Consumer Behavior Test 2
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Chapter 5
Learning and Memory
Learning
the process of acquiring new information and knowledge about products and services for application to future behavior. (taking something that is unknown and making it known)
Knowledge
occurs when a person makes associations
Memory
enables past experiences and learning to influence current behavior
Classical Conditioning: Pavlovian Conditioning
The stimulus precedes the response
Unconditional Stimulus (US): The attractor (Meat)
Unconditional Response: Positive Response (Salivation)
Conditional Stimulus (CS): The Brand (Bell)
Conditional Response: A positive response (Salivation)
Operant Conditioning
Operant or Instrumental Conditioning: the stimulus follows the response.
Goal: to increase (via reinforcement) or decrease (via punishment) the probability of a response
Reinforcement
Increase the probability of a response.
Positive Reinforcement
Addition of a positive stimulus (free breakfast if you attend a sales pitch)
Negative Reinforcement
Removal of a negative stimulus (annoying noise in car ends when you click in your seatbelt)
Punishment
decrease the probability of a response
Positive Punishment
addition of a negative stimulus (scold student in class for bad grades)
Negative Punishment
removal of a positive stimulus (favorite toy gets taken for bad behavior)
Memory
short term = RAM (finite)
long term = hard drive (infinite storage)
Transcience
forgetting overtime. recently processed information is more accessible, or easy to retrieve
Absent-minded
forgetting as a result of shallow or superficial processing during encoding or retrieval. (NAMES)
Encoding Issues
Attention, comprehension, and transference of information from short to long term memory. (not able to store it)
Retrieval Issues
Transference of information from long to short term memory
Blocking
retrieval failure due to inference from related information stored in memory - “the tip of the tongue effect”
Associative Network
closely related nodes, ideas, or pieces of information connected directly by a single association.
Associative Interference
New associations increase the complexity of consumers’ associative networks
these new associations compete with and block old associations
What are the three different type of memory confusion or misattribution?
Source confusion, feelings of familiarity, false memory
Suggestibility
misleading questions and suggestions can lead to memory distortion. Lawyers: savy ways of asking questions, can this consumer research.
Bias
ambiguous product experiences are open to multiple interpretations
- prior beliefs can bias current beliefs and experiences
- current beliefs can bias memory for pror beliefs
(Ex’s)
Persistence
not forgetting things we want to forget
- earworm or “stuck song syndrome” (white polar bear)
Chapter 7
Motivation - Betty Crocker Mix Example
Motivation
A driving force that moves or incites consumers to act
motivation focuses attention on goal-relevant objects.
motivation comes when we have an unmet need that we want satisfied
The Process of Motivation
Needs and Wants
Needs
desires that arise when a consumer’s actual state does not meet his or her desired needs
physiological needs - innate or primary
psychological needs - secondary
Wants
Learned manifestation of needs
product specific needs
need satisfiers
ie. when you wake up in the night and you need water but you want milk. or need shoes but want nike
Needs are aroused via three routes
Physiological
Emotional
Cognitive
Aroused needs create tension or drives
Physiological
Your body will let you know
Emotional
loneliness - needs a hug
Cognitive
looking at a context clues as to realize that we have unmet needs (looking at a calendar and remembering)
Theories of Motivation
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
Need theory / the trio of needs
Self-determination theory
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
The Pyramid
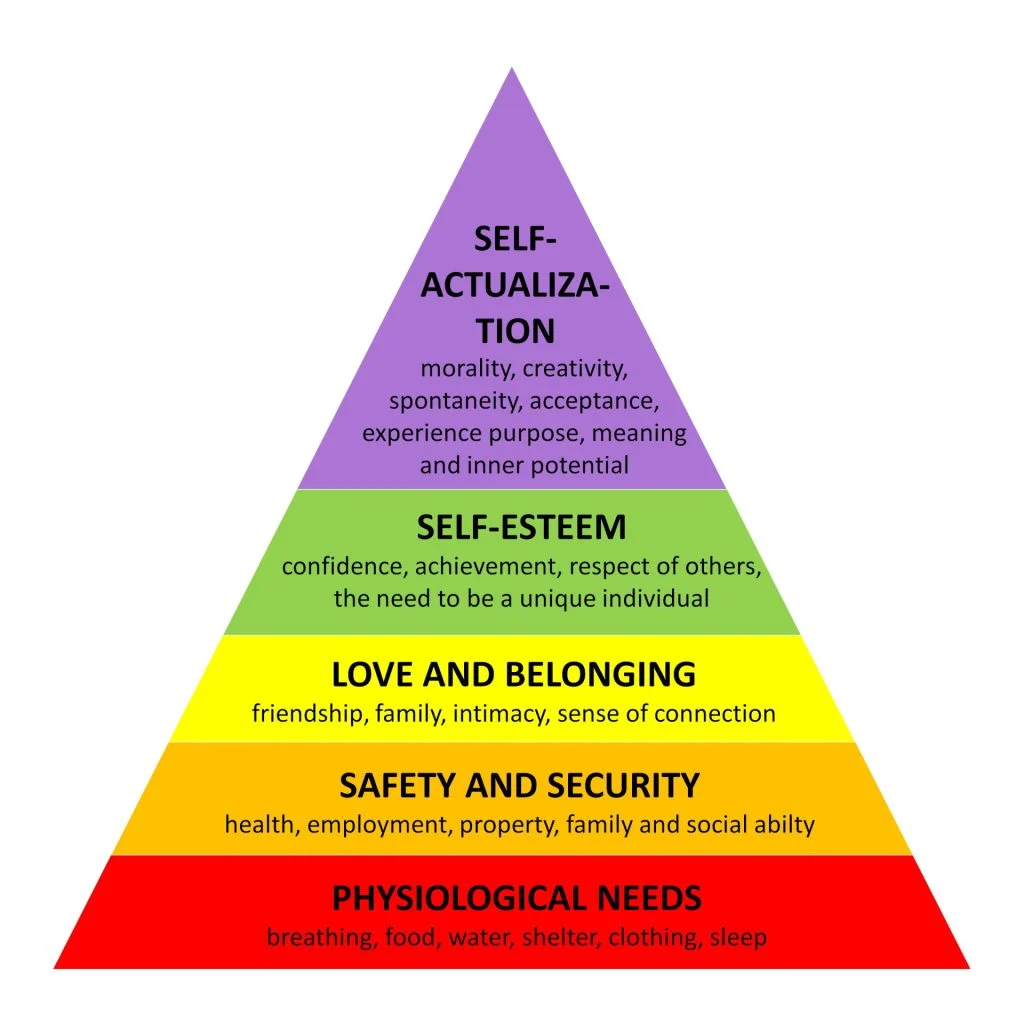
Need Theory / The Trio of Needs
Power: the need to control other people, objects, and the environment to acquire desired things.
Affiliation: the need for belongingness and friendship or to be a member of an important group
Achievement: the need to accomplish difficult tasks
Self-Determination Theory
intrinsic motivation: pursuing an activity for its own sake - autonomy, mastery and purpose
extrinsic motivation: pursuing an activity in or to receive a reward (this hinders the ability to be creative but is good for basic tasks
Cognitive Dissonance Theory
Consumers strive for consonance between a specific behavior and attitudes related to that behavior
behavior-attitude inconsistency created dissonance
consumer seek to reduce dissonance by changing their attitudes to match their behaviors
Chapter 4
Consumer Perception
Perception
Process of retrieving, selecting, and interpreting environmental stimuli with the five senses
Perception is a matter of…
Illusion (starry night) , perspective, and interpretation
Perceptual Process
Sensory Exposure - Attention - Comprehension
- your senses take in a lot of information. we only focus on a few senses at a time. (gorilla video = selective attention)
Sensory Threshold
The minimum level of stimuli needed to experience sensation. dogs v. human hearing
Just Noticeable Difference (JND)
The incremental change required to detect a difference between two similar stimuli (her brother’s roomate wine bottles)
Weber’s Law
The ability to sense change in a stimulus depends on the strength of the original stimulus (haircuts)
Marketing Implications - Sensory Thresholds
Logo updating & product quality
Adaptation
The process of becoming desensitized to stimuli
- high repetition
- simplicity
- low intensity
Physical Influences on Attention
Short term memory, Miller’s rule, Arousal
Short Term Memory
Where small bits of information are stored for short periods of time
working memory
active memory
conscious awareness
Miller’s Rule
People are able to consider 7 ± 2 (5-9) units of information at one time
- we only have 7 buckets available, 5-9 cereal brands off the top of our head
Arousal
low arousal = low attention intensity
moderate arousal = high attention
high arousal = overstimulation, low attention
How do marketer generate attention?
Salient Stimuli & Vivid Stimuli
Salient Stimuli
Draw consumers’ attention because they are interesting and different. Salience is context dependent
Vivid Stimuli
Draw consumers’ attention because they are inherently engaging. Vivid is context independent.
Chapter 6
Information Processing
2 styles of thinking
Style 1 & Style 2
Style 1
automatic
quick
going with your gut
(think of a bunny)
Style 2
deliberate
mentally exhausting
focusing on thought
think of a turtle
Automatic information processing
the mental processes that occur without awareness of intention, but influence judgment, feelings, goals, and behaviors
minimal thought & repetitive purchases
Benefits of unconscious thought
mental processes become automatic through practice and eventually subject to unconscious control
Why beneficial?
using the subconscious mind frees-up mental resources for the conscious ming
the conscious mind cannot navigate complex environments without assistance from the subconscious
Thin Slice Theory
brief observation of another person’s behavior that provide surprisingly accurate information about this peron’’s personality, feelings, and goals
Thin Slices are more accurate when…
Observations are brief (focus on intuition)
focused on nonverbal information (harder to control
consumers have lots of practice (calibrated)
Explicit Memory
consumers are aware that they are searching for information stored in memory. (im hungry - EV)
Implicit Memory
searching for information without awareness or intention (i am hungry - i am craving - )
The priming effect
consumers are subtly led to think about a concept, such as a brand name, attribute, or benefit
- simply thinking about a concept activates other related concepts from memory
Implicit Associations
consumers don’t always speak their minds
consumers don’t always know their own minds
Distraction Effects
Consumers initially believe everything in order to understand
unbelieving: is a separate process, requiring time and effort
distraction: can inhibit unbelievingly
distraction mimics automaticity
Habits
repeated behaviors that occur in stable contexts (cued by the environment)
Breaking habits
establish implementation intentions
establish a routine
monitor progress