AUBF 311: Microscopic Exam of Urine
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Microscopic Exam
3rd part of routine urinalysis with the purpose to detect and identify insoluble materials present in urine
10 - 15 mL
Standard amount of urine specimen volume
12 mL
Recommended amount of urine specimen volume
Cintrifugation
400 RCF for 5 minutes
20 uL or 0.02 mL
Recommended volume of sediment for microscopy
10
Minimum number of fields observed for microscopic exam of urine
LPO
Objective lens used to detect casts and to ascertain general composition of the sediment
Near edges of cover slip
Casts tend to locate in this are when using conventional glass-slide method for urinary microscopy
Reduced Light
Due to many sediment constituents having a refractive index, it is essential that they’re observed under what condition when using bright-field microscopy?
Casts
This sediment is reported as average number per LPF
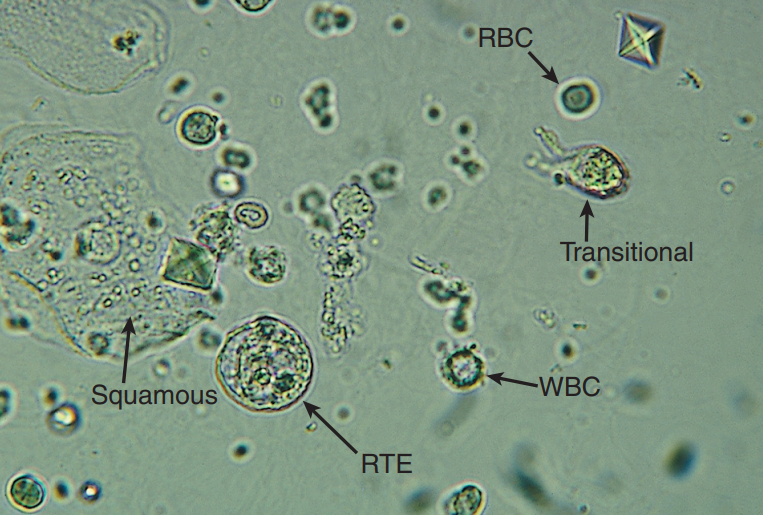
RBC
WBC
These sediments are reported as average number per HPF
Epithelial cells
Crystals
These sediments are reported as semi-quantitative terms:
Rare (1+)
Few (2+)
Moderate (3+)
Many (4+)
Addis Count
Quantitative measurement of formed elements of urine (12-hr specimen)
Uses hemacytometer
Sternheimer-Malbin Stain
Most commonly used supravital stain
Consists of Crystal Violet + Safranin O
WBCs
Epithelial cells
Casts
Toluidine Blue
0.5%
Metachromatic stain that enhances nuclear detail
WBCs
Renal tubular epithelial (RTE) cells
Acetic Acid
2%
Lyses RBCs and enhances nuclei of WBCs
RBCs
WBCs
Yeast
Oil droplets
Crystals
Oil Red O + Sudan III
Lipid stains that dyes TAGs and neutral fats into orange-red, but not cholesterol
Uses polarizing microscopy
Free fat droplets
Lipid-containing sediments
Gram Stain
Stain used for bacterial casts (ewan ko na lang sayo kung ‘di mo pa alam ‘to)
Hansel Stain
Stain used to identify EOs in urine
Composed of:
Eosin Y
Methylene blue
Prussian Blue
Stains structures containing iron
yellow-brown granules of hemosiderin (cells and casts)
Bright-Field Microscope
Microscope used for routine urinalysis
Phase-Contrast Microscope
Microscope that enhances visualization of elements with low refractive index
Hyaline cast
Mixed cellular cast
mucous threads
Trichomonas vaginalis
Bacteria that has low refractive index, observed using phase-contrast microscope
Polarizing Microscope
Microscope that detects presence/absence of birefringence and aids in identification of:
lipids
crystals
Dark-Field Microscope
Microscope that aids in identification of Treponema pallidum (Syphilis)
Fluorescence Microscope
Microscope that allows visualization of naturally fluorescent microorganisms or those stained by fluorescent dyes
“Immunofluorescence”
Bacteria
Viruses
Interference-Contrast Microscope
Microscope that produces a 3-Dimensional, layer-by-layer imaging of a specimen
Modulation-Contrast Microscope (Hoffman)
Differential Interference-Contrast Microscope (Nomarski)
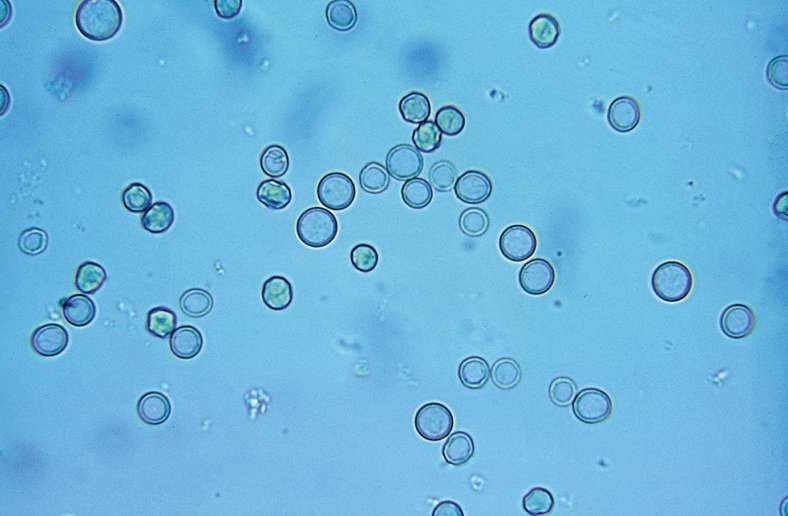
RBC
0 - 3 HPF
Hematuria
Crenate or Shrink = hypersthenuric / concentrated urine
Swell and Hemolyze = hyposthenuric / diluted urine
Sources of Identification Error:
Yeast
Oil droplets
Air bubbles
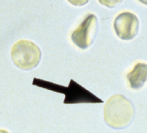
Ghost Cells
Term used to refer to RBCs that only contains the cell membrane due to leakage of Hgb caused by hemolysis
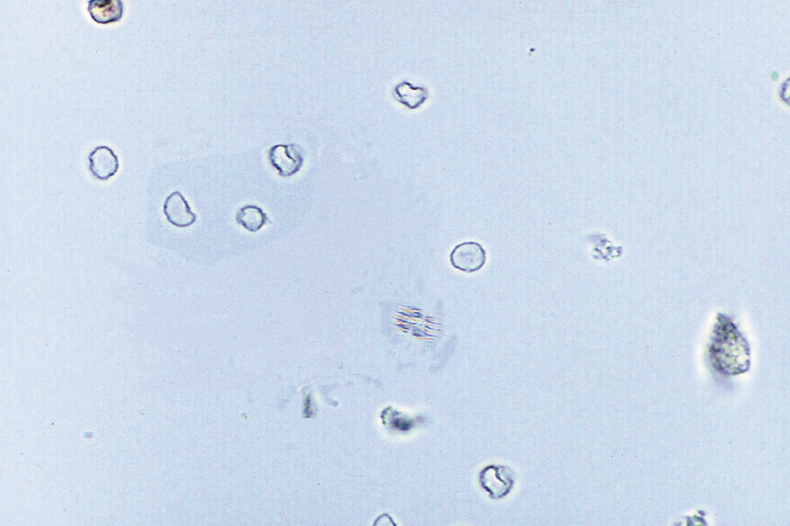
Dysmorphic RBCs
RBCs that exhibit varying size (anisocytosis) and shape (poikilocytosis)
Primarily associated with glomerular bleeding = acanthocytes
Strenous exercise
WBCs
0 - 8 HPF
Pyuria (pus) / Leukocyturia
NEUTs: predominant WBC, swells and lyse in hyposthenuric urine
EOs: primarily associated with drug-induced interstitial nephritis (acute)
Mononuclear cells: LYMPHs, MONOs, macrophages, and histiocytes
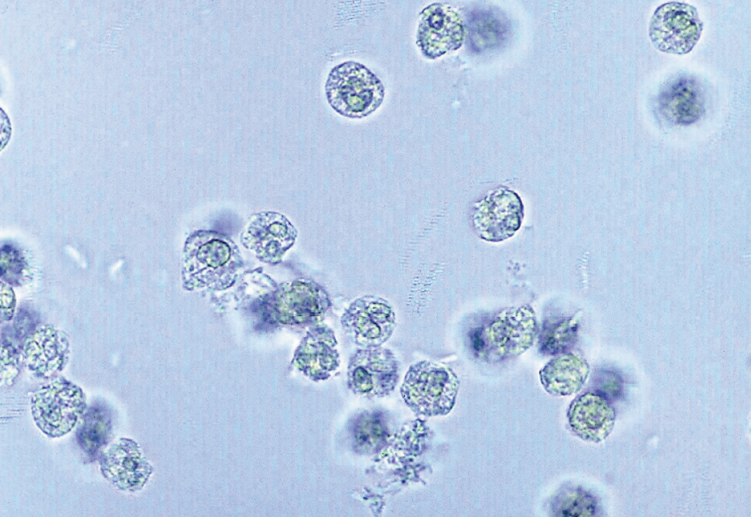
Glitter Cells
Other term for Neutrophil; granules undergo brownian movement, producing sparkling appearance
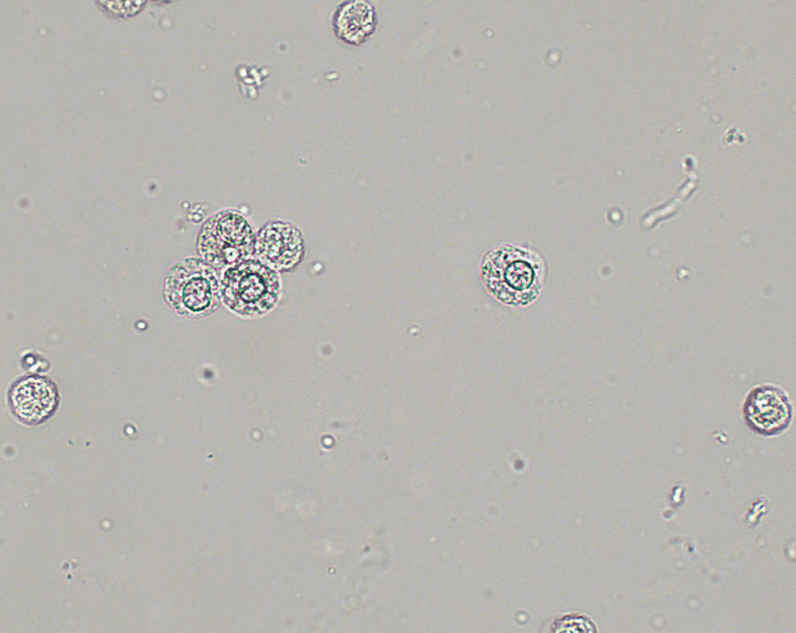
Squamous Epithelial Cells
Largest cells w/ abundant, irregular cytoplasm
Represent normal cellular sloughing and have no pathological significance
Originate from linings of:
Female: vagina + urethra
Male: lower urethra
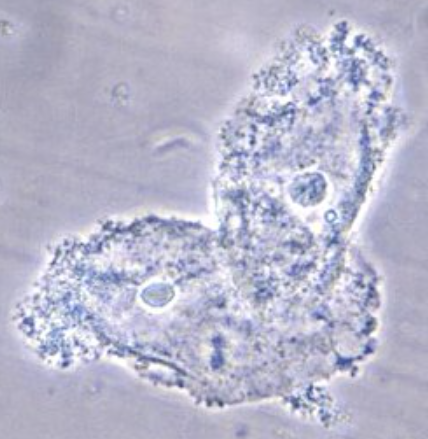
Clue Cell
Squamous epithelial cell variation that is indicative of bacterial vaginosis by Gardnerella vaginalis
must be 70% covered with Gardnerella coccobacillus
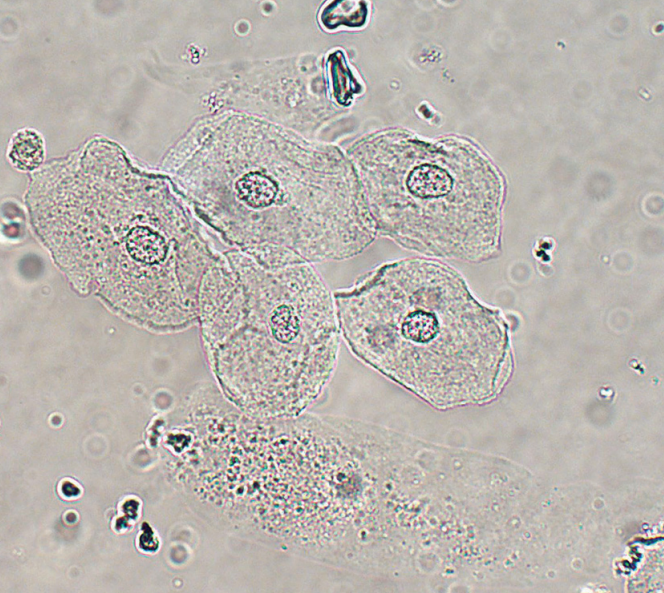
Transitional Epithelial Cells
Smaller than squamous cells and have centrally located nucleus; water absorbability
Originates from lining of:
Both: renal pelvis, calyces, ureters, and bladder
Male: upper urethra
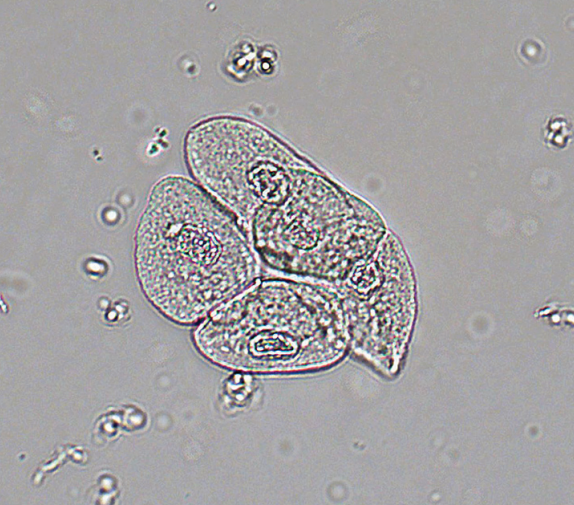
Renal Tubular Epithelial (RTE) Cells
Epithelial cells that vary in size and shape depending on are of origin and is indicative of necrosis of renal tubules
PCT: “columnar/convoluted cells”; larger, rectangular, resemble casts
DCT: smaller, round, resemble WBCS and spherical transitional cells
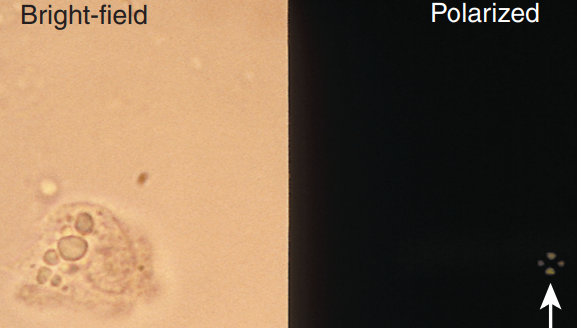
Oval Fat Bodies
Lipid-containing RTE cell (may also be mononuclear cells)
Highly refractile
Seen together with free-floating fat droplets
Maltese cross formation in polarizing microscope
“Lipiduria”
glomerular damage (nephrotic syndrome)
severe tubular necrosis
diabetes mellitus
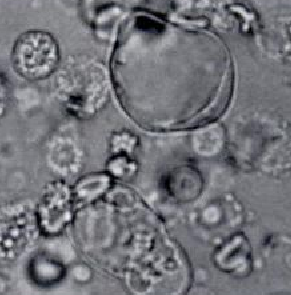
Bubble Cells
RTE cell containing large, nonlipid-filled vacuole
Acute Tubular Necrosis
False
True or False: Urine specimen found with bacteria indicates UTI
True
True or False: Urine specimen found with bacteria and WBCs indicates UTI
Enterobacteriaceae
Bacterial family that commonly cause UTIs
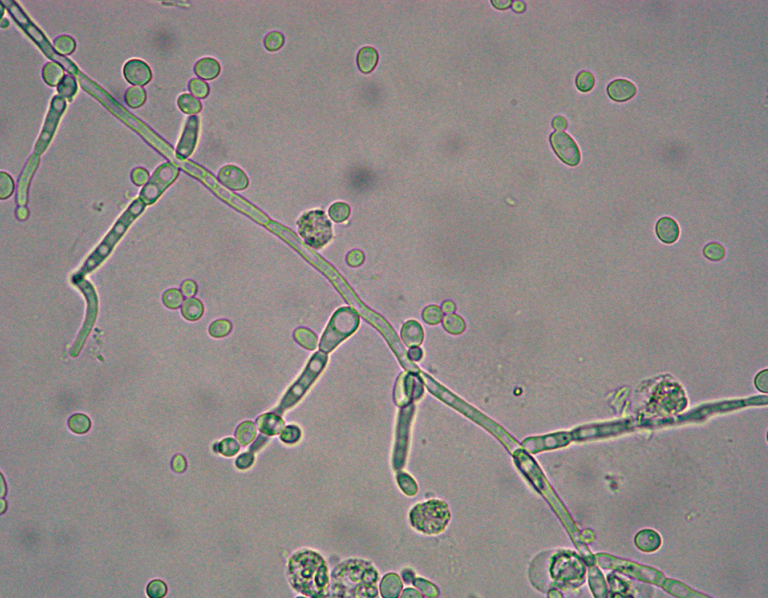
Yeast
Small, refractile oval structures
Severe infection = branched / mycelial form
Candida albicans
Trichomonas vaginalis
Most encountered parasite in urine
Pear-shaped flagellate
Rapid darting motility
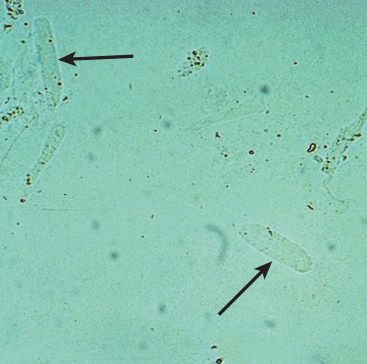
Hyaline Cast
Cast most frequently seen
“Prototype cast”
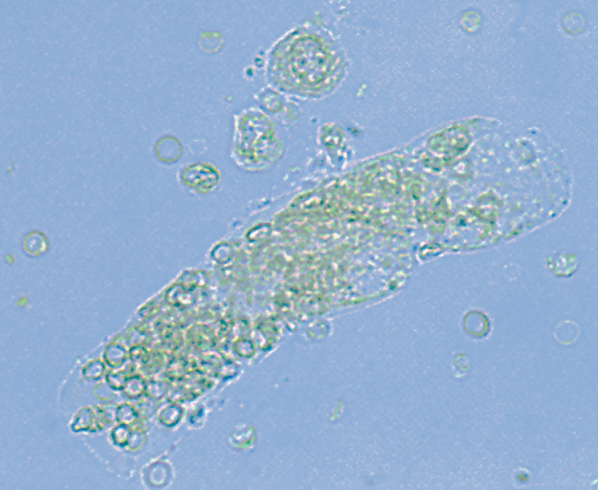
Cylindruria
Presence of urinary casts
RBC Cast
Most fragile cast that indicates bleeding w/n the nephron
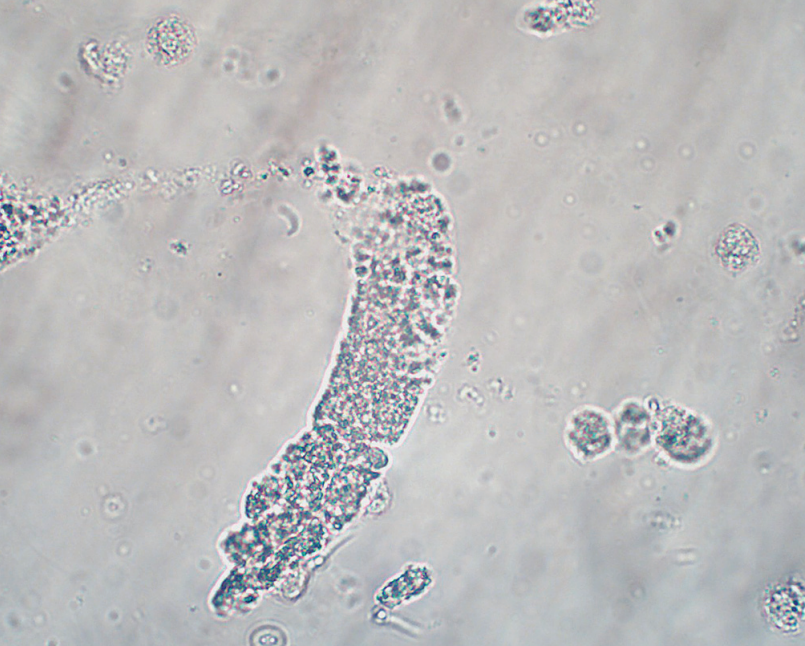
WBC Cast
Indicates infection or inflammation w/n nephron
“Pyelonephritis”
Pseudoleukocyte Cast
Clump of WBC typically seen in lower UTI
Not a true cast
Absence of cast matrix
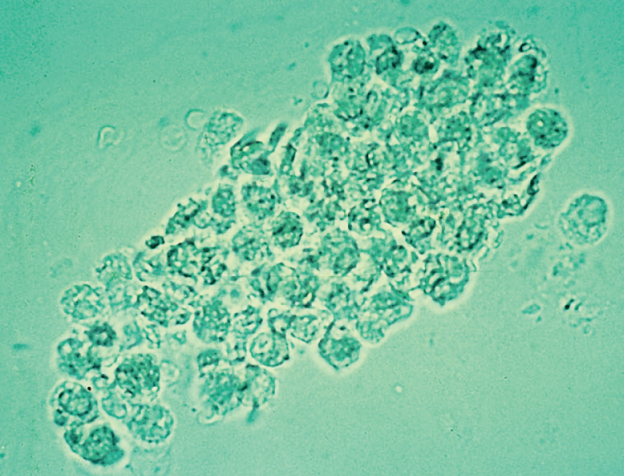
Bacterial Cast
Their presence should be considered when WBC CAST and many free WBCs and bacteria are seen in the sediment
“Pyelonephritis”
Similar to granular cast
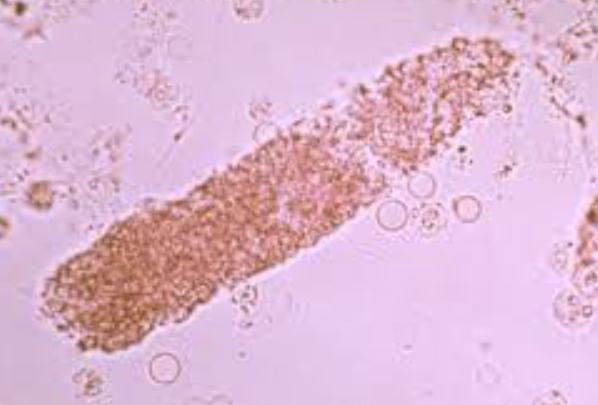
Uromodulin
Major constituent of casts
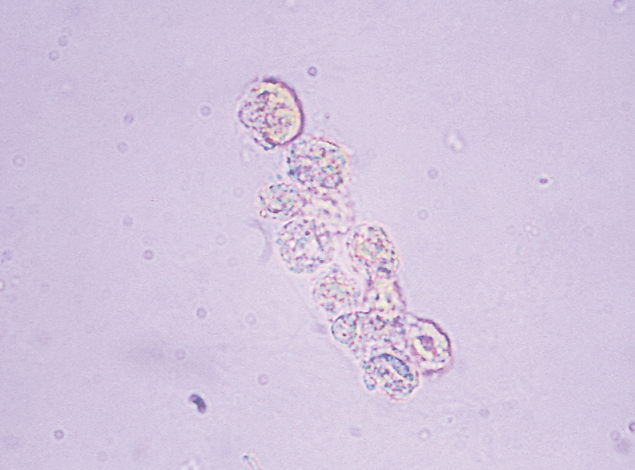
Epithelial Cell Cast
Casts containing RTE due to advanced tubular destruction
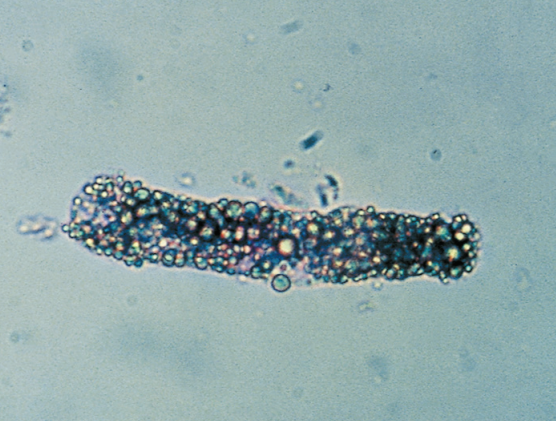
Fatty Cast
Highly refractile cast matrix that contains fat droplets and oval fat bodies
Granular Cast
Casts that are coarsely and finely granular
Granules originate from RTE cell lysosomes
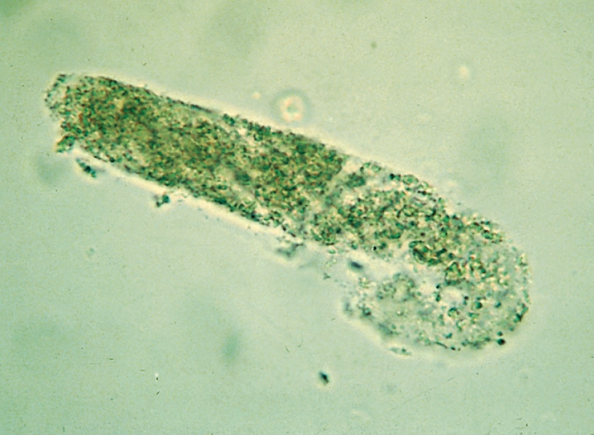
Waxy Cast
Final degenerative form of all types of cast
Brittle and w/ jagged ends
“Chronic Renal Failure”
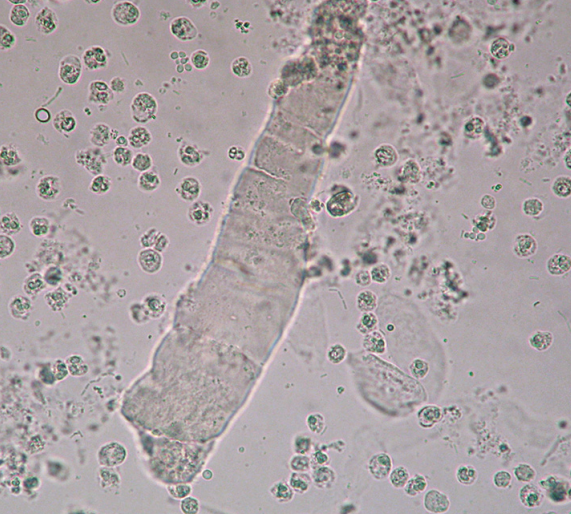
Broad Cast
Cast that indicates destruction (widening) of tubular walls
“Renal Failure Cast”
Any cast can be broad
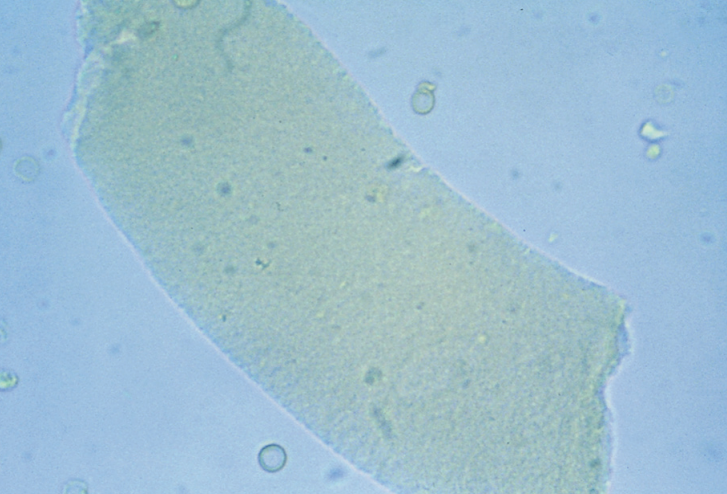
Crystal Formation
Precipitation of urine solutes and medications with iatrogenic compounds in
Low temperature
High SG