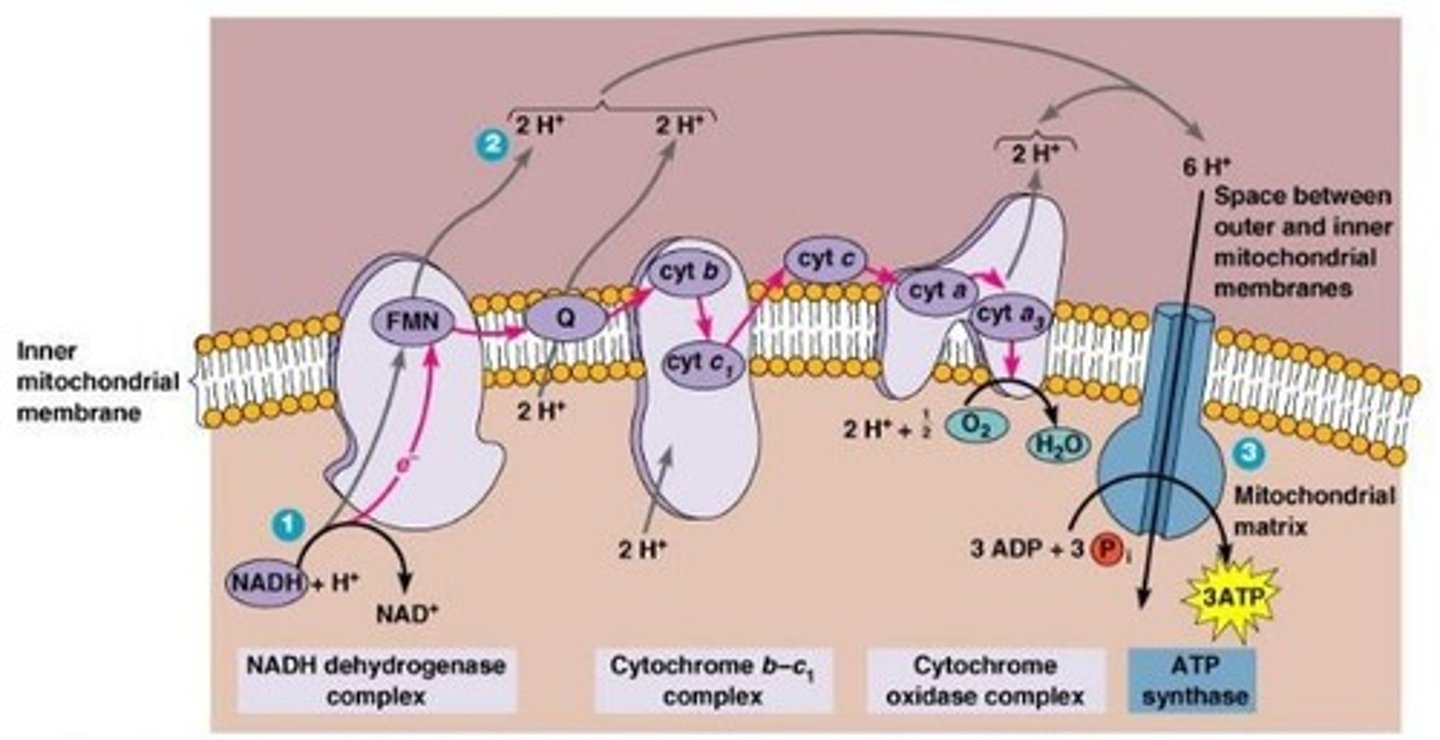
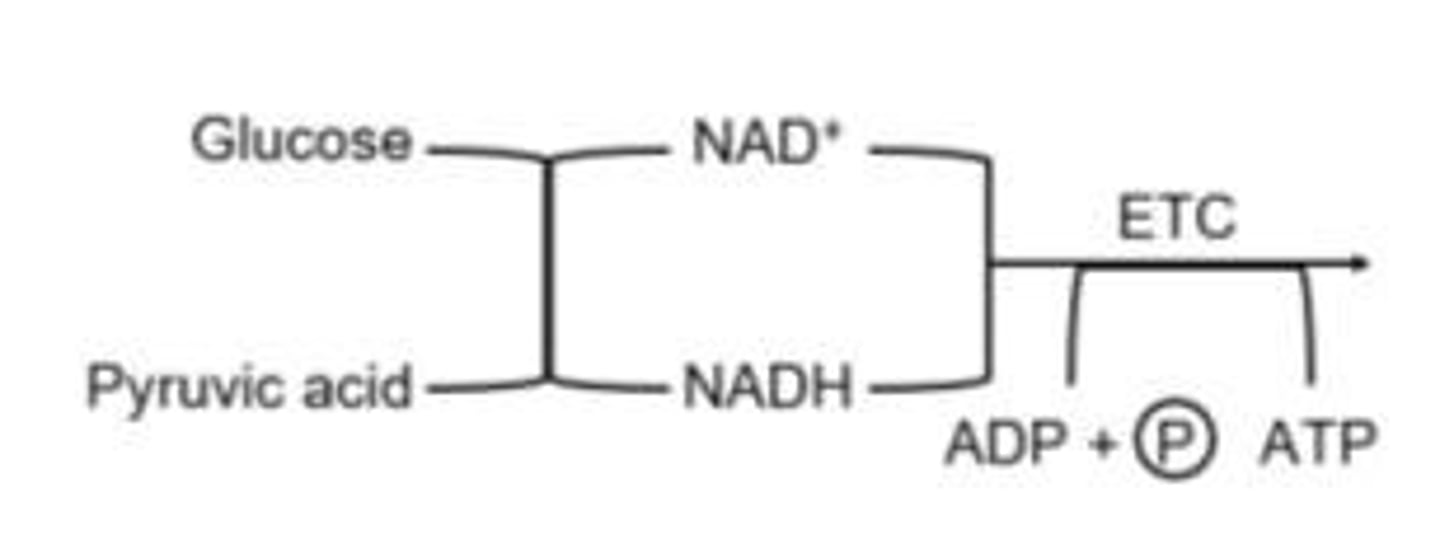
What is the role of the electron transport chain in cellular respiration?
To transfer electrons and drive proton pumps for ATP generation.
What is the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration?
Oxygen.
What happens to organic molecules during cellular respiration?
They are oxidized.
What is the significance of NADH in metabolism?
It carries electrons to the electron transport chain.
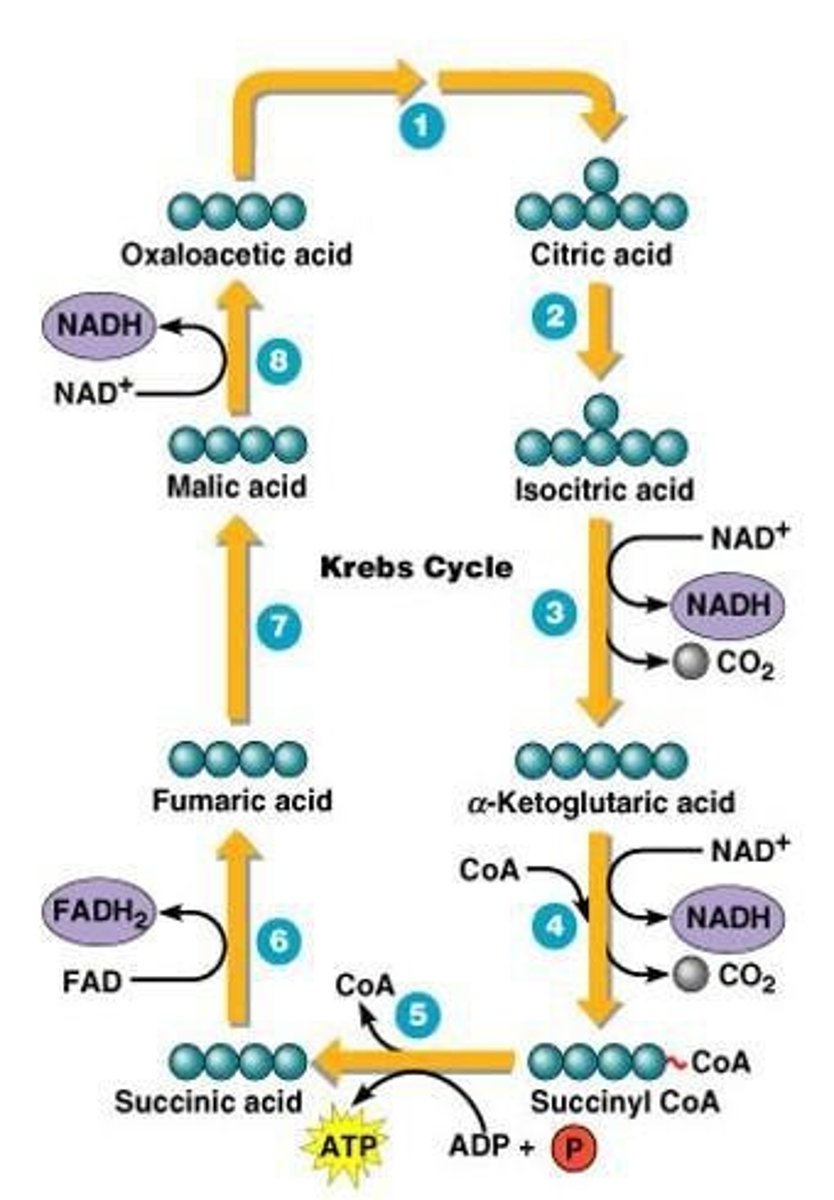
What is the main outcome of the Krebs cycle?
It produces energy carriers like NADH and FADH2 for the electron transport chain.
What is produced during oxidative phosphorylation?
ATP
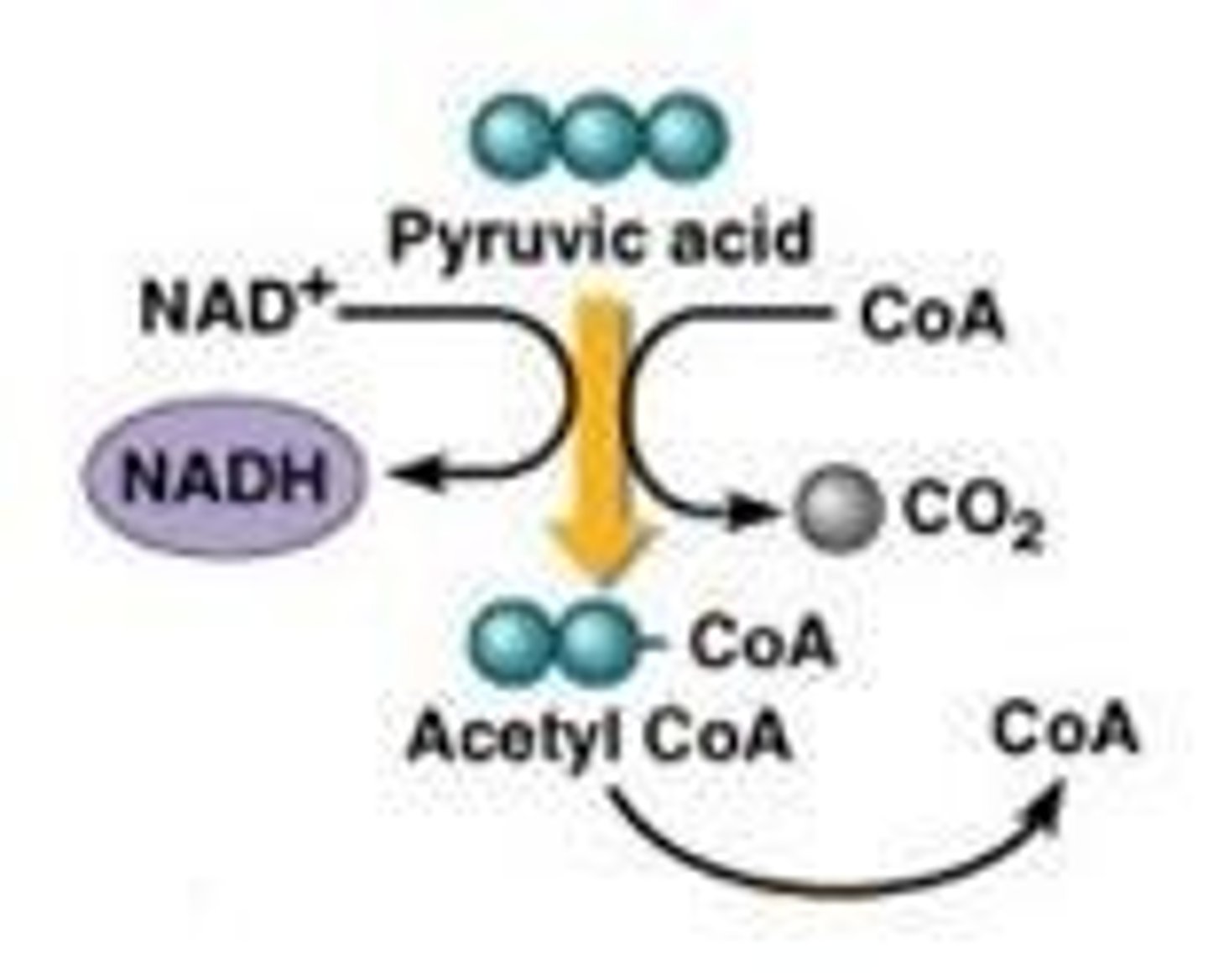
What occurs during the intermediate step between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle?
Pyruvic acid is oxidized and decarboxylated to produce acetaldehyde.
What is the role of coenzyme A in the decarboxylation process?
It helps remove a carbon dioxide molecule from pyruvic acid.
What are the main products of the Krebs cycle from one molecule of glucose?
Six molecules of NADH, two molecules of FADH2, and two molecules of ATP.
What is chemiosmosis?
The movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane down their electrochemical gradient, generating ATP.
What is the function of the electron transport chain?
To pass electrons through a series of carrier molecules, releasing energy used to produce ATP.
What happens to protons during the electron transport chain?
They are pumped across the membrane, generating a proton motive force.
What is fermentation?
A process that releases energy from sugars or other organic molecules by oxidation without requiring oxygen.
What is the final electron acceptor in fermentation?
An organic molecule.
How many ATP molecules are produced during fermentation?
Two ATP molecules by substrate-level phosphorylation.
What is the difference between anaerobic respiration and fermentation?
Anaerobic respiration uses the Krebs cycle and electron transport chain, while fermentation does not.
Where are electron carriers located in eukaryotes?
In the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Where are electron carriers located in prokaryotes?
In the plasma membrane.
What is the significance of NAD+ in cellular respiration?
It is reduced to NADH, carrying electrons to the electron transport chain.
What is produced during the decarboxylation of pyruvic acid?
One CO2 molecule and one acetyl group linked to CoA (acetyl CoA).
What is the role of ATP synthase in cellular respiration?
It uses the energy from protons moving back across the membrane to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate.
What type of reactions occur in metabolic pathways?
Catabolic reactions (breaking down molecules) and anabolic reactions (building up molecules).
What is the relationship between glycolysis and fermentation?
Fermentation uses glycolysis to generate ATP in the absence of oxygen.
What is the process of oxidation in the Krebs cycle?
Acetyl CoA is oxidized, producing NADH and FADH2.
What is the purpose of the Krebs cycle?
To convert acetyl CoA into energy carriers (NADH, FADH2) and ATP.
What happens to electrons as they move through the electron transport chain?
They are passed down a series of carrier molecules, causing them to be oxidized and reduced.
How does anaerobic respiration differ from aerobic respiration?
Anaerobic respiration uses an inorganic molecule other than O2 as the final electron acceptor.
What is the goal of respiration in cells?
The production of energy (ATP from ADP and phosphate).
What is aerobic respiration?
A process where the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain is molecular oxygen (O2).
What are some final electron acceptors in anaerobic respiration?
NO3- (nitrates), SO4 2- (sulfates), and CO3 2- (carbonates).
What products result from the reduction of nitrate (NO3-) in anaerobic respiration?
Nitrite (NO2-), nitrogen gas (N2), and water (H2O).
What is produced when sulfate (SO4 2-) is reduced in anaerobic respiration?
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) and water (H2O).
What is the end product of carbonate (CO3 2-) reduction in anaerobic respiration?
Methane (CH4) and water (H2O).
What occurs during lactic acid fermentation?
Pyruvic acid is reduced by NADH to lactic acid.
Which organisms are known as lactic acid fermenters?
Streptococcus and Lactobacillus.
What do yeast produce during alcohol fermentation?
Ethanol and carbon dioxide (CO2).
What is the difference between homolactic and heterolactic fermentation?
Homolactic fermentation produces only lactic acid, while heterolactic fermentation produces lactic acid and other compounds.
What is the role of Acetobacter in fermentation?
It ferments ethanol to acetic acid (vinegar).
What is the function of fermentation tests in microbiology?
To determine whether an organism can ferment a carbohydrate to produce acid and gas.
What are the ATP yields from glycolysis, the intermediate step, and the Krebs cycle in aerobic respiration?
Glycolysis: 4 ATP, Intermediate step: 0 ATP, Krebs cycle: 2 ATP.
What is the total ATP produced from the complete oxidation of 1 glucose using aerobic respiration?
38 ATP (4 from substrate-level phosphorylation and 34 from oxidative phosphorylation).
What is the process of lipid catabolism?
Lipases hydrolyze lipids into glycerol and fatty acids, which are then catabolized by beta oxidation.
What does beta oxidation produce?
Two carbon units linked to CoA to make acetyl CoA.
Where does the Krebs cycle occur in eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
In eukaryotes, it occurs in the mitochondrial matrix; in prokaryotes, it occurs in the cytoplasm.
What are the light-dependent reactions in photosynthesis?
The conversion of light energy into chemical energy (ATP).
What is the purpose of the synthesis phase in photosynthesis?
Fixing carbon into organic molecules.
What are the end products of fermentation by Escherichia coli?
Ethanol, lactic acid, succinic acid, acetic acid, CO2, and H2.
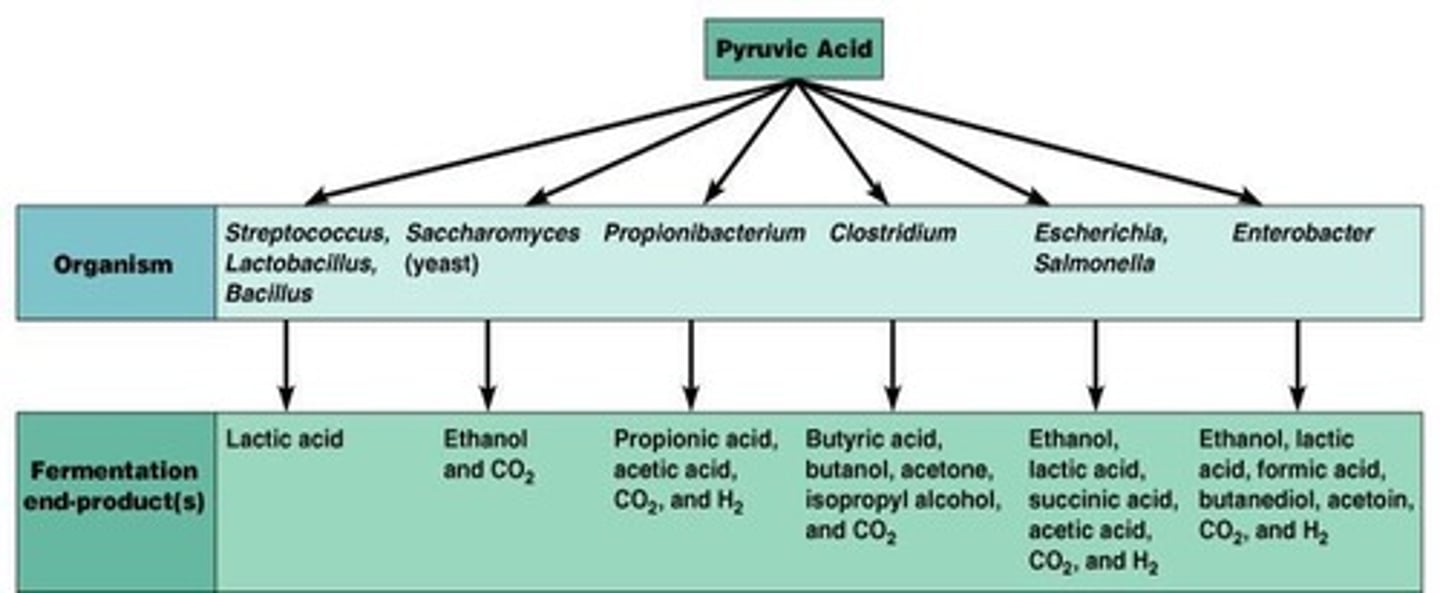
What are the end products of fermentation by Enterobacter?
Ethanol, lactic acid, formic acid, butanediol, acetoin, CO2, and H2.
What is the significance of the inverted Durham tube in fermentation tests?
It traps gas produced during fermentation, indicating positive fermentation.

What is the process of decarboxylation in the intermediate step of respiration?
It involves the removal of a carboxyl group from pyruvate, producing acetyl CoA.
What is the primary role of lipids in biological membranes?
To serve as structural components.
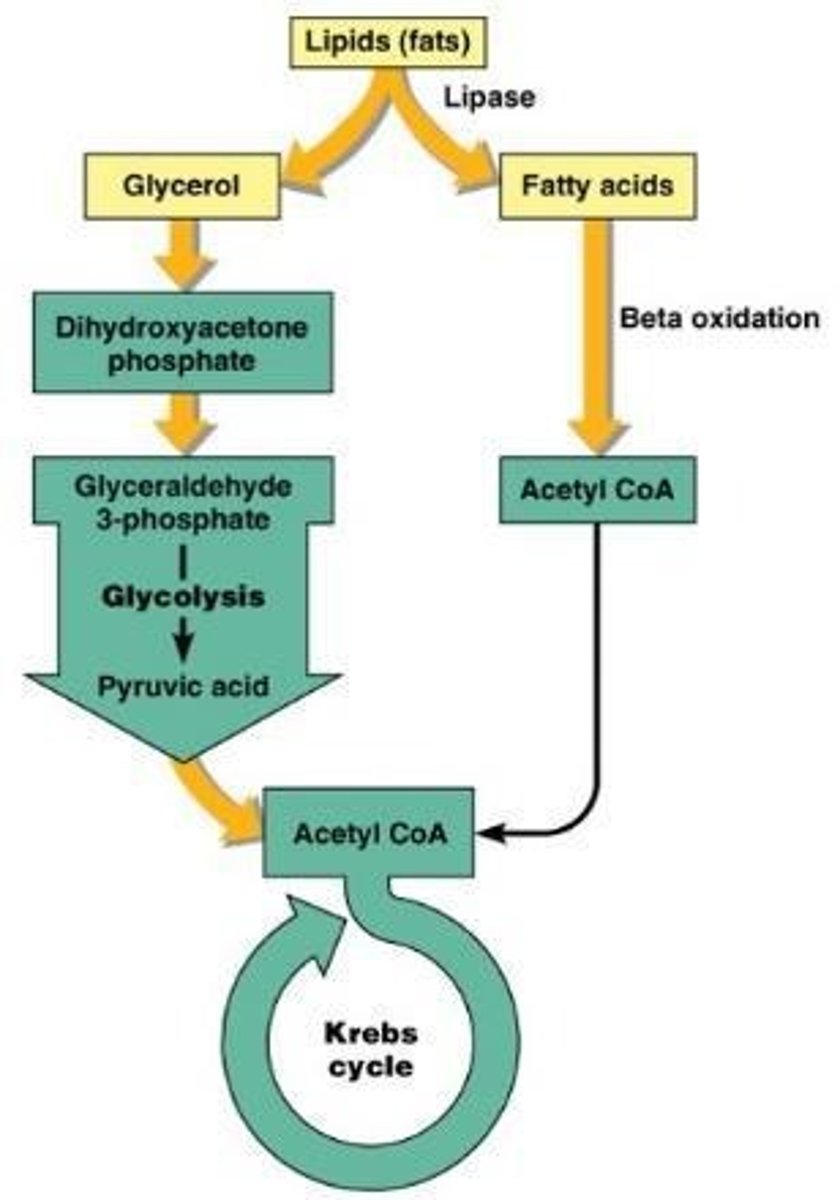
What type of lipids are most commonly found in biological membranes?
Phospholipids.
What lipid is found in plasma membranes of eukaryotic cells and has a different structure from phospholipids?
Cholesterol.
What are waxes and their significance in bacteria?
Waxes are lipids that are important components of the cell wall of acid-fast bacteria.
What pigments do carotenoids provide in some microorganisms?
Red, orange, and yellow pigments.
What is the function of lipids besides serving as structural components?
They function as energy storage.
What is the process by which proteins are broken down into amino acids?
Protein catabolism.
What are the products of protein catabolism by extracellular proteases?
Amino acids.
What is the Krebs cycle's role in amino acid synthesis?
It provides precursors or intermediates for amino acid synthesis.
What is the light-dependent reaction in photosynthesis?
It converts light energy into ATP and reduces NADP+ to NADPH.
What is the main difference between oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis?
Oxygenic photosynthesis uses water as a hydrogen donor and releases O2, while anoxygenic photosynthesis uses H2S and produces sulfur granules.
What is the overall equation for oxygenic photosynthesis?
6CO2 + 12H2O + Light energy → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O.
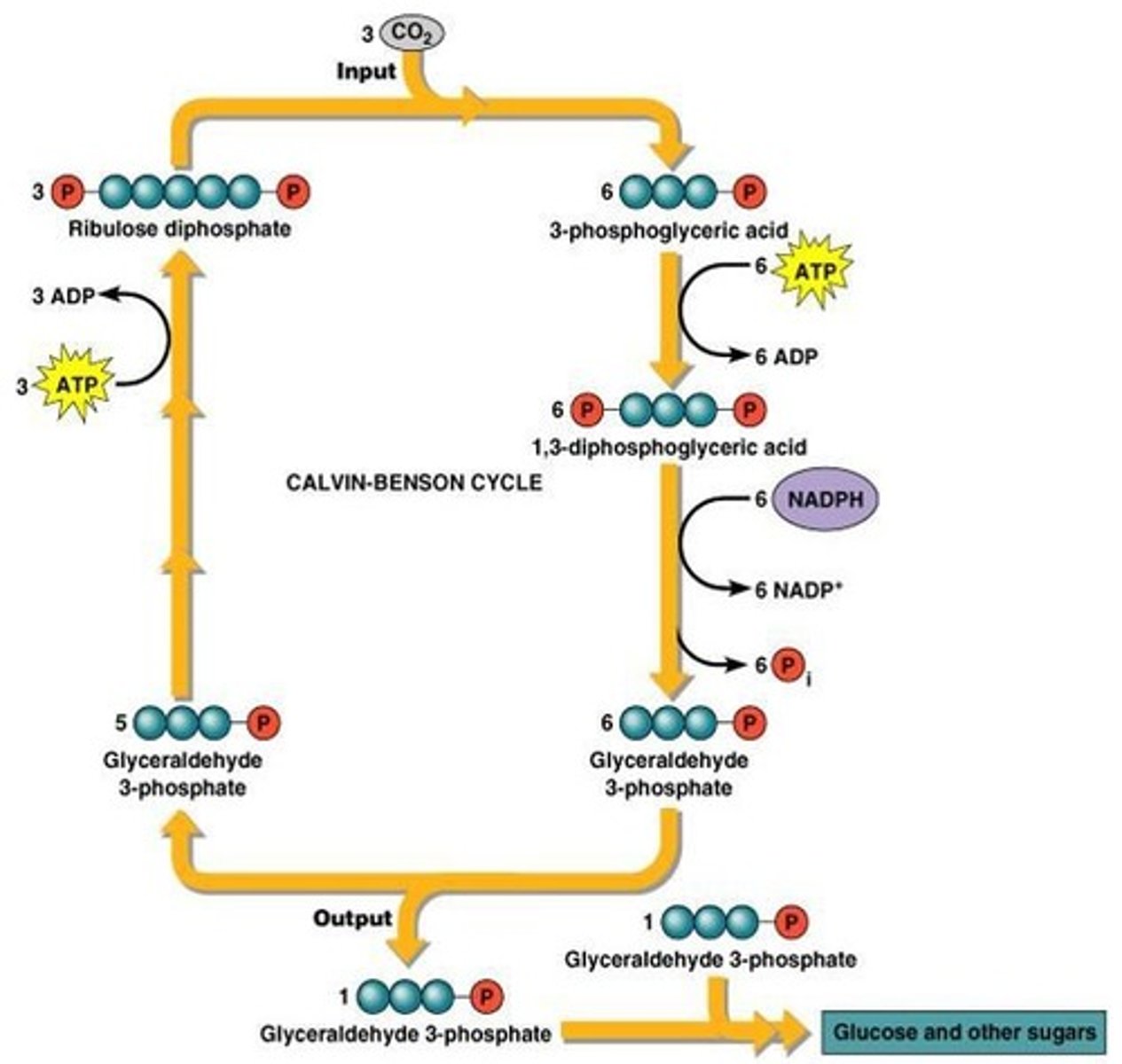
What is carbon fixation?
The conversion of CO2 from the atmosphere into more reduced carbon compounds, primarily sugars.
What are the two stages of photosynthesis?
Light-dependent reactions and light-independent (dark) reactions.
What is amination in the context of amino acid synthesis?
The process of adding an amine group to pyruvic acid to convert it into an amino acid.
What is cyclic photophosphorylation?
A process in which electrons are released from chlorophyll by light, pass through the electron transport chain, and return to chlorophyll, generating ATP.
What is the role of NADPH in photosynthesis?
It acts as an energy-rich carrier of electrons.
What happens during the light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
Electrons and energy from ATP are used to reduce CO2 to sugar.
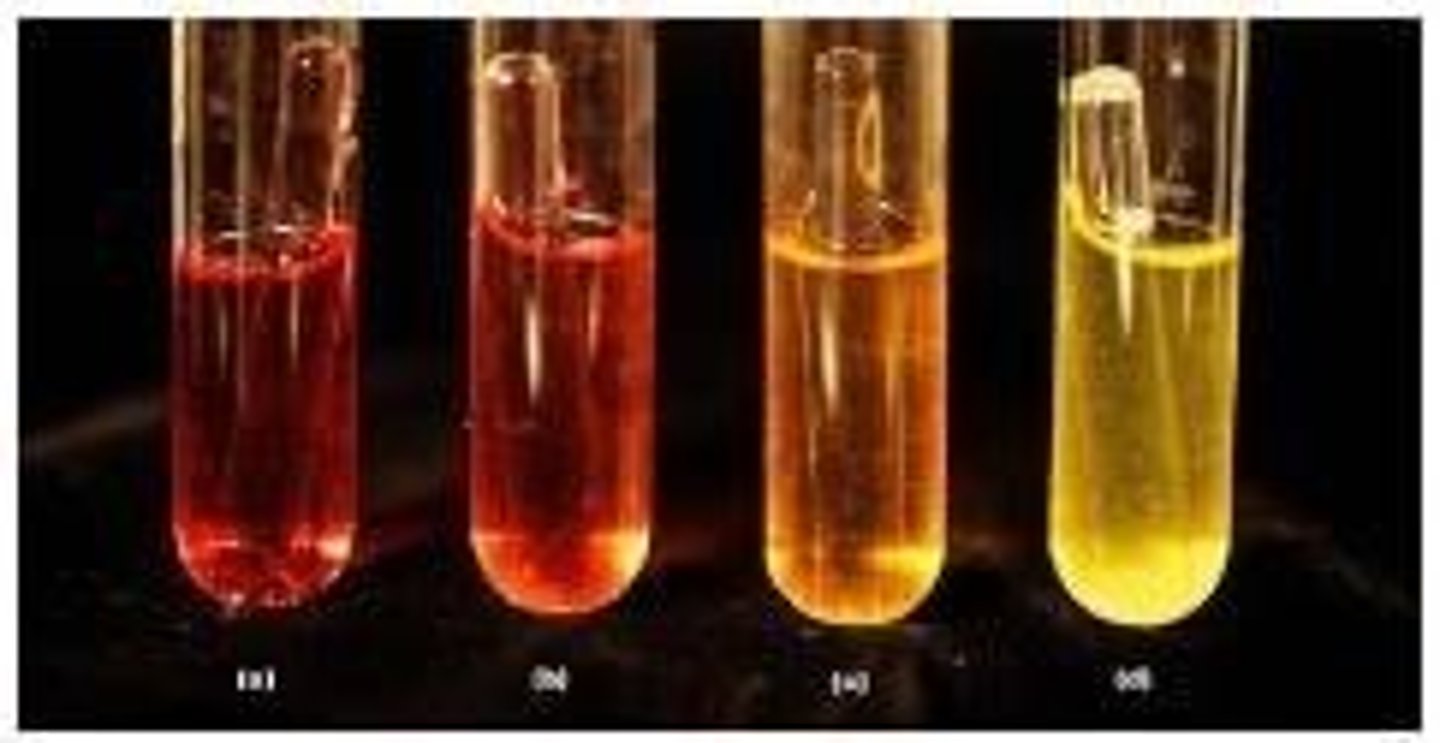
What is the significance of biochemical tests in microbiology?
They are used to identify bacteria based on their metabolic capabilities.
What color does a pH indicator turn when bacteria produce acid from glucose?
Yellow.
What color indicates alkaline products from decarboxylation in a biochemical test?
Purple.
What is the purpose of using dichotomous keys in identifying bacteria?
To provide a systematic method for identifying bacteria based on specific metabolic traits.
What is the role of light energy in cyclic photophosphorylation?
It excites electrons in chlorophyll, leading to ATP formation.
What is the relationship between photosynthesis and the recycling of carbon?
Photosynthesis converts CO2 into organic compounds, facilitating the recycling of carbon essential for life.
Which bacteria can use citric acid as their sole carbon source?
Enterobacter can use citric acid as their sole carbon source.
Which bacteria generally produce H2S?
Salmonella generally produces H2S.
Which bacteria produces lysine decarboxylase?
Shigella produces lysine decarboxylase.
What type of bacteria are characterized by anoxygenic photosynthesis?
Green bacteria and purple bacteria are characterized by anoxygenic photosynthesis.
What type of chlorophyll do green and purple bacteria use?
Green bacteria use bacteriochlorophyll, while purple bacteria use bacteriochlorophyll a.
What is the process by which electrons are replaced in noncyclic photophosphorylation?
Electrons released from chlorophyll are replaced by electrons from H2O.
What is produced as a result of noncyclic photophosphorylation?
NADPH is produced as a result of noncyclic photophosphorylation.