bio final test 2
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for review of key concepts from Principles of Biology II, including cellular respiration, enzyme function, cell signaling, and cell division.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What is the rate of ATP production through substrate-level phosphorylation starting with one molecule of isocitrate in the citric acid cycle?
1 ATP.
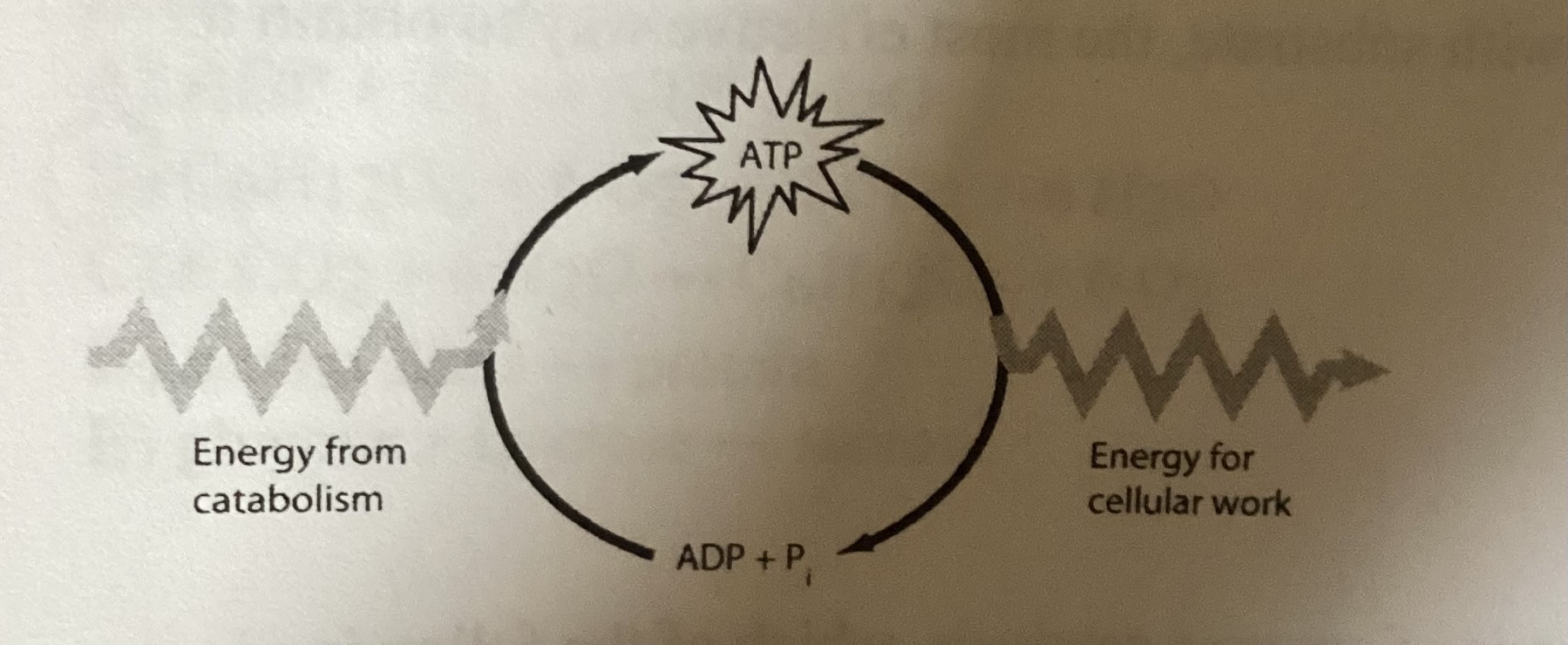
What is the correct interpretation of this figure
ATP stores energy for cell work
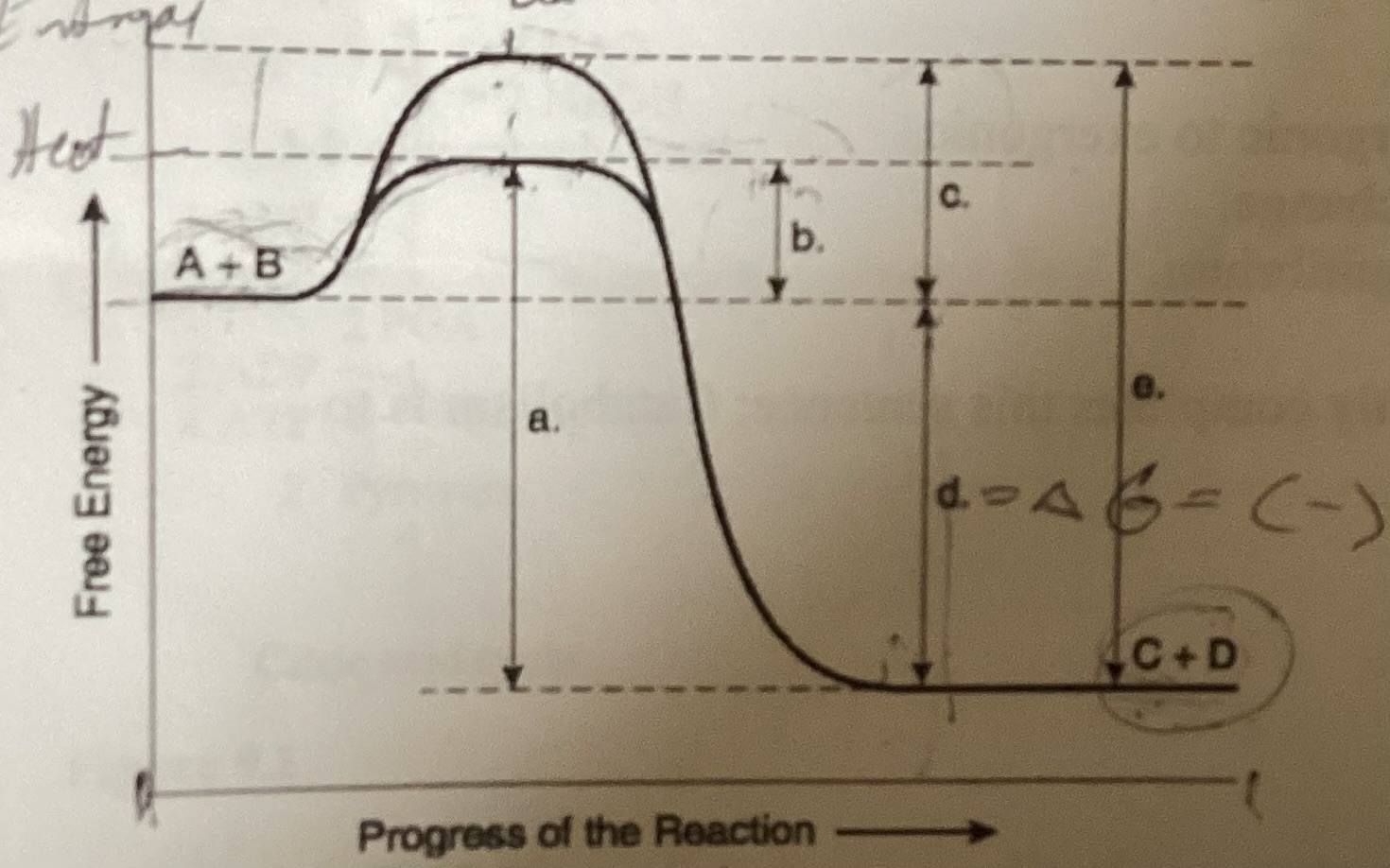
What is the forward reaction in this figure
Exergonic G<0
Catabolism is to anabolism as - is to -
Exergonic, endergonic
Apoptosis does not involve
Lysis of the cell
Why is apoptosis potentially threatening to the healthy neighbors of a dying cell
Lysosomal enzymes exiting the cell would damage surrounding cells
In C. Elegans, ced 9 prevents apoptosis in a normal cell in what ways
It cleaves to produce ced 3 and ced 4

What step in the figure shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules
B
What are scaffolding proteins
Ladderlike proteins that allow receptor ligand complexes to climb through cells

What part of the pathway contains a phosphorylation reaction in which ATP is the phosphate source
A
Through a microscope, you can see a cell plate beginning to develop across the middle of a cell and nuclei forming on either side of the cell plate. The cell is most likely
A plant cell in cytokinesis
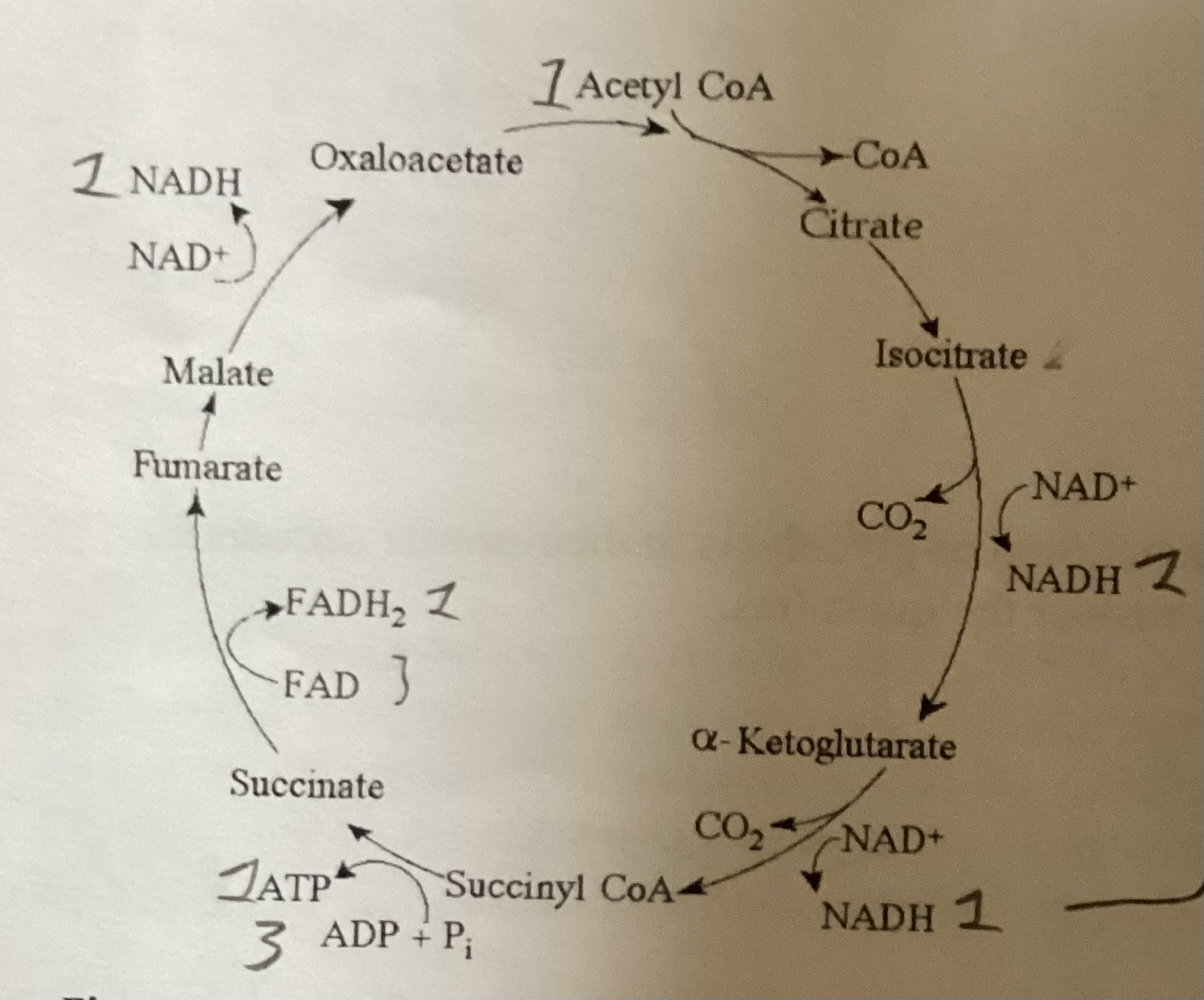
Starting with citrate, what combination of products would result from 3 acetyl CoA molecules entering the citric acid cycle
3 ATP 6 CO2 9 NADH 3 FADH2
Vinblastine is a standard chemotherapeutic drug used for cancer treatment. Because it interferes with the assembly of microtubules, its effectiveness must be related to
Disruption of mitotic spindle formation
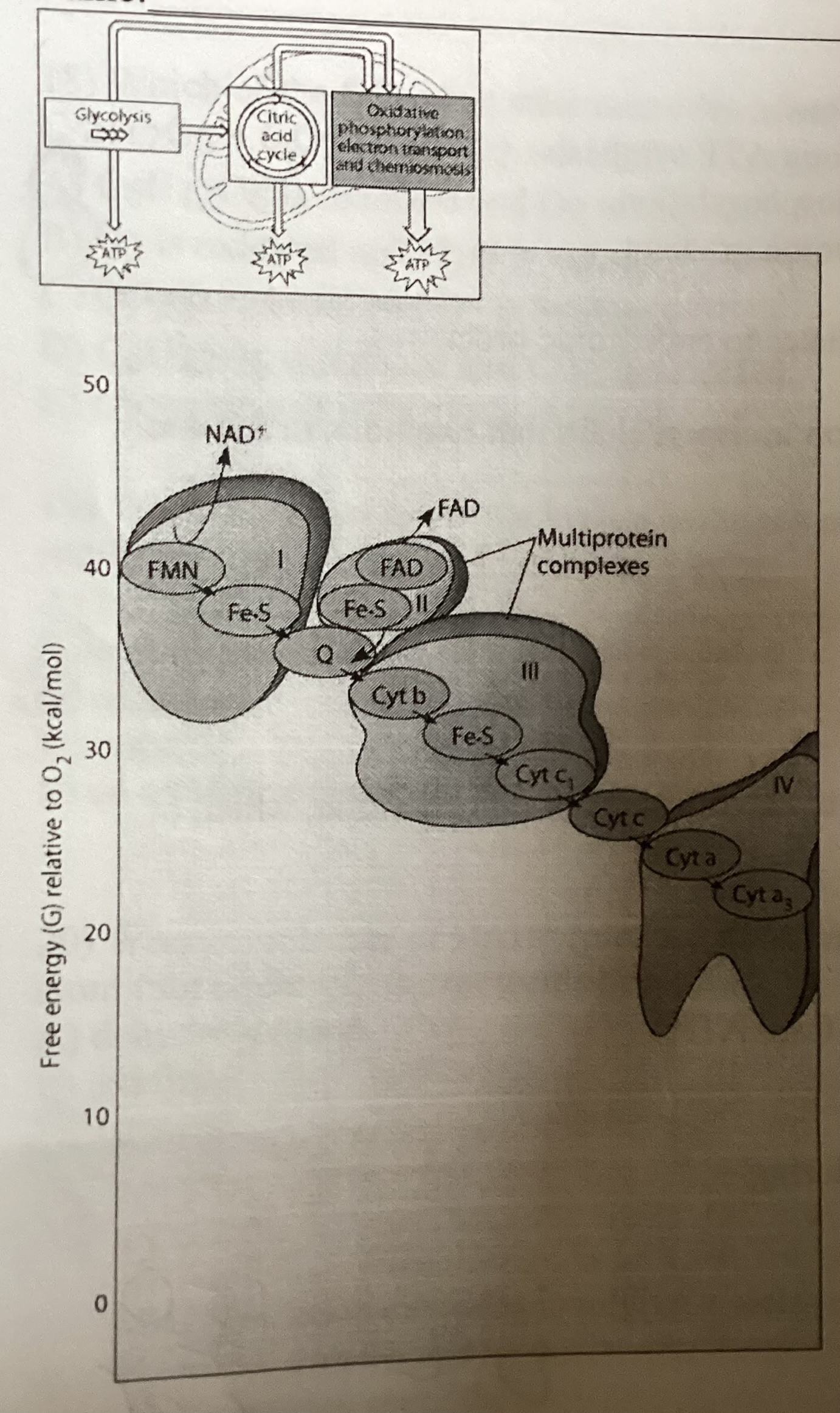
What is the combination of substances initially added to the chain
NADH, FADH2 O2
One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is
Cancer cells continue to divide even when packed together
Which process can occur without a net influx of energy?
C6H12O6 + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O.
The decline of MPF activity at the end of mitosis is due to
The degradation of cyclin
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
In the cells or some organisms, mitosis occurs without cytokinesis. This will result in
Cells with more than one nucleus
What happens to the free energy of a system when an enzyme is added to its reaction at equilibrium?
Nothing; the reaction will stay at equilibrium.
What does not occur during mitosis
Condensation of chromosomes
What is the correct statement regarding the induced fit hypothesis of enzyme catalysis?
The binding of the substrate changes the shape of the enzyme's active site.
A particular cell has half the DNA as some other cells in a mitotically active tissue. The cell in question is most likely in
G1
Which gas is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain during aerobic respiration?
Oxygen.
The drug cytochalasin B blocks the function of actin. What aspect of the cell cycle would be most distrupted by this drug
Cleavage formation and cytokinesis
How does the Vibrio cholerae toxin cause diarrhea?
It modifies a G protein involved in regulating salt and water secretion.
The centromere is the region in which
Chromatids are attached to each other
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation reduction reaction the molecule becomes
Oxidized
What is a cleavage furrow
Groove im plasma membrane between daughter nuclei
What is a characteristic feature of apoptosis?
Fragmentation of the DNA.
What describes the results of this reaction: C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy
Glucose is oxidized and O2 is reduced
Identify the second messenger in the pathway: epinephrine → G protein-coupled receptor → G protein → CAMP.
cAMP.
How many chromosomes would be present if there are 20 chromatids in a cell?
10 centromeres.
Which cellular event does not occur during mitosis?
Replication of the DNA.
What happens when electrons move closer to a more electronegative atom?
The more electronegative atom is reduced, and energy is released.
What is the role of density-dependent inhibition in cell division?
As cells become more numerous, they stop dividing due to contact with neighboring cells.
When a molecule of NAD+ gains a hydrogen atom the molecule becomes
Reduced
Phosphorylation cascades involving a series of protein kinases are useful for cellular signal transduction because
They amplify the original signal
The activation of receptor tyrosine kinases is characterized by
Dimerization and phosphorylation
In mitochondria, exergonic redox reactions
Provide energy that establishes proton gradient
When electrons flow along electron transport chains of mitochondria, what change occurs
pH of matrix increases
Most CO2 from catabolism, is released during
Citric acid cycle
Th molecule that functions as the reducing agent in a redox or oxidation reduction reaction
Loses electrons and loses potential energy