PBSI 336 Chapter 6: Cocaine and Amphetamines
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
stimulants, psychomotor stimulants, psychostimulants, or “uppers”
cocaine and amphetamines are a part of a larger class of drugs known as
stimulate alertness and arousal
stimulate motor activity
major behavioral properties of psychomotor stimulants
cocaine, amphetamines, nicotine, and caffeine
stimulants include
cocoa leaves
cocaine is a psychoactive alkaloid found in
weak base
cocaine is a
raw cocoa leaves chewed with lime powder or ash
enhances absorption by decreasing the ionization of cocaine
< 2% of cocaine
absorption from mouth
coca paste
crude extraction from leaves
~80% of cocaine sulfate
coca paste concentration
smoked
coca paste administration
cocaine HCl
crystalline powder extracted and purified from coca paste
very high
cocaine HCl concentration
orally, intranasally, or injected IV
cocaine HCl administration
cocaine free base
made from cocaine HCl + water + base
vaporized and smoked
cocaine free base administration
Crack or Rock cocaine
cruder preparation of free base, made from cocaine HCl
75-90%
crack cocaine concentration
smoked
crack cocaine administration
crack cocaine
led to a new epidemic of cocaine use in 1980s-90s
blocks monoamine transporters, like DAT
primary mechanism of cocaine
high doses of cocaine
inhibits voltage gated Na+ channels (action potential)
extremely rapid absorption
cocaine with smoking or IV
~1-2 minutes
peak subjective effect for crack cocaine
0.5-1.5 hours
half life of cocaine
detectable in urine for several days
inactive major metabolite benzoylecgonine
formed when cocaine and ethanol are ingested simultaneously
active metabolite cocaethylene
amphetamine
chemical family of synthetic and natural psychostimulants
ephedrine
natural, decongestants
cathinone
comes from khat or qat shrub, chewed
methcathinone and mephedrone (bath salts)
synthetic variants of cathinone
1920-30s
medical use of amphetemine developed
1940s
widespread adoption of amphetamine during WWII
early 1970s
peak use of speed
1887
amphetamine synthesized
1919
methamphetamine synthesized
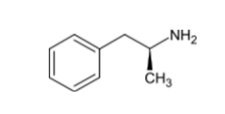
D-amphetamine
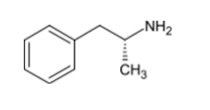
L-amphetamine
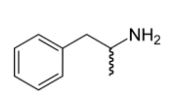
amphetamine (adderall)
orally or by injection (IV, SC)
amphetamine administration
methamphetamine
most potent of amphetamines
oral, snorted, injected Iv, or smoked
methamphetamine administration
methylphenidate and modafinil
amphetine like stimulants
narcolepsy, mild depression, and as a diet pill
amphetamine was used for
military during WWII and subsequent conflicts
amphetamines used widely by
> 10%
percent of population that used amphetamine in 1970
smoking
faster route of methamphetamine
narcolepsy, ADD/ADHD
current medical uses of amphetamine
slower metabolism and elimination
compared to cocaine, amphetamines have a
7-30 hrs
half life of amphetamines
increased blood pressure, hypothermia, bronchodilation
autonomic effects of amphetamines
shorter duration of action, worse cardiovascular effects, higher convulsive/seizure properties
effects of cocaine compared to amphetimines
go down because rats perform stereotypy behavior instead
locomotor activity appears to what with high AMPH doses
chronic, high dose users of stimulants
withdrawal symptoms are mostly psychological and not fatal
autonomic effects, anorexic effects
tolerance to some effects of psychostimulants
rewarding effects, psychotomimetic effects, locomotor stimulant effects
sensitization to other effects of psychostimulants
psychosis, anorexia, physical damage
negative effects of chronic amphetamine use
MDA
MDE or MDEA
MDMA related drugs
never used clinically
MDMA was
enhance communication and openness
recent evidence shows that MDMA can
club drug during 1980s-90s
MDMA first became popular as
Schedule 1
MDMA classification
mostly orally
MDMA administration
8 hrs
MDMA half life
increased energy/sociability; mild euphoria
increased heart rate and temp
MDMA effects at low doses
mild hallucinogenic
hyperthermia and dehydration; increase HR and BP » stroke
MDMA effects at high doses
cocaine
blocks reuptake of monoamines
very high DA in synaptic cleft
actions of amphetamines lead to
catecholamines and indolamines
monoamines synthesize to
dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine
catecholamines synthesize to
seratonin
indolamines synthesize to
tyrosine hydroxylase
rate limiting step in catecholamine synthesis
tyrosine
amino acid and the precursor for catecholamines
classical neurotransmitters
all monoamines are
reuptake via transporters and/or enzymatic degradation
catecholamines are inactivated by
primary mechanism for inactivation and is much faster than metabolism
catecholamine reuptake into the axon terminal is the
vesicular monoamine transporter VMAT 2
all monoamines packaged into vesicles by
synaptic transporters
each monoamine has its own unique
DAT
dopamine transporter
NET
norepinephrine transporter
SERT
serotonin transporter
MAO and COMT
types of enzymes involved in catecholamine metabolism
D1 D2 D3 D4 D5
dopamine receptors
coupled to Gs
D1 and D5 (D1 like receptors)
coupled to Gi
D2 D3 and D4 (D2 like receptors)
D2
presynaptic auto receptors are mostly
prefrontal cortex area
dopamine receptors are concentrated in
neurons in brainstem
send broad diffuse projections to large areas of forebrain
midbrain, substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area (VTA)
majority of dopamine neurons can be found in
nigrostriatal pathway
DA neurons in substantia nigra target dorsal striatum
mesolimbic pathway
DA neurons in ventral tegmental area (VTA) target ventral striatum and amygdala
mesocortical pathway
DA neurons in VTA target prefrontal cortex
send axon projections to striatum
no DA neurons in striatum but rather DA neurons
DA fibers, DA release at synapses, and DA receptors/transporters
striatum has a lot of
death of midbrain dopamine neurons and their striatal terminals
parkinsons disease
MPP+
a potent DA neurotoxin
MPTP
used in research to produce dopamine lesions in non human primates
6-OHDA is used instead
rats are resistant to MPTP so
α1 α2 β1 β2
primary adrenergic receptors found in brain
coupled to Gq
alpha 1
coupled to Gi and autoreceptor
alpha 2