A&P integumentary system
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Last updated 6:12 PM on 3/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
1
New cards
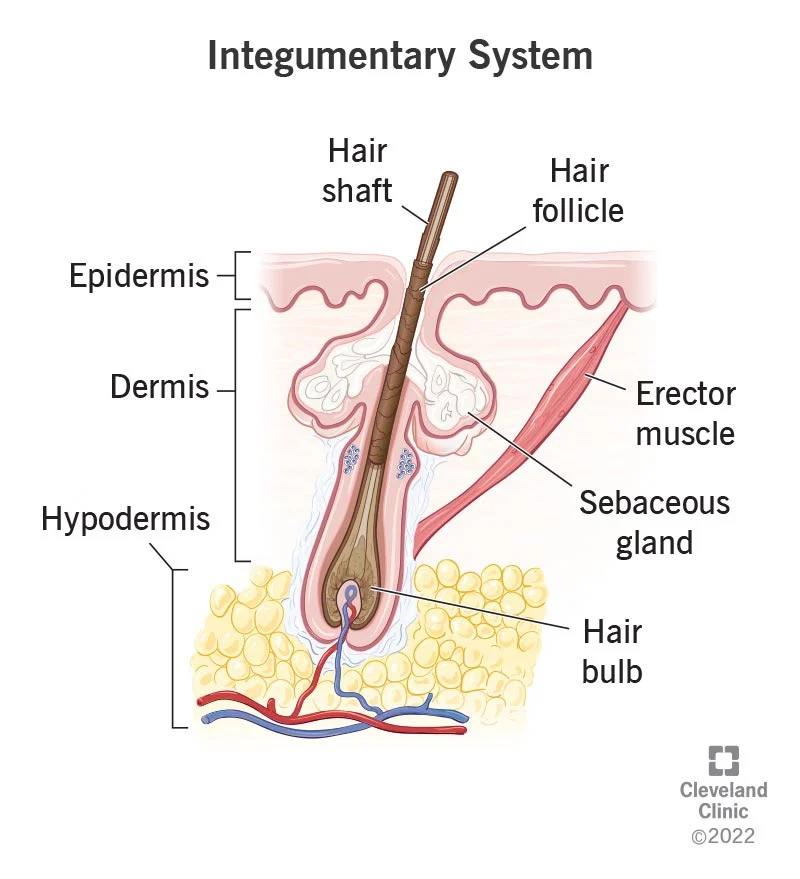
parts of the integumentary system
epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, hair shaft, hair follicle, erector muscle, sebaceous gland, hair root, nails
2
New cards
how does skin provide biological protection?
protects the body from external factors such as bacteria, chemicals, and temperature.
3
New cards
how does skin provide mechanical protection?
skin cells form special anchoring points known as desmosomes, which increase the adhesion between cells.
4
New cards
how does skin provide chemical protection?
skin contains secretions that can kill bacteria and the pigment melanin provides a chemical pigment defense against ultraviolet light that can damage skin cells.
5
New cards
how is vitamin D synthesized
ultraviolet radiation penetrates into the epidermis and photolyzes provitamin D3 to previtamin D3.
6
New cards
what is keratin
A type of protein found on epithelial cells, which line the inside and outside surfaces of the body. Keratin helps form the tissues of the hair, nails, and outer layer of the skin.
7
New cards
what is melanin
Brown, yellow-brown, or black pigment. Produced by melanocytes in stratum basale. Packaged into melanosomes (vesicles). Provides some protection against effects of UV radiation by shading cell nuclei.
8
New cards
what is keritinization
the process in which the outermost cells of the epidermis in vertebrates are replaced by cells containing keratin. This process occurs in the stratum corneum layer of the skin.
9
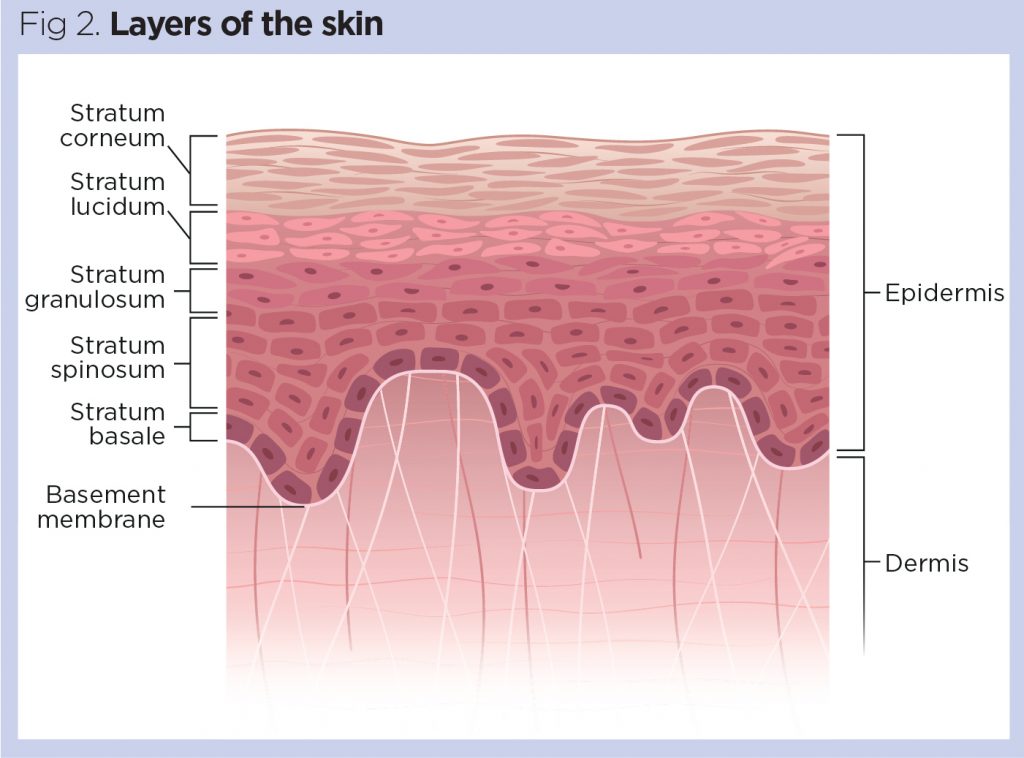
New cards
5 layers of thick skin epidermis (deep to superficial)
stratum basale, stratum spinosum, stratum granulosum, stratum lucidum, stratum corneum.
10
New cards
what is the germinal layer of the epidermis
basal layer (or stratum germinativum)
11
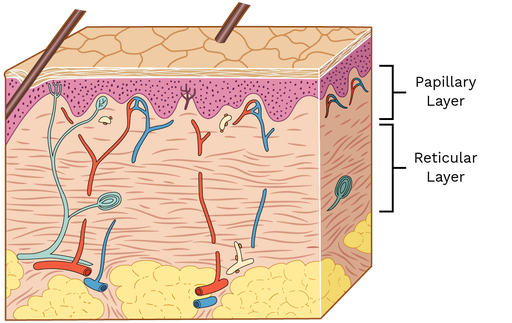
New cards
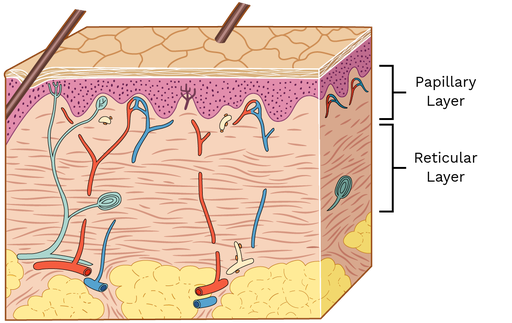
what is the papillary layer
named for dermal papillae in this region, composed of areolar tissue
12
New cards
what is the reticular layer
Composed of dense irregular connective tissue, contains both collagen and elastic fibers, contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerve fibers, and accessory organs (hair follicles, sweat glands)
13
New cards
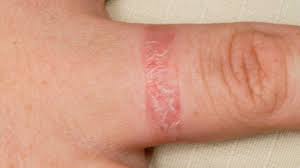
what is dermatitis
a general term that describes inflammation of the skin, a common cause of dermatitis is contact with something that irritates your skin or triggers an allergic reaction.
14
New cards
what is bilirubin
a yellowish pigment that is made during the breakdown of red blood cells.
15
New cards
what is hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is red pigment found in red blood \n cells
16
New cards
what is carotene
Orange-yellow pigment
17
New cards
what are clinical signs given by skin color
blue/purple skin, pale skin, Jaundice (yellow skin), flushed skin.
18
New cards
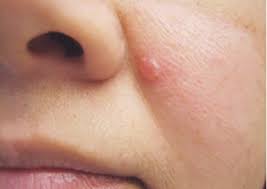
what is basal cell carcinoma
Most common form of skin cancer, originates in stratum basale due to mutations caused by overexposure to UV radiation.
19
New cards
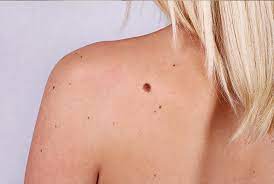
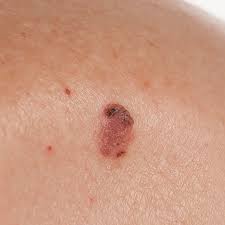
what is malignant melanoma
Most serious form of skin cancer, extremely dangerous, cancerous melanocytes grow rapidly and metastasize through \n lymphatic system, if detected early and removed surgically, the \n 5-year survival rate is 99 percent.
20
New cards
what is squamous cell carcinoma
a common form of skin cancer that develops in the squamous cells that make up the middle and outer layers of the skin. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is usually not life-threatening, though it can be aggressive.
21
New cards
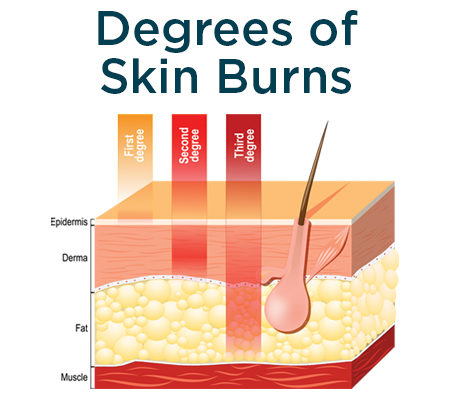
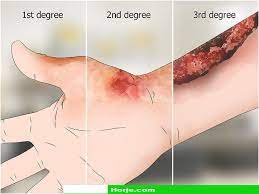
what are the 3 stages of burns
first, second, and third degree
22
New cards
what are the signs and symptoms of a first degree burn
Only the surface of the epidermis affected. \n Example: most sunburns. \n Painful, skin redness (erythema) results.

23
New cards
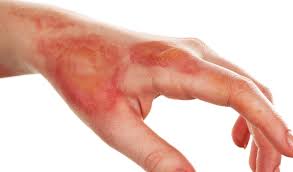
what are the signs and symptoms of a second degree burn
Entire epidermis and maybe some of dermis damaged. \n Blistering, pain, and swelling occur. \n Infection can develop from ruptured blisters.
24
New cards
what are the signs and symptoms of a third degree burn
Full-thickness burns. \n Destroys epidermis, dermis, and damage extends into hypodermis. \n Sensory nerves are destroyed. \n Skin grafting usually necessary.
25
New cards
what are the main health concerns of a burn
Bacterial infection, which may lead to a bloodstream infection (sepsis) Fluid loss, including low blood volume (hypovolemia) Dangerously low body temperature (hypothermia).
26
New cards
what is the rule of nines of burns
Method of estimating percentage of surface area affected by burns, modified for children (different body proportions).
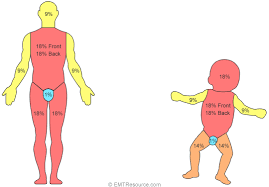
27
New cards
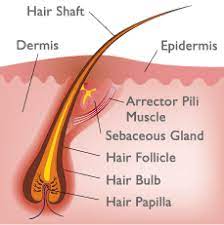
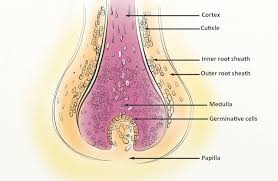
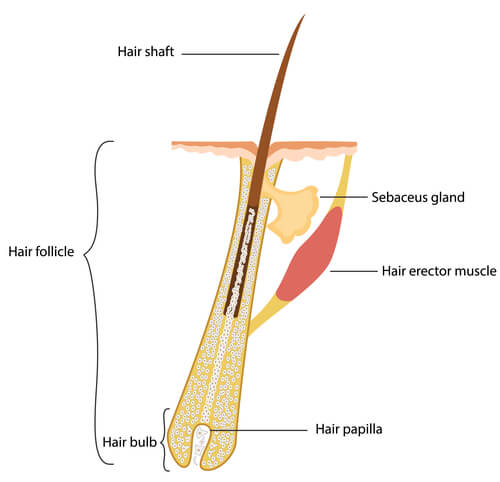
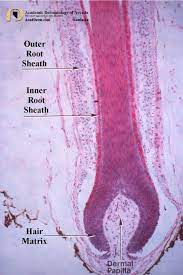
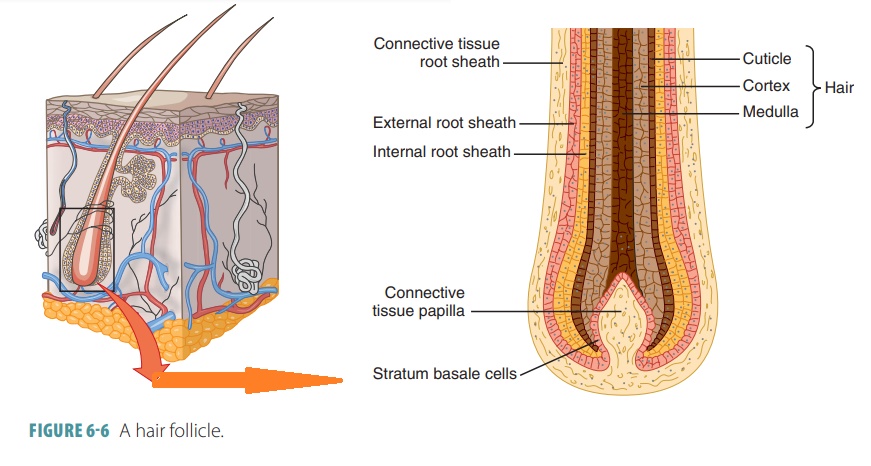
what are the parts of a hair
hair bulb, hair papilla, hair matrix, medulla, cortex, cuticle.
28
New cards
what is the hair bulb
expanded base of hair follicle
29
New cards
what is a hair papilla
peg of connective tissue filled with blood vessels and nerves
30
New cards
what is a hair matrix
actively dividing basal cells in contact with hair papilla
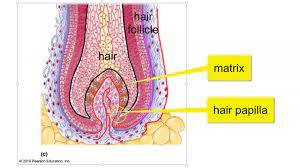
31
New cards
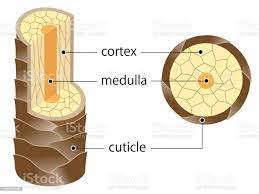
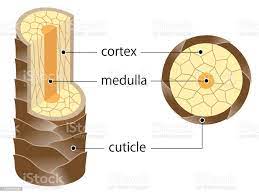
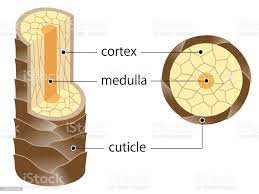
what is a medulla (part of hair)
layer of daughter cells formed at the center of the matrix
32
New cards
what is a cortex (part of hair)
intermediate layer deep to the cuticle
33
New cards
what is the cuticle
daughter cells produced at edges of the matrix; forms surface of the hair
34
New cards
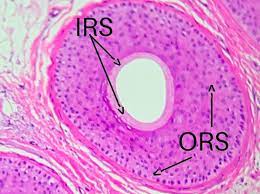
what is the internal root sheath
Surrounds hair root and deeper portion of shaft, produced from hair matrix
35
New cards
what is the external root sheath
Extends from skin surface to hair matrix
36
New cards
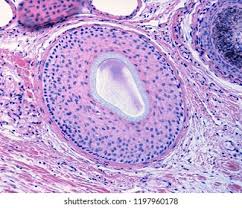
what is the glassy membrane
Thickened, clear basement membrane
37
New cards
what is the connective tissue sheath
Surrounds the epithelial cells of the hair follicle
38
New cards
what is an apocrine sweat gland
secretes into hair follicles, surrounds the epithelial cells of the hair follicle, strongly influenced by hormones, include ceruminous glands and mammary glands.
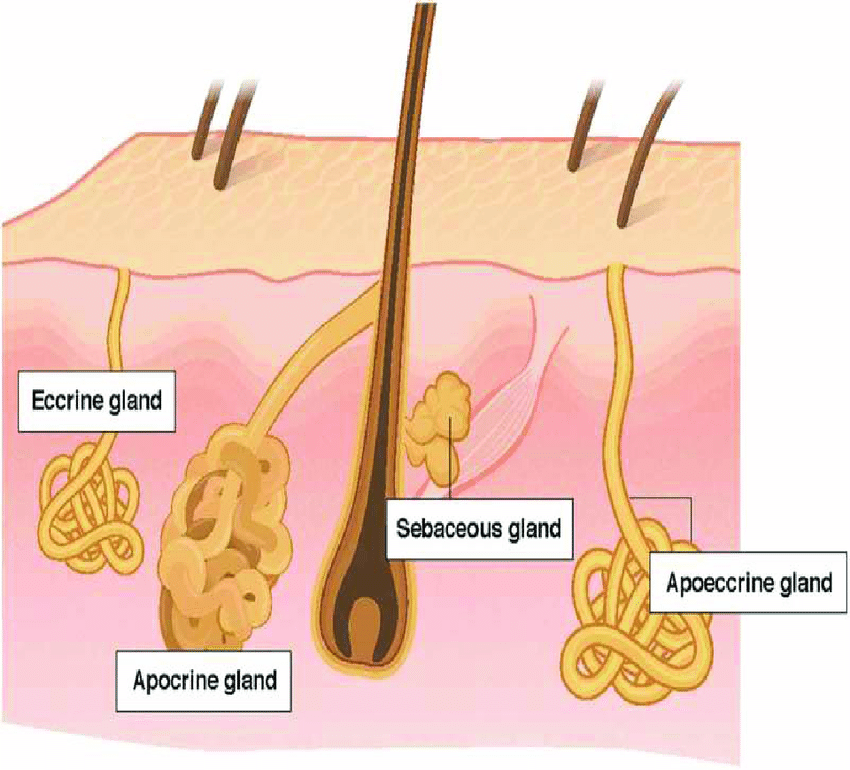
39
New cards
what is a merocrine sweat gland
found on palms and soles, produce watery secretions with electrolytes, controlled primarily by nervous system, important in thermoregulation and excretion, some antibacterial action, secrete directly onto surface of the skin.
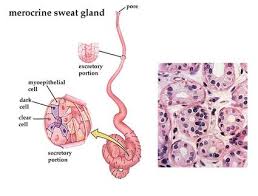
40
New cards
what are the three types of baldness
alopecia areata, telogen effluvium, anagen effluvium.
41
New cards
what is alopecia areata
sudden hair loss that starts with one or more circular bald patches that may overlap.
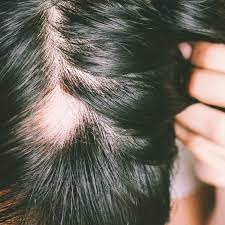
42
New cards
what is telogen effluvium
a reversible condition in which hair falls out after a stressful situation.
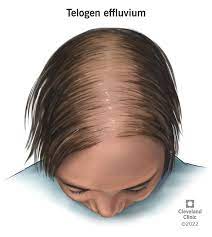
43
New cards
what is anagen effluvium
an abnormal loss of hair during the first stage (anagen) of the hairs growth cycle.