DPT 745 Week 4 Lecture Notes Pt. 1
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
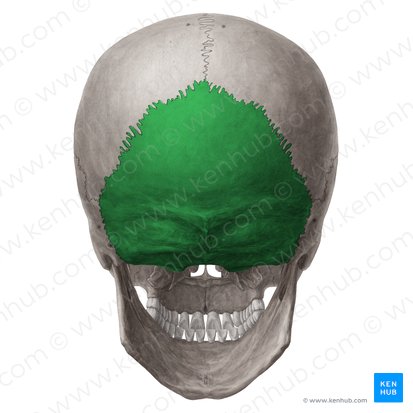
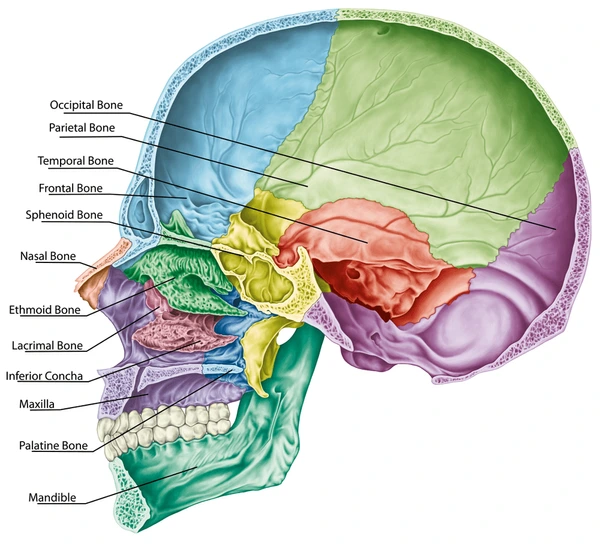
Occipital
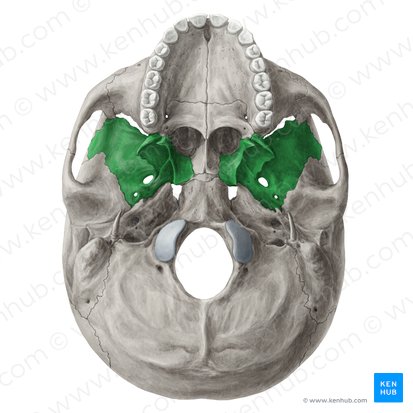
Sphenoid
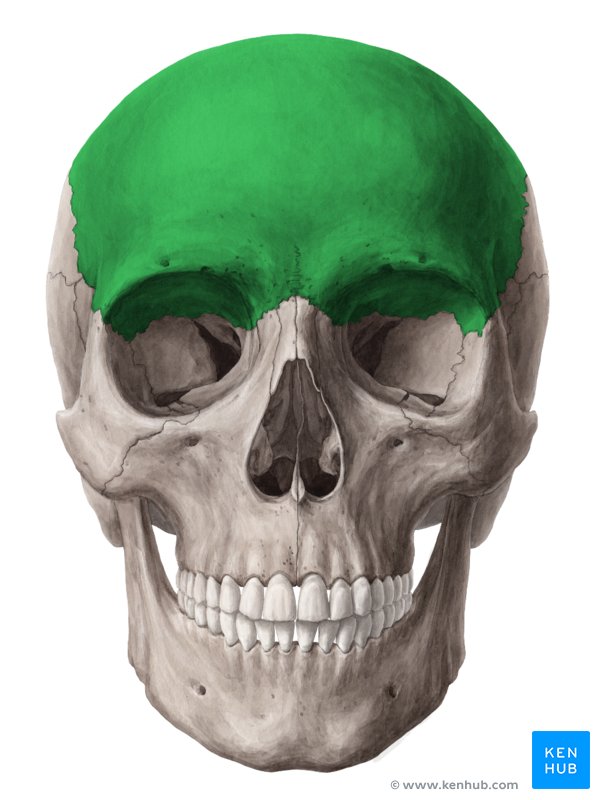
Frontal
Parietal
Temporal
Ethmoid
Name the bones of the neurocranium
Palatine
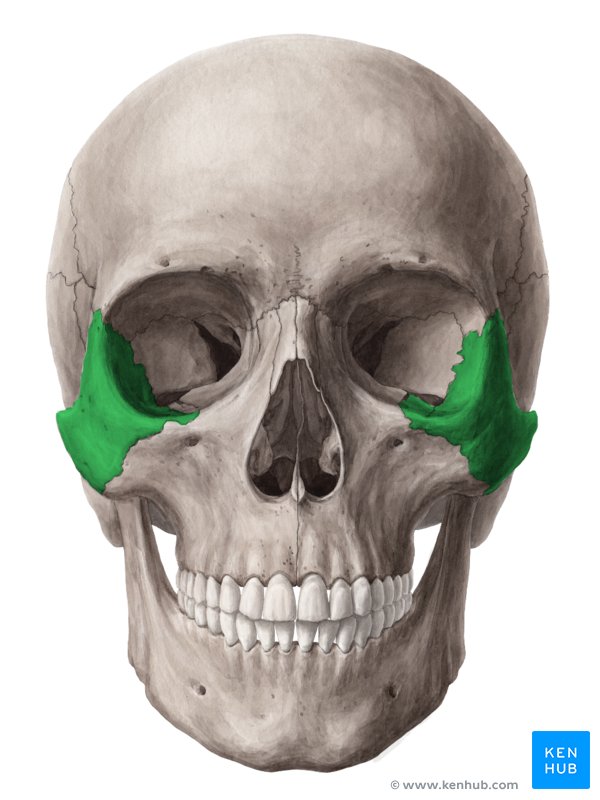
Zygomatic
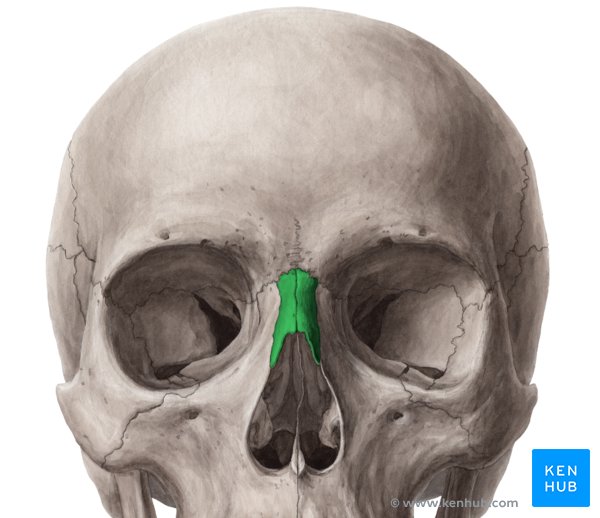
Nasal
Vomer
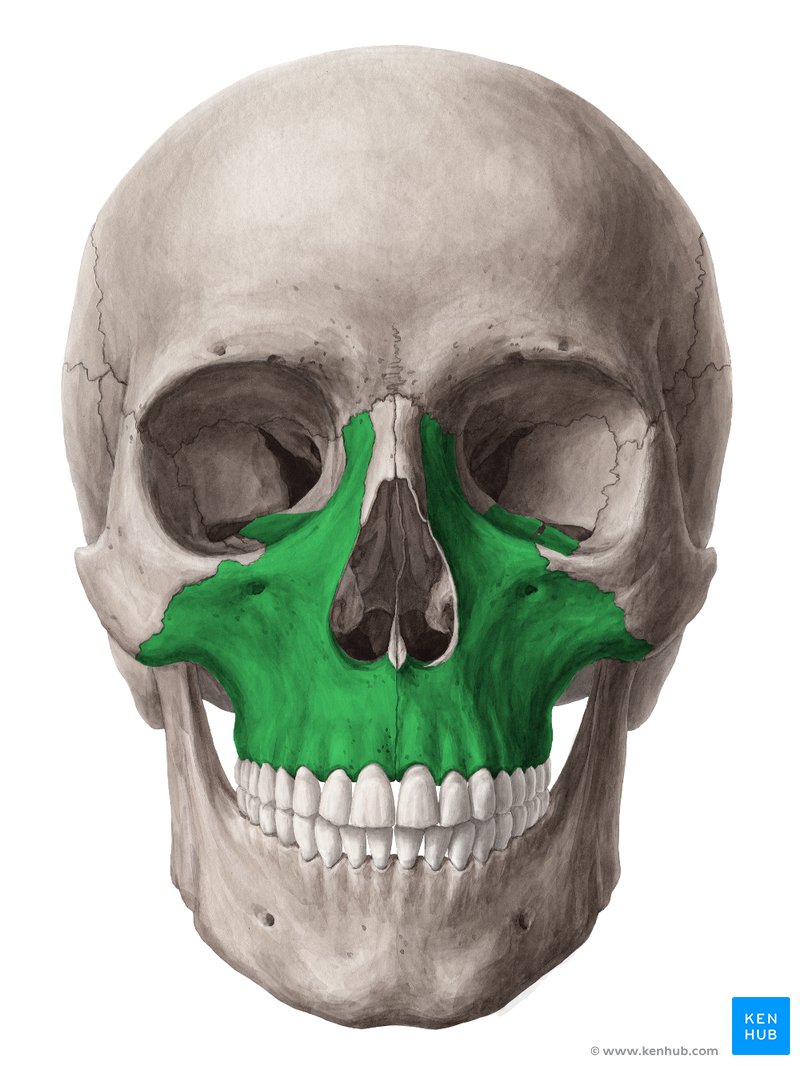
Maxillae
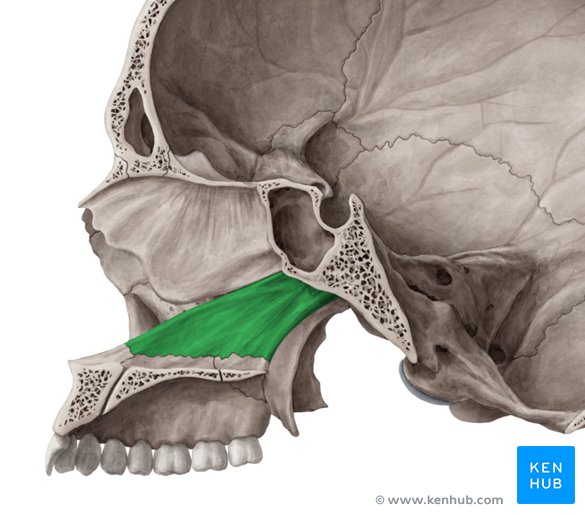
Mandible
Name the bones of the viscerocranium
Occipital
Sphenoid
Frontal
Parietal
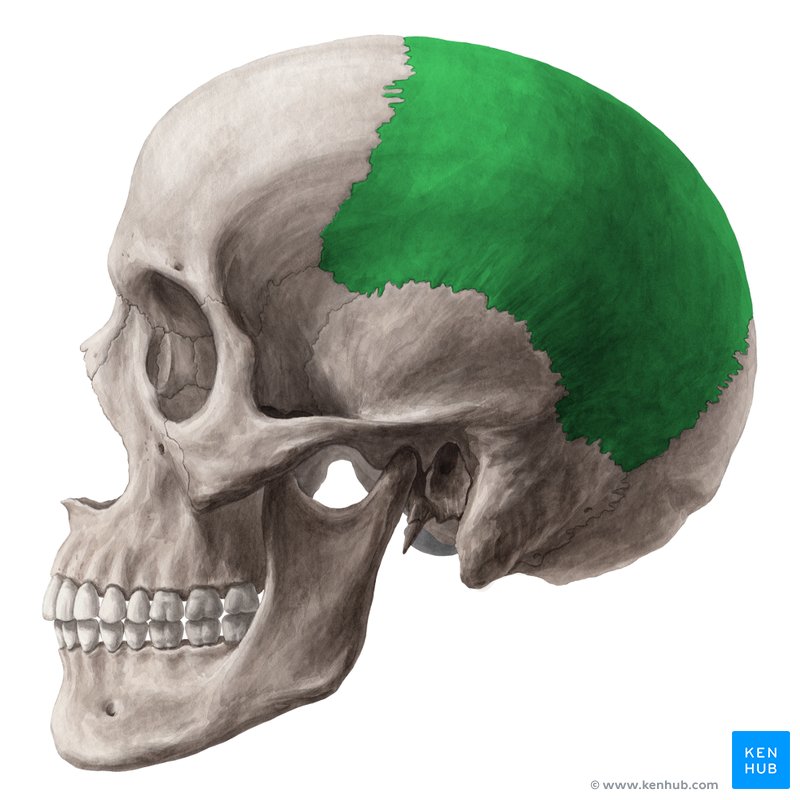
Temporal
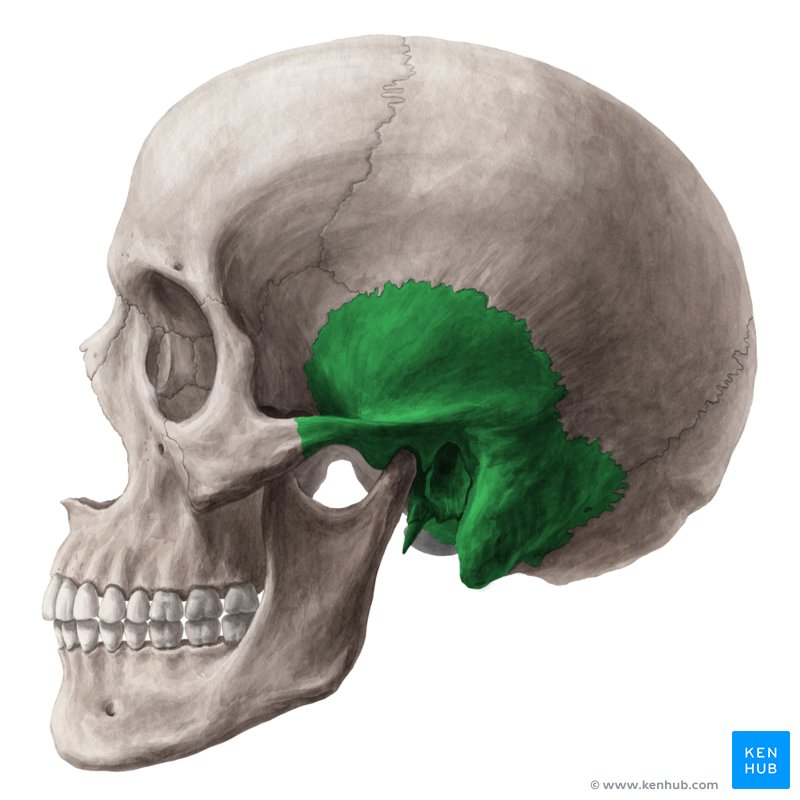
Ethmoid
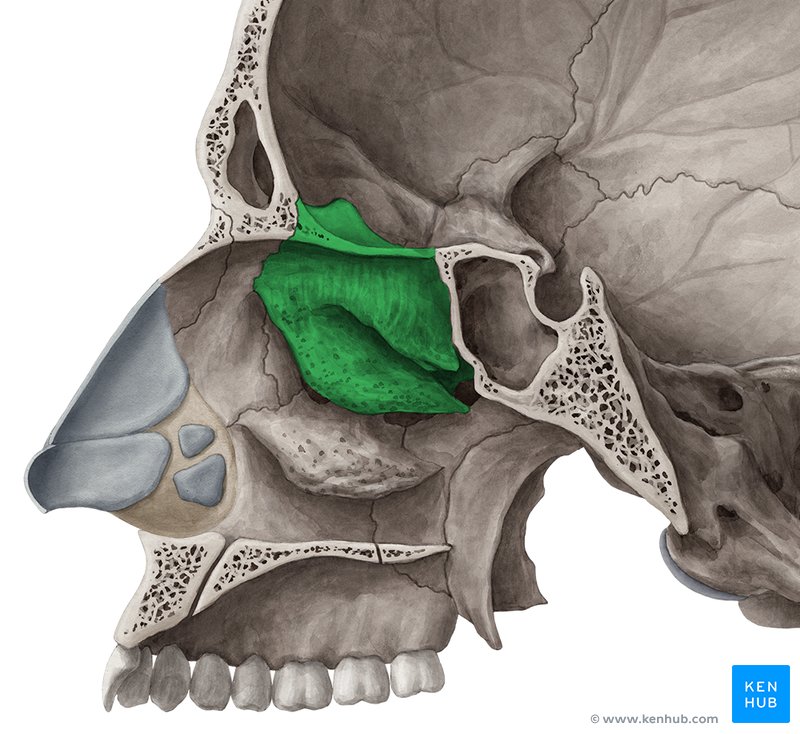
Palatine
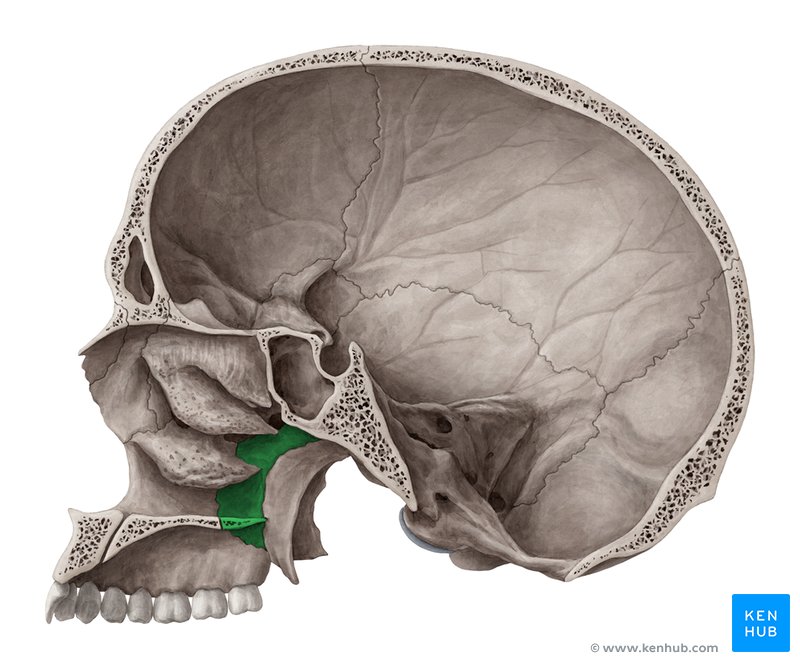
Zygomatic
Nasal
Vomer
Maxillae
Mandible
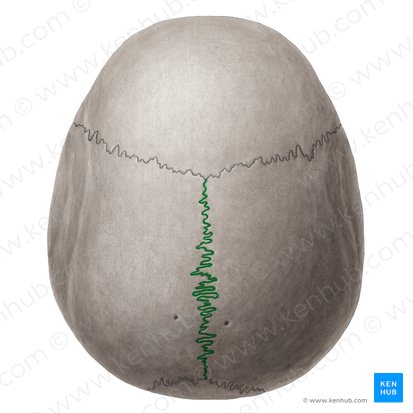
Coronal suture
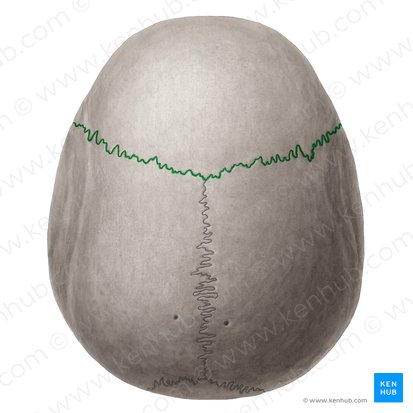
Sagittal suture
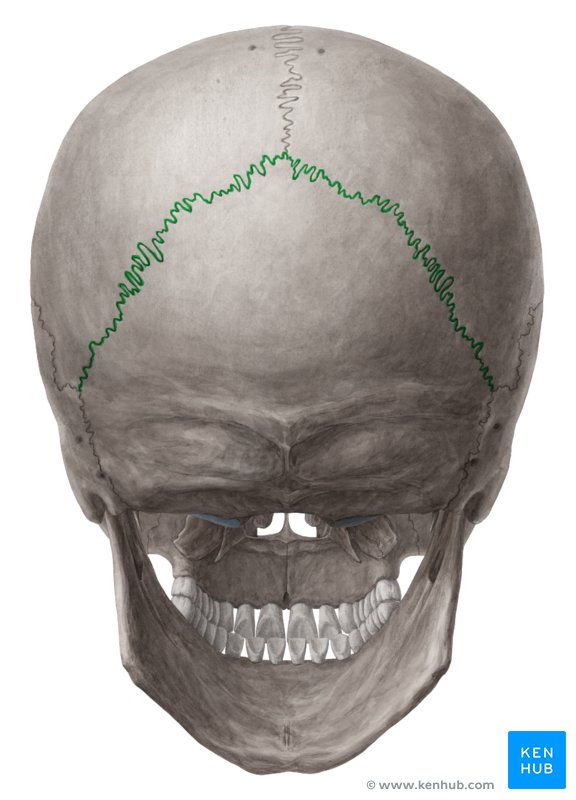
Lambdoid suture
External occipital protuberance
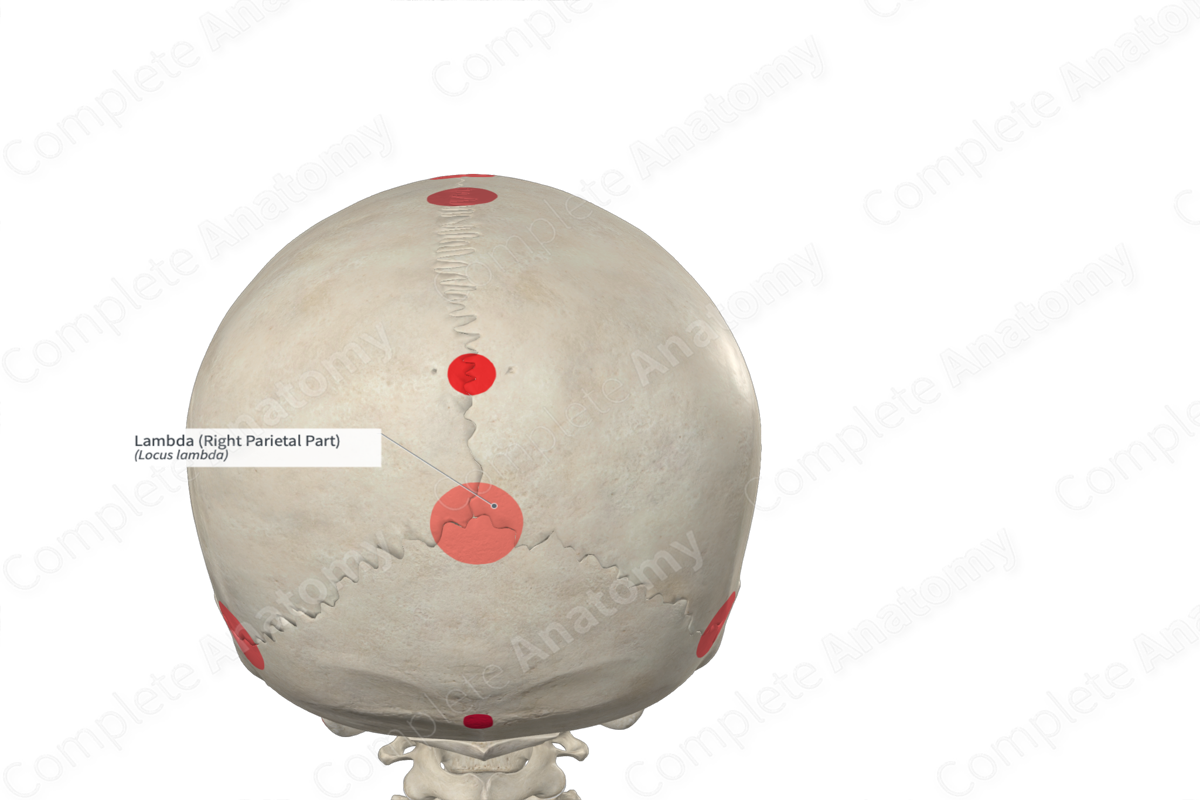
Lambda
Posterior skull
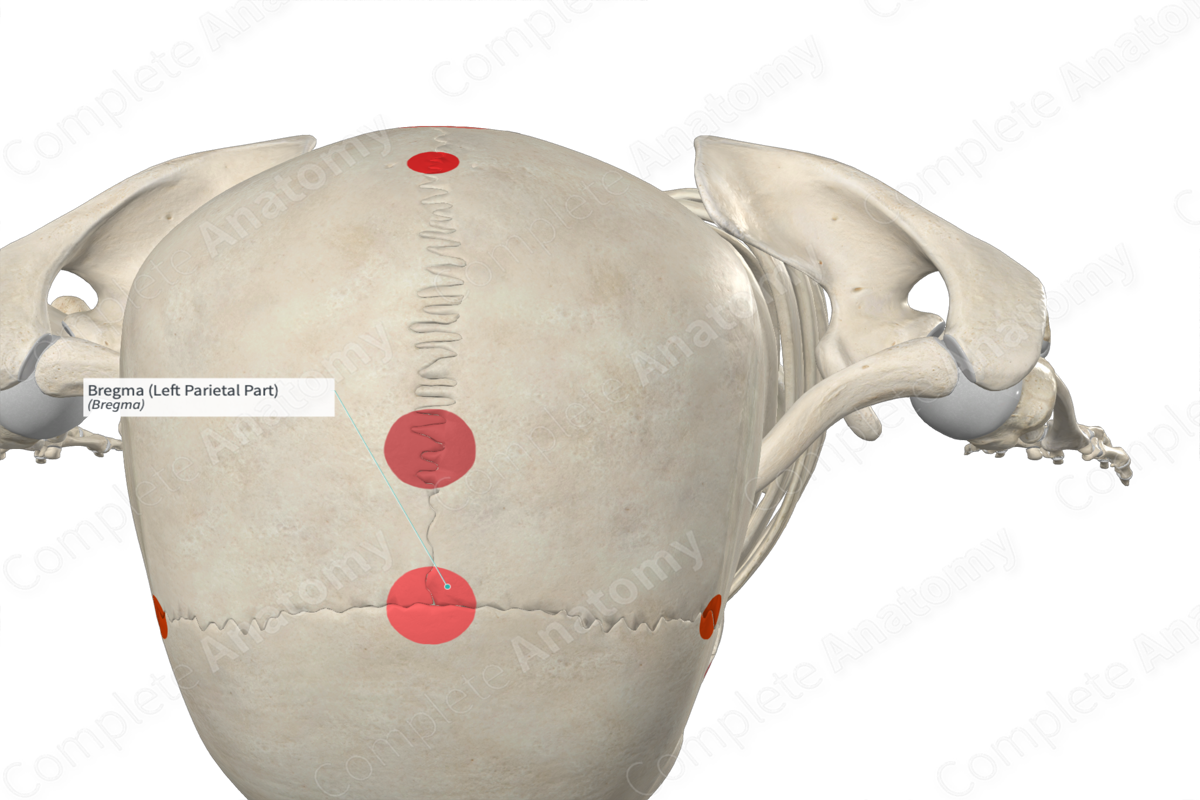
Bregma
Superior skull
External acoustic meatus
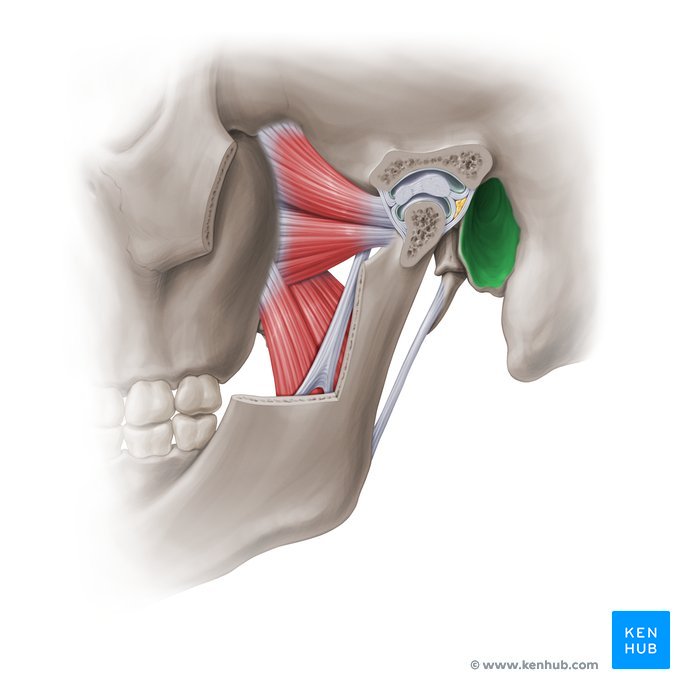
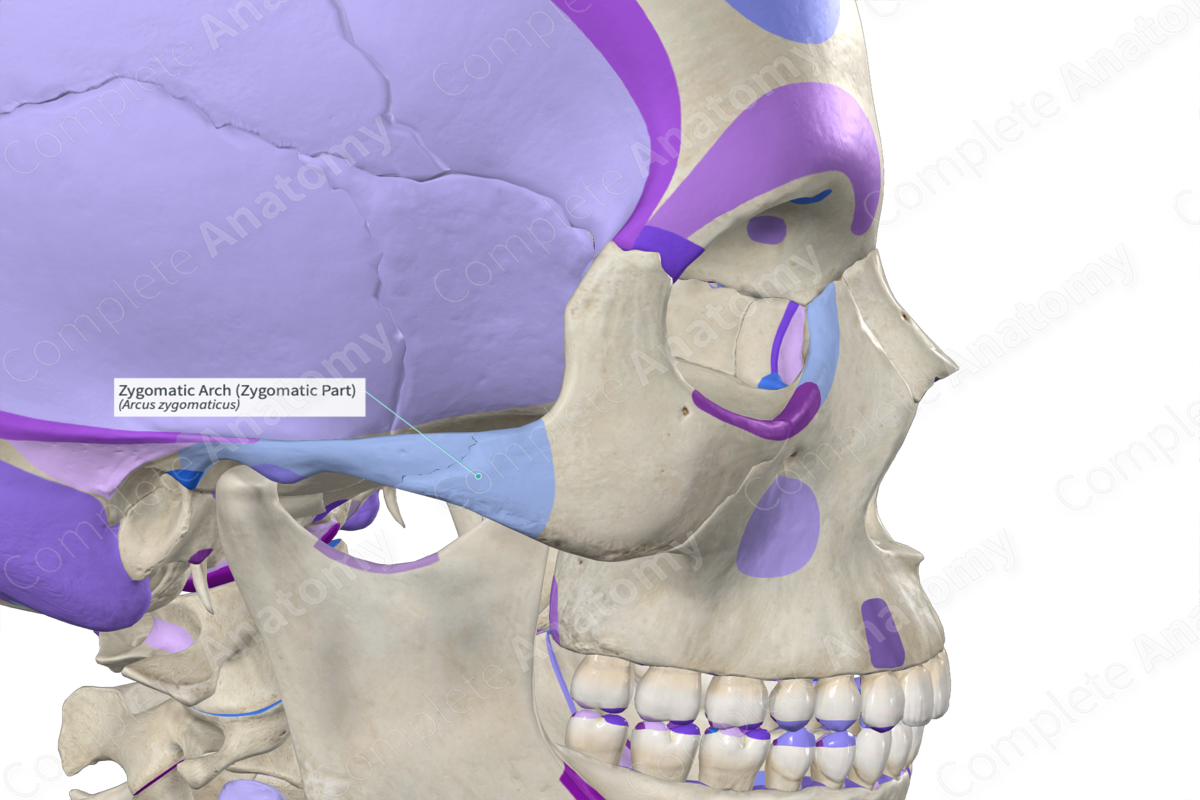
Zygomatic arch
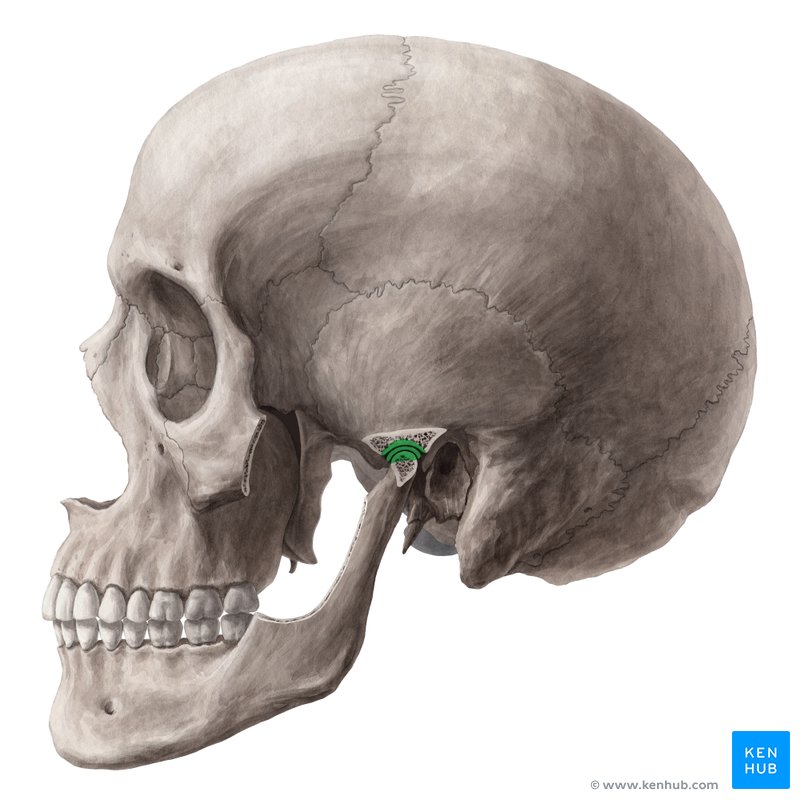
Temporomandibular joint
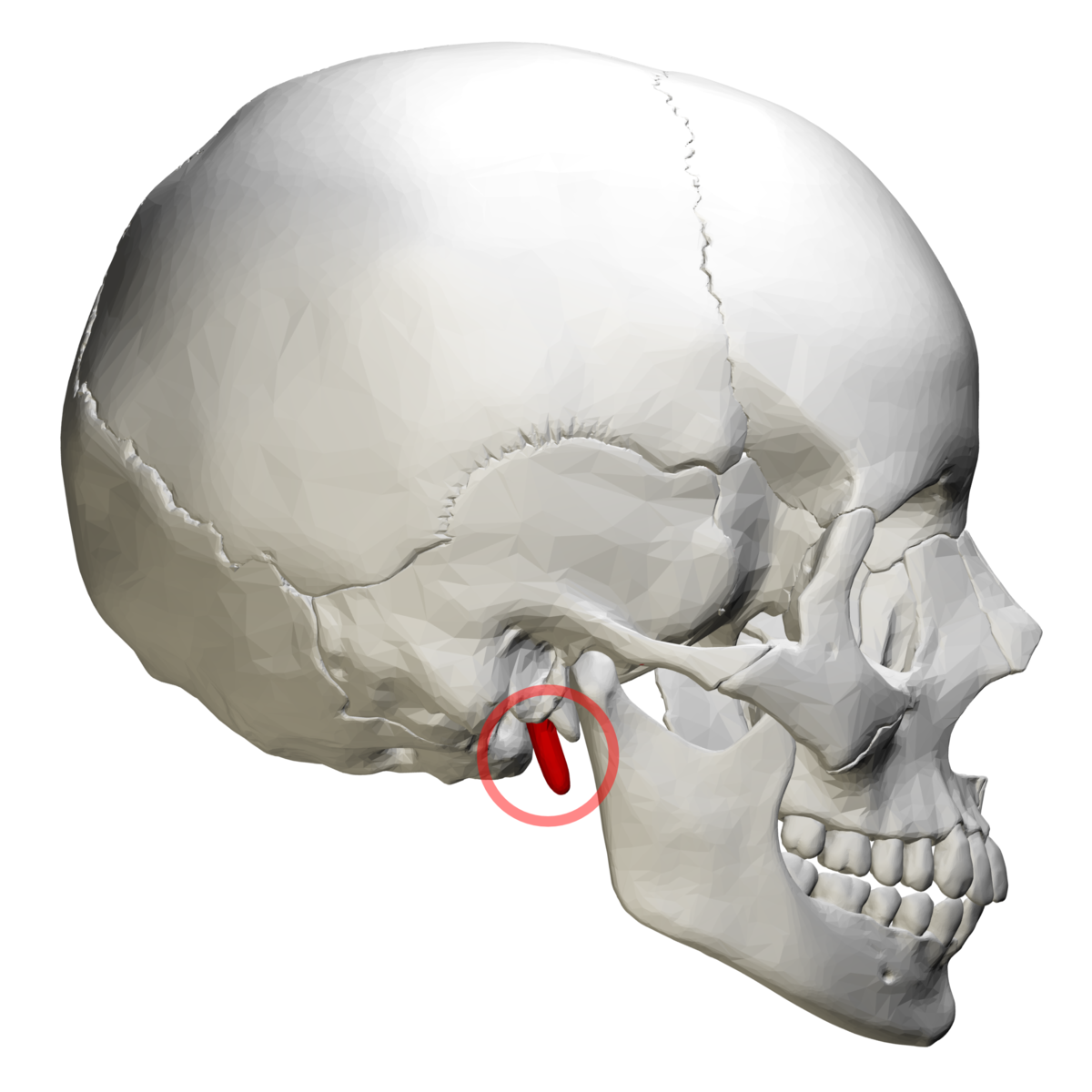
Styloid process
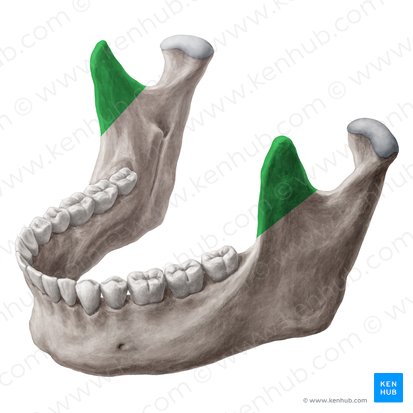
Coronoid process of mandible
Condyloid process of mandible
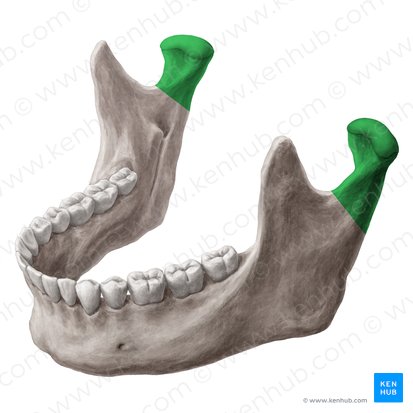
Zygomatic process
temporal process
What are the two processes of the zygomatic arch?
Zygomatic process
Temporal process
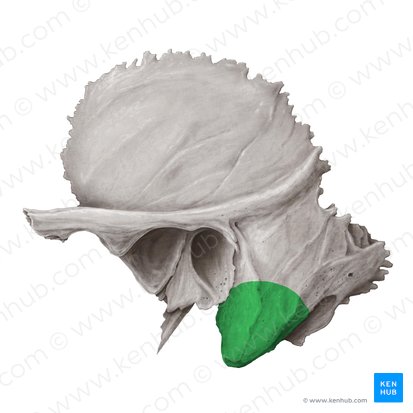
Palatine process
Horizontal plate
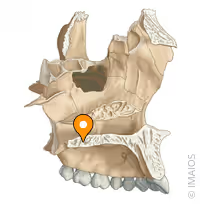
Mandibular fossa
Mastoid proces
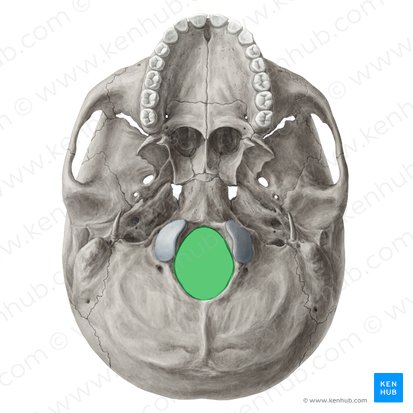
Foramen magnum
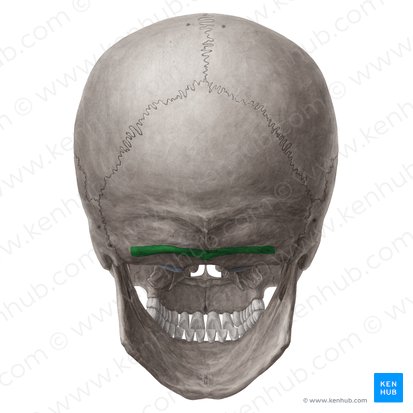
Superior nuchal line
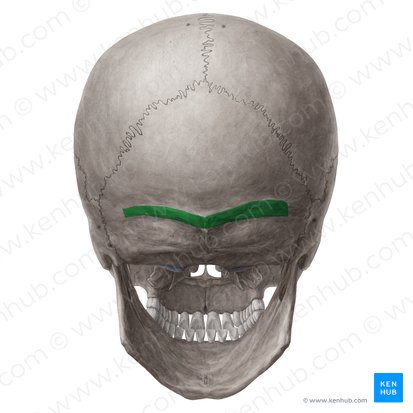
Inferior nuchal line
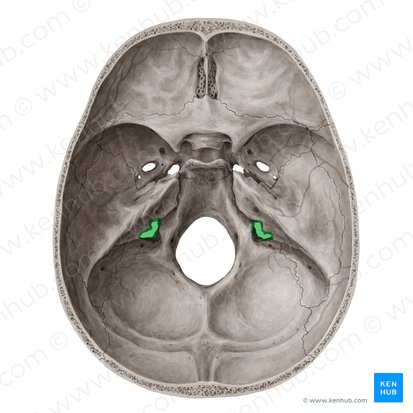
Jugular foramen
Medial plate of pterygoid process
Lateral plate of pterygoid process
Diploë
The spongy, cancellous bone found between the inner and outer layers of the flat bones of the skull
Optic canal
Superior orbital fissure
Inferior orbital fissure
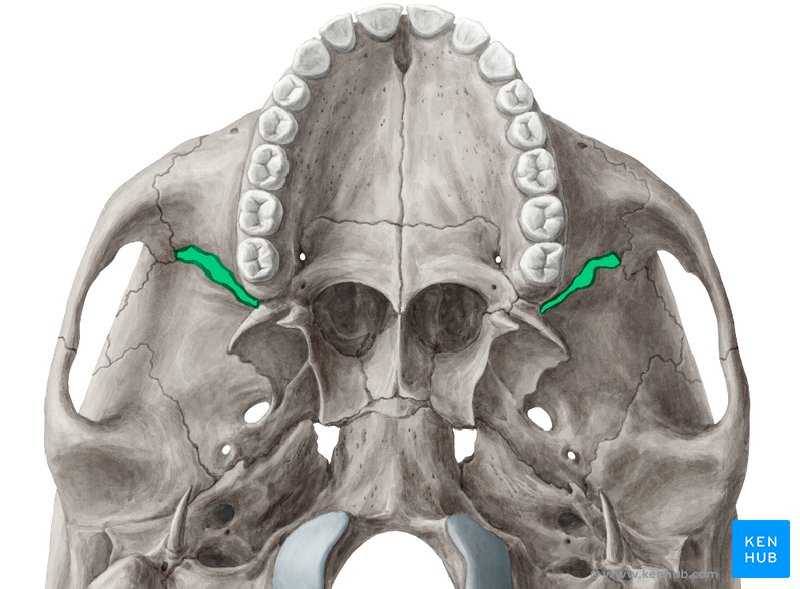
Foramen ovale
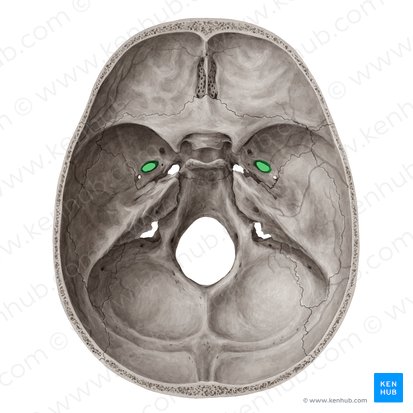
Foramen spinosum
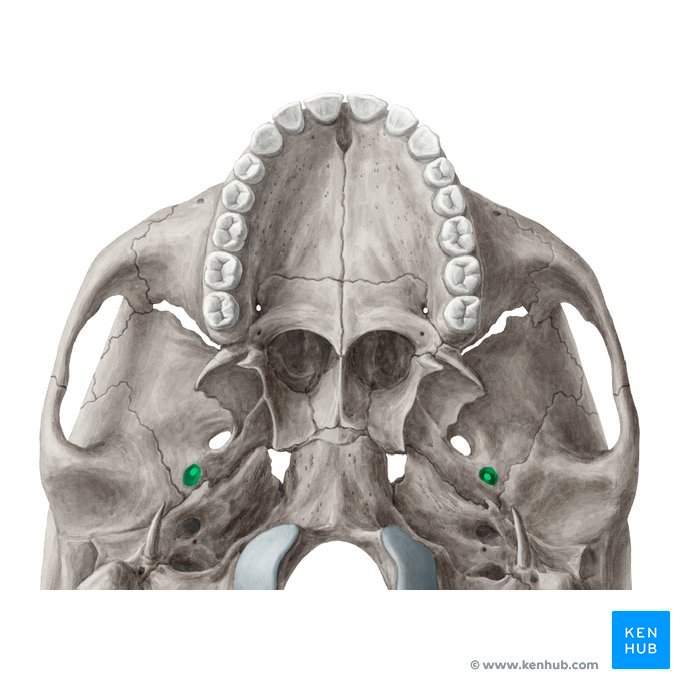
Internal acoustic meatus
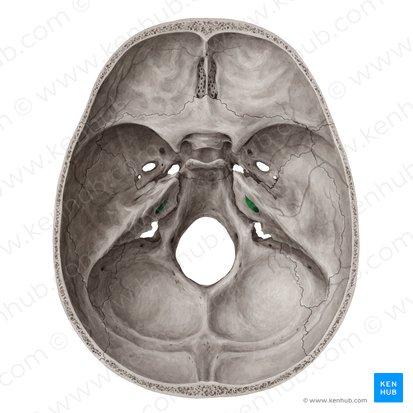
Hypoglossal canal
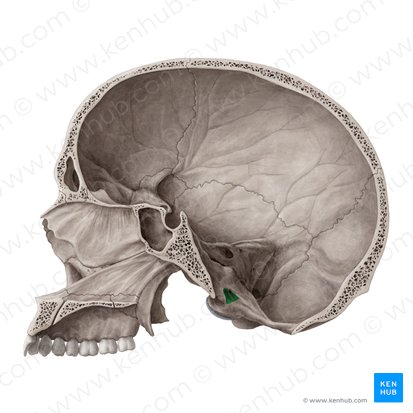
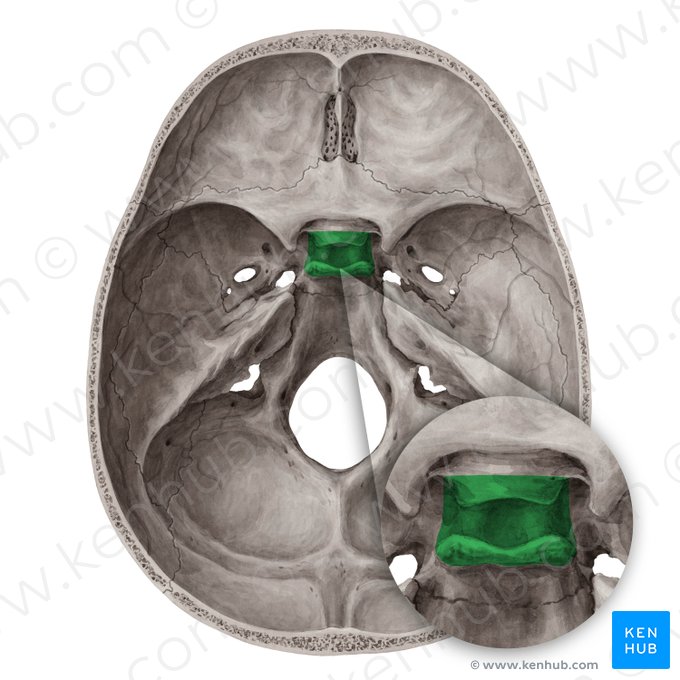
Sella turcica
Hypophysial fossa
A critical anatomical structure located within the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone
Dorsum sellae
A bony projection located on the sphenoid bone, specifically at the posterior boundary of the sella turcica
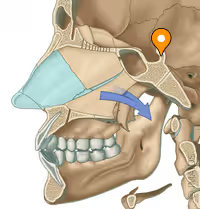
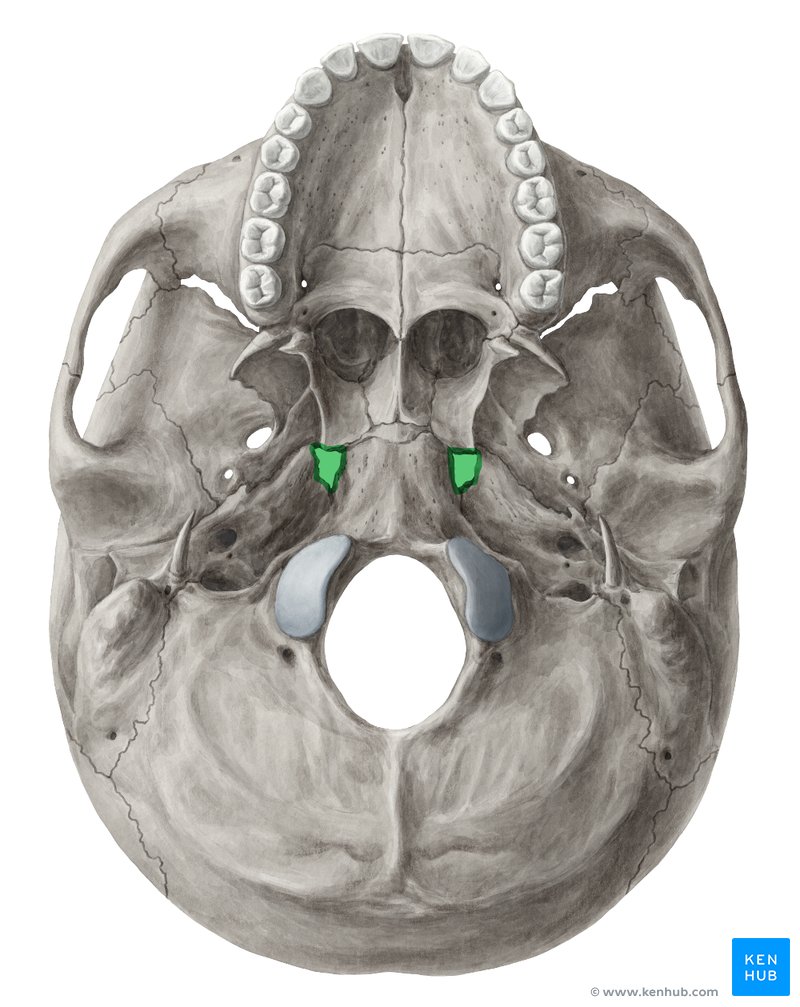
Foramen lacerum
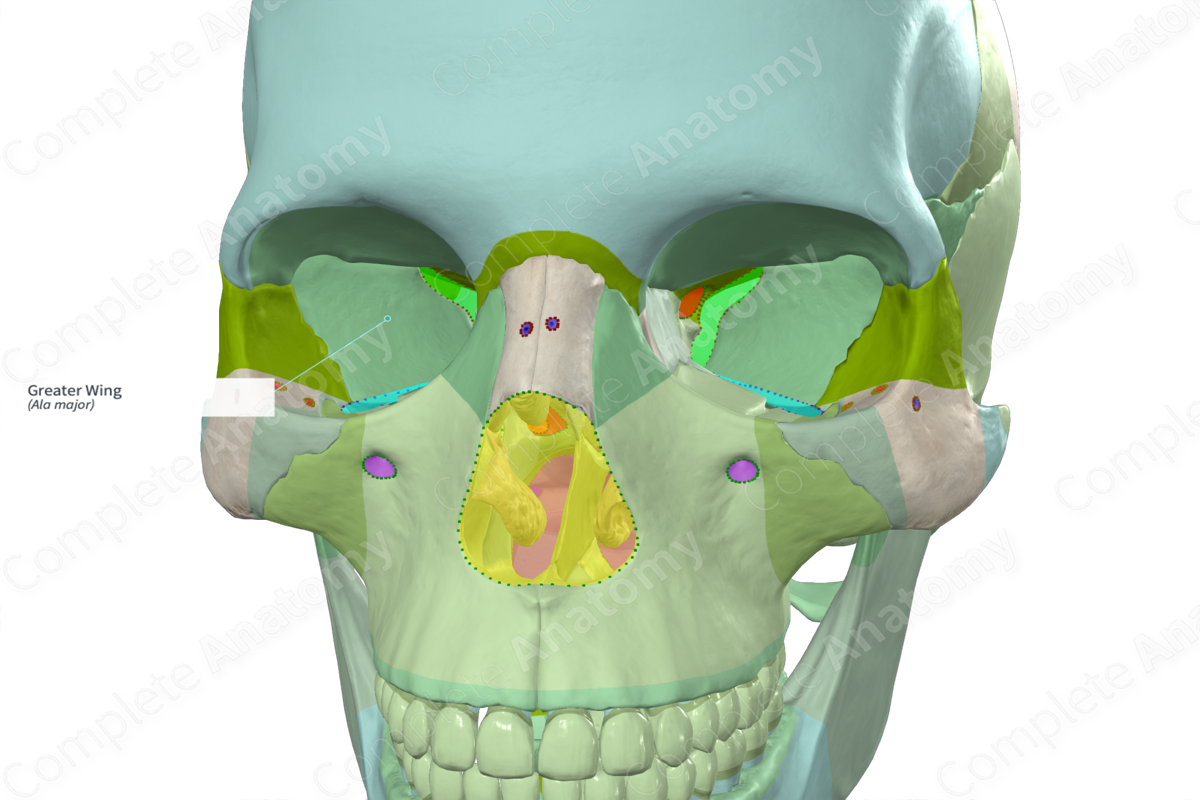
Greater wing of sphenoid
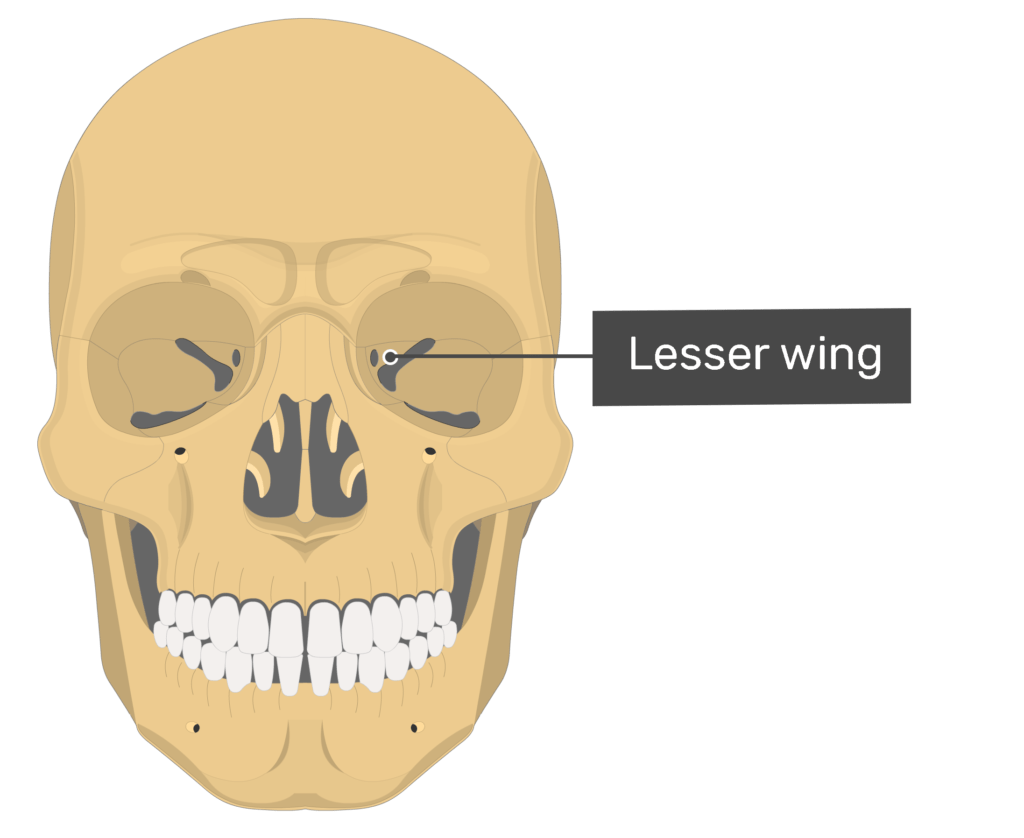
Lesser wing of sphenoid
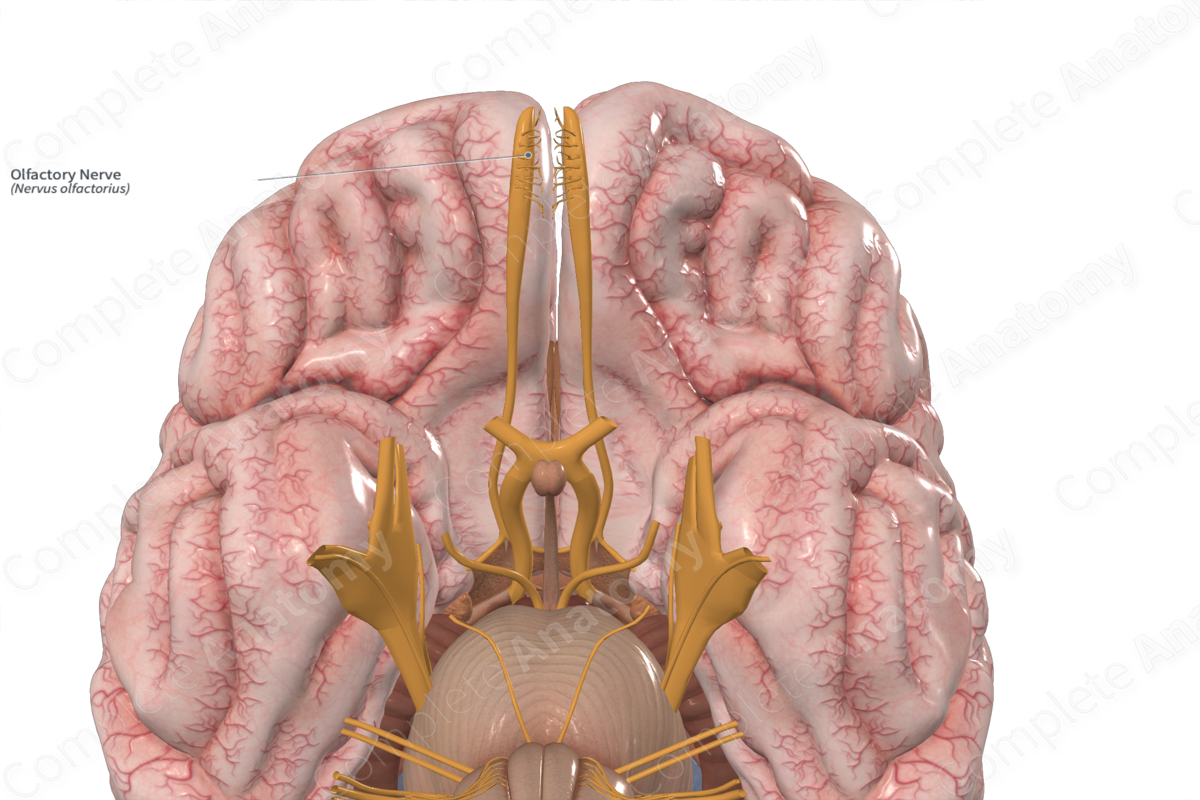
Olfactory nerve
Sensory nerve
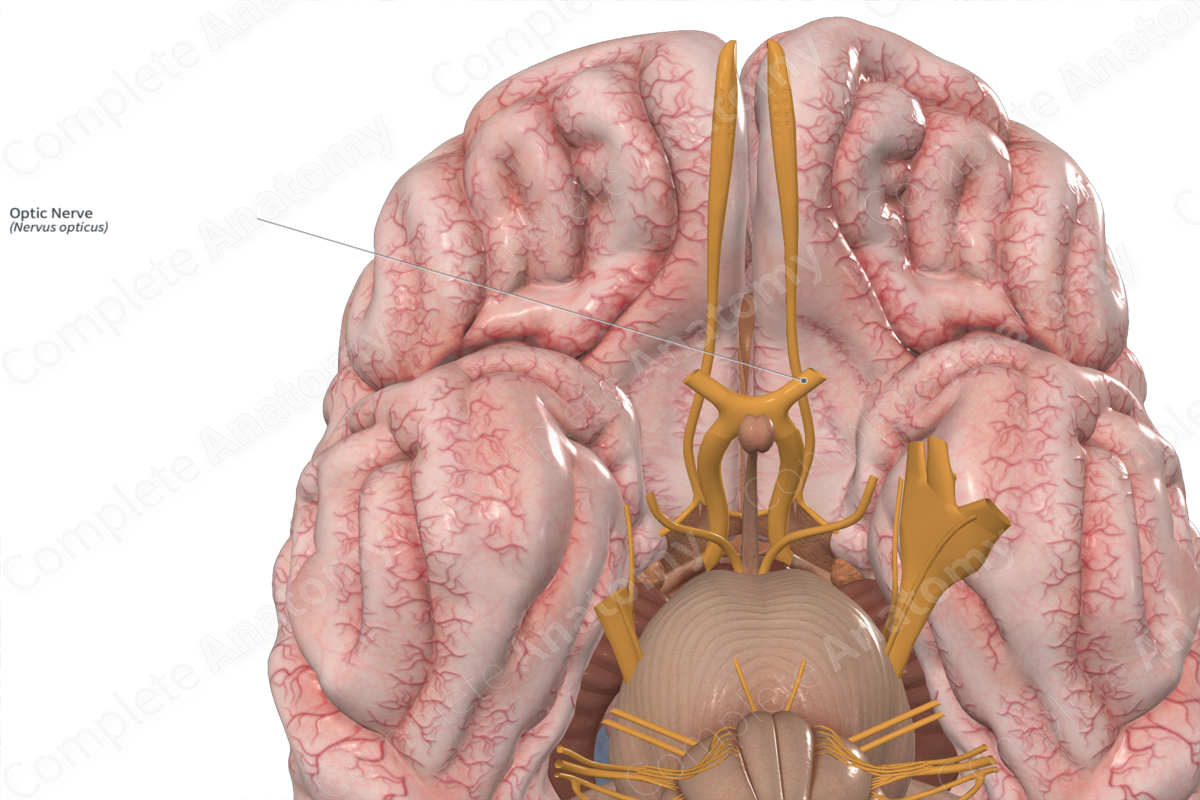
Optic nerve
Sensory nerve
It plays a role in various visual functions, including brightness perception, color perception, contrast sensitivity, and reflexes like the light reflex and accommodation reflex.
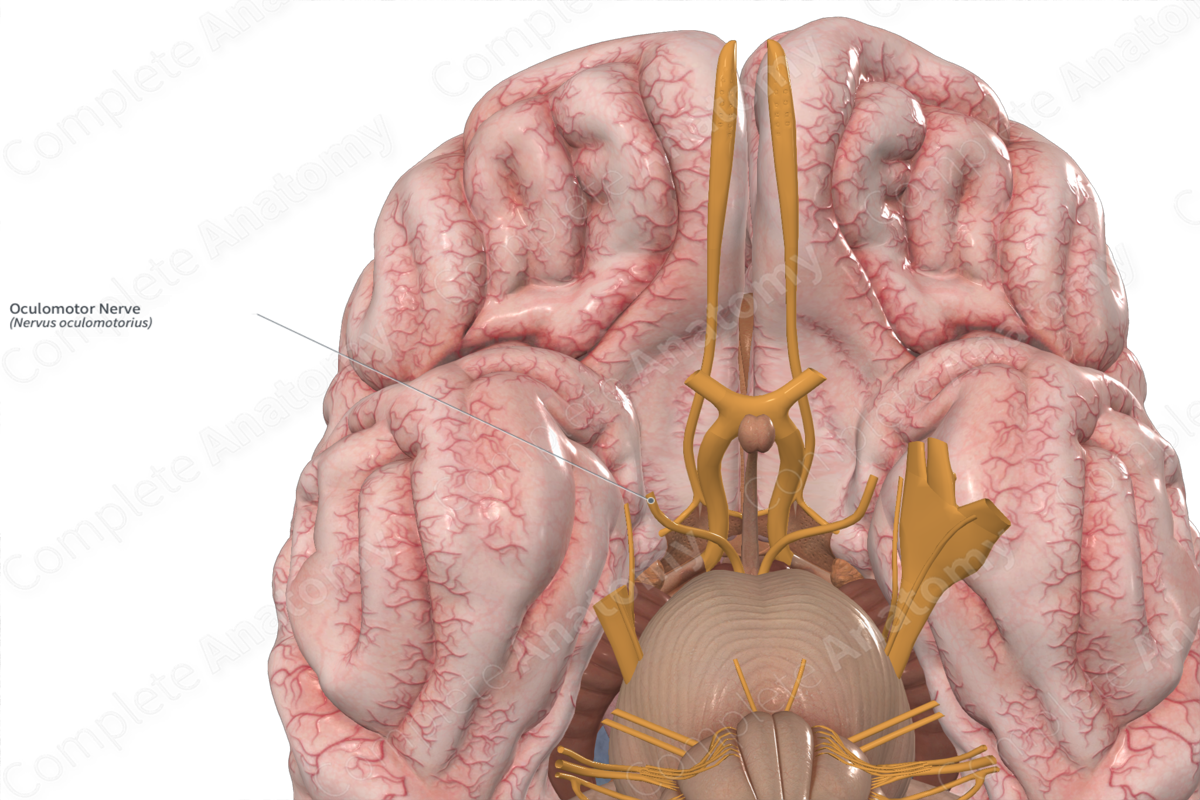
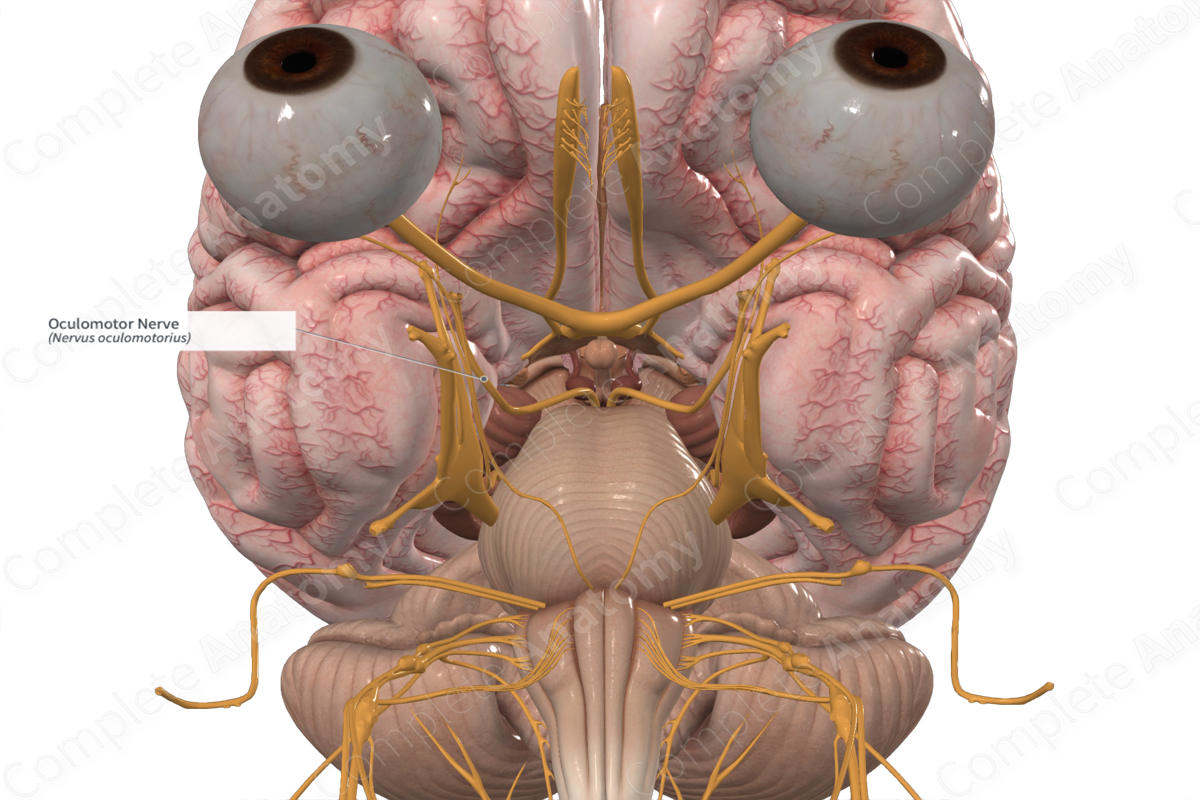
Oculomotor
Motor nerve
Controlling several muscles that move the eye and eyelid, as well as regulating pupil size and lens shape
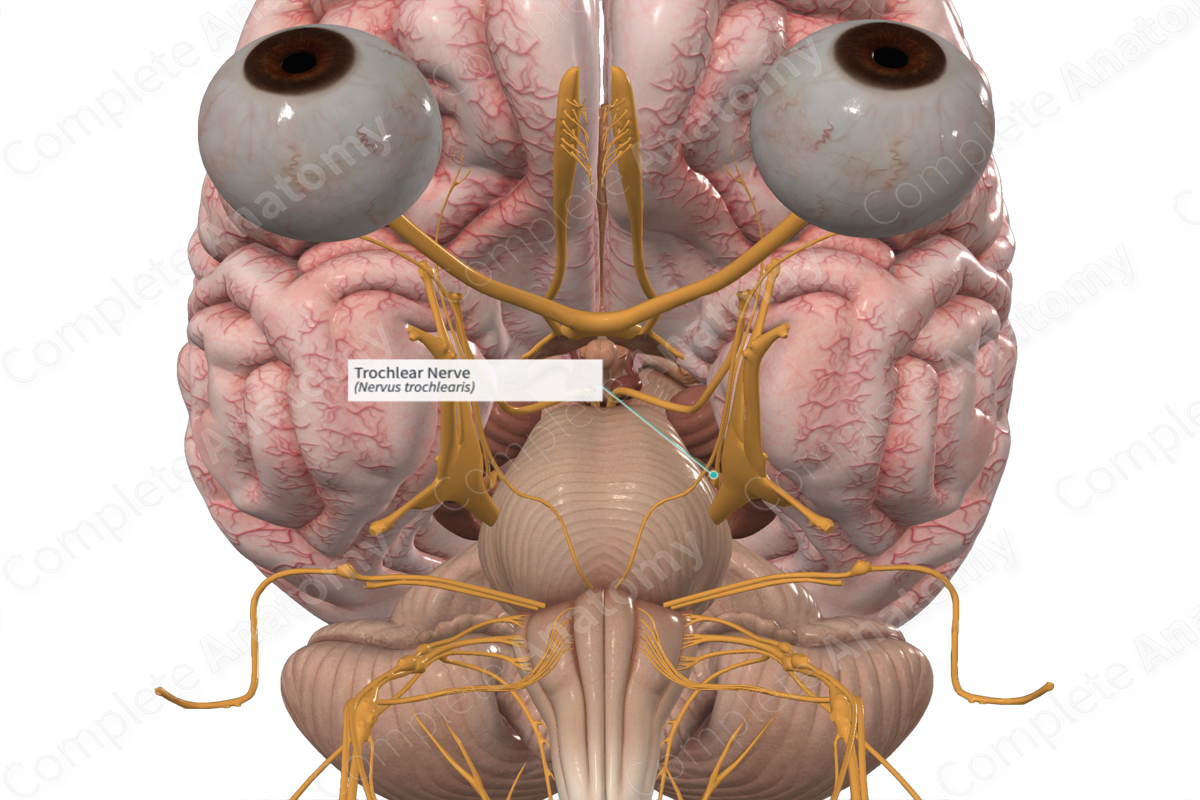
Trochlear
Motor nerve
Controlling the superior oblique muscle of the eye
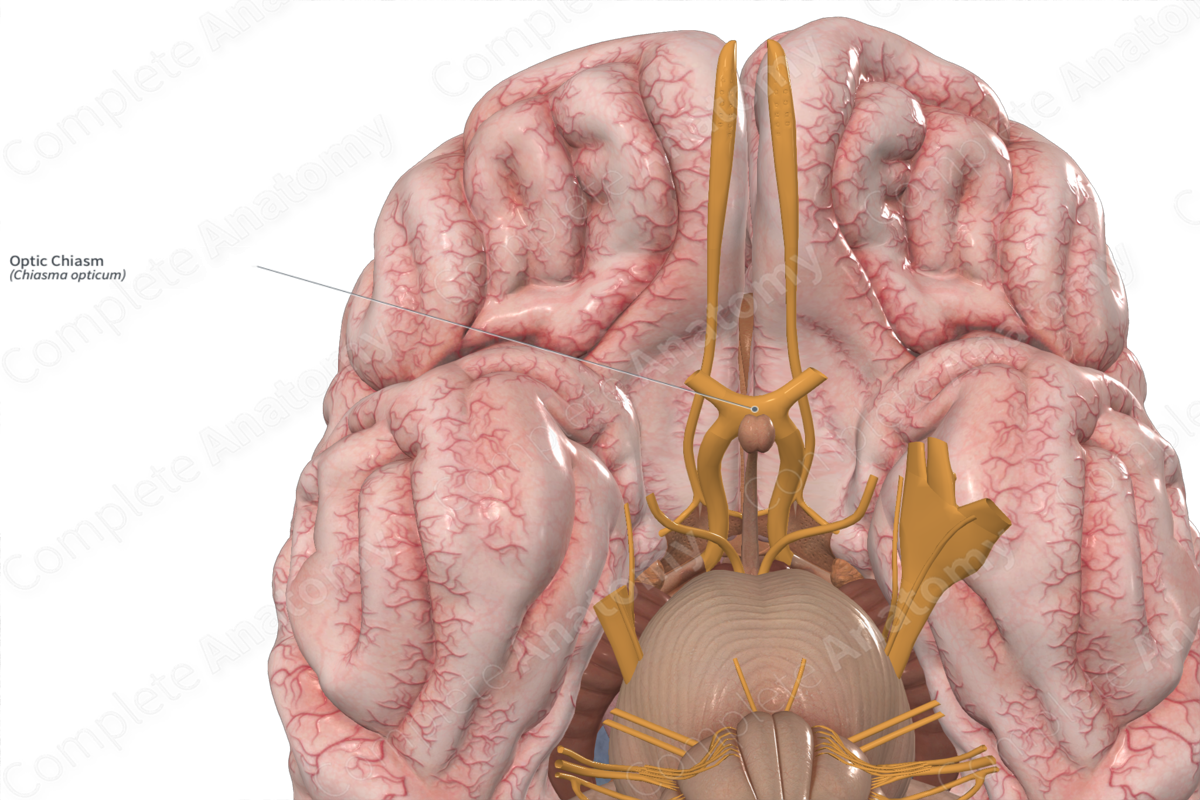
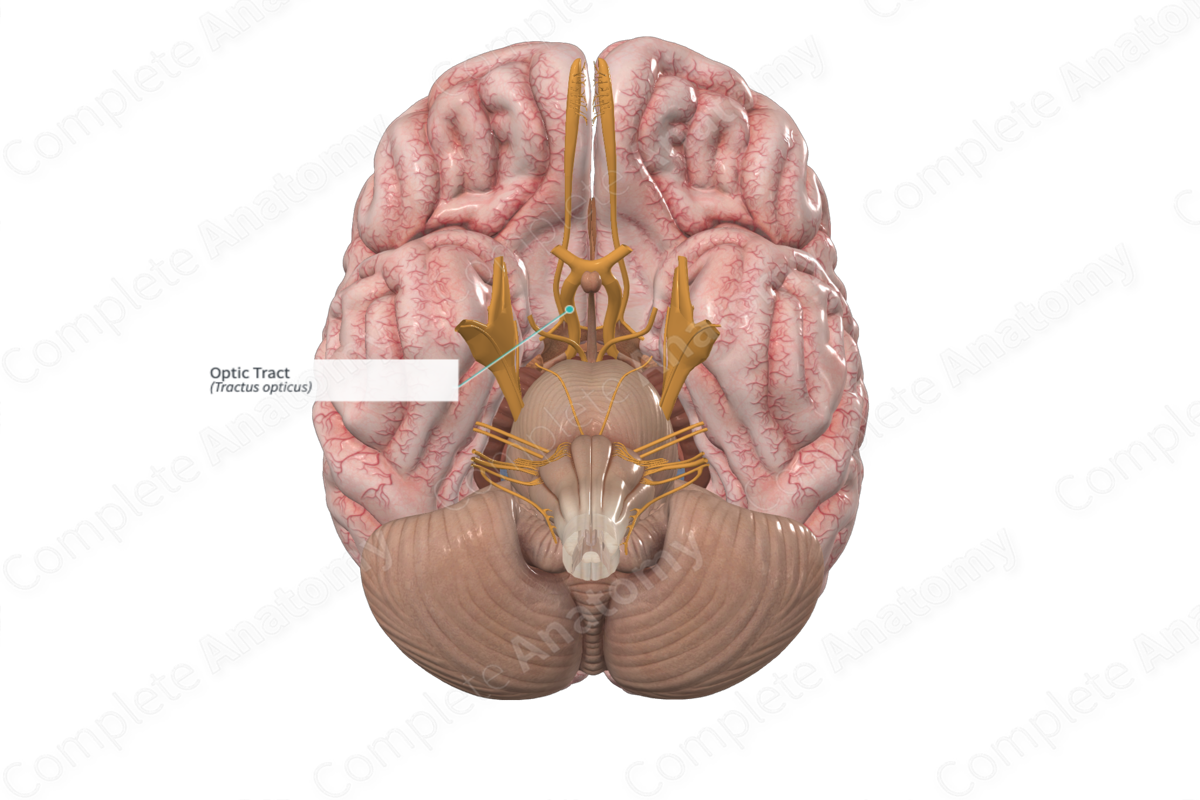
Optic chiasm
Optic tract
Opthalmic (V1)
Maxillary (V2)
Mandibular (V3)
Trigeminal (CN 5) nerve splits into what three nerves?
Oculomotor nerve
Controlling several muscles that move the eye and eyelid, as well as regulating pupil size and lens shape
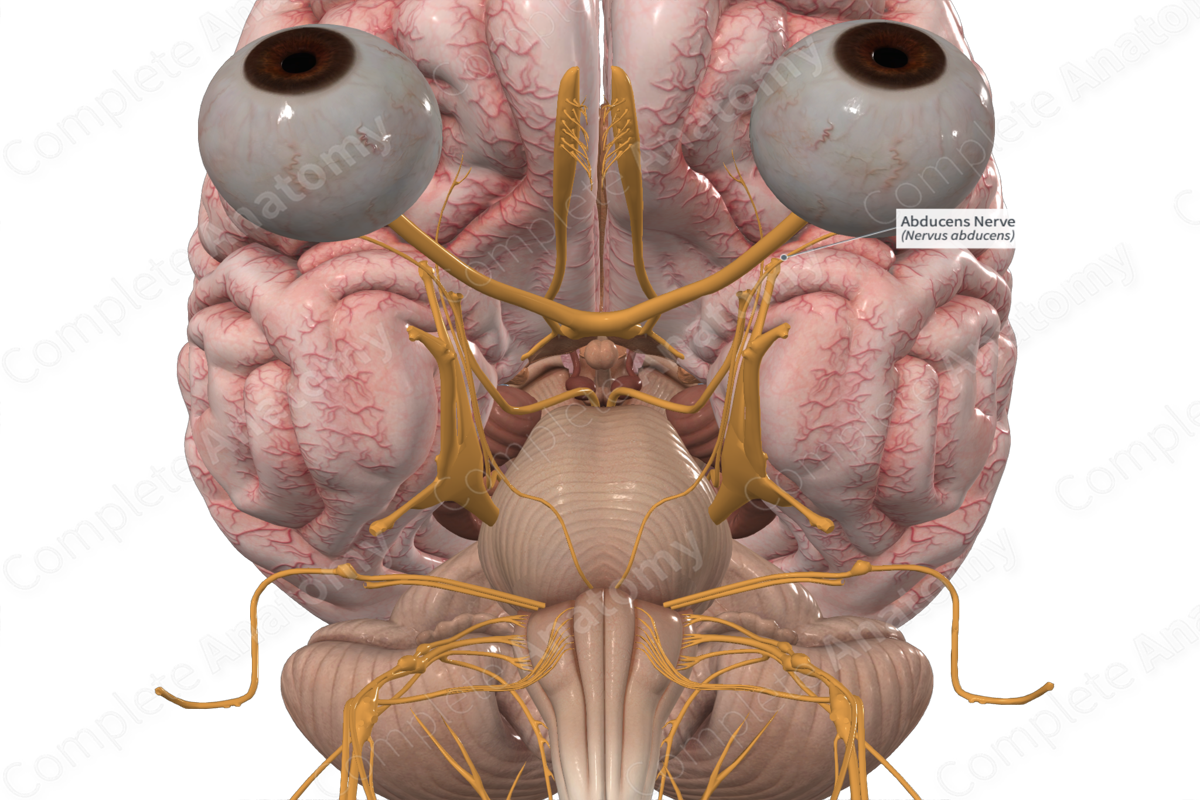
Abducent nerve
Nerve responsible for controlling the lateral rectus muscle of the eye, which abducts (moves the eye outward)
Intermediate nerve
A distinct component of the facial nerve; carries both sensory and parasympathetic fibers. Plays a crucial role in various functions, including taste perception, glandular secretion, and sensation from the external ear and parts of the head
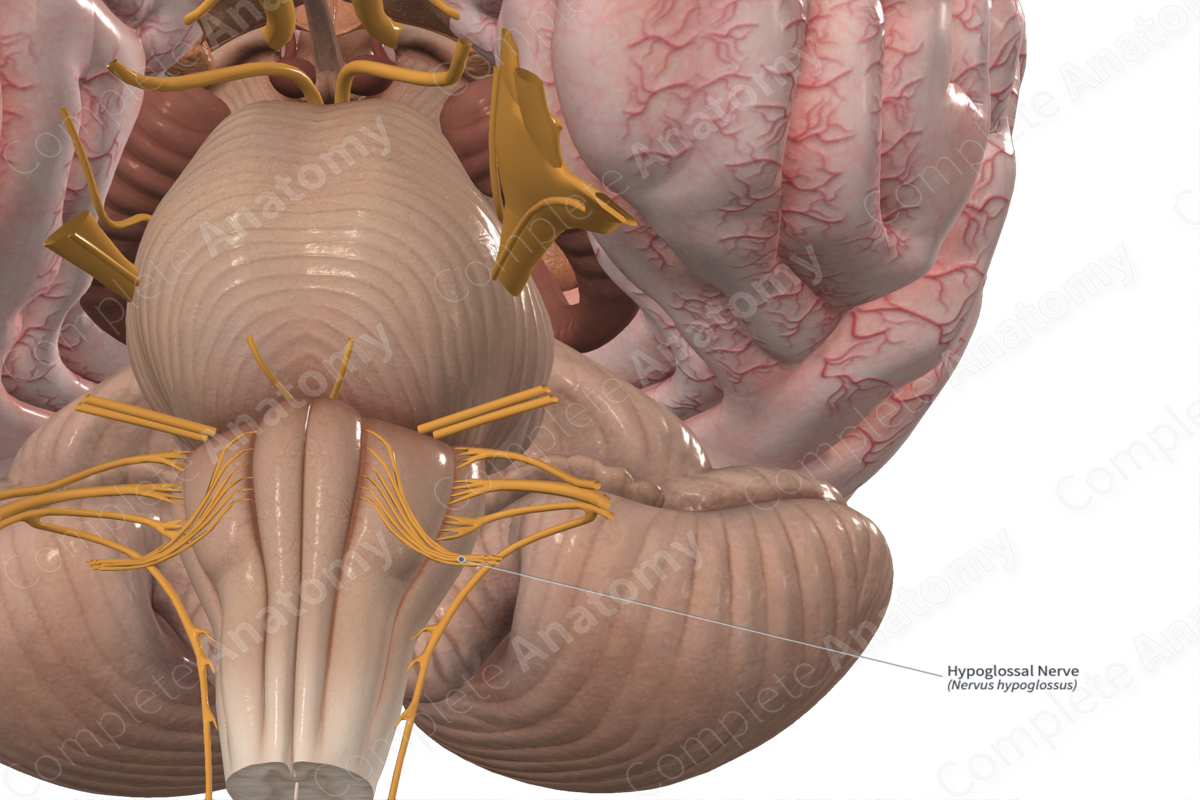
Hypoglossal nerve
Starts from the hypoglossal nuclei pair in the lower medulla. The 2 nerves travel laterally and ventrally from the respective nucleus. The nerve splits in 2 before exiting the medulla and passes through the hypoglossal canal in the skull's occipital bone
Anterior
_____ Cranial Fossa
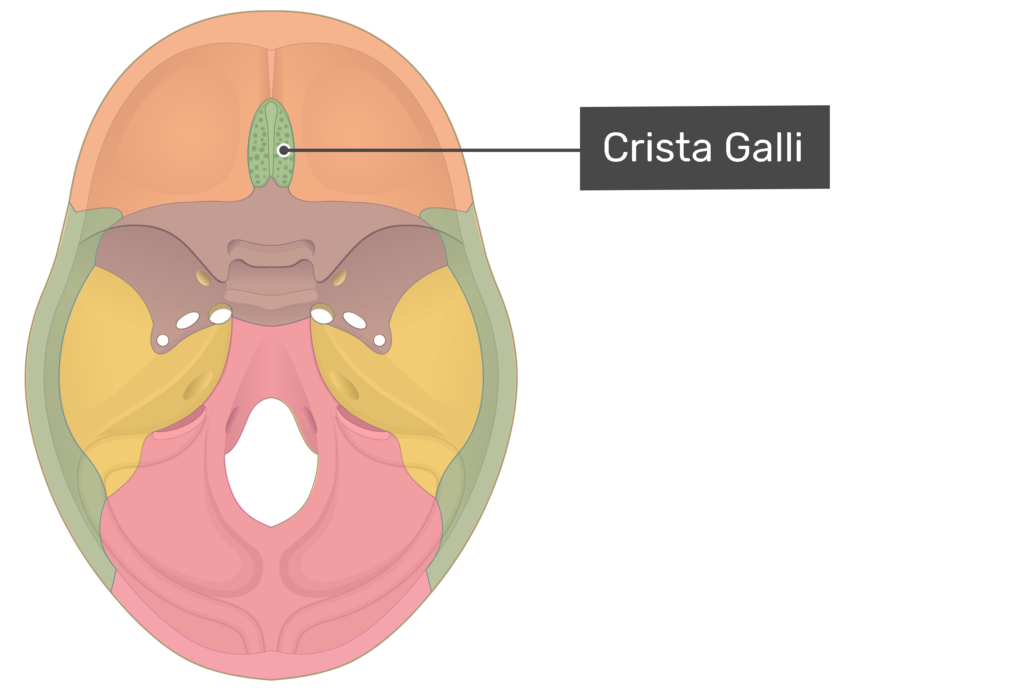
• Crista galli and cribiform plate
– numerous tiny foramina transmit the olfactory nerves (CN I) from the olfactory areas of the nasal cavities to the olfactory bulbs of the brain, which lie on this plate
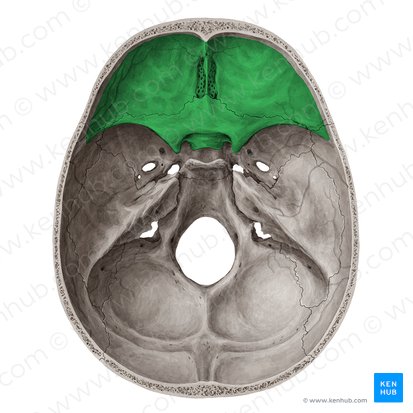
Crista galli
Acts an attachment point for the falx cerebri, a membrane that separates the two hemispheres of the brain. It also helps to anchor the brain and protect it from movement
Cribriform plate
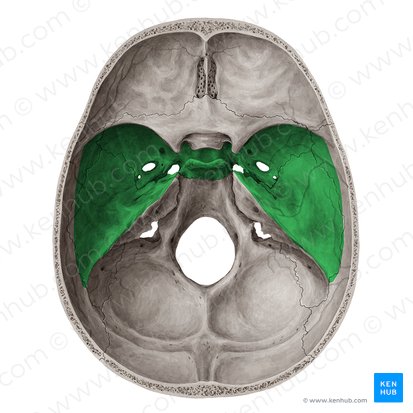
Middle
_____ Cranial Fossa
• Optic Canals
– Optic nerves (CN II) and ophthalmic arteries
• Superior Orbital Fissure
– Opthalmic veins, ophthalmic nerve (CN V1), CN III, IV, and VI
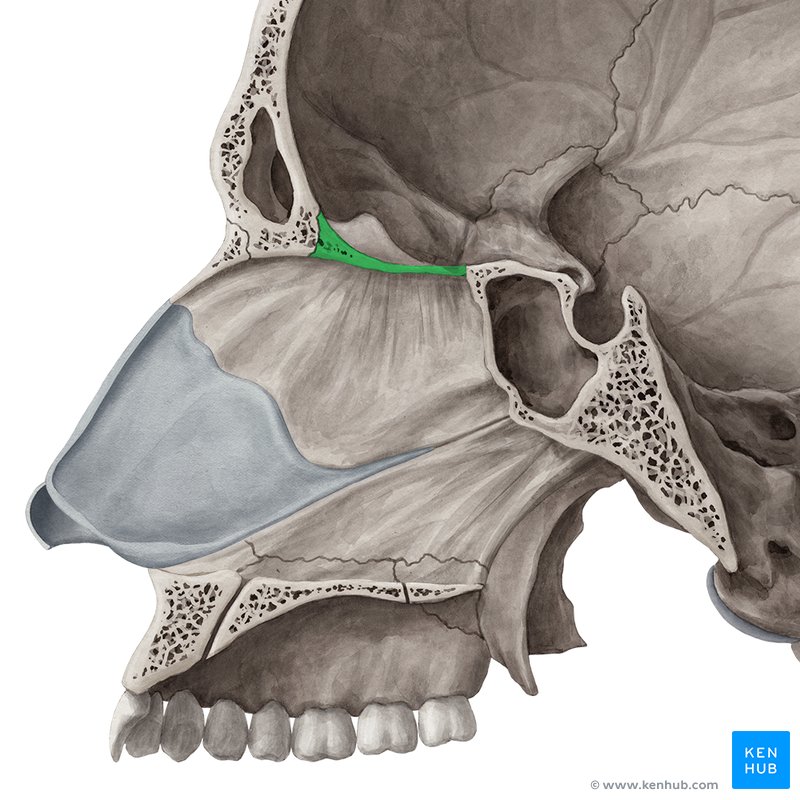
• Foramen Rotundum
– Maxillary nerve (CN V2)
• Foramen Lacerum
– Internal carotid artery (and its sympathetic and venous plexi)
• Foramen Spinosum
– Middle meningeal artery/vein; meningeal branch of CN V3
• Foramen Ovale
– Mandibular nerve (CN V3), and accessory meningeal artery
Foramen rotundum
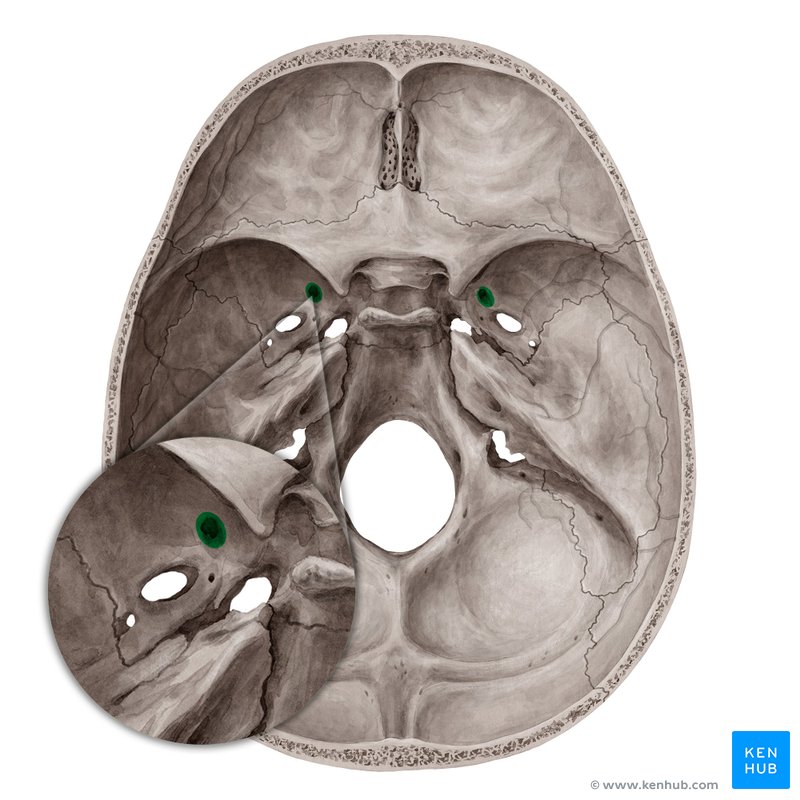
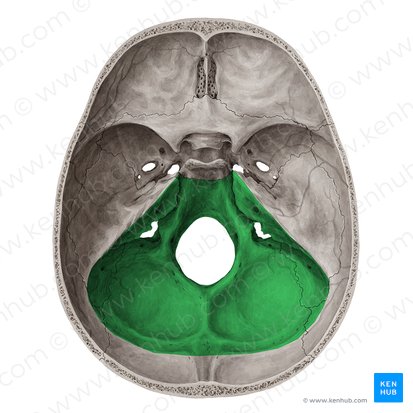
Posterior
_____ Cranial Fossa
• Foramen Magnum
– Medulla and meninges, vertebral arteries, CN XI, dural veins, anterior and posterior spinal arteries
• Jugular Foramen
– CN IX, X, and XI; superior bulb of internal jugular vein, inferior petrosal and sigmoid sinuses, meningeal branches of ascending pharyngeal and occipital arteries
• Hypoglossal Canal
– Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
Cranial
meninges
_____ Cavity
• Walls
– Consist of inner and outer tables of compact bone that are separated by spongy bone called diploë
– Cranial _____
• Three membranes that surround the brain and are continuous with the meninges of the spinal cord.
• Dura mater
– Periosteal dura
– Meningeal dura
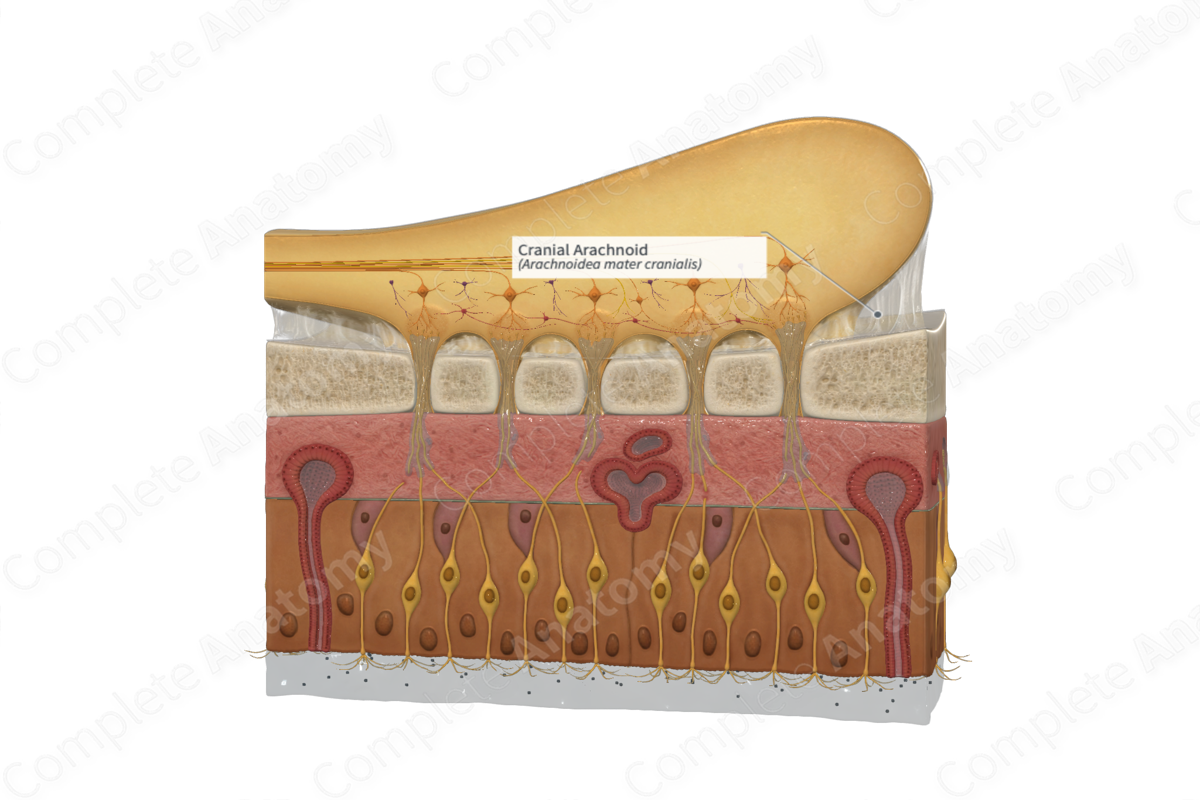
• Arachnoid mater
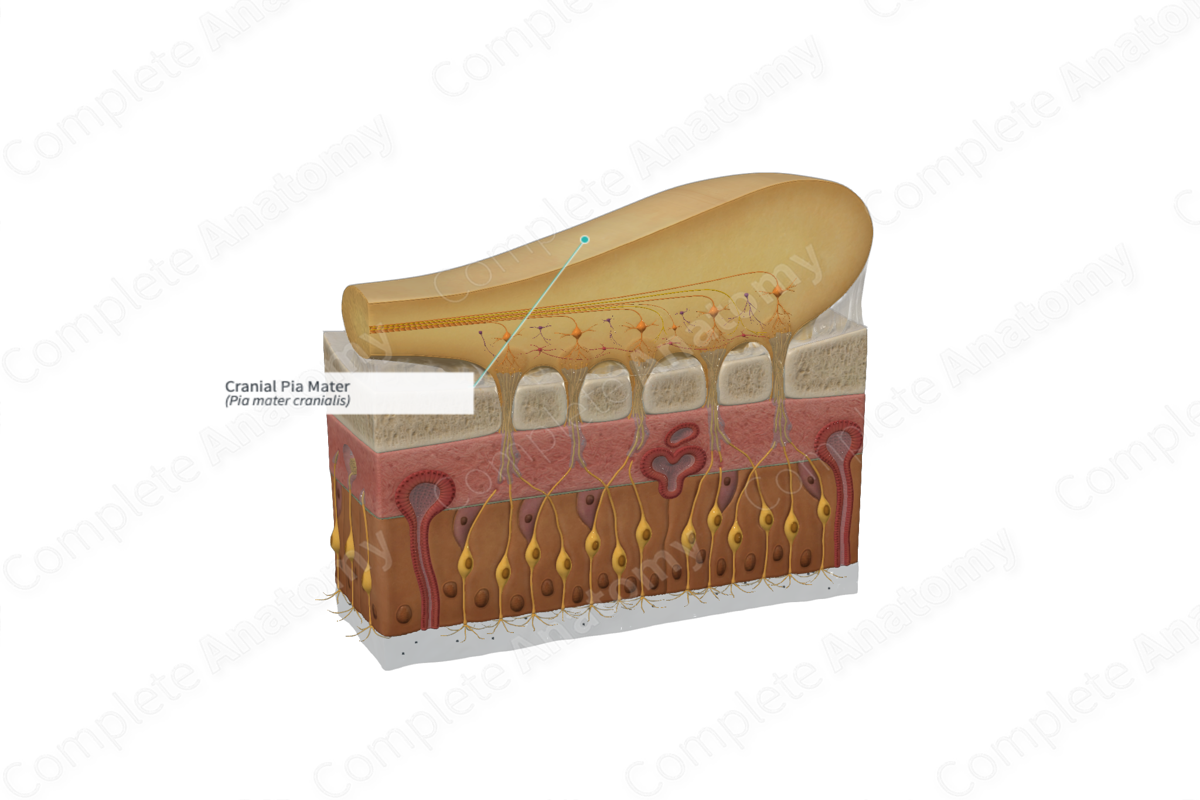
• Pia mater
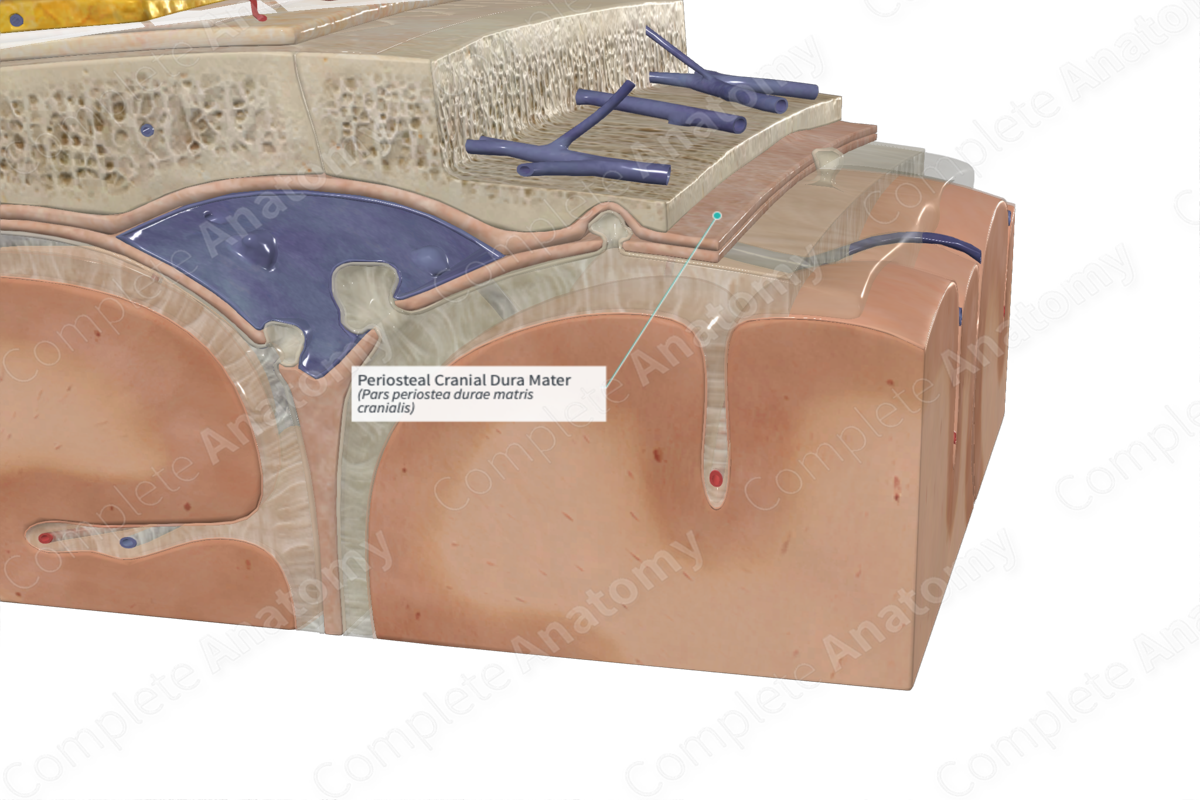
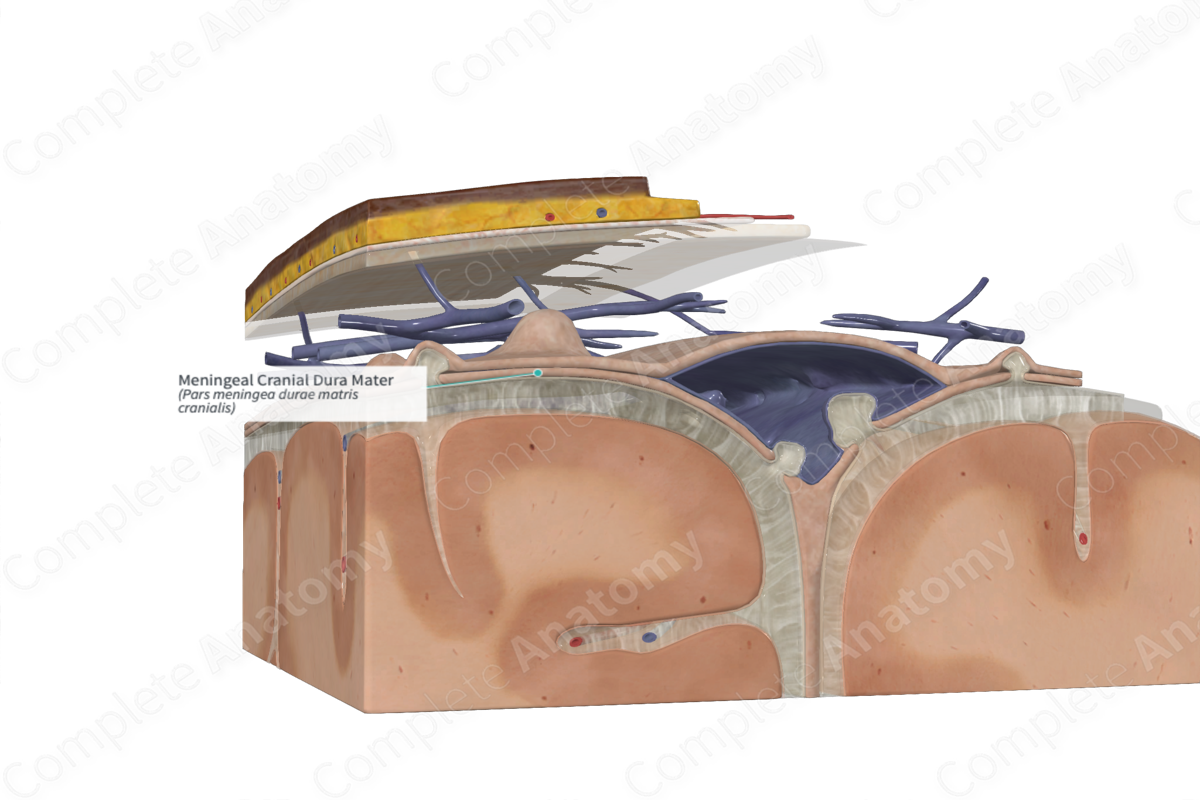
Dura mater
Fused to the periosteum, therefore it is considered to have two parts
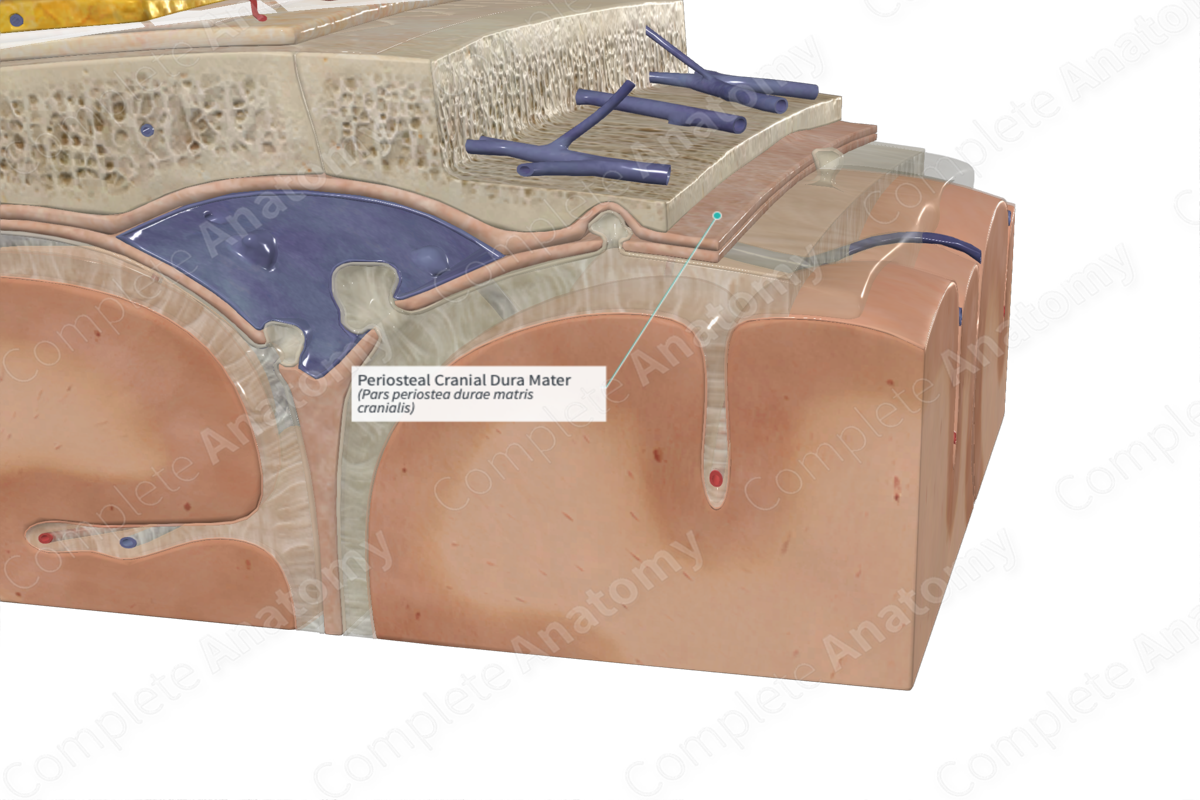
Periosteal dura
Continuous with the periosteum of the inner surface of the skull
Meningeal dura
Continuous with the dura of the spinal cord
Arachnoid mater
Delicate membrane that lines the inner surface of the dura. Arachnoid trabeculae are fine extensions that span across the subarachnoid space and attach to the pia mater.
Pia mater
Vascular delicate membrane that attaches to the brain.
Subarachnoid space
Filled with CSF
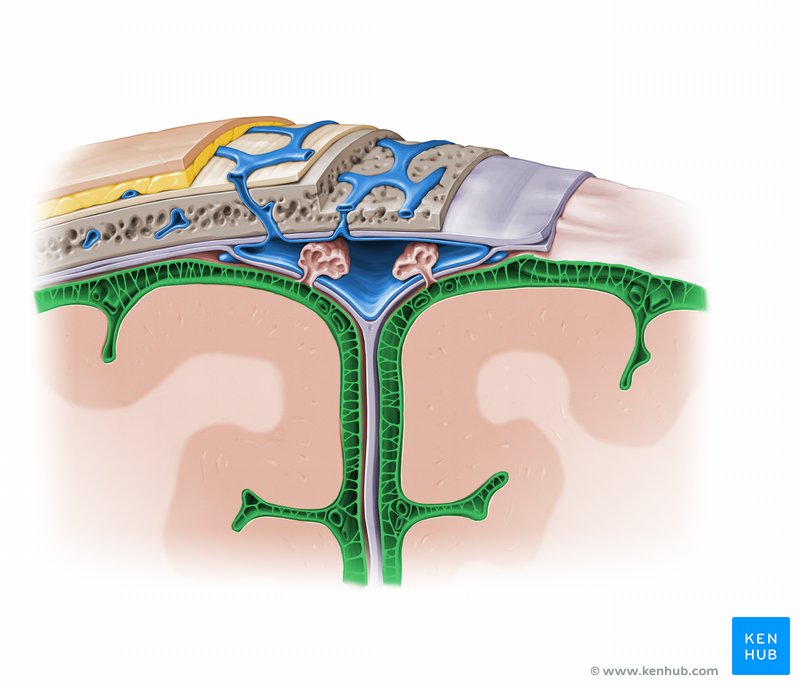
Dural
_____ Folds and Sinuses
• The separation of meningeal dura from periosteal dura creates channels.
These channels are lined with an endothelium and they receive veins that drain the brain and the meninges.
• They are in effect venous channels responsible for draining the contents of the cranial cavity.
• At other locations, the meningeal dura form folds that dip into fissures between parts of the brain.
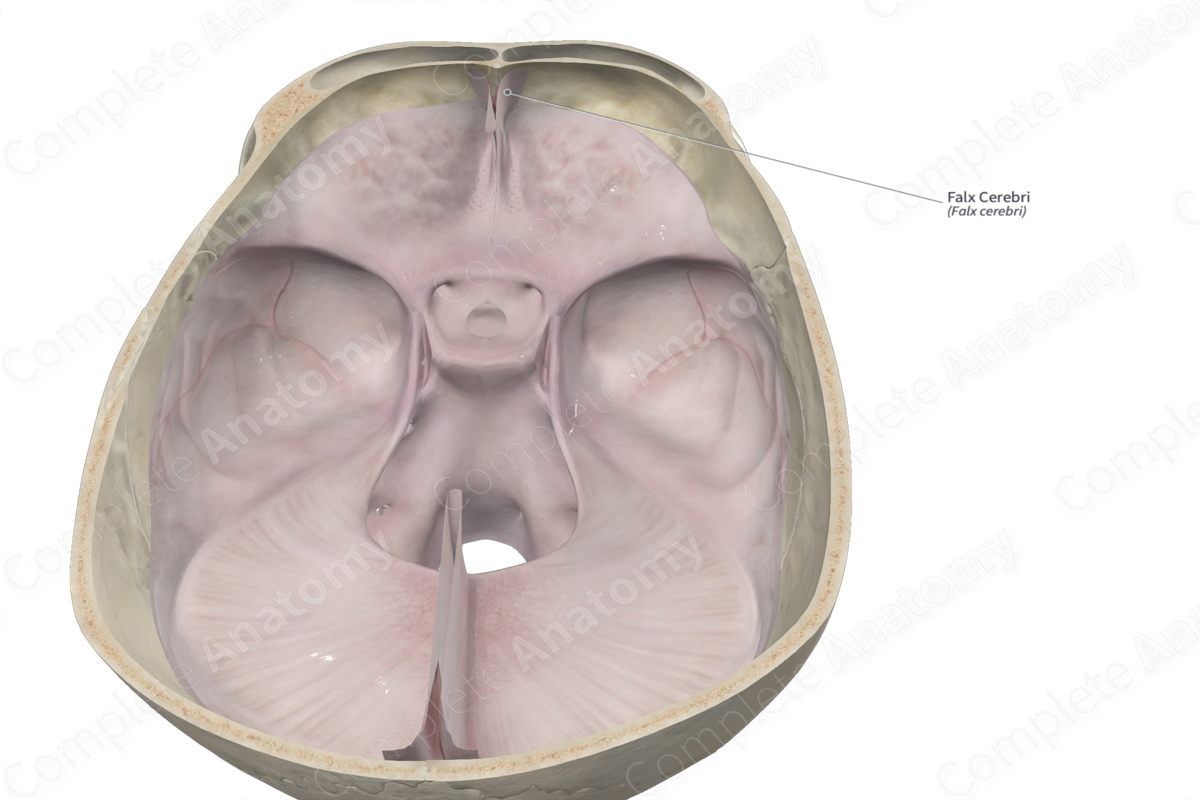
Falx cerebri
Separates cerebral hemispheres (longitudinal fissure
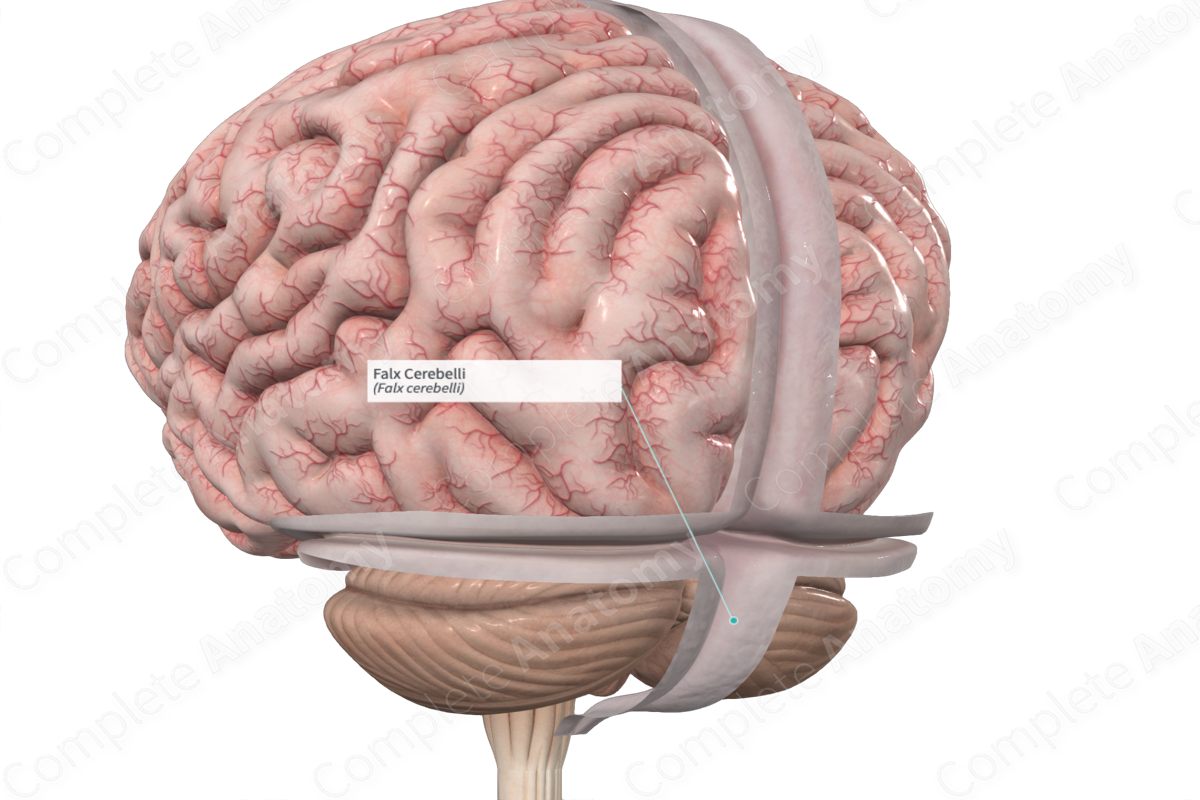
Falx cerebelli
Separates cerebellar hemispheres
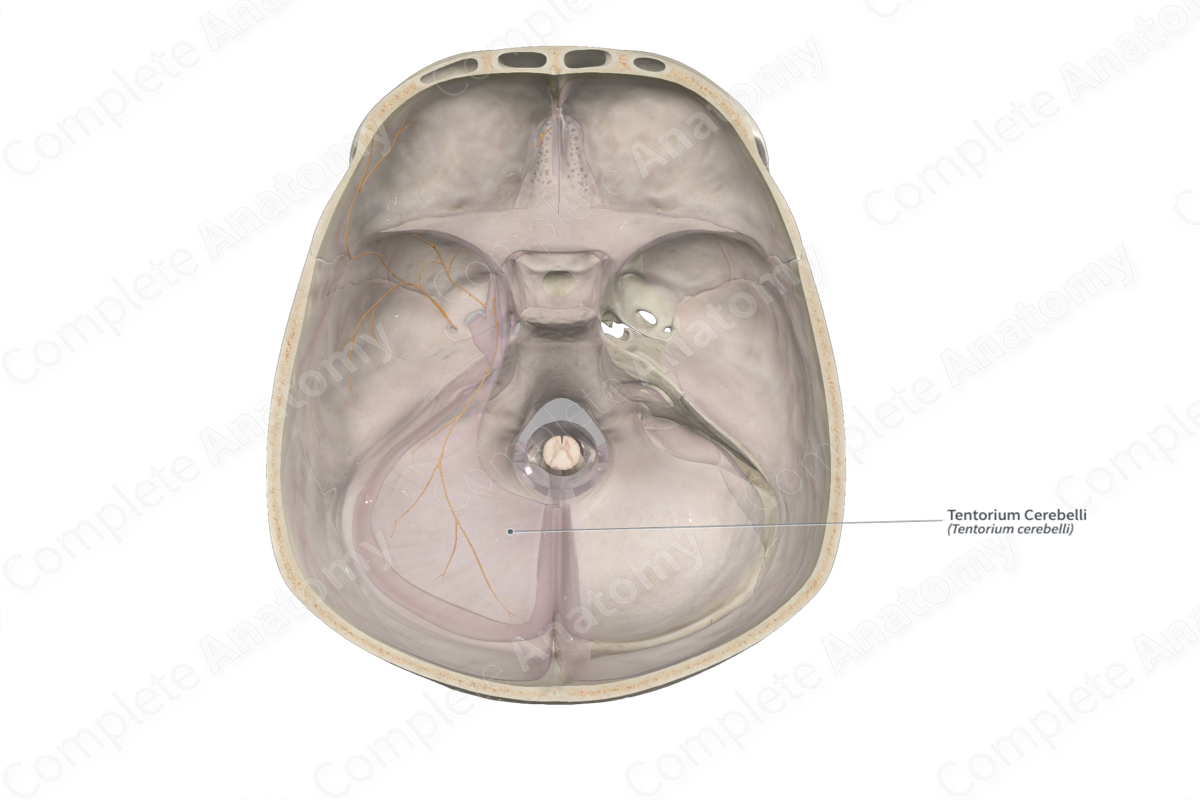
Tentorium cerebelli
Separates cerebellum from cerebrum
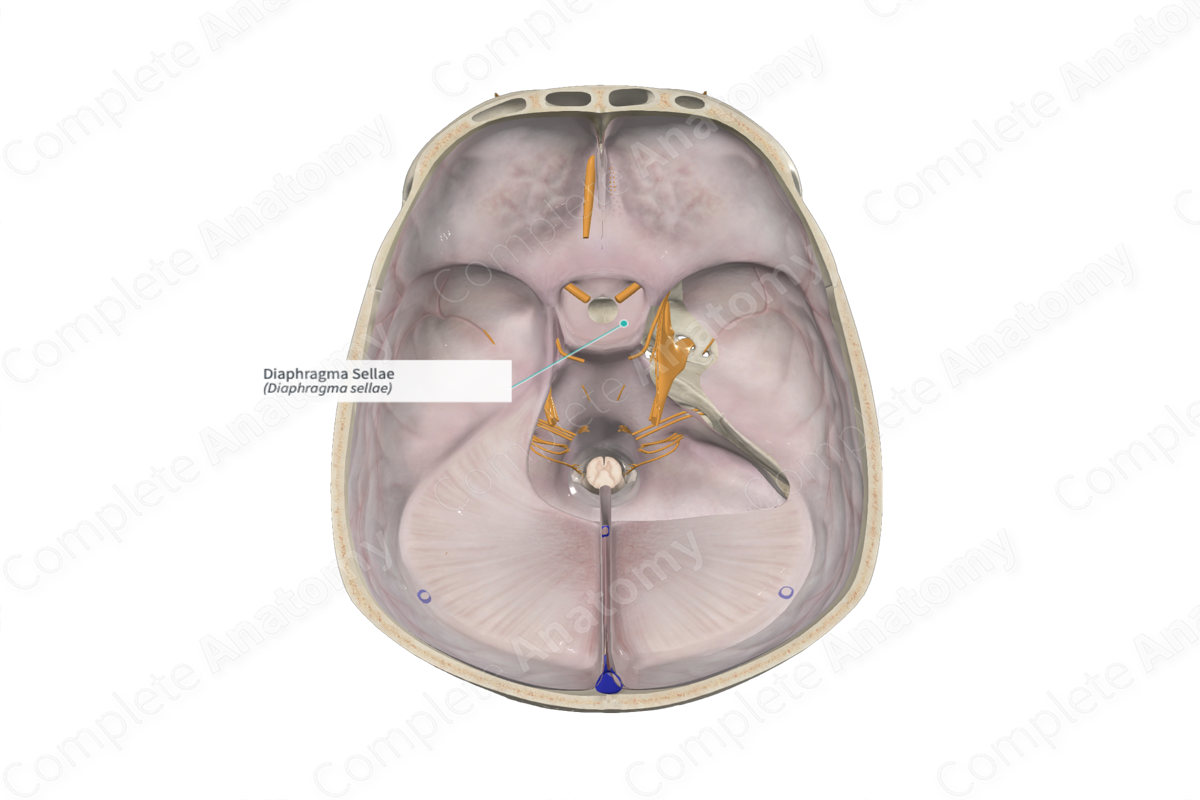
Diaphragma sellae
Closes off pituitary gland
Arachnoid granulations
Primary sites of CSF reabsorption into the dural venous sinuses
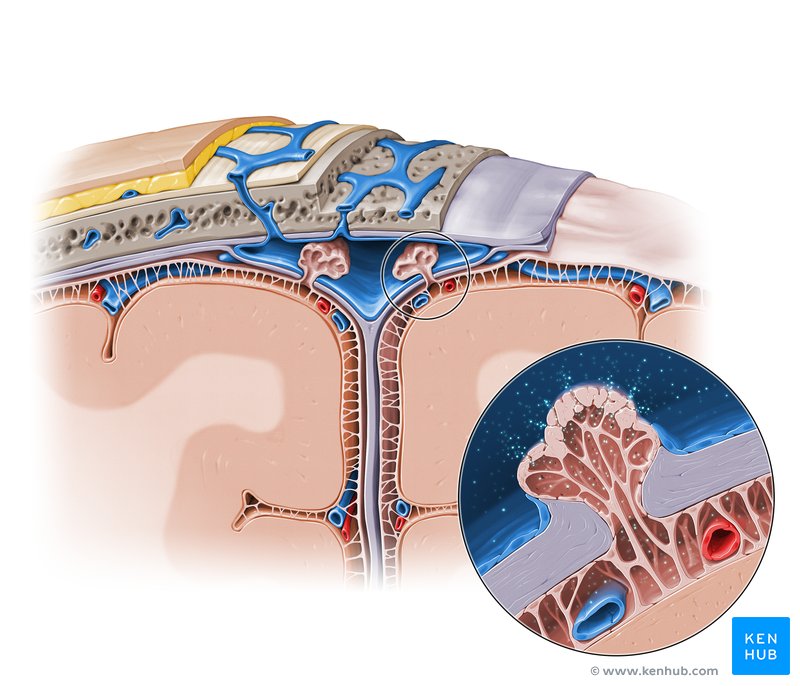
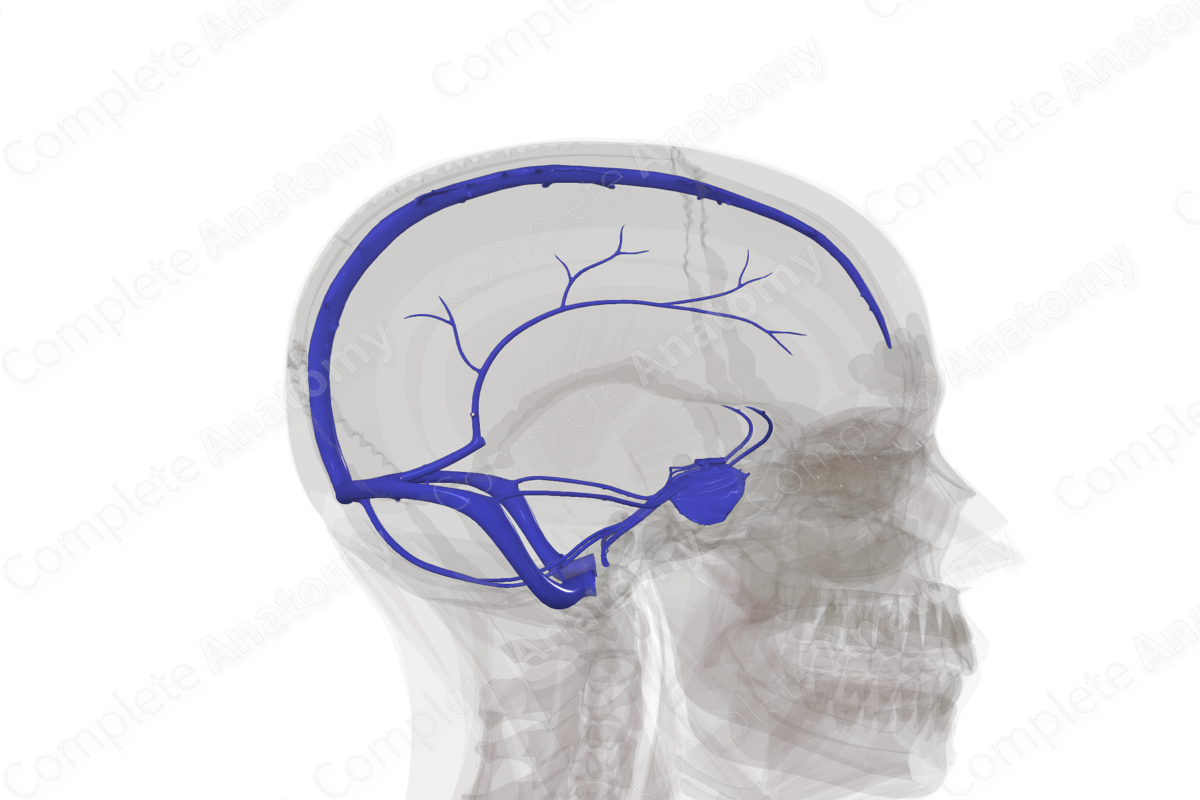
Lumen of dural venous sinus
Network of channels within the cranial cavity, sandwiched between the two layers of the dura mater. They are distinct from typical veins as they are devoid of valves and muscle, and instead, are lined with endothelial cell
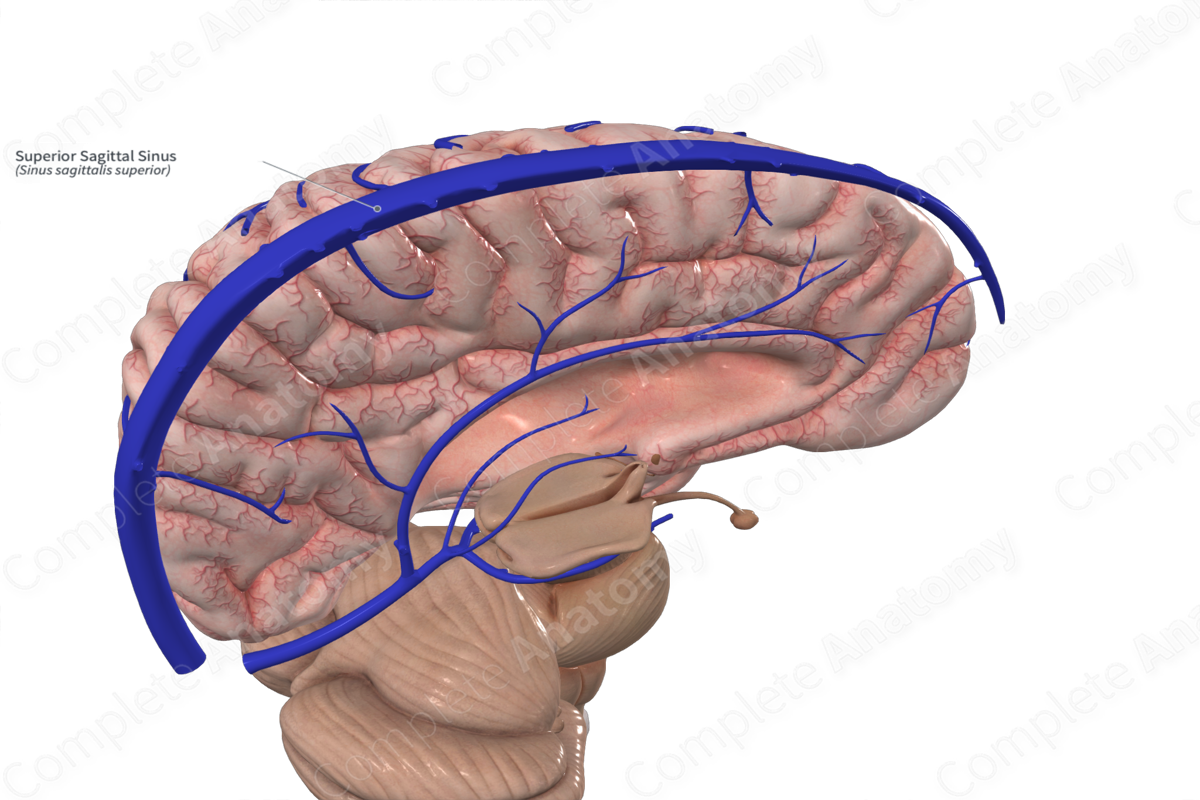
Superior sagittal sinus
Inferior sagittal sinus
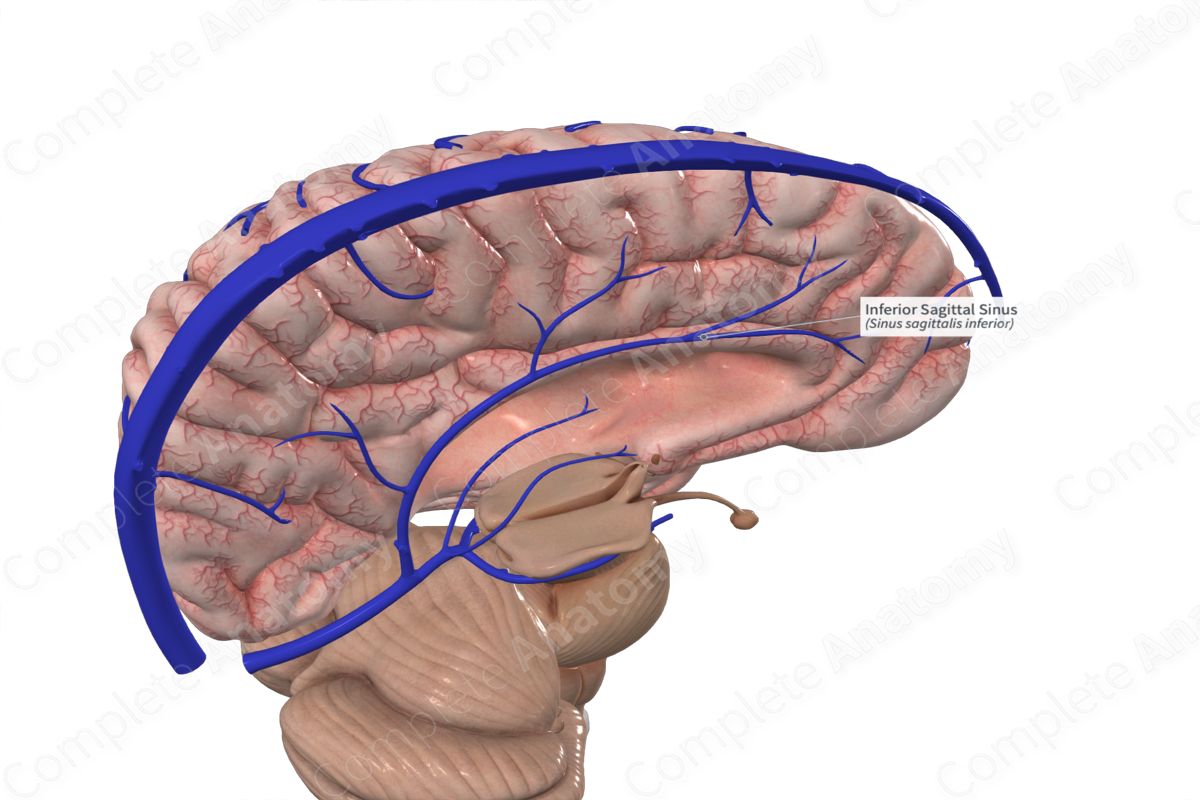
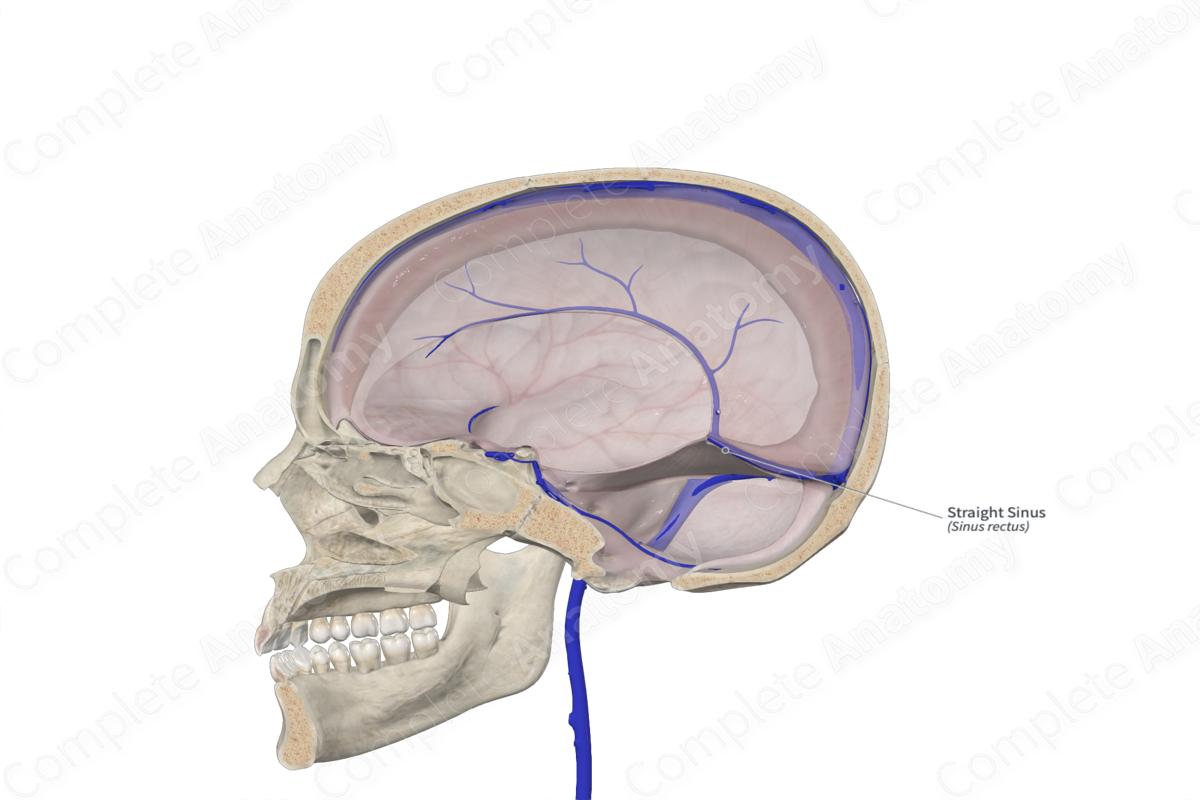
Straight sinus
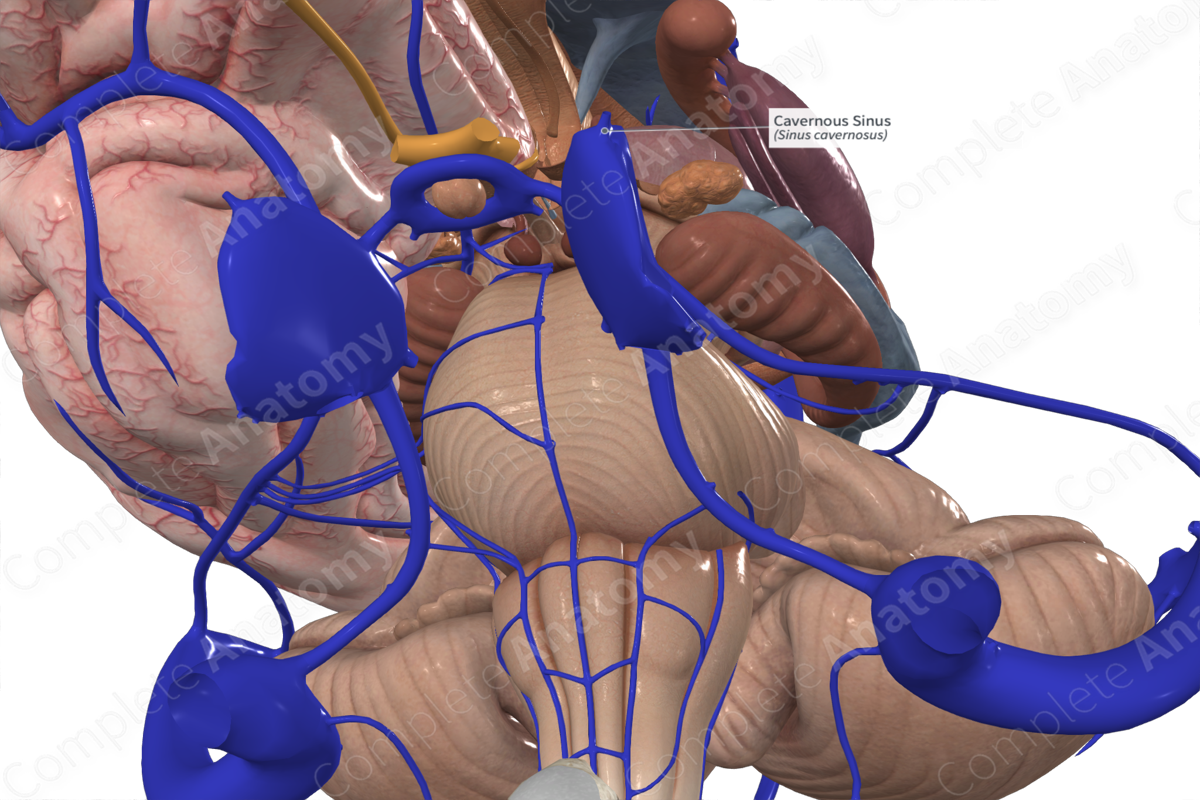
Cavernous sinuses
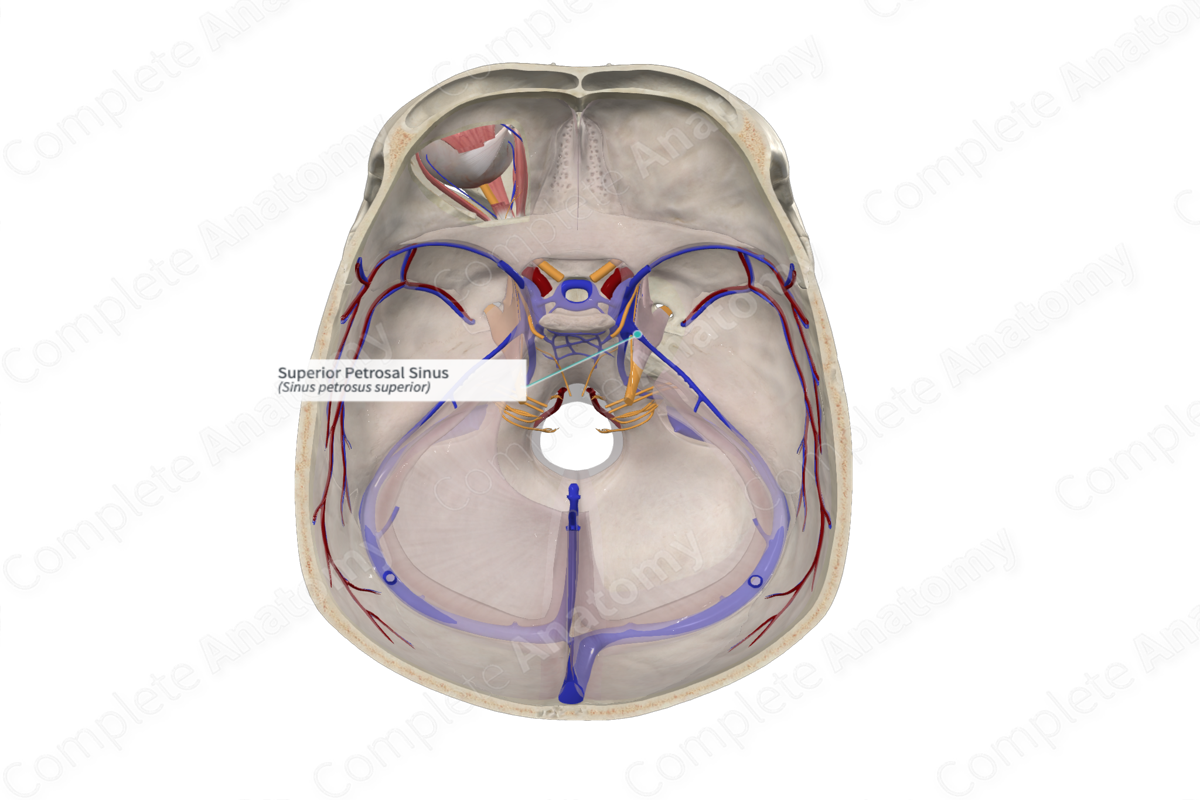
Superior petrosal sinus
Inferior petrosal sinus
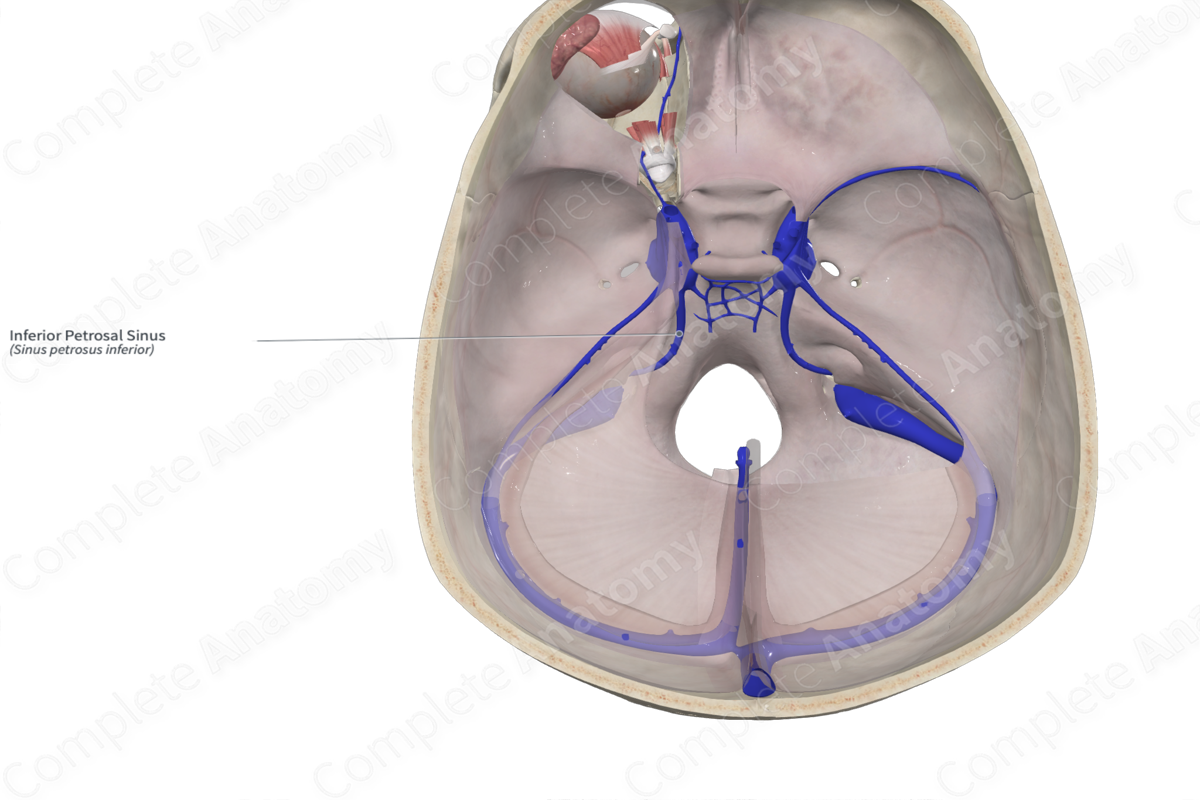
Sigmoid sinus