W6 - Hypothalamus, Pituitary and Thyroid Gland
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Endocrine/ Neuroendocrine System
function
composition
key players
regulation of growth, metabolism, and reproduction
glands and secretory cells
hormones/neurohormones
Neuroendocrine Stimulus in the CNS
neural control/aspect in the secretion of hormones which is the hypothalamus; neurohormone release through efferent neurons
Types of Neurohormones
catecholamines = class of hormones and neurotransmitters that take part in stress response, produced by adrenal medulla, brain, nervous tissue
hypothalamic neurohormones
stored and secreted by the post. pituitary
controls hormone release by the ant. pituitary
Releasing vs. Effector Hormone
releasing - acts on endocrine cells to secrete hormones (eg. GHRH and GHIH produced by the hypothalamus)
effector - acts on target producing a physiological response (eg. GH released by the ant.pituitary gland)
Hormonal Secretion Regulation
regulated through feedback
negative = responds to maintain homeostasis
positive (less common) = amplifies a stimulus
What links the NS and the Endocrine System
the hypothalamus which is connected to the pituitary glands via the infundibulum
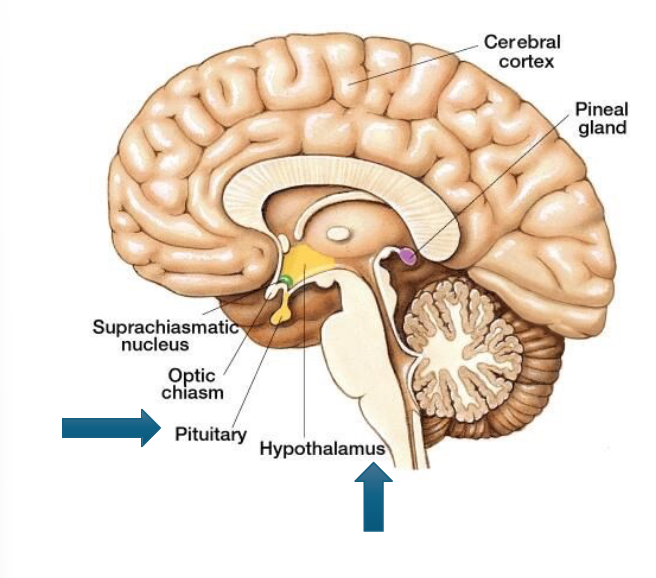
Endocrine Functions of the Hypothalamus
stimulates the release of effector hormones from the ant. pituitary that control other endocrine organs
produces ADH and oxytocin which is stored and released in the post. pituitary
contains sympathetic neurons that innervate the adrenal gland which secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
Anterior vs. Posterior Pituitary
anterior/ adenohypophysis = true endocrine gland, produce and secretes hormones
posterior/ neurohypophysis = extension of neural tissue and secretes neurohormones produced in the hypothalamus
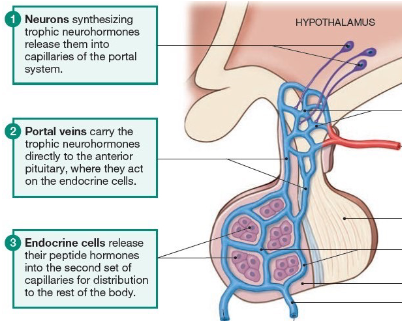
Hypothalamic-hypophyseal Portal System
major interface between the brain and the endocrine system which is via a portal system
trophic neurohormones are released into the capillaries of the portal system
portal veins carry them directly to the ant.pituitary
endocrine cells in the ant.pituitary release their peptide hormones into the second set of capillaries for bodily distribution
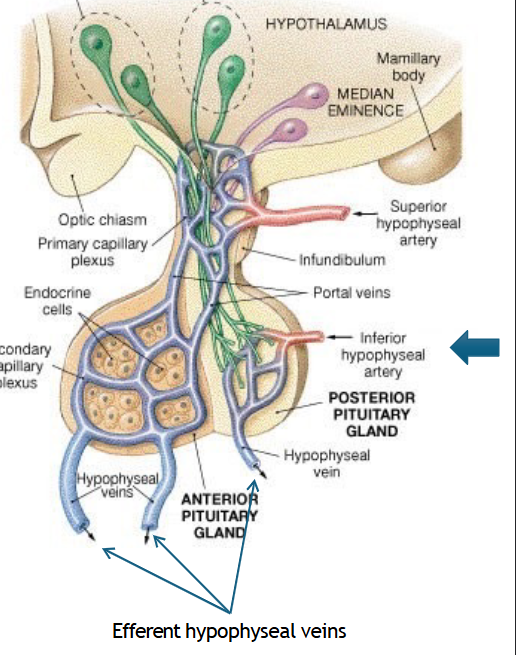
Blood System of the Posterior Pituitary
arterial blood enter via the inferior hypophyseal artery → branch of the ICA
venous/plexus drained via efferent hypophyseal veins → which is drained into the cavernous sinus
Posterior Pituitary Gland stores and releases
oxytocin and vaspressin, important to note that the hypothalamus produces these hormones
Vasopressin
an anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) produced when the hypothalamic osmoreceptors detect changes in blood solute concentrations
ADH Effects
increases water reabsorption by the kidneys (inhibits urine output)
constriction of blood vessels (BP)
decreases water loss by sweat glands
Oxytocin Functions
childbirth = levels rise in response to positive feedback, stimulated by the stretching of the cervix
breast milk = stimulated by breast feeding, sensory neurons innervating the nipples project info to hypothalamus
Anterior Pituitary Hormones
a major endocrine gland
two sections
pars intermedia = MSH → skin
pars distalis = hormones to mammary glands, musculoskeletal system, thyroid gland, adrenal cortex, sex organs
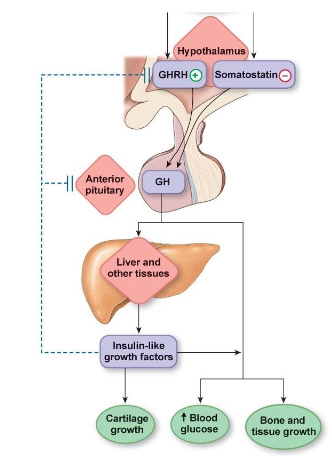
Growth Hormones (GH)
function
regulation
feedback control type
functions in growth by releasing the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) in the liver
GHRH and GHIH which is released by the hypothalamus
negative feedback
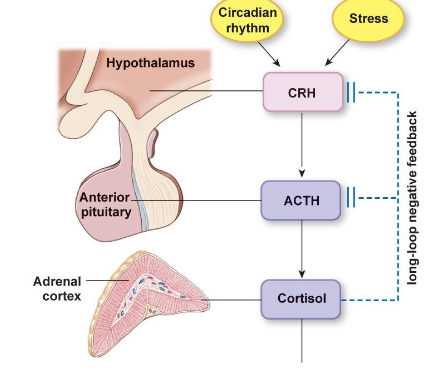
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
function
regulation
feedback control type
stimulates synthesis and secretion of cortisol by the adrenal cortex
release is stimulated by the corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) from hypothalamus (no IH)
controlled by negative feedback
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
function
regulation
feedback control type
development of gametes and sex hormones (acts on ovaries/testes)
stimulated by gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) from hypothalamus
controlled by positive and negative feedbacks
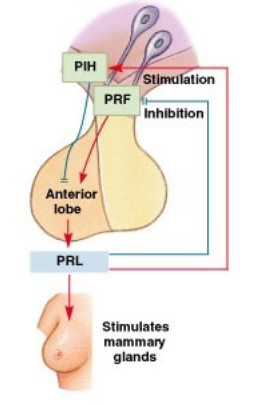
Prolactin (PRL)
function
regulation
initiates and maintains mammary gland development and milk production
regulated by PRH and PIH from the hypothalamus
Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (MSH)
function
regulation
exact role is unknown, but enhances skin pigmentation
release is stimulated by CRH and MIF from the hypothalamus
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
function
regulation
feedback control type
TSH stimulates the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland
stimulated by the TRH from hypothalamus
negative feedback
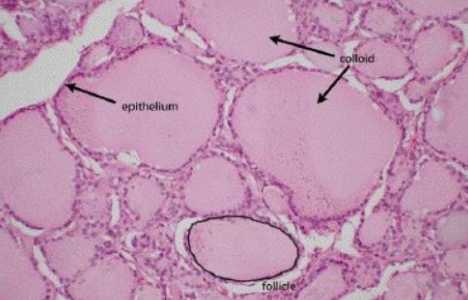
Thyroid Follicle Contents
follicular cells = synthesize thyroid hormones
colloid = viscous fluid that stores inactive thyroid hormones
parafollicular cells = lies between thyroid follicles, secrete calcitonin
Types of Thyroid Hormones
thyroxine (T4) = 90% production, inactive hormone which gets converted in T3 in the circulation
triiodothyronine (T3) = active form
Key Functions of Thyroid Hormone
increases basal metabolic rate and body temp → increased production of ATP
fetal development and growth in children (nervous and skeletal)
increases HR and contractility
Transportation of Thyroid Hormones
T3 and T4 are lipid soluble and in blood they bound to thyroxine-binding globulin (TBG)
Effect of TSH on Follicular Cells
TSH binds to the receptors on follicular cells and
increases activity of Na+/I- transporter
increases thyroglobulin synthesis
release of stored thyroid hormones
increases number and size of follicular cells
Calcium Balance Regulation
calcitonin builds bone
parathyroid resorbs bone