Anatomy intro quiz
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Anatomy
the study of the structure of an organism
Physiology
The study of how the organism’s body functions
The smallest unit of all living things (1st level)
Cell
Similar cells with a common function (2nd level)
tissue
Made of 2 or more types of tissues (3rd level)
Organ
Group of organs working toward a common goal (4th level)
Organ system
highest level of structural organization for an individual
organism
What are the necessary life functions
Maintaining boundaries, movement, Responsiveness, Digestion,Metabolism, Excretion, Reproduction, and growth
What are the 5 survival needs
Nutrients, Oxygen, Normal Body Temp., Water, normal atmospheric pressure
Integumentary Organs
skin
Nervous system organs
Brain,Sensory receptor, spinal cord, and nerves
Skeletal System organs
Cartilages, joint, bones
Endocrine System
Pineal gland, Pituitary gland, thyroid gland, thymus gland, adrenal glands , pancreas, tetis (male), ovary (female)
Muscular Systems organ
Skeletal muscles
Cardiovascular System Organ
Heart, Blood vessels
Lymphatic Systems Organ
Thoracic duct, Lymph nodes, Lymphatic vessels
Digestive System Organ
Oral cavity, Esophagus, Stomach, Small Intestine, LArge Intestine, Rectum, Anus
Respiratory System Organs
Nasal cavity, Pharynx, LArynx, Trachea, Bronchus, Left lung
Urinary System
Kidney, Ureter, Urinary bladder, Urethra
Male and female Reproductive Systems Organ
MALE prostate gland, Seminal vesicles, PEnis, Vas deferens, Testis, Scrotum
FEMALE mammary glands, Uterine tube, Ovary, Uterus, Vagina
Integumentary function
Acts as a abarrier to protect deeper tissues, regulates temperature, controls water loss
Nervous functions
Acts as a signla to the body that send messages tot he brain and or the spinal cord if there is a change or irritant from the outsde of the body
Skeletal functions
SUpports and provides a framework to help the skeletal muscles use to move and acts as a protective layer
Endocrine functions
Controls the bodies activities produces hormones and releases them to the blood to travel to organ
Muscular function
Contract and shorten to create movement in the body
Cardiovascular functions
Uses blood to transfer oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and other things to and from the tissue cells
Lymphatic functions
Returns fluids to the blood to help the blood recycle blood through the blood vessels to keep it circulating: They also help cleanse the blood and house cells involved with immunity
Digestive functions
Break down food and deliver products to the blood to be dispersed through the blood or comes out of the body as feces
Respiratory Functions
Keeps the body supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide
URinary Functions
Produces wastes as by-products and removes the nitrogen-containing waste form the blood and flushes them from the body in urine; maintains the body’s water and salt balance and the acids in the blood
Reproductive functions
To produce offspring
MAle produces sperms
Female produces eggs or ova and provide the sit for the development of the fetus once fertilized
Anatomical position
Terminology helps anatomists discuss parts of the body easily and efficiently
-Body is straight with feet slightly apart and thumbs pointed away from the body
directional terms
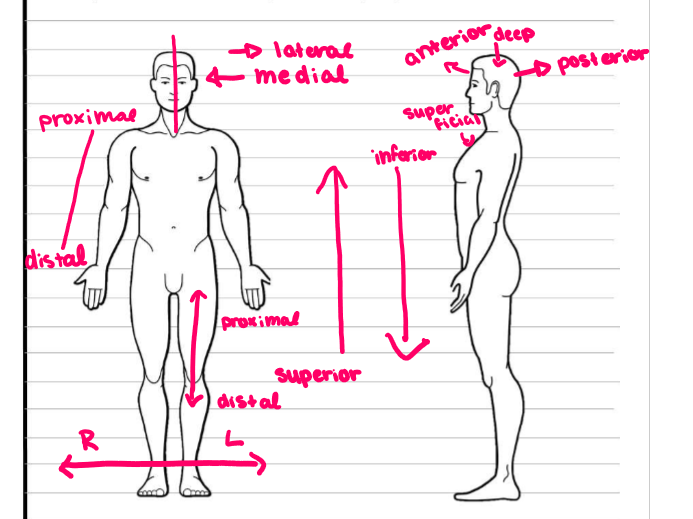
median surface
Separates left from right evenly
Frontal plane
separates anterior from posterior
transverse plane
separates superior from inferior