AUBF lab bile acids, calcium, chloride, microalbumin (copy)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
acids and salts
Bile is composed of
T
[T or F] Bile pigments can be extracted from blood
Bilirubin
Principle pigment of bile
Bilirubin
degradation product of hemoglobin
oxidation; derivatives
Tests for bile depends upon the __ of bile pigments by acids with the formation of a series of colored _ of bilirubin
Green
color of biliverdin
Blue
color of bilicyanine
Yellow
color of choletellin
alcoholic iodine
Reagent for smith’s test
First morning
Preferred urine speciment for smith’s
F
[T or F] freshly voided or random urine cannot be used for smiths test
emerald green ring at contact
Positive result for smiths
presence of bile pigments
Positive result of smith indicates
Fauchet’s reagent
10% barium chloride
“Harry’s FB Group”
Reagent for harrison’s spot test
FIrst morning
Preferred specimen for harrison’s spot test
F
[T or F] freshly voided or random urine cannot be used for harrisons spot test
blue to green color on filter paper
Positive result of harrison’s spot test
Ictotest
This test uses the same chemical reaction as bilirubin pad on multi reagent dipstick but in a tablet form
Purple color around the tablet
Positive result of ictotest
True color reaction is less affected by color of urine
More sensitive to bilirubin
Advantage of ictotest
T
[T or F] Ictotest can confirm or refute false-positive reactions on dipstick in cases where urine is deeply colored
0.1 mg/dL of bilirubin
Sensitivity of ictotest to bilirubin
Colorimetric method DMSO
Method where bilirubin reacts with diazotized sulphanilic acid (DMSO) to form a purple colored azobilirubin complex
conjugated bilirubin
What reacts with the aqueous solution in colorimetric method
unconjugated bilirubin
What reacts with the DMSO in colorimetric method
T
[T or F] the intensity of the color formed ins proportional to the bilirubin concentration in the sample
Na, Cl, K
What are the major inorganic chemicals found in urine
Absorption in the intestinal tract
Filtration in the glomerulus
Passive reabsorption by the proximal convoluted tubules, with sodium
How is chloride ingested in food
Sweat and urine
Excess chloride is excreted where
24-hour/ timed urine
preferred specimen for chloride determination
F
[T or F] freshly voided or random urine cannot be used for chloride determination
Precipitation
What is the principle behind chloride determination
silver chloride; silver nitrate; nitric acid
Chloride is precipitated as ___ upon addition of ___ and ___in urine
nitric acid; silver nitrate; quantitative
In a test, place 5 mL urine and add 3 to 4 drops of 6 N ___. Centrifuge.
To the filtrate, add 2 to 3 drops of ___ solution.
Record results as positive or negative.
If positive, proceed to the ___ estimation.
Clouded precipitate
positive reaction for qualitative chloride determination
8-15 g/day
Normal chloride excreted in 24hr urine sample
Increased
“PDA”
Polydipsia
use of Diuretics
Addisons disease
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Polydipsia
Increased
“PDA”
Polydipsia
use of Diuretics
Addisons disease
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
use of Diuretics
Increased
“PDA”
Polydipsia
use of Diuretics
Addisons disease
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Addisons disease
Increased
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Associated with Volume expansion and hypokalemia
Increased
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
excess aldosterone, severe K deficiency, bartter syndrome
Decreased
“DICE”
Diabetes insipidus
Infections
Cushing’s syndrome
Excessive sweating, fasting, diarrhea, vomiting
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Excessive sweating, fasting, diarrhea, vomiting
Decreased
“DICE”
Diabetes insipidus
Infections
Cushing’s syndrome
Excessive sweating, fasting, diarrhea, vomiting
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Excessive sweating, fasting, diarrhea, vomiting
Decreased
“DICE”
Diabetes insipidus
Infections
Cushing’s syndrome
Excessive sweating, fasting, diarrhea, vomiting
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Diabetes insipidus
Decreased
“DICE”
Diabetes insipidus
Infections
Cushing’s syndrome
Excessive sweating, fasting, diarrhea, vomiting
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Infections
Decreased
“DICE”
Diabetes insipidus
Infections
Cushing’s syndrome
Excessive sweating, fasting, diarrhea, vomiting
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Cushing’s syndrome
decreased (<10 mEq/L)
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Associated with volume depletion
decreased (<10 mEq/L)
Increased or decreased Chloride levels:
Respond to saline infusion
Bartter syndrome
An inborn autosomal recessive defect in Na-K-2Cl cotransporter at the thick ascending loop of henle.
increased renal prostaglandin E2 production
Microalbuminuria
Increase in urinary albumin below the detectable range of standard protein reagent strips tests.
Microalbuminuria
Occurs long before clinical proteinuria becomes evident.
Microalbuminuria
Standard test for screening, monitoring, and detection of deteriorating renal function in diabetic patients
Microalbuminuria
Also used to monitor compliance of blood pressure control, glucose control, and protein restriction
>200 mg/L
Albuminuria is the term used when albumin levels reach _ in the urine
20-200 mg/L.
Microalbuminuria is the term used when albumin levels in the urine are _
<30 mg/24 hours (<30 mg/day)
<20 mg/L (10-hour collection)
Reference value of microalbuminuria (in 24hr collection and 10hr collection)
Increased
Increased or Decreased microalbumin:
Diabetes with early diabetic nephropathy
Increased
Increased or Decreased microalbumin:
Hypertension
Increased
Increased or Decreased microalbumin:
Generalized vascular disease (increased risk of cardiovascular disease)
Increased
Increased or Decreased microalbumin:
Preeclampsia
Strenuous exercise
Hematuria
High-protein diet or high salt levels
Interfering factors in microalbumin testing resulting in false positive result
Micral test principle
contains a gold-labeled antihuman albumin antibody-enzyme conjugate that binds to albumin present in urine
Immunochemical
MIcral test is a __ assay
white to red
urine albumin-bound conjugates move up the strip to an area containing the enzyme substrate (Detection pad) to produce colors ranging from ___
T
[T or F] The amount of color produced in micral test is proportional to the albumin concentration in the urine.
0 to 10 mg/dL
MIcral test results range from _.
Immunodip
Albumin in urine is bound by blue latex particles coated with antihuman albumin antibody. The albumin- latex complex migrate through capillary action and form a second blue band (first blue band is for unconjugated particles).
Immunochromatographic
Immunodip uses a __ technique
Band 1
Which band on the Immunodip
Blue conjugate that has not reacted with albumin in the urine sample will bind to the HSA immobilized in this Band
Band 2
Which band on the Immunodip
A capture antibody binds any blue conjugate that does not bind in Band 1
3 min
Immunodip should be read within how many minutes
<1.2mg/dL [NEGATIVE]
Interpret microalbumin readings:
Darker bottom band (first band)
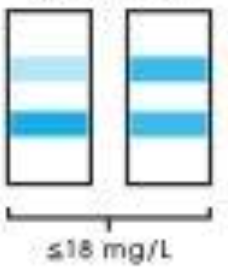
1.2 to 1.8 mg/dL [BORDERLINE]
Interpret microalbumin readings:
Equal band colors
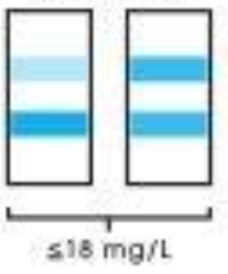
2.0 to 8.0 mg/dL [POSITIVE]
Interpret microalbumin readings:
Darker top band (2nd band)
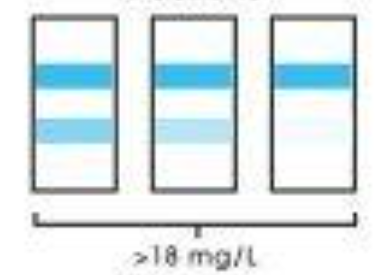
INVALID
Interpret microalbumin readings:
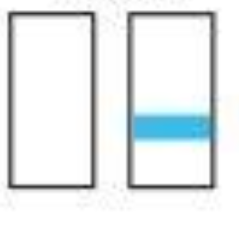
99% ; 1%
Cation that is mostly seen in the bones (___%) with the remaining __ in blood and in extracellular fluid (ECF)
serum
Most common specimen for calcium determination
calcium chloride
calcium sulfate
calcium phosphate
Calcium in urine is seem as these compounds
12-hour or 24-hour timed specimen
Preferred specimen for calcium analysis
Sulkowitch’s test
Test for calcium
buffered oxalate solution
Reagent for sulkowitch test
turbidity
positive result for sulkowitch test
T
[T or F] turbidity in sulkowitch is equivalent to calcium concentration