Parasitology: Key Concepts, Organisms, and Diagnostic Methods
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Agglutination test
Used to diagnose leishmaniasis and Chagas disease.
EIA
Used to identify antigens or antibodies for organisms such as Giardia duodenalis, Cryptosporidium, and Entamoeba histolytica.
DNA probes and polymerase chain reactions
Used to diagnose selected parasite infections.
Intestinal Protozoa
Includes Amoebae, Flagellates, Ciliates, and Sporozoa.
Infective stage
Cysts.
Reproductive stage
Trophozoites.
Entamoeba histolytica
The only true pathogen in the intestinal amoebae group.
Entamoeba coli
Nonpathogenic amoeba.
Iodamoeba butschlii
Cyst has a large, iodine staining vacuole.
Giardia duodenalis
A principal pathogen among intestinal flagellates.
Traveler's diarrhea
Diarrhea caused by drinking contaminated water in streams and ponds while hiking or camping.
EIA methods
Preferred methods for identification over visual methods.
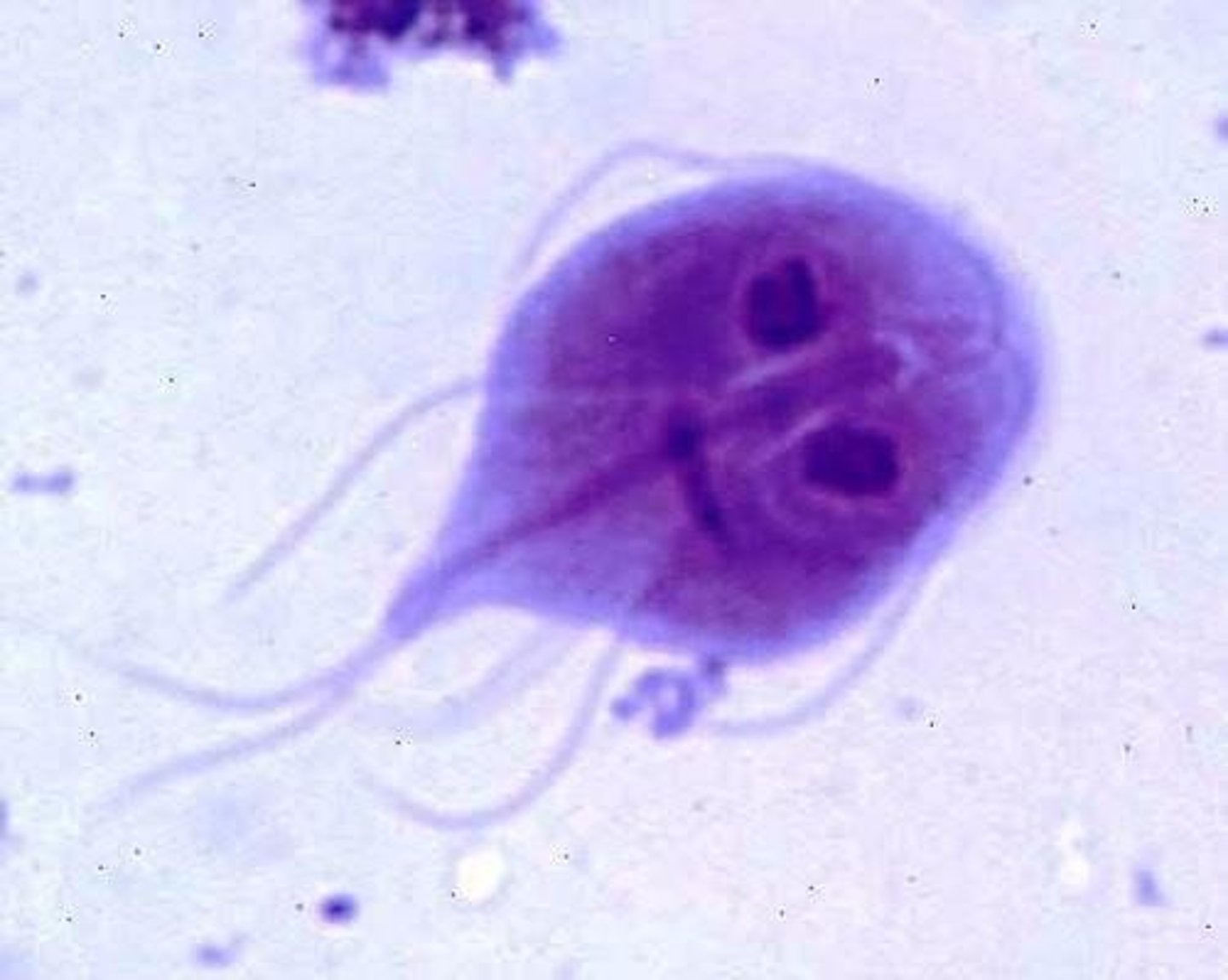
Trophozoites (Giardia duodenalis)
Kite shaped with central axoneme, 2 nuclei, flagella not always visible.
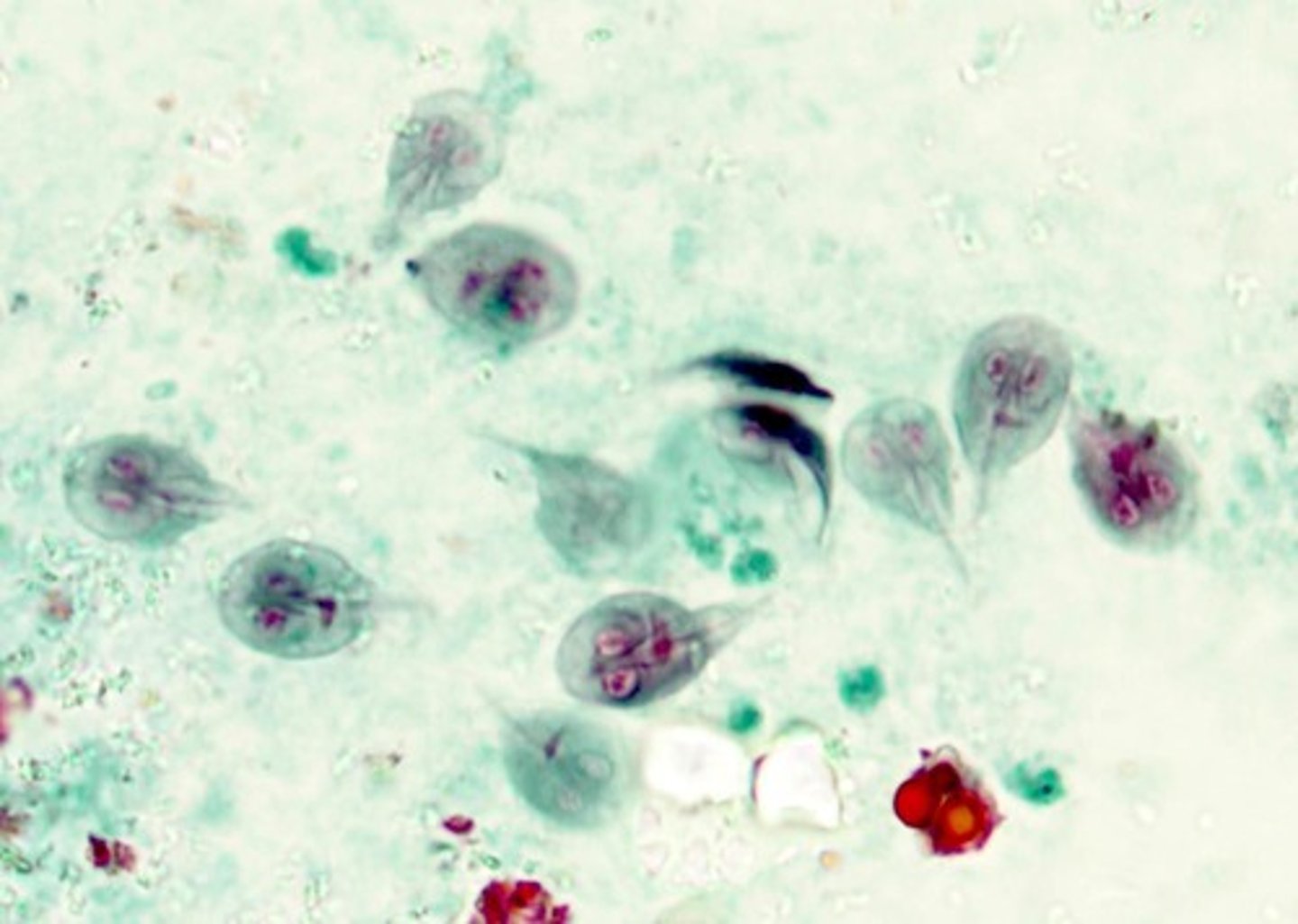
Cysts (Giardia duodenalis)
4 nuclei along central axoneme.
Dientamoeba fragilis
Worldwide distribution causing diarrhea and anal pruritis.
Trophozoites (Dientamoeba fragilis)
Round and binucleate.
Cysts (Dientamoeba fragilis)
None known.
Intestinal Ciliates
Use cilia for motion.
Balantidium coli
Only known pathogen among intestinal ciliates, causes self-limiting diarrhea.
Cyst (Balantidium coli)
Double walled (cilia in between), very large, kidney-shaped macronucleus.
Trophozoite (Balantidium coli)
Large macronucleus, cilia often visible.
Intestinal Sporozoa
No locomotive structures.
Cryptosporidium parvum
Major cause of watery diarrhea and severe dehydration in patients with AIDS.
Identification (Cryptosporidium parvum)
Acid-fast staining oocytes in stool.
Cystoisospora belli
Acid-fast oocysts in stool with large, ellipsoid shape and 1-2 visible cysts.
Naegleria fowleri
Amoeba found widely in the environment, causes primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM).
Identification (Naegleria fowleri)
Trophozoites found in CSF or brain tissue, single nucleus with large, dense karyosome.
Acanthamoeba spp.
Cause amoebic keratitis and encephalitis.
Identification (Acanthamoeba spp.)
Trophozoites or cysts visible in corneal scrapings or brain tissue.
Trichomonas vaginalis
Sexually transmitted flagellate that mostly causes vaginitis.
Identification (Trichomonas vaginalis)
Trophozoites found in urine or vaginal wet prep, characteristic 'jerky', non-directional motility.
Hemoflagellates
Flagellates that inhabit the blood and tissue of humans.
Leishmania spp.
Causes leishmaniasis, a cutaneous or disseminated infection contracted from the bite of a sandfly.
Identification (Leishmania spp.)
Flagellated form or nonmotile stage found in blood or tissue.
Trypanosoma cruzi
Causes Chagas disease, contracted from the feces and bite of the reduviid (kissing) bug.
Identification (Trypanosoma cruzi)
Flagellate found in peripheral blood smears, C-shape, large, dark posterior kinetoplast.
Trypanosoma brucei
Causes African sleeping sickness, contracted from tsetse flies.
Identification (Trypanosoma brucei)
Flagellate found in peripheral blood smears, delicate curve with smaller kinetoplast.
Plasmodium spp.
Sporozoa that cause malaria, a life-threatening illness with 250 million new cases and over 600,000 deaths each year.
Identification (Plasmodium spp.)
Diagnosis made primarily through thick and thin blood smears to view developmental stages of the life cycle.
Plasmodium falciparum
Large, banana-shaped gametocyte with multiple rings per RBC and a 'double dot' or 'headphones' ring form.
Plasmodium malariae
Single ring form, no Schuffner's dots, with a band form trophozoite.
Plasmodium ovale and vivax
Ring and trophozoite forms with Schuffner's dots.
Babesia microti
Sporozoa that cause babesiosis, a bloodborne, usually self-limiting infection spread through tick bites.
Babesia microti Identification
Ring forms similar to Plasmodium and trophozoites in blood smears, usually multiple ring forms per cell, with 'plus-sign' or 'maltese cross' morphology.
Toxoplasma gondii
Causes toxoplasmosis, associated with cat feces and ingestion of undercooked meat, especially in pregnant people.
Toxoplasma gondii Identification
Mostly serological testing; organisms can be found, but not easily; large, curved structures found in CSF, blood, or occasionally tissue samples.
Trematodes
Flukes that are flat, hermaphroditic, with at least two suckers.
Trematodes Life cycles
Eggs usually passed through feces into water where they hatch into free-living organisms.
Schistosoma spp.
Blood flukes; eggs found in feces or urine are diagnostic.
Schistosoma mansoni
Eggs have large lateral spine.
Schistosoma japonicum
Eggs have small lateral spine.
Schistosoma haematobium
Eggs have a terminal spine.
Paragonimus westermani
Lung fluke; identification through eggs in feces or (occasionally) sputum, with eggs having a shouldered operculum.
Clonorchis sinensis
Intestinal fluke; identification through eggs in feces with dome shaped, shouldered operculum opposite a small knob.
Fasciola hepatica
Liver fluke; identification through eggs in feces which are rounded, with a non-shouldered operculum.
Cestodes
Tapeworms; adult worms live in humans who shed eggs, which infect an intermediate host.
Taenia saginata
Beef tapeworm; diagnosis through eggs indistinguishable from T. solium and proglottid segments that are wide with more lateral segments.
Taenia solium
Pork tapeworm; diagnosis through eggs indistinguishable from T. saginata and proglottid segments that are more narrow with fewer lateral segments.
Diphyllobothrium latum
Fish tapeworm; identification through eggs that are oblong and smooth with a smooth operculum.
Hymenolepis nana
Dwarf tapeworm caused by accidental ingestion of infected arthropods; identification through eggs that have 2 layers and 3 hooklets inside.
Nematodes
Roundworms that cause a wide variety of infections, with very complex life-cycles.
Enterobius vermicularis
Pinworms, a common infection in school-age children, causing pruritus and itchiness around the anus.
Enterobius vermicularis Diagnosis
Gravid females deposit eggs in perianal folds.
Trichuris trichiura
Whipworm
Diagnosis of Trichuris trichiura
Eggs in stool; Barrel shaped eggs with transparent plugs at each end
Ascaris lumbricoides
Giant intestinal tapeworm
Diagnosis of Ascaris lumbricoides
Larger worms are so big they can cause intestinal blockages, and can be visualized coming out of the rectum/anus, or in the stool; Eggs in stool have a thick shell with a bumpy outer layer
Strongyloides stercoralis
Threadworm
Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis
Eggs rarely found in stool; Feces contain rhabditiform larvae; Larvae very similar to hookworms, but have a short buccal (mouth) cavity and a prominent genital primordium
Necator americanus
Hookworms
Diagnosis of Necator americanus
Eggs found in stool with translucent wall and clusters of spherical embryos; Rhabditiform larvae also found in stool have long buccal cavity
Trichinella spiralis
Infection of skeletal muscle causes edema and swelling in muscle tissue
Contracted from Trichinella spiralis
Ingestion of undercooked pork
Diagnosis of Trichinella spiralis
Encysted larvae and worms seen in skeletal muscle
Dracunculus medinensis
Guinea worm infections
Diagnosis of Dracunculus medinensis
Adult worms found in ulcerations; Treated by removing worms around a stick, 1 inch per day
Habitat of Filariae
Mainly inhabit the circulatory and lymphatic systems, but can also invade the sinus cavities and skeletal muscles.
Wuchereria bancrofti
Causes elephantiasis
Contracted from Wuchereria bancrofti
Through the bite of mosquitoes
Diagnosis of Wuchereria bancrofti
Adults worms have no tail nuclei
Brugia malayi
Causes elephantiasis
Contracted from Brugia malayi
Through the bite of mosquitoes
Diagnosis of Brugia malayi
Adults worms have 2 distinct tail nuclei
Loa loa
Migrate to the eyes
Diagnosis of Loa loa
Adult worms have nuclei that go all the way to the tip of the tail